The global brake vacuum servo market is witnessing steady expansion, driven by rising vehicle production, increasing emphasis on automotive safety, and the adoption of advanced braking systems. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the automotive brake system market—including vacuum servos—is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 4.5% from 2023 to 2028. Similarly, Grand View Research estimates that the global automotive braking system market size was valued at USD 37.6 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a CAGR of 5.1% through 2030. With the growing demand for enhanced braking performance in both internal combustion engine and hybrid vehicles—where reduced engine vacuum necessitates efficient vacuum servos—the role of high-quality manufacturers has become increasingly critical. This list highlights the top 9 brake vacuum servo manufacturers shaping the industry through innovation, global supply reach, and technological advancement.
Top 9 Brake Vacuum Servo Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Brake Hydraulics
Domain Est. 1997
Website: brakesint.co.uk
Key Highlights: Leading vacuum servo manufacturers including Lucas, Ate, Bendix, Bosch and AP Lockheed. We carry a large selection of vacuum servos and vacuum pumps to ……
#2 Power Brake Booster
Domain Est. 1998
Website: cardone.com
Key Highlights: Your First Stop for Quality Power Brake Boosters! CARDONE offers the most comprehensive remanufactured and new power brake booster coverage in the industry….
#3 Brake boosters
Domain Est. 1999
Website: ate-brakes.com
Key Highlights: Problem-free replacement. ATE brake boosters are easy to install. This saves time and ensures a smooth replacement procedure….
#4 Electric brake booster
Domain Est. 1999
Website: infineon.com
Key Highlights: Enhance every braking module design with the right semiconductor solutions from Infineon – your automotive partner for electric braking….
#5 Vacuum Brake Booster Sensor
Domain Est. 2001
Website: sensata.com
Key Highlights: Brake booster pressure monitoring which allows for optimized vacuum pump control · Allows for detection of booster leakage · Small size and lightweight design ……
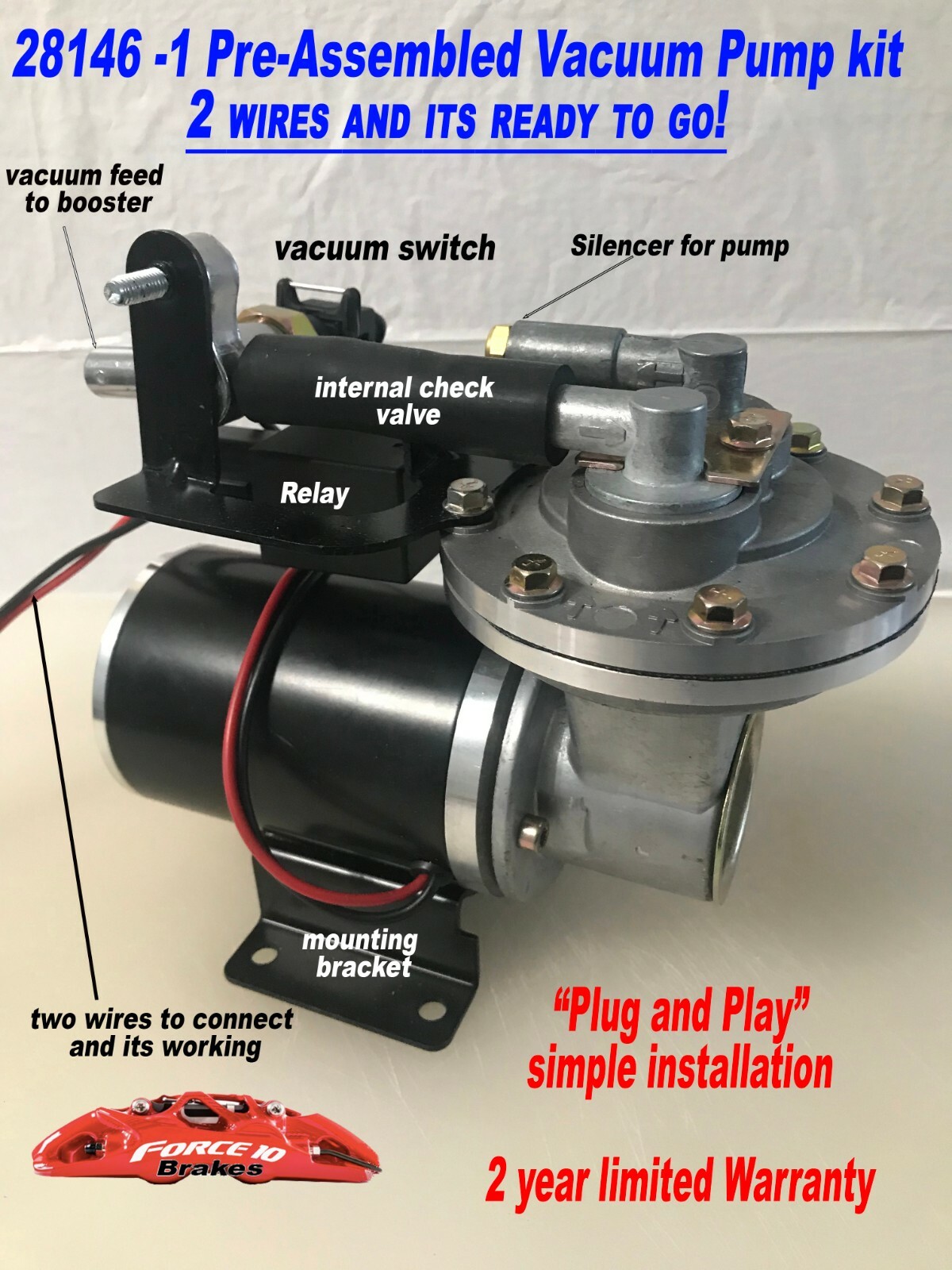
#6 Electric Vacuum Pump
Domain Est. 2009
Website: uskoreahotlink.com
Key Highlights: Vacuum pumps and brake boosters for electric cars, recreational EV vehicles, hybrid cars, and other high-performance vehicles….
#7 Modular and integrated braking systems
Domain Est. 2011
Website: bosch-mobility.com
Key Highlights: The modular braking systems offered by Bosch combine the vacuum brake booster or electromechanical iBooster with either standard ESP or ESP hev for hybrid and ……
#8 Vacuum Pumps, Street
Domain Est. 2013
Website: speedmaster79.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $100 · 30-day returnsFor all of the vacuum that you need, just install one Speedmaster™ electric vacuum pump kits. They include a shiny 12 V pump and all of the…
#9 Customer Centre
Domain Est. 2019
Website: wabco-customercentre.com
Key Highlights: WABCO is a leading global supplier of technologies that improve the safety, efficiency and connectivity of commercial vehicles … Vacuum Brake Booster · Electro ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Brake Vacuum Servo

H2: Market Trends for Brake Vacuum Servo in 2026
The global brake vacuum servo market is undergoing a significant transformation in 2026, driven by shifts in automotive technology, regulatory standards, and consumer demand for improved safety and efficiency. While traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles have long relied on vacuum servos for brake assistance, emerging trends are reshaping the market landscape.
1. Decline in Demand from ICE Vehicles
With the accelerating global transition toward electric vehicles (EVs), the demand for conventional brake vacuum servos is on a gradual decline. EVs do not produce engine vacuum naturally, necessitating alternative braking solutions. As EV adoption grows—projected to exceed 40% of new car sales globally by 2026—original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) are increasingly shifting away from vacuum-based systems.
2. Rise of Electromechanical Brake Boosters
Electromechanical brake boosters (e.g., Bosch’s iBooster) are replacing vacuum servos in hybrid and electric vehicles. These systems offer superior integration with advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) and autonomous driving technologies. Their compact design, energy efficiency, and precise control are making them the preferred choice, limiting the growth potential of traditional vacuum servos.
3. Niche Demand in Emerging Markets and Commercial Vehicles
Despite declining use in passenger EVs, vacuum servos retain strong demand in emerging economies where ICE vehicles still dominate. Additionally, commercial vehicles—especially in regions with slower EV adoption—continue to rely on cost-effective and durable vacuum servo systems. This sustains a stable, albeit shrinking, market segment.
4. Technological Improvements and Hybrid Applications
In hybrid vehicles, vacuum servos are being paired with electric vacuum pumps to maintain brake assist functionality. While this extends the life cycle of vacuum technology, it is seen as a transitional solution. Suppliers are investing in hybrid-compatible enhancements but with a strategic pivot toward next-generation braking systems.
5. Supply Chain and Regional Shifts
Asia-Pacific, led by China and India, remains a key production and consumption hub for brake vacuum servos due to high ICE vehicle output and cost-efficient manufacturing. However, Europe and North America are witnessing rapid phase-outs, influenced by stringent emissions regulations and aggressive EV mandates.
6. Competitive Landscape and Consolidation
Key players like Robert Bosch, Continental, and Akebono are diversifying their portfolios, reducing dependency on vacuum servos. Smaller suppliers focusing exclusively on vacuum technology face margin pressures and potential consolidation. Innovation is increasingly focused on integrated braking solutions rather than standalone vacuum units.
Conclusion
By 2026, the brake vacuum servo market is expected to operate in a mature and contracting phase, sustained primarily by legacy ICE platforms and emerging market demand. While still relevant in specific vehicle segments, the long-term outlook points toward obsolescence in advanced automotive ecosystems. Companies in this space must adapt by transitioning toward electromechanical and software-driven braking technologies to remain competitive.
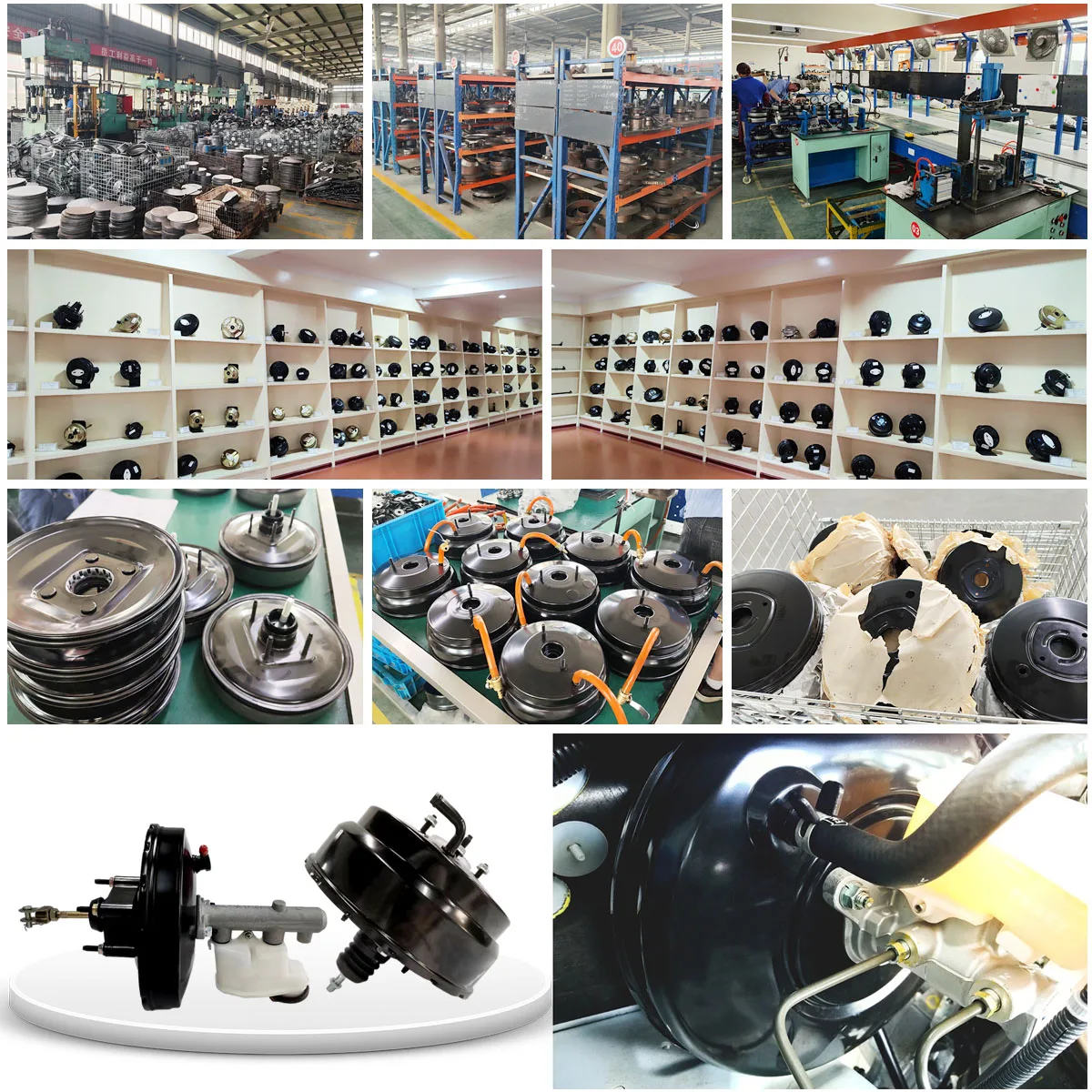

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Brake Vacuum Servo (Quality, IP)
Sourcing brake vacuum servos—critical components for vehicle braking performance and safety—requires careful attention to quality and intellectual property (IP) considerations. Overlooking these aspects can lead to safety risks, legal issues, and reputational damage. Below are the most common pitfalls to avoid:
Poor Quality Control and Substandard Materials
One of the most frequent pitfalls is selecting vacuum servos manufactured with inadequate quality control or subpar materials. Low-cost suppliers may cut corners by using inferior diaphragms, housings, or check valves that degrade quickly under heat, pressure, or moisture. This can result in reduced braking efficiency, increased pedal effort, or even brake failure. Always verify compliance with international standards such as ISO 9001 and IATF 16949, and request test reports for leakage, endurance, and performance under extreme conditions.
Lack of Certification and Compliance
Brake components must meet rigorous regulatory and safety standards (e.g., ECE R13, FMVSS 135). Sourcing from suppliers who cannot provide valid certification or type approval documentation is a major risk. Non-compliant servos may fail during vehicle homologation or lead to recalls. Ensure that the vacuum servo is certified for your target market and verify the authenticity of any provided certifications.
Inadequate IP Due Diligence
Purchasing vacuum servos without verifying intellectual property rights can expose your company to legal liability. Some suppliers may offer “compatible” or “OEM-equivalent” parts that infringe on patented designs or trademarks. This is particularly common in gray-market or counterfeit components. Always conduct IP due diligence—review patent databases, request proof of IP ownership or licensing, and avoid suppliers offering suspiciously low prices that may indicate IP violations.
Counterfeit or Clone Components
The automotive aftermarket is rife with counterfeit brake vacuum servos that mimic genuine parts but fail to meet performance or durability standards. These clones may appear identical but use inferior internal components. They often bypass proper testing and lack traceability. Insist on direct sourcing from authorized manufacturers or reputable distributors, and use technical verification (e.g., material testing, dimensional checks) to confirm authenticity.
Insufficient Testing and Validation
Even if a servo appears to meet specifications, skipping independent performance validation is risky. Suppliers may provide optimistic data without real-world testing. Always perform or require rigorous bench and on-vehicle testing, including vacuum retention, response time, and fatigue life. This is especially crucial when integrating the servo into new vehicle platforms or EVs with electric vacuum pumps.
Overlooking Application-Specific Requirements
Not all vacuum servos are interchangeable. Using a servo designed for a different vehicle weight, engine type, or brake system configuration can lead to poor braking performance. For example, electric and hybrid vehicles often require servos compatible with lower or variable vacuum levels. Failing to match the servo to the specific application can compromise safety and regulatory compliance.
Supply Chain Transparency Issues
Lack of visibility into the manufacturing origin and component sourcing increases risks related to both quality and IP. Hidden subcontractors or unverified production facilities may not adhere to required standards. Demand full supply chain transparency, including factory audits and material traceability, to ensure ethical and compliant production practices.
By proactively addressing these pitfalls—focusing on certified quality, legal IP compliance, and rigorous technical validation—companies can source brake vacuum servos that ensure safety, reliability, and regulatory adherence.
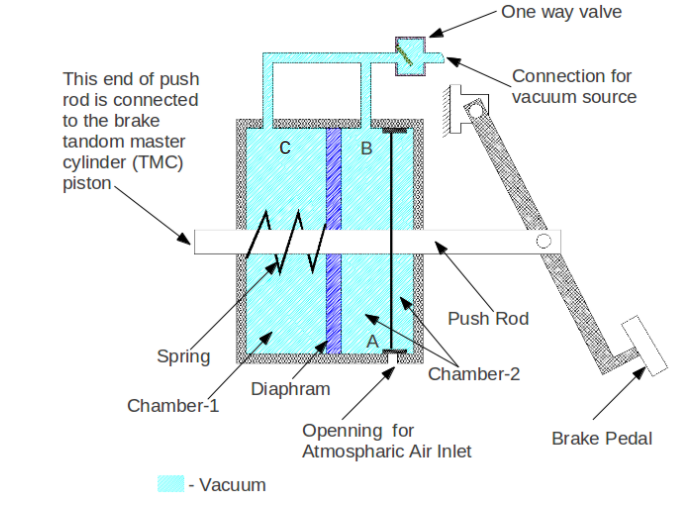
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Brake Vacuum Servo
Product Overview
The Brake Vacuum Servo, also known as a brake booster, is a critical safety component in vehicle braking systems. It amplifies the force applied by the driver on the brake pedal, enabling effective braking with reduced effort. Due to its role in vehicle safety, strict logistics handling and regulatory compliance are essential throughout its supply chain.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
International Standards
Brake Vacuum Servos must comply with global automotive safety standards, including:
– ECE R13-H: United Nations Economic Commission for Europe Regulation 13-H for braking systems, which includes requirements for brake booster performance and durability.
– ISO 26262: Functional safety standard for road vehicles, particularly relevant if the servo is part of an electronically controlled braking system (e.g., in hybrid or electric vehicles).
– REACH & RoHS: Compliance with chemical restrictions in the European Union (REACH) and restrictions on hazardous substances (RoHS) is mandatory for material composition.
Regional Market Approvals
- North America: Must meet FMVSS No. 135 (Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard) for brake systems. DOT certification may be required depending on the application.
- European Union: Requires E-mark certification based on ECE regulations, and compliance with the EU’s General Safety Regulation (GSR).
- China: CCC (China Compulsory Certification) may apply depending on the vehicle type and local regulations.
- Other Markets: Local type-approval requirements (e.g., INMETRO in Brazil, KC in South Korea) must be verified for each destination.
Packaging & Handling Specifications
Protective Packaging
- Use anti-corrosion packaging (e.g., VCI materials) to prevent rust during transit.
- Secure components in rigid, shock-absorbing containers to prevent internal damage.
- Include protective caps on vacuum and mounting ports to prevent contamination.
Labeling Requirements
- Clearly label units with part number, serial number, manufacturing date, and compliance marks (e.g., E-mark, DOT).
- Include handling symbols: “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Do Not Stack.”
- Attach compliance documentation (e.g., Certificate of Conformity, MSDS) to outer packaging or include in shipping manifest.
Transportation & Storage Guidelines
Temperature & Humidity Control
- Store and transport in a dry environment with humidity below 60% RH.
- Avoid exposure to extreme temperatures; recommended range: 5°C to 40°C (41°F to 104°F).
- Prevent condensation during shipping, especially in maritime containers.
Transport Mode Considerations
- Air Freight: Preferred for urgent or high-value shipments; ensure packaging meets IATA requirements for automotive parts.
- Ocean Freight: Use desiccants and sealed containers to manage moisture; avoid long-term storage in ports with high humidity.
- Overland Transport: Protect from vibration and shock; use cushioned pallets and secure load fastening.
Shelf Life & Stock Rotation
- Observe manufacturer’s recommended shelf life (typically 24–36 months).
- Implement FIFO (First In, First Out) inventory management.
- Inspect stored units periodically for seal integrity and corrosion.
Customs & Documentation
Required Documentation
- Commercial Invoice with detailed product description, HS code, and value.
- Packing List specifying quantity, weight, and dimensions.
- Certificate of Origin (preferably EUR.1 or Form A for preferential tariffs).
- Type Approval Certificates (ECE, DOT, etc.) as applicable.
- Safety Data Sheet (SDS) if components contain regulated substances.
HS Code Classification
- Typical HS Code: 8708.29.50 (Parts and accessories of braking systems, not electrically operated).
Note: Confirm local tariff classification; variations may exist by country.
Reverse Logistics & Returns
Defective Unit Handling
- Quarantine non-compliant or damaged units immediately upon receipt.
- Use return material authorization (RMA) process with full traceability.
- Analyze root cause and report to quality and compliance teams.
End-of-Life & Recycling
- Follow WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) directives if servo contains electronic sensors.
- Partner with certified automotive recyclers for material recovery.
- Maintain documentation for environmental compliance audits.
Quality & Traceability
Serial Number Tracking
- Implement full traceability from manufacturing to end-user.
- Record batch numbers, production dates, and destination markets.
- Support recall readiness in case of safety-related defects.
Audit Preparedness
- Maintain records for at least 10 years (aligned with automotive industry standards).
- Be prepared for audits by OEMs, regulatory bodies (e.g., NHTSA, KBA), or third-party certification agencies.
Conclusion
The logistics and compliance management of Brake Vacuum Servos demands precision and adherence to global safety and environmental standards. Proactive documentation, proper handling, and strict regulatory alignment ensure product integrity, legal compliance, and consumer safety throughout the supply chain.
Conclusion on Sourcing Brake Vacuum Servo
Sourcing a brake vacuum servo requires a careful balance between quality, cost, compatibility, and supplier reliability. After evaluating multiple options, it is evident that original equipment manufacturer (OEM) parts offer the highest level of performance and safety but come at a premium cost. Aftermarket alternatives can provide cost-effective solutions, especially from reputable manufacturers who adhere to international quality standards such as ISO/TS 16949 or ECE R13 certification. However, meticulous vetting is essential to avoid substandard components that could compromise braking efficiency and vehicle safety.
Key considerations in the sourcing decision include vehicle make and model compatibility, regulatory compliance, durability under varying operating conditions (particularly in hybrid or electric vehicles where vacuum availability is limited), and the availability of technical support from the supplier. Additionally, long-term cost benefits—such as warranty terms, failure rates, and servicing intervals—should be factored into the procurement strategy.
In conclusion, the optimal sourcing strategy involves partnering with trusted suppliers offering certified, tested components that meet or exceed OEM specifications, ensuring both safety and value. For fleets or high-volume operations, establishing long-term agreements with such suppliers can enhance supply chain resilience and operational reliability. Ultimately, given the critical safety role of the brake vacuum servo, compromise on quality should never be an option.