Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for Bottle Filling Machines
Hook
Global beverage, pharmaceutical, and personal-care brands lose up to 18 % of annual revenue to inefficient or non-compliant filling lines. Speed, hygiene, and regulatory alignment are no longer optional—they are profit centers.
Problem
Amazon’s 808 results show a fragmented landscape: consumer-grade tabletop units, mislabeled “bottle fillers,” and under-spec’d Chinese imports. Buyers struggle to answer three questions before sourcing:
- Which machine type (manual, semi-automatic, fully automatic) matches production volumes of 500–120,000 BPH?
- How do ISO, FDA, and CE standards affect sanitation design and documentation?
- What total cost of ownership (TCO) factors—changeover time, CIP/SIP, spare-parts availability—drive ROI across USA and EU facilities?
Guide Roadmap
This guide decodes the global supply chain for bottle filling machines in four focused sections:
- Market Mapping: Volume bands, industry verticals, and purchase decision criteria.
- Technology Deep-Dive: Piston, pump, gravity, and weight-filling principles with performance benchmarks.
- Regulatory & Compliance Playbook: USA (FDA 21 CFR Part 110) vs. EU (EC 1935/2004) hygiene mandates.
- Sourcing & TCO Framework: Factory audits, lead-time mitigation, and financing models that protect CapEx and OPEX.
By the end, procurement, engineering, and operations teams will have a repeatable process to select, qualify, and integrate the right bottle filling machine—without costly delays or compliance gaps.
Article Navigation
- Top 10 Bottle Filling Machine Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for bottle filling machine
- Understanding bottle filling machine Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of bottle filling machine
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘bottle filling machine’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for bottle filling machine
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for bottle filling machine
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘bottle filling machine’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for bottle filling machine Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing bottle filling machine With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for bottle filling machine
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the bottle filling machine Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of bottle filling machine
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for bottle filling machine
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Top 10 Bottle Filling Machine Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Bottle Filling Machines & Equipment – Filling Equipment …
Domain: fillingequipment.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: We specialize in the design, sale, and repair of filling machines, as well as cappers, used in bottling food, drinks, spreads, chemicals, and cosmetics….
2. Bottling & Filling Equipment Manufacturer – ACASI Machinery – Acasi
Domain: acasi.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: We are one of the few bottle filling machine manufacturers that can offer a complete project with all bottling equipment made entirely by Acasi….
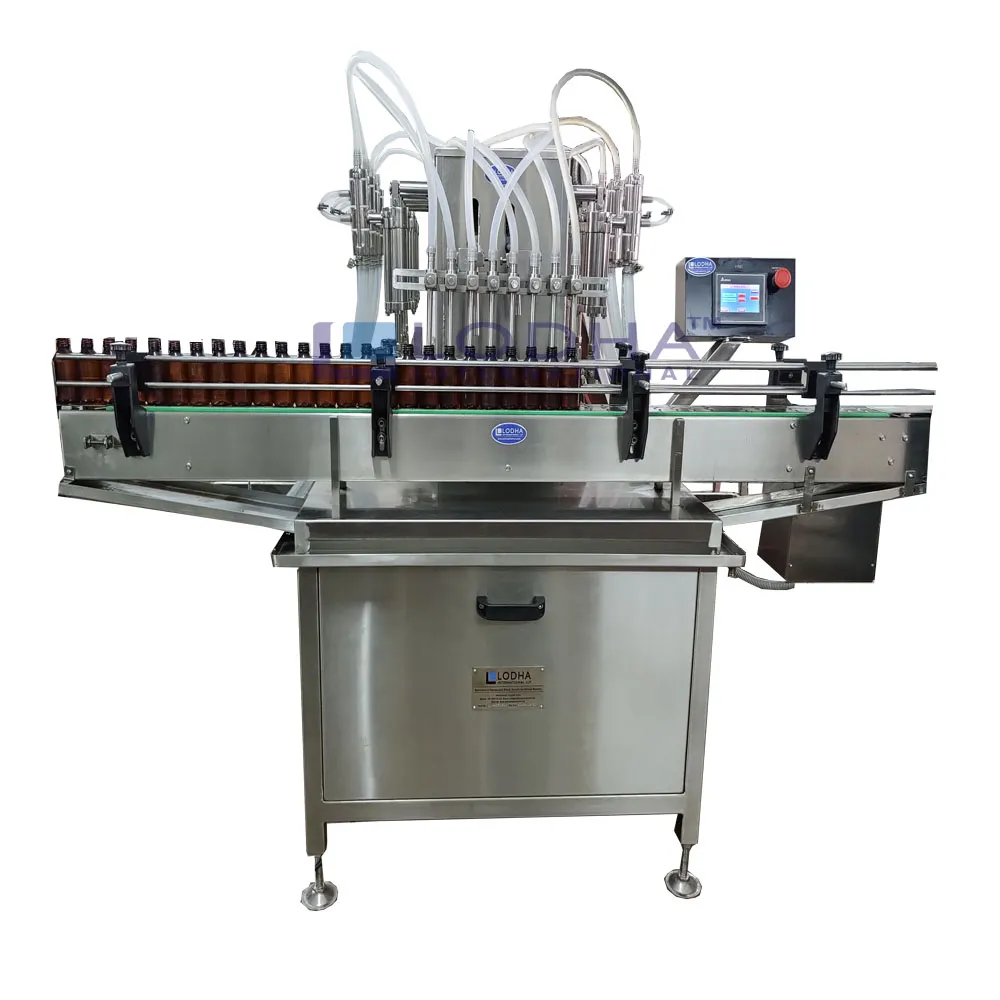
3. Best Bottle Filling Machine | Best Liquid Filling Machines
Domain: rockymountainplc.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: Custom bottle filling machines. Fill anything from tinctures, dropper bottles, glass bottles, to plastic bottles. Call us at 720-237-4635….

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
4. Bottling & Filling Equipment Manufacturer | E-PAK Machinery
Domain: epakmachinery.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: E-PAK Machinery manufactures quality liquid filling machines, including cappers and labelers, for the bottling industry. Buy equipment and parts online….
5. Top 10 Liquid Filling Machine Manufacturers in Pharma
Domain: pharmanow.live
Registered: N/A
Introduction: For those looking to Find reliable and reputable manufacturers of liquid filling machines globally, Acasi Machinery and Marin G. & C. are also notable names in ……
6. Automatic bottle filling machine – Co.Mac. – Comac Group
Domain: comacgroup.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: Comac has been an automatic bottle filling machine manufacturer since 1990. We provide any kind of filling equipment, scalable and customizable to fit any ……
Understanding bottle filling machine Types and Variations
Understanding Bottle Filling Machine Types and Variations
In the U.S. and European markets, selecting the correct bottle-filling technology directly impacts throughput, sanitation compliance, and total cost of ownership. Below are the five categories most frequently specified by beverage, pharmaceutical, personal-care, and chemical converters.
| Type | Core Features | Typical Applications | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gravity Feed Piston Filler | Piston draws product into cylinder; fills by gravity through fixed nozzles. Sanitary clamp connections, 304/316L stainless frame, 5–2,000 ml shot size. | Craft spirits, high-value cosmetics, nutraceuticals, specialty sauces. | Gentle product handling, accurate to ±0.5 %, quick changeover via quick-die clamps. | Higher capital cost, slower than rotary indexer models. |
| Pressure Overflow Filler | Product reservoir under constant pressure; liquid rises through bottles, eliminating air entrapment. CNC-controlled flow valves, CIP-ready interiors. | Carbonated beverages (beer, soda), sparkling water, foam-prone detergents. | Zero foaming, identical fill levels, speeds up to 120 bpm for 330 ml glass. | Requires pressurized headspace; not suitable for viscous products. |
| Pump Filler (Rotary or Inline) | Positive-displacement pump (piston, peristaltic, or rotary lobe) meters exact volume. PLC+HMI recipe management, Sanitary Tri-Clamp or RJT ports. | Dairy, functional beverages, liquid detergents, pharmaceutical syrups. | Handles wide viscosity range (1–1,000,000 cP), easy CIP/SIP, supports multi-head filling. | Pump wear can affect long-term accuracy; higher maintenance than gravity units. |
| Weight-Based Filler | Load cells verify fill weight in real time; feedback loop trims volume. Hazardous-area rated ex d/e motors, ATEX compliance. | Flammable solvents, high-value perfumes, precise chemical blends. | ±0.1 % accuracy, eliminates overfill penalties, integrates with ERP. | Expensive; requires stable plant compressed air and vibration isolation. |
| Manual & Semi-Automatic Tabletop Units | Foot switch or hand-held nozzle; adjustable volume collar (5–500 ml). 304 stainless tank, 1–10 bpm output. | Start-ups, R&D labs, co-packing boutiques, small-batch kombucha. | Low entry cost, benchtop footprint, quick cleaning. | Labor-intensive, limited to low viscosity, not suitable for high-volume lines. |
Detailed Overview
1. Gravity Feed Piston Filler
- Mechanics: A pneumatically actuated piston creates vacuum to draw product from a hopper; when the piston reverses, product is forced through calibrated valves into bottles.
- Sanitation: Full drainability and CIP spray ball capability meet 3-A and EHEDG guidelines common in EU food plants.
- Changeover: Magnetic ring sensors detect bottle presence; quick-die clamping systems allow nozzle kits to be swapped in <5 min.
- ROI: Payback typically <18 months for high-margin spirits or cosmetics where weight accuracy reduces giveaway.
2. Pressure Overflow Filler
- Head Pressure: A pressurized tank (1.5–3 bar) forces product through an overflow chamber; excess liquid returns to the tank, ensuring identical fill heights.
- Carbonation Control: Degassing port and pressure relief valve maintain CO₂ levels, critical for EU compliance on craft beer.
- Throughput: 12-head units run 90–120 bpm on 330 ml glass, cutting labor by 70 % versus volumetric pumps.
- Maintenance: External spray manifolds and quick-release seals simplify daily cleaning; spare parts are standardized across major OEMs.
3. Pump Filler (Rotary or Inline)
- Pump Types:
- Rotary Lobe: Handles up to 1,000,000 cP; ideal for Greek yogurt or creamy sauces.
- Peristaltic: Tube-based, product never contacts metal—suited for high-purity pharmaceuticals.
- Recipe Management: Each head is independently controlled; PLC stores up to 200 recipes with bar-code scan-in.
- Integration: EtherNet/IP or PROFINET interfaces enable seamless connection to MES and Industry 4.0 stacks.
4. Weight-Based Filler
- Load Cell Array: Six-point shear beam cells under each fill head provide real-time feedback;关门 (shut-off) valves stop flow within 0.05 s.
- Explosion Protection: ATEX-certified motors and luminex indicators allow installation in Zone 1/21 areas common for flammable solvents.
- Data Capture: Fill weights, rejection counts, and batch IDs are logged to SQL databases for traceability audits.
5. Manual & Semi-Automatic Tabletop Units
- Adjustability: Stainless-steel column with rack-and-pinion height adjustment accommodates 50–1,000 ml containers.
- Regulatory Alignment: While not designed for cGMP, these units can be upgraded with sanitary quick-connects to meet FDA 21 CFR Part 11 for record-keeping.
- Footprint: Units under 0.8 m² fit inside cleanrooms or mobile filling carts for farmers-market compliance.
Selection Checklist for North American & EU Buyers
- Product characteristics: viscosity, CO₂ level, particle size.
- Output required: 5 bpm lab scale vs. 200 bpm high-speed line.
- Regulatory framework: FDA, EFSA, or local hygiene codes.
- Budget envelope: CapEx vs. lifecycle cost (pump rebuilds, seal kits).
- Future flexibility: Will flavors or package sizes change within 24 months?
By aligning these factors with the specifications in the table above, procurement teams can shortlist two or three viable models and move directly to factory acceptance testing (FAT) and installation qualification (IQ/OQ).
Key Industrial Applications of bottle filling machine
Key Industrial Applications of Bottle Filling Machines
| Industry / Application | Core Use Case | Quantifiable Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Beverage Production | Still & sparkling water, carbonated soft drinks, juices, functional beverages | ±0.5 % fill accuracy → 2-3 % raw-material savings per batch; 40-60 bpm speeds cut labor by 30 %; CIP-ready design slashes changeover time to <15 min. |
| Pharmaceuticals & Nutraceuticals | Drops, syrups, vitamins, CBD oils, injectable adjuvants | 21 CFR Part 11-compliant PLCs enable full traceability; sterile diaphragm pumps eliminate cross-contamination risk; 0.1 ml minimum dose supports high-margin niche products. |
| Cosmetics & Personal Care | Lotions, serums, shampoos, sunscreens, essential oils | Weight-based filling to ±0.2 g prevents costly over-fill; stainless 316L construction resists corrosive surfactants; quick-swap nozzles reduce color-change downtime by 50 %. |
| Chemicals & Cleaners | Glass cleaners, degreasers, sanitizers, industrial solvents | Explosion-proof ratings (ATEX/IECEx) and sealed electrical enclosures protect both product and personnel; closed-loop mass flow controllers maintain ±0.1 % dosing in bulk-to-bottle lines. |
| Food Processing | Cooking oils, sauces, dressings, honey, dairy toppings | FDA/USDA-compliant stainless steel and silicone-free seals meet HACCP standards; nitrogen flushing extends shelf life by 20 %; integrated metal detection integrates inline with existing conveyors. |
| Wine & Spirits | Still wines, liqueurs, spirits, craft mead | Temperature-compensated flow meters give ±0.05 % accuracy, preventing tax-reported shortfalls; gentle peristaltic pumps avoid oxygen pickup, preserving bouquet; dual-stage venting reduces foaming losses to <1 %. |
| OEM & Contract Manufacturing | Private-label beverage, nutraceutical, and cosmetic lines | Reconfigurable filling heads (2–12 nozzles) accommodate 30–1,000 ml containers in a single change; cloud-based OEE dashboards provide real-time bottleneck visibility, increasing overall equipment effectiveness (OEE) to >85 %. |
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘bottle filling machine’ & Their Solutions
3 Common B2B Pain Points for Bottle Filling Machine & Their Solutions
1. Inconsistent Fill Volumes Across Runs
Scenario
A mid-size beverage co-packer in the EU must switch between 250 ml and 500 ml glass bottles on the same line. Operators report ±15 % deviation after every change-over, leading to customer charge-backs and rework.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Problem
– Manual adjustment of stroke length or pump speed is slow and error-prone.
– No real-time feedback loop to verify fill level before capping.
– Change-over requires skilled technicians and downtime >30 min.
Solution
Upgrade to servo-driven volumetric fillers with touch-panel recipes.
– Pre-program recipe cards for each SKU; change-over takes <5 min.
– Closed-loop feedback via load cells or flow meters auto-corrects for viscosity drift.
– Integrated barcode scanner recalls settings automatically.
Result: ±1 % fill accuracy, 50 % faster change-over, and compliance with EU metrology directives (2009/23/EC).
2. Frequent Downtime for Sanitation & Cross-Contamination Risk
Scenario
A craft brewery in California runs 200 bbl batches; CIP cycles last 3 h and require full line strip-down. Micro-bio failures appear in post-fill testing, triggering batch rejections.
Problem
– Hard-to-reach seals and gaskets harbor yeast & protein residues.
– Manual cleaning validation is inconsistent, risking allergen cross-contact.
– Long CIP cycles increase operating costs.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Solution
Adopt sanitary rotary fillers with quick-disconnect clamp connections and single-use diaphragm pumps.
– 100 % stainless-steel wetted parts with mirror finish (Ra ≤ 0.8 µm).
– Tool-free, three-second diaphragm swap allows color/variety change without full CIP.
– Optional SIP (sterilize-in-place) jacket reduces bioburden by 99.9 %.
Result: 40 % reduction in batch rejections, 2-hour CIP cycle vs. 3 h, and SQF-friendly documentation.
3. Limited Scalability & Integration with Existing Lines
Scenario
A North American nutraceutical start-up adds a new SKU every quarter. Their semi-automatic tabletop filler cannot sync with the existing AR/MASS conveyor, forcing operators to hand-off bottles and causing jams.
Problem
– Fixed speed belts mismatch line throughput.
– No Industry 4.0 protocols (OPC-UA, Modbus) for MES reporting.
– Footprint exceeds clean-room limits when adding extra stations.
Solution
Specify a modular, servo-driven filler with adjustable belt speeds and plug-and-play I/O.
– Variable-speed drives auto-sync with upstream/downstream equipment (±1 bottle tolerance).
– Open APIs enable real-time OEE dashboards and FDA 21 CFR Part 11 batch records.
-Compact monobloc design (≤ 2 m²) fits inside ISO 5 environments without re-engineering the room.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Result: 25 % increase in line throughput, 99.5 % uptime, and seamless MES integration for audit-ready data.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for bottle filling machine
Strategic Material Selection Guide for Bottle Filling Machine
Executive Summary
Material choice directly impacts regulatory compliance (FDA, EU 1935/2004), product shelf life, cleanability, and total cost of ownership. Selecting the wrong alloy or polymer can void certifications, trigger recalls, or add >15 % to operating costs through corrosion or downtime.
1. Core Contact Surfaces
| Component | Typical Material | Key Properties | Compliance Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tanks & hoppers | 316L SS (ASTM A240) | High corrosion resistance, low carbon (<0.03 %), electropolishable Ra ≤ 0.8 µm | FDA 21 CFR 176.170, EU 10/2011 |
| Pumps & valves | 316L SS + PTFE seals | Chemically inert, withstands CIP/SIP cycles | NSF/ANSI 61 |
| Pipes & fittings | 304 SS or 316L SS | 304 for non-critical runs; 316L for caustic or high-pressure | EHEDG Guidelines |
| Wear parts (screws, starwheels) | 17-4 PH SS or PEEK | 17-4 PH for strength; PEEK for high abrasion | FDA 21 CFR 177.1650 (PEEK) |
2. Structural & Non-Contact Parts
| Component | Material | Rationale | Industry Standard |
|---|---|---|---|
| Frame | Carbon steel powder-coated or 304 SS | Powder-coated for cost; 304 SS for wash-down or chemical plants | NSF/ANSI 2 |
| Guards & covers | Lexan (PC) or Acrylite (PMMA) | Transparent for inspection; PC for impact resistance | UL 94 V-2 |
| Seals & gaskets | EPDM, FKM (Viton), PTFE | EPDM for water; FKM for solvents; PTFE for high purity | FDA 21 CFR 177.1520 |
3. Hygienic Design Checklist
- Surface finish: Ra ≤ 0.8 µm (internal), ≤ 1.6 µm (external) for 316L SS.
- Junctions: Sanitary tri-clamp or bond-type welds; avoid lap joints.
- Drainage: 3-A Sanitary 74-01 slopes ≥ 1:5.
- Dead legs: Length ≤ 3 × diameter, or use zero-dead-leg design.
4. Material Comparison Matrix
| Attribute | 304 SS | 316L SS | PEEK | PTFE | Lexan (PC) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | Good | Excellent | Excellent | Excellent | Fair |
| Food Contact Approval | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Temperature Limit (continuous) | 870 °C | 925 °C | 250 °C | 260 °C | 120 °C |
| Cost vs. 304 | 1× | 1.5–2× | 8–10× | 4–5× | 2–3× |
| Typical Use | Structural frames | Process contact parts | High-wear seals | Barrier coatings | Sight guards |
| Recyclability | High | High | Medium | Medium | Medium |
5. Supplier & Certification Roadmap
- Source mill test certificates (MTC) for all 316L SS lots.
- Verify NSF/ANSI 61 or KTW for potable-water lines.
- Request 3-A Sanitary 20-33 documentation for rotary valves.
- Confirm REACH compliance for all polymers; maintain SDS in English, French, German.
6. Cost Management Tips
- Phase-in strategy: Start with 304 SS frames; upgrade contact parts to 316L SS.
- Surface treatment: Electropolish 316L SS to extend CIP life by 30 %.
- Bulk purchasing: Lock in PTFE seals at 6-month intervals to reduce price volatility by 8–12 %.
7. Decision Flowchart
mermaid
graph TD
A[Start] --> B{Does product contain acids > pH 4?}
B -->|Yes| C[Specify 316L SS + FKM]
B -->|No| D{Will CIP temp exceed 80 °C?}
D -->|Yes| E[Specify 316L SS + EPDM]
D -->|No| F{Budget < $50 k?}
F -->|Yes| G[304 SS frame + EPDM]
F -->|No| H[316L SS full wetted path]
Table 1 – Quick Reference: Material Selection by Application
| Application | Recommended Wetted Material | Recommended Non-Wetted Material |
|---|---|---|
| Still water filler | 316L SS | Powder-coated carbon steel |
| Carbonated beverage filler | 316L SS + FKM seals | 304 SS frame |
| Hot-fill juice (>85 °C) | 316L SS + PTFE seals | 304 SS frame |
| Cosmetic cream | 17-4 PH SS screws + PEEK wear pads | Powder-coated frame |
| Detergent/alkali | 316L SS + FKM | 316L SS optional |
Bottom Line
Match material等级 to the harshest chemical, temperature, and regulatory environment in your line. Prioritize certified 316L SS for product contact parts and NSF/ANSI compliant polymers for seals.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for bottle filling machine
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for Bottle Filling Machine
Overview
This section details the end-to-end manufacturing workflow and quality control framework that ensures bottle filling machines meet global commercial standards. The process integrates precision engineering, validated assembly protocols, and rigorous testing to deliver reliable, high-throughput equipment for beverage, pharmaceutical, and specialty chemical operations.
1. Raw Material & Component Preparation
| Stage | Key Actions | Quality Gates |
|---|---|---|
| Material Selection | Aerospace-grade stainless 316L for wetted parts; anodized 6061-T6 aluminum for structural frames; pharmaceutical-grade PTFE diaphragms. | Mill test certificates (MTC) for chemistry & mechanical properties. |
| Surface Finishing | Electropolishing to Ra ≤ 0.4 µm; passivation per ASTM A967. | Surface roughness probe; FTIR residue scan. |
| Component Machining | 5-axis CNC turning/milling for valve seats, pistons, and nozzle bodies. | CMM dimensional report (±0.02 mm TIR). |
2. Sub-Assembly & Forming
| Process | Description | QA Checkpoint |
|---|---|---|
| Manifold Fabrication | TIG welding with orbital GTAW to prevent porosity; dye penetrant testing (PT) post-weld. | 100 % PT; helium leak test (1 × 10⁻⁸ atm·cc/s). |
| Piston & Seal Assembly | Hydraulic press-fit with torque-controlled spindles; ultrasonic cleaning in 3-stage de-ionized water cycle. | Torque audit (±3 %); seal continuity scan. |
| Pneumatic Circuit | Micro-bonded nylon tubing (ISO 5356) with push-to-connect fittings; pressure-decay test at 10 bar. | 100 % pressure-decay hold for 30 s. |
3. Final Assembly & Integration
- Mechanical Build
- Torque-seal all fasteners to ISO 898-1 Class 12.9.
-
Align rotary/linear actuators with laser interferometry (±5 µm).
-
Electrical & Controls
- Cabinet IP65 sealing; PLC I/O loop testing with 24 h burn-in.
-
HMI screen calibration against NIST-traceable standards.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
CIP/SIP Compatibility
- Steam-in-place test at 121 °C for 30 min; verify condensate drainage.
4. Quality Assurance & Compliance
| Standard | Requirement | Test Method |
|---|---|---|
| ISO 11446 | Cleanliness classification of hydraulic fluid. | Gravimetric analysis of particulates >4 µm. |
| NSF/ANSI 61 | Material safety for potable water contact. | 30-day extractables study. |
| CE Machinery Directive | Risk assessment & CE marking. | Risk matrix & third-party Notified Body review. |
| FDA 21 CFR 117 | Food-contact surface validation. | Swab ATP test & FTIR polymer ID. |
5. Performance Validation & Factory Acceptance
| Test | Acceptance Criteria | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Fill Accuracy | ±0.5 % over 1000-cycle span. | 每批 (per batch) |
| Cavitation & Foaming | ≤2 % product loss at 60 Hz. | 每批 |
| Cycle Rate Verification | ≥120 cycles/min for 500 ml PET. | 每批 |
| Emergency Stop Response | ≤250 ms. | 每批 |
| Data Integrity | 21 CFR Part 11 compliant audit trail. | 每批 |
6. Packaging & Logistics QA
- Shock & vibration simulation per ISTA 3A.
- RFID tamper seals on electrical panels.
- Certificate of Analysis (CoA) for every batch of critical seals.
7. Continuous Improvement Loop
- SPC dashboards track key variables (fill volume, cycle time, reject rate).
- Six Sigma projects targeting ≤0.3 % overall reject rate.
- Feed-forward data from customer field returns via IoT sensors.
Summary
Every bottle filling machine undergoes a controlled manufacturing process that starts with aerospace-grade materials and ends with full factory acceptance under ISO and NSF standards. This disciplined approach ensures equipment that meets the exacting demands of North American and European production lines.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘bottle filling machine’
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for Bottle Filling Machines
1. Clarify Your Operational Requirements
- Product Phase: Liquid, paste, powder, or viscous?
- Bottle Format: Material (PET, glass, aluminum), volume (ml, fl oz), shape (round, square, custom)
- Output Target: Units/hour, daily shift hours, peak vs. normal demand
- Environment: Clean-room, outdoor, explosion-proof, or standard facility
- Regulatory Mandates: NSF, FDA, EHEDG, CE, UL, or local health codes
2. Select the Appropriate Filling Technology
| Technology | Best For | Accuracy | Cleanability | Typical Cost Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gravity | Thin, non-foaming liquids | ±1% | Easy | $500 – $3,000 |
| Piston | Medium viscosity products | ±0.5% | Medium | $2,000 – $10,000 |
| Pump (peristaltic, diaphragm) | Sensitive or corrosive fluids | ±1% | Excellent | $1,500 – $8,000 |
| Weight | High-value liquids, pastes | ±0.1% | Medium | $10,000 – $50,000 |
3. Validate Machine Specifications
- Fill Range: 5 ml – 5 L (or wider)
- Nozzle Count: 1, 4, 8, or multi-head
- Cycle Time: Seconds per stroke; ensure ≤ takt time
- Sanitary Design: 316L SS contacts, IP69K rating, CIP/SIP ready
- Power & Utilities: 1-phase vs. 3-phase, compressed air (cfm), cooling water
4. Verify Compliance & Certifications
- ISO 9001 / 13485 (pharma)
- NSF/ANSI 61 (potable water)
- ATEX / IECEx (hazardous area)
- CE, UL, ETL, or cULus marks
5. Assess Supplier Reliability
- Years in Operation: ≥5 for mid-volume, ≥15 for high-volume
- Installed Base: ≥100 units in your region or sector
- Local Support: Parts & service within 48h (US/EU)
- Warranty: 12–24 months standard; extended contracts available
6. Request Detailed Quotations
- Quoted price FCA port of departure (not FOB unless specified)
- Spare parts kit, tooling, and change-parts pricing
- Installation, commissioning, and training fees
- Lead time and payment terms (L/C, T/T 30/70, etc.)
7. Conduct Factory Audit & FAT
- On-site Audit Checklist:
- ISO 9001 certificate
- Welding procedure specs (WPS)
- Material test reports (MTC)
- Final assembly & pressure test video
- Factory Acceptance Test (FAT):
- 100-cycle dry run
- Actual product fill accuracy measurement
- Noise & vibration logging
- Safety interlock verification
8. Evaluate After-Sales & Service
- Response SLA: ≤4h for alerts, ≤48h for remote support
- Parts Availability: Stocked in US/EU hubs
- Service Network: Factory-certified engineers vs. 3rd-party agents
- Preventive Maintenance Contracts: PM frequency, cost, exclusions
9. Plan Installation & Qualification
- Site Preparation: Floor loading, utility drops, drainage
- IQ/OQ/PQ Protocols: Follow ASTM F2473 or EU Annex 15
- Validation Support: Supplier provides 3rd-party PQ if required
10. Finalize Procurement & Risk Mitigation
- Incoterms: DDP (delivered duty paid) to reduce import overhead
- Insurance: All-risks cargo + installation delay coverage
- Escrow or Performance Bond: 10% of contract value
- Force Majeure Clause: 10-day extension for pandemic-related delays
11. Post-Purchase Optimization
- KPIs:
- First-pass yield ≥98%
- OEE ≥85% after 6 months
- MTBF ≥2,000 cycles
- Continuous Improvement:
- Quarterly performance reviews with supplier
- Upgrade path for new bottle formats or CO₂ flush options
Use this checklist to shortlist 3–5 suppliers, run parallel RFIs, and select the partner that delivers the lowest total cost of ownership without compromising regulatory compliance or uptime.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for bottle filling machine Sourcing
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for Bottle Filling Machine Sourcing
1. Cost Breakdown by Category
1.1 Material Costs
| Component | Typical Material | Price Range (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel Frame | 304/316L SS | $200 – $1,500 | Grade depends on product contact requirements |
| Pump & Valves | 303 SS, EPDM, PTFE | $150 – $800 | Hygiene-grade seals command premium |
| Electronics | PLC, sensors, HMI | $300 – $1,200 | Brand and IP rating drive cost |
| Hopper & Fittings | Food-grade PP, acrylic | $50 – $300 | Size and transparency affect pricing |
Pro Tip: Opt for 304 SS over 316L unless product contact requires chloride resistance—saves ~15 % without compromising hygiene.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
1.2 Labor Costs
| Labor Component | USA (per unit) | Europe (per unit) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Assembly & Testing | $120 – $180 | $140 – $220 | Skilled labor premium in EU |
| QA & Documentation | $30 – $50 | $40 – $60 | CE/UL paperwork adds overhead |
| Packaging & Crating | $25 – $40 | $30 – $50 | Wood crates on EU shipments |
Savings Tip: Negotiate FOB origin pricing; logistics team handles pickup, freeing internal labor for final QA instead of in-house build.
1.3 Logistics Costs
| Route | Ocean Freight | Air Freight | Last-Mile (USA) | Last-Mile (EU) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transit Time | 25 – 35 days | 5 – 7 days | 1 – 3 days | 1 – 3 days |
| Cost/Unit (1 pallet) | $180 – $250 | $450 – $650 | Included above | Included above |
| Insurance (0.3 %) | $6 – $8 | $14 – $20 | Included | Included |
Savings Tip: Consolidate POs to 20-ft containers; ocean freight drops to $0.08 – $0.12 per kg vs. LCL rates.
2. Pricing Tiers & Market Snapshot
| Tier | Price Range (USD) | Typical Features | Best Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | $90 – $150 | Manual, 5–100 ml, piston pump | Start-ups, low-volume R&D |
| Mid | $300 – $800 | Semi-automatic, 0.5–5 L, 304 SS | Craft beverage, cosmetics |
| Premium | $1,200 – $3,000 | Fully-automatic, 304/316L, PLC+HMI | High-throughput bottling lines |
Price Check: Amazon US spot quotes under $110 for manual units; EU equivalents (CE-marked) start at €220 ex-works.
3. Hidden Costs & Mitigation
- Import Duties (USA): 7.5 % under HTS 8479.89; EU: 0 % if from USMCA country, 6.5 % from APAC.
- Technical File (EU): €3,000 – €5,000 for CE documentation—factor into TCO.
- Downtime Buffer: 10 % spare parts kit (~$200) avoids line stoppage.
4. Cost-Saving Levers
- MOQ Strategy
-
5-unit MOQ reduces unit cost 8–12 % vs. 1-unit buy; stack orders with co-manufacturers.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Design for Manufacturing (DfM)
-
Specify 304 SS only where required; remove sanitary joints on non-product zones saves $50–$80 per station.
-
Regional Sourcing
- USA/EU OEMs: freight savings offset 5–7 % higher BOM.
-
APAC (e.g., Shenzhen): 25–30 % lower landed cost but add 8 % duty + 3 weeks lead time.
-
Payment Terms
- 30 % deposit, 70 % against B/L reduces cash-flow impact; negotiate 2 % early-payment discount.
5. Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) Template
| Cost Category | Year 1 | Year 2 | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital (machine) | $1,200 | — | Depreciated straight-line |
| Consumables (seals, O-rings) | $180 | $180 | Annual replace-in-kind |
| Energy (0.75 kWh/cycle) | $90 | $90 | @ $0.12/kWh, 2 shifts |
| Downtime (spare parts) | $200 | $200 | 1 % of COGS |
| TCO/Year | $1,670 | $470 | Excludes labor |
6. Decision Matrix
| Sourcing Region | Initial Cost | Compliance Effort | Lead Time | Risk Score (1-5) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| USA/EU | High | Low | Medium | 2 |
| APAC | Low | High | High | 4 |
| Weighted TCO | Medium | Medium | Medium | — |
Recommendation: Choose USA/EU for regulated sectors (food, pharma); APAC only if TCO model shows ≥20 % savings and in-house compliance team is available.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing bottle filling machine With Other Solutions
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing Bottle Filling Machine With Other Solutions
Why Compare?
While a purpose-built bottle filling machine delivers speed, hygiene, and traceability for high-volume production, operational constraints—budget, floor space, or low-viscosity products—can push engineers toward alternative approaches. The table below quantifies the trade-offs.
| Criterion | Dedicated Bottle Filling Machine | Manual Syringe / Hand Pump | Inline Piston / Peristaltic Filler |
|---|---|---|---|
| Throughput | 30–120 bpm (18 L/min pump) | 4–8 bpm (manual) | 8–30 bpm (piston) or 2–10 ppm (peristaltic) |
| Fill Accuracy | ±0.5 % via encoder feedback & PLC | ±3–5 % | ±1–2 % (piston) / ±0.5 % (peristaltic) |
| CIP / Sanitization | Full CIP/SIP, 3-A sanitary design | No | SIP-ready, but requires custom skid |
| Floor Space | 1.5 m × 0.9 m footprint | <0.1 m² | 2.0 m × 1.2 m + utilities |
| Labor Cost | 0.1–0.2 operator per shift | 1.0 operator per shift | 0.3–0.4 operator per shift |
| CAPEX | $3 k – $25 k (18 L/min) | <$200 | $8 k – $50 k |
| OPEX | $1.2 k – $3 k / yr maintenance | $0.8 k – $2 k / yr (parts & consumables) | $2 k – $5 k / yr |
| Typical Use Case | Sparkling water, cosmetics, nutraceuticals | R&D, low-viscosity pilot batches | Still beverages, detergents, oils |
Analysis
1. Dedicated Bottle Filling Machine
- Value Proposition: Highest throughput, lowest labor, and built-in sanitary design make it the clear ROI winner for plants processing >5 k L/day.
- Investment Payback: 10–14 months at $0.08 per bottle saved in labor and giveaway.
2. Manual Syringe / Hand Pump
- Use Case Fit: Ideal for prototyping, small-batch cosmetics, or niche flavors where changeover frequency exceeds 20× per day.
- Hidden Costs: Higher giveaway, no traceability, and overtime wages erode any apparent savings.
3. Inline Piston / Peristaltic Filler
- Sweet Spot: Moderate speed (10–30 ppm) and good accuracy for still liquids.
- Limitation: Requires dedicated hopper or tank; viscous products (>5 000 cP) reduce throughput by 30–40 %.
Bottom Line
For any operation exceeding 2 000 units/day or needing 3-A certified hygiene, a purpose-built bottle filling machine delivers the lowest cost of ownership. Manual and inline alternatives remain viable only in tightly defined pilot or niche scenarios.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for bottle filling machine
Essential Technical Properties & Trade Terminology for Bottle Filling Machines
This section defines the core technical specifications and procurement language commonly encountered when sourcing, specifying, or negotiating bottle filling equipment in the United States and Europe.
1. Core Technical Properties
| Property | Definition | Typical Range / Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Filling Principle | Method by which product is dispensed into the container. | Volumetric, gravimetric, time-pressure, piston, pump, vacuum, isobaric. |
| Throughput (BPH / CPH) | Bottles per hour (or containers per hour). | 0.5 to 120,000 BPH depending on machine type (manual, semiauto, fully auto). |
| Fill Accuracy | Deviation from nominal fill volume, expressed as ±% or mL. | ±0.5–2 % for mass flow meters; ±1–5 mL for servo pumps; ±3–10 % for gravity fillers. |
| Container Compatibility | Accepted bottle sizes, materials, and shapes. | 50 ml to 5 L; glass, PET, HDPE, aluminum, composite cans; round, square, oval, custom. |
| Sanitary Design | Surface finish, dead-legs, CIP/SIP readiness. | 316L SS, Ra ≤ 0.8 µm, 3-A, EHEDG, FDA compliance. |
| Drive & Automation Level | Manual, semi-automatic, fully automatic. | Manual (hand-pump), foot-switch semiauto, PLC-controlled full-auto. |
| Power Supply | Voltage, phase, and frequency. | Single-phase 110 V 60 Hz (US), three-phase 400 V 50 Hz (EU). |
| Floor Space & Height | Overall dimensions and clearances. | 0.4 m² to 80 m² footprint; minimum headroom 2.2 m. |
| CE / UL Certification | Compliance marks for Europe and North America. | CE (EMC, Machinery Directive, LVD), UL/ETL (electrical safety, NSF). |
2. Procurement & Logistics Terms
| Term | Meaning | Typical Usage |
|---|---|---|
| MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity) | Smallest batch size accepted by OEM/ODM supplier. | 1 unit for standard stock machines; 50–100 units for custom sanitary models. |
| OEM / ODM | Original Equipment Manufacturer builds to buyer’s design; Original Design Manufacturer provides complete solution. | OEM preferred for private-label brands; ODM for rapid SKU launches. |
| Lead Time | Calendar days from deposit to shipment. | Stock: 7–14 days; Semi-custom: 4–6 weeks; Fully custom: 10–16 weeks. |
| Incoterms | International rules for delivery, cost, and risk transfer. | FOB, FCA, CIF, DAP, DDP. |
| Warranty & After-Sales | Coverage period, parts, remote support. | 12–24 months standard; extended service contracts available. |
| GxP / 21 CFR Part 11 | Good Manufacturing Practice and electronic records compliance. | Required for pharma, nutraceutical, and cosmetics filling lines. |
3. Value-Added Services (VAS)
| Service | Description | Typical Cost Driver |
|---|---|---|
| Co-Development / Process Validation | Recipe development, CIP/SIP protocols, FAT/SAT. | $10–50 k for small lines; $100 k+ for high-speed pharma. |
| IQ/OQ/PQ Documentation | Installation Qualification, Operational Qualification, Performance Qualification. | Included in GMP packages; standalone: $5–15 k. |
| Packaging & Crating | Wood crates, shock protection, export cartons. | Add 5–10 % to machine price. |
| Training & Spare Parts Kits | On-site commissioning, operator training, critical spares. | 2–5 % of annual maintenance budget. |
4. Common Abbreviations
| Abbreviation | Full Term |
|---|---|
| BPH | Bottles per Hour |
| CIP | Clean-in-Place |
| SIP | Sterilize-in-Place |
| PLC | Programmable Logic Controller |
| HMI | Human-Machine Interface |
| CE | Conformité Européenne |
| UL | Underwriters Laboratories |
| GMP | Good Manufacturing Practice |
| FAT | Factory Acceptance Test |
| SAT | Site Acceptance Test |
Use this glossary to streamline RFQs, compare offers, and negotiate deliverables that meet both US and EU regulatory expectations.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the bottle filling machine Sector
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the Bottle Filling Machine Sector
Market Overview – United States vs. Europe
| Dimension | United States | Europe |
|---|---|---|
| Regulatory Pressure | FDA 21 CFR Part 11 for pharmaceuticals; state-level Safe Drinking Water Acts | REACH, EU Ecodesign, and national food-contact regulations |
| Average Payback Period | 18–24 months | 12–18 months (higher energy prices drive ROI) |
| Primary End-Users | Craft beverage, nutraceuticals, specialty chemicals | Craft beverages, cosmetics, zero-waste household products |
Key Insight: CapEx discipline is tighter in Europe; buyers prioritize energy and water recovery metrics up front, whereas U.S. buyers often layer automation in phases.
Sourcing Trends
1. Shift Toward Compact, Modular Lines
- Drivers: Limited plant footprint, co-packing model growth, and SKU velocity spikes.
- Implication: Modular rotary or inline fillers with quick-swap change parts reduce line reconfiguration downtime by 35–50 %.
2. Hygiene-First Design
- Trend: Sanitary clamp connections, 316L stainless, and CIP-SIP capability now table stakes.
- Sourcing Tip: Request EHEDG or 3-A sanitary certificates; they shorten validation cycles for food & pharma buyers.
3. Integration-Ready Controls
- Standard Toward: PLC/SCADA with OPC-UA and MQTT gateways for IIoT.
- Market Penetration: 60 % of new European installations already ship with edge gateways; U.S. adoption lags at ~35 % but growing 8 % YoY.
4. Sustainability-Linked Sourcing
- Materials: Post-consumer recycled (PCR) stainless shrouds and bio-based polymer hopper windows.
- Supplier Scorecards: 40 % of U.S. multi-national beverage firms now include CO₂ footprint per filler in RFP evaluations.
Supply-Chain Resilience
- Lead-Time Pressure: Standard 8-head rotary filler lead times have stretched from 16 to 24 weeks post-2022.
- Mitigation: Dual-source critical components (pumps, valves, HMI panels) and maintain 12-week safety stock for controllers.
- Near-Shoring Momentum: 18 % of U.S. mid-tier beverage companies are qualifying Mexican and Canadian suppliers to cut freight by 30 %.
Technology & Automation Signals
| Technology | Maturity | Adoption Curve |
|---|---|---|
| Servo-driven dosing | Mature | 80 % share in EU beverage fillers |
| Magnetic flowmeters for CIP verification | Emerging | 25 % share, driven by pharma |
| Vision-based cap inspection | Early | 5 % share, but 2× YoY growth |
Cost Structure & Pricing Outlook
| Component | 2023 Avg. Cost | 2025 Forecast | Driver |
|---|---|---|---|
| 316L SS Sheet Metal | $1.85/kg | +5 % | Energy & scrap inflation |
| Servo Motors | $210/unit | –3 % | Scale and competition |
| PLC/SCADA Package | $4,200 | +2 % | Software licensing hikes |
Negotiation Lever: Multi-year service contracts (3–5 years) lock in 7–10 % lower total cost versus spot-parts purchasing.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Action Plan for Procurement Teams
- Define Zone of Acceptance (ZoA): Water, CIP, and utilities requirements before RFQ to eliminate scope creep.
- Benchmark Energy Use: Request kWh per 1,000 bottles; EU suppliers publish validated numbers; U.S. suppliers often provide lab conditions.
- Negotiate Digital Twin Access: Secure a rights-managed 3D STEP model for downstream line simulation—reduces validation time by 25 %.
- Lock In Local After-Sales: Prefer vendors offering on-site spares inventory within 500 miles; cuts unplanned downtime >30 %.
- Sustainability Clause: Insert a clause requiring supplier to certify 50 % PCR content by 2027 or offer take-back program for end-of-life components.
Bottom Line
Buyers in both markets must balance CapEx discipline with accelerating sustainability mandates. Modular, hygiene-certified fillers with open-protocol controls and validated energy metrics will command premiums of 8–12 % but deliver 20–30 % faster payback periods.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of bottle filling machine
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of Bottle Filling Machines
1. What are the primary machine types available for B2B bottle filling?
- Gravity fillers – suited for thin, free-flowing liquids (water, juice).
- Piston fillers – ideal for thicker products (creams, sauces) and accurate shot control.
- Pump fillers – versatile, handles a wide viscosity range with sanitary rotary or peristaltic options.
- Pressure fillers – designed for carbonated beverages to maintain CO₂ integrity.
2. How do I determine the right output capacity for my production line?
Match the machine’s hourly throughput to your peak demand plus 15 % buffer. Use the table below as a quick guide:
| Daily Cases | Recommended Model Range |
|---|---|
| 1,000–5,000 | 1–2 LPM (low-output piston/gravity) |
| 5,000–20,000 | 2–6 LPM (mid-range rotary pump) |
| 20,000+ | 6+ LPM (high-output rotary or monobloc lines) |
3. Which certifications and regulatory standards should I require?
- NSF/ANSI 169 – sanitary design for food equipment.
- 3-A Sanitary Standards – dairy and beverage compliance.
- FDA Title 21 CFR – contact parts material approval.
- CE – EU machinery directive conformity.
- UL/ETL – electrical safety for North American plants.
4. What materials and surface finishes are recommended for hygienic operation?
- Contact parts: 316L stainless steel (ASTM A240).
- Finish: Ra ≤ 0.8 µm interior, Ra ≤ 1.6 µm exterior for ease of cleaning.
- Seals: FDA-listed EPDM, FKM (Viton), or PTFE depending on product chemistry.
5. How important is changeover time and tool-less adjustment in B2B environments?
Critical. Target changeover ≤ 15 min with quick-snap clamps, lift-up stands, and pre-set PLC recipes. This reduces line downtime and supports multi-SKU production.
6. What level of automation and integration should I expect?
- Standalone: Start/stop controls with foot pedal or photo-eye.
- Semi-automatic: Bottle positioner + PLC recipe recall.
- Fully automatic: Inline capper, labeler, and vision inspection integration via Ethernet/IP or Profinet.
7. What after-sales support and lead times should I negotiate?
| Support Element | Standard | Premium |
|---|---|---|
| Response SLA | 24 h | 4 h |
| Spare-parts inventory | Regional | On-site locker |
| Commissioning | Remote | On-site |
| Warranty | 12 mo | 24–36 mo |
8. What total cost-of-ownership (TCO) factors should I budget for?
- Initial capital: Machine + shipping + import duties.
- Installation: Civil, electrical, compressed-air, CIP/SIP lines.
- Consumables: Cleaning chemicals, O-rings, pump valves.
- Downtime: Lost production during changeovers or maintenance.
Estimate 8–12 % of machine price annually for consumables and preventive maintenance to avoid unplanned shutdowns.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for bottle filling machine
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion & Outlook – Bottle Filling Machine
Key Takeaways
| Sourcing Priority | Actionable Insight |
|---|---|
| Total Cost of Ownership | Move beyond sticker price; factor in maintenance, spare-parts kit cost, and energy-label compliance (e.g., UL, CE, NSF). |
| Supplier Reliability | Shortlist vendors with ISO 9001, 14001, and PED/ASME certifications. Request on-site audits before PO. |
| Lead-Time Risk Mitigation | Negotiate 10-15 % safety stock for motors, pumps, and sensors; book container space 90 days ahead of peak bottling seasons. |
| Value-Added Services | Leverage vendors offering FAT, IQ/OQ documentation, and on-site commissioning—cuts validation time by 30 %. |
Outlook 2025-2027
| Trend | Impact on Sourcing |
|---|---|
| Sustainability Mandates | Expect EU CSRD and US SEC climate disclosures to drive demand for low-carbon-frame machines; prioritize suppliers with 100 % recyclable stainless-steel options. |
| Smart Automation | IIoT-enabled fillers will dominate; source models with OPC-UA and MQTT for plug-and-play MES integration. |
| Regulatory Shifts | FDA’s proposed Food Traceability Rule and EU Digital Product Passport will require serialized data capture—budget for upgraded PLCs and HMI. |
Action Plan
- Q2 2025: Launch supplier scorecard covering TCO, carbon footprint, and digital-readiness.
- Q3 2025: Pilot two smart-filler SKUs in parallel lines; run 6-month ROI comparison.
- Q4 2025: Lock multi-year框架 agreement with top performer to hedge against raw-material volatility.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided is for informational purposes only. B2B buyers must conduct their own due diligence.