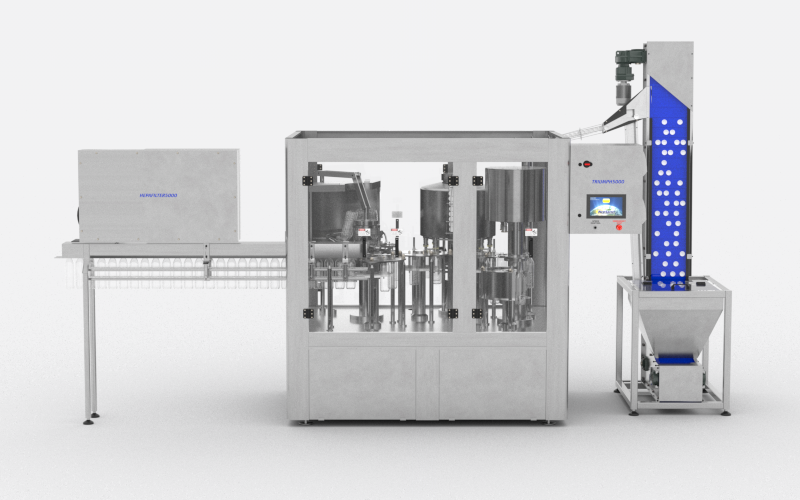
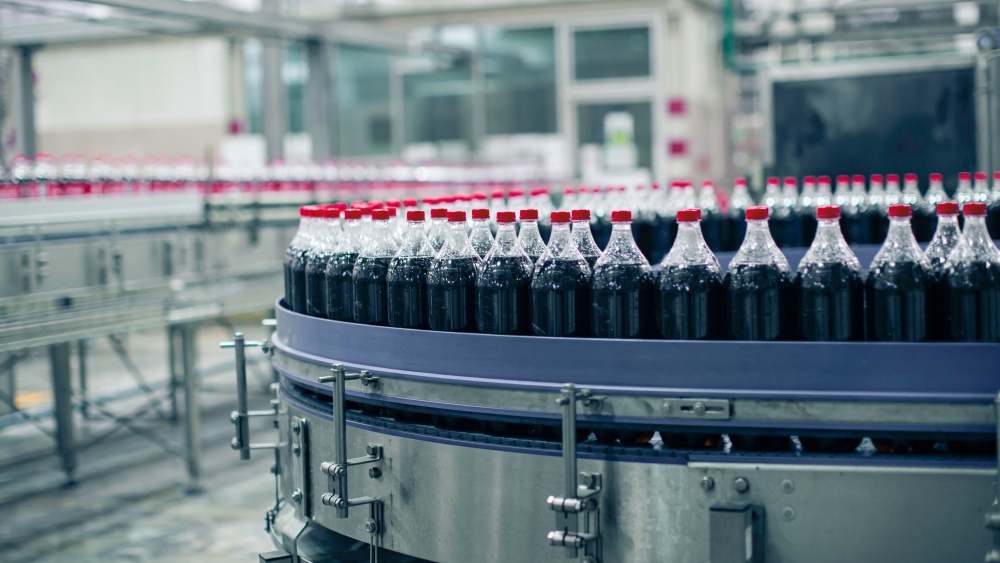
The global bottling line equipment market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by rising demand across the beverage, pharmaceutical, and food industries. According to Grand View Research, the market size was valued at USD 12.8 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.4% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by increasing automation, stringent hygiene standards, and the need for high-speed, precision filling and packaging solutions. Mordor Intelligence further supports this trajectory, noting accelerating adoption of advanced bottling systems in emerging economies and a shift toward sustainable, energy-efficient machinery. As manufacturers strive for operational efficiency and compliance with global quality benchmarks, investment in innovative bottling line equipment continues to rise. In this evolving landscape, identifying leading suppliers becomes critical for businesses aiming to optimize production and maintain competitive advantage. Here’s a data-informed look at the top 10 bottling line equipment manufacturers shaping the industry’s future.
Top 10 Bottling Line Equipment Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 KHS Website
Domain Est. 1995
Website: khs.com
Key Highlights: As an international manufacturer of filling and packaging equipment for the beverage, food, and non-food sectors KHS Group holds a leading position within the ……
#2 Bottling & Filling Equipment Manufacturer
Domain Est. 2001
Website: epakmachinery.com
Key Highlights: E-PAK Machinery manufactures quality liquid filling machines, including cappers and labelers, for the bottling industry. Buy equipment and parts online….
#3 Bottling & Filling Equipment Manufacturer
Domain Est. 2001
Website: acasi.com
Key Highlights: We are one of the few bottle filling machine manufacturers that can offer a complete project with all bottling equipment made entirely by Acasi….
#4 Sidel
Domain Est. 1996
Website: sidel.com
Key Highlights: Sidel is a leading provider of equipment, services and complete solutions for packaging liquids, foods, home and personal care products in PET, can, ……
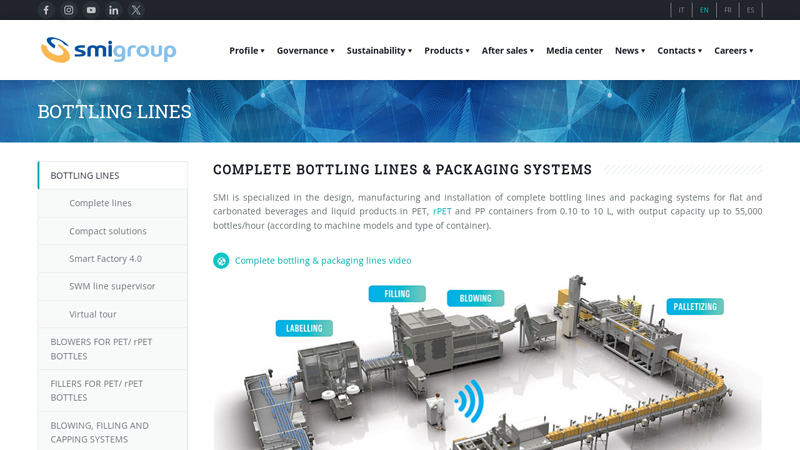
#5 BOTTLING LINES
Domain Est. 1998
Website: smigroup.it
Key Highlights: SMI is specialized in the design, manufacturing and installation of complete bottling lines and packaging systems for flat and carbonated beverages and liquid ……
#6 Small Water Bottling Equipment
Domain Est. 1998
Website: norlandintl.com
Key Highlights: Our bottling equipment including blow molders, water filling machines, and water bottling systems are perfect for your bottled water operations or bottled ……
#7 Lines for filling and packing glass and PET bottles as well as cans
Domain Est. 2000
Website: krones.com
Key Highlights: A customised bottling line for each container type. Whether for glass bottles, PET containers or cans, for filling, labelling or packing, for water, beer or ……
#8 Bottling equipment
Domain Est. 2002
Website: comacgroup.com
Key Highlights: Comac bottling equipment includes machines to provide the rinsing, the filling and the capping of beverage in bottles. Discover more!…
#9 MBF NORTH AMERICA
Domain Est. 2013
Website: mbfnorthamerica.com
Key Highlights: MBF North America is an independent American Corporation fully owned by MBF SpA (Italy), a leading company in the production of bottling systems….
#10 In
Domain Est. 2013
Website: inlinepack.com
Key Highlights: At In-Line Packaging, we’re proud to produce all different kinds of equipment that will help you produce the best food and beverages you can….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Bottling Line Equipment
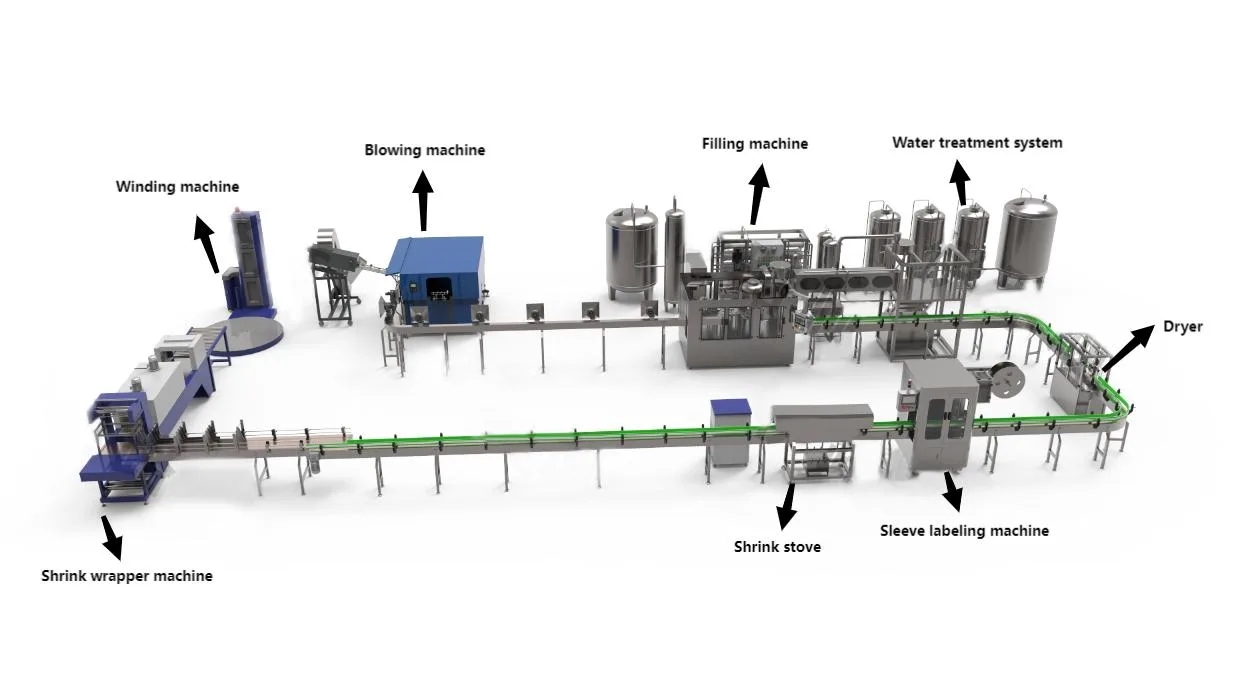
2026 Market Trends for Bottling Line Equipment
The global bottling line equipment market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological innovation, shifting consumer preferences, and evolving sustainability mandates. Key trends shaping the industry include:
H2: Rise of Smart Manufacturing and Industry 4.0 Integration
Bottling lines are rapidly evolving into intelligent, interconnected systems. By 2026, widespread adoption of IoT sensors, real-time data analytics, and AI-driven predictive maintenance will become standard. This enables greater operational efficiency, reduced downtime, and enhanced quality control. Digital twins—virtual replicas of physical bottling lines—will allow for simulation, optimization, and remote monitoring, improving both design and performance.
H2: Accelerated Demand for Sustainable and Eco-Friendly Solutions
Environmental regulations and consumer pressure are pushing manufacturers to reduce their carbon footprint. Bottling line equipment in 2026 will increasingly feature energy-efficient motors, water-saving rinsing systems, and lightweighting capabilities to support reduced material usage. Equipment designed for handling recycled PET (rPET), bioplastics, and alternative packaging materials (e.g., paper bottles) will experience strong demand. Closed-loop water recovery systems and modular designs for easier recycling will also gain prominence.
H2: Growth in Flexible and Modular Line Configurations
As consumer demand for variety increases—across flavors, sizes, and packaging formats—bottling lines must adapt quickly. By 2026, modular and reconfigurable equipment will dominate, allowing manufacturers to switch between products with minimal downtime. Quick-change tooling, standardized interfaces, and scalable designs will enable small-to-medium enterprises (SMEs) to remain competitive and respond agilely to market trends.
H2: Expansion Driven by Emerging Markets and Beverage Diversification
Emerging economies in Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Africa will be key growth drivers, fueled by rising disposable incomes and urbanization. Additionally, the surge in functional beverages—such as kombucha, plant-based drinks, and enhanced waters—will require specialized bottling lines capable of handling sensitive ingredients, carbonation, and non-standard viscosities. This diversification will spur innovation in filling and capping technologies.
H2: Increased Emphasis on Hygiene and Food Safety Automation
Post-pandemic, hygiene standards remain paramount. Bottling lines by 2026 will incorporate advanced Clean-in-Place (CIP) systems, sterile filling environments, and automated sanitation protocols. Use of antimicrobial materials and seamless, easy-to-clean designs will minimize contamination risks, especially critical for dairy, juice, and pharmaceutical applications.
H2: Adoption of Robotics and Advanced Automation
Robotic palletizing, case packing, and depalletizing systems will become more affordable and accessible, reducing reliance on manual labor and improving throughput. Collaborative robots (cobots) will integrate safely into bottling environments, assisting with inspection, labeling, and quality checks. Vision systems and machine learning will enhance defect detection and ensure packaging consistency.
In conclusion, the bottling line equipment market in 2026 will be defined by intelligence, sustainability, flexibility, and precision. Manufacturers investing in integrated, future-ready solutions will be best positioned to thrive in an increasingly dynamic and competitive landscape.
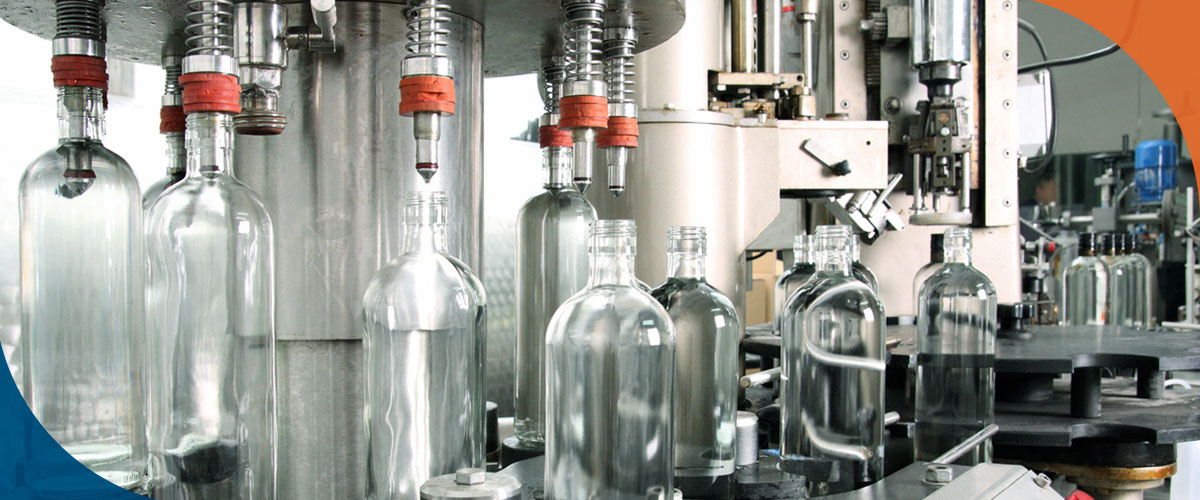

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Bottling Line Equipment (Quality & Intellectual Property)
Sourcing bottling line equipment involves significant investment and long-term operational impact. Overlooking key quality and intellectual property (IP) aspects can lead to costly problems, production delays, and legal risks. Being aware of these common pitfalls is crucial for making informed procurement decisions.
Inadequate Quality Verification and Testing Protocols
Many buyers assume equipment meets specifications based on vendor claims alone, leading to acceptance of substandard machinery. Insufficient on-site testing or lack of detailed performance criteria in contracts can result in equipment that fails under real production conditions—such as inconsistent fill levels, capping defects, or frequent breakdowns. Always demand factory acceptance tests (FAT) and site acceptance tests (SAT) with clear KPIs tied to performance, reliability, and sanitation standards.
Overlooking Compliance with Industry and Regional Standards
Bottling equipment must comply with food safety regulations (e.g., FDA, EHEDG, 3-A Sanitary Standards) and regional electrical and mechanical codes. Sourcing from suppliers unfamiliar with target market requirements—especially for export markets—can result in non-compliant equipment that cannot be legally operated. Verify certifications and material traceability (e.g., stainless steel grade) early in the procurement process.
Hidden Costs from Poor Build Quality and Maintenance Design
Low initial pricing can be misleading if equipment uses inferior materials or lacks modular design. Poorly built machines often require frequent maintenance, have higher spare parts costs, and suffer from reduced uptime. Additionally, designs that don’t allow for clean-in-place (CIP) systems or easy access for servicing increase labor costs and contamination risks. Evaluate total cost of ownership (TCO), not just purchase price.
Failure to Protect Intellectual Property in Custom Equipment
When developing bespoke solutions or integrating proprietary processes (e.g., unique filling mechanisms, labeling systems), buyers often neglect to secure IP rights. Suppliers may retain ownership of designs or modifications unless explicitly stated in contracts. This can limit future scalability, lead to dependency on the original supplier, or result in legal disputes if third parties replicate the technology.
Insufficient Vendor Due Diligence on IP Infringement Risks
Using equipment that incorporates patented technologies without proper licensing exposes the buyer to infringement claims—even if unintentional. Some suppliers, especially in less regulated markets, may use copied or reverse-engineered components. Conduct IP audits or require warranties from suppliers confirming that their equipment does not violate third-party intellectual property rights.
Lack of Documentation and Technical Know-How Transfer
Poor documentation—including incomplete schematics, missing operating manuals, or absence of control software source code—hinders maintenance and troubleshooting. If the supplier retains exclusive control over software or firmware, it creates vendor lock-in and operational vulnerabilities. Ensure contracts mandate full documentation delivery and, where possible, access to programmable logic controller (PLC) code or APIs.
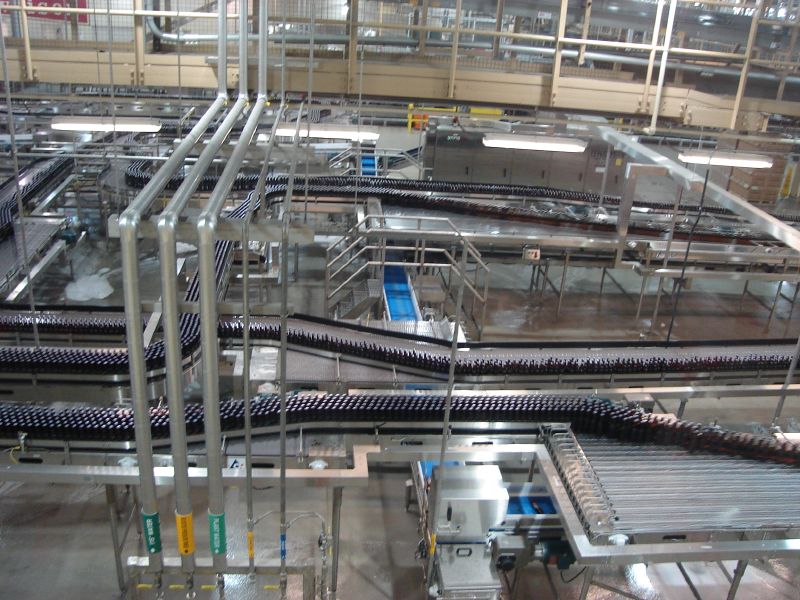

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Bottling Line Equipment
Equipment Procurement and Supplier Evaluation
Before acquiring bottling line equipment, conduct thorough due diligence on suppliers. Verify their certifications, such as ISO 9001 for quality management and ISO 14001 for environmental responsibility. Ensure suppliers comply with regional and international standards (e.g., CE marking for Europe, UL/CSA for North America). Assess lead times, warranty terms, and after-sales service availability. Request detailed technical documentation, including schematics, operation manuals, and compliance declarations.
Transportation and Handling Requirements
Coordinate logistics with experienced freight partners familiar with heavy industrial machinery. Use secure, enclosed transport to protect against weather, dust, and impact. Ensure proper crating, shock monitoring, and lifting points are used during loading/unloading. Equipment must be secured with straps or braces to prevent shifting. For international shipments, comply with Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) and ensure all customs documentation—commercial invoice, packing list, and certificate of origin—is accurate and complete.
Import/Export Compliance
Verify export control regulations (e.g., U.S. EAR or EU Dual-Use Regulation) if technology components are involved. Obtain required export licenses when necessary. For imports, classify equipment under the correct Harmonized System (HS) code to determine duties and tariffs. Comply with destination country-specific requirements, such as NRCan efficiency standards (Canada) or BIS certification (India). Maintain records of all compliance documentation for audit purposes.
Installation and Site Preparation
Prepare the facility to meet equipment specifications, including floor load capacity, utility connections (water, air, power), and drainage. Ensure adequate space for operation, maintenance access, and future expansion. Verify that electrical systems comply with local codes (e.g., NEC in the U.S., IEC in Europe). Engage certified technicians for installation and validate alignment, calibration, and safety interlocks before commissioning.
Regulatory and Safety Compliance
Ensure the bottling line meets relevant safety standards such as OSHA (U.S.), Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC (EU), or CSA Z432 (Canada). Install required safety features—emergency stops, guarding, lockout/tagout points—and conduct risk assessments (e.g., CE conformity assessments). Maintain up-to-date equipment logs, inspection records, and operator training certifications. Implement hygiene standards per FDA 21 CFR Part 117 (food safety) or EC 1935/2004 (materials in contact with food).
Operational Maintenance and Documentation
Establish a preventive maintenance schedule aligned with manufacturer recommendations. Document all service activities, spare part replacements, and equipment modifications. Keep a compliance file including CE/UL declarations, validation reports (e.g., IQ/OQ/PQ), and calibration records. Use serialized traceability systems for critical components to support recalls or audits.
Environmental and Sustainability Considerations
Adhere to environmental regulations such as EPA emissions standards or EU REACH/ROHS for hazardous substances. Optimize energy and water use through efficient equipment design and monitoring systems. Implement waste reduction and recycling programs for packaging materials and machine byproducts. Report environmental performance metrics as required by local laws or ESG frameworks.
Training and Personnel Certification
Provide comprehensive training for operators, maintenance staff, and supervisors on equipment operation, safety protocols, and compliance procedures. Maintain training records and ensure personnel are certified where required (e.g., pressure system operators, electricians). Conduct regular refresher courses and safety drills to reinforce compliance culture.
Audit and Continuous Improvement
Schedule regular internal and third-party audits to verify compliance with all applicable regulations. Use audit findings to update procedures, improve logistics planning, and enhance equipment performance. Stay informed about regulatory changes and industry best practices to ensure long-term operational and legal compliance.
Conclusion: Sourcing Bottling Line Equipment
Sourcing bottling line equipment is a critical investment that directly impacts production efficiency, product quality, and long-term operational scalability. After evaluating various suppliers, equipment capabilities, automation levels, and total cost of ownership, it is evident that selecting the right bottling line requires a strategic balance between performance, reliability, and cost-effectiveness.
The ideal solution should align with current production demands while offering flexibility for future expansion. Key considerations such as equipment compatibility with product type (liquid viscosity, container size, etc.), level of automation, ease of maintenance, and regulatory compliance (e.g., FDA, CE) must be prioritized. Additionally, partnering with reputable suppliers who offer strong technical support, training, and warranty services ensures minimal downtime and sustained productivity.
In conclusion, a well-researched and carefully executed sourcing strategy will result in a bottling line that enhances operational efficiency, reduces waste, supports product consistency, and delivers a strong return on investment. By focusing on quality, scalability, and supplier reliability, organizations can establish a robust foundation for long-term success in their packaging operations.