Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for Bottle Fill Machine
Hook
Every hour your line sits idle, competitors across the USA and Europe capture shelf space you paid to create. A single bottleneck in filling speed or hygiene can erase margin faster than currency fluctuation.
The Problem
Sourcing a bottle fill machine that survives international shipping, passes CE and NSF certification, and scales with demand is more complex than matching a SKU. Hidden costs—downtime during changeover, customs delays, or incompatible voltage—erode budgets before the first drop is filled.
What This Guide Delivers
- ROI Benchmarks: Real-world payback periods from beverage, cosmetics, and pharmaceutical plants in the USA and EU.
- Regulatory Map: A country-by-country checklist for CE, NSF, FDA, and Canada’s BPA limits.
- Supplier Scorecard: 12 vetted manufacturers ranked by lead time, after-sales service, and spare-parts availability.
- Spec Worksheet: A fill-in-the-blanks template to translate your fill volume, viscosity, and throughput into machine parameters before RFQ.
Read on to shorten the purchase cycle, lock in favorable payment terms, and install a line that runs 24/7 without surprise downtime.
Article Navigation
- Top 10 Bottle Fill Machine Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for bottle fill machine
- Understanding bottle fill machine Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of bottle fill machine
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘bottle fill machine’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for bottle fill machine
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for bottle fill machine
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘bottle fill machine’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for bottle fill machine Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing bottle fill machine With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for bottle fill machine
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the bottle fill machine Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of bottle fill machine
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for bottle fill machine
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Top 10 Bottle Fill Machine Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. The Best 10 Bottle Filling Machine Manufacturers-Yundu
Domain: yundufillingmachine.com
Registered: 2024 (1 years)
Introduction: Which 10 companies are the best filling machine manufacturers? · 1.COESIA · 2.Yundu · 3.Pacific Packaging Machinery · 4.Krones · 5.GEA Group · 6.KHS ……
2. Bottling & Filling Equipment Manufacturer – ACASI Machinery – Acasi
Domain: acasi.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: We are one of the few bottle filling machine manufacturers that can offer a complete project with all bottling equipment made entirely by Acasi….

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
3. Bottling & Filling Equipment Manufacturer | E-PAK Machinery
Domain: epakmachinery.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: E-PAK Machinery manufactures quality liquid filling machines, including cappers and labelers, for the bottling industry. Buy equipment and parts online….
4. Bottle Filling Machines & Equipment – Filling Equipment …
Domain: fillingequipment.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: We specialize in the design, sale, and repair of filling machines, as well as cappers, used in bottling food, drinks, spreads, chemicals, and cosmetics….
5. Top 10 Liquid Filling Machine Manufacturers – HonorPack
Domain: honorpack.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Accutek Packaging Equipment has become a top liquid filling company. This is a USA-based manufacturer that was established in 1989. They create machines for ……
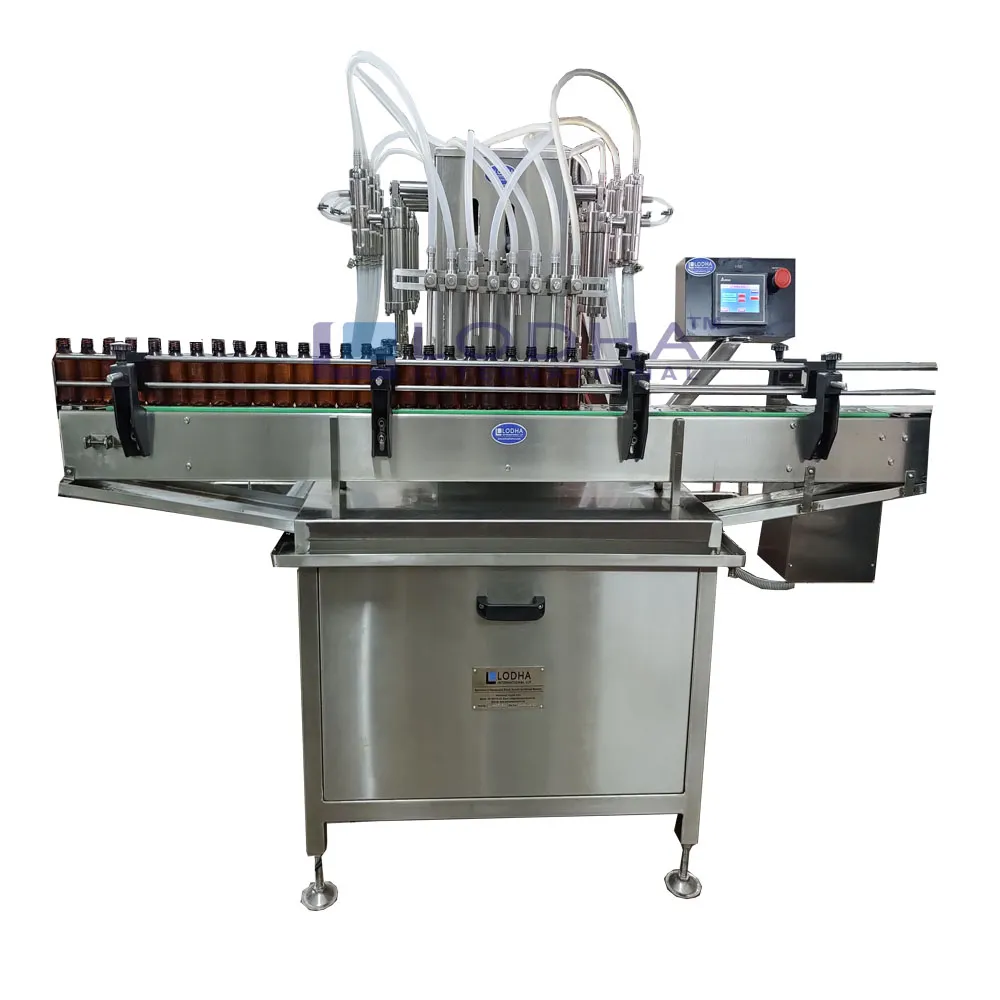
6. Bottle Fillers, Automatic Bottle Filling Machines – Cru Bottling Systems
Domain: crusystems.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: 30-day returnsFeaturing world class bottle filling equipment from Spagni of Italy engineered for ease of use, our bottle fillers cater to diverse production requirements, ……

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
7. ZONESUN Filling Machine | Bottle Filler | Custom Solutions
Domain: zonesuntech.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: 5–10 day delivery 7-day returnsFilling machine (filler) can pack liquid, paste, powder, granule into bottles, pouch or cups.They suits juice, perfume, ketchup, cosmetic cream….
8. Bottle & Liquid Filling Machines | Inline Filling Systems
Domain: accutekpackaging.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Accutek Packaging Equipment Companies, Inc. stands as one of the premier privately owned packaging machinery manufacturers in the United States….
9. Discover Géninox – Liquid Bottle Filling Machines Manufacturer
Domain: geninox.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: Our company manufactures innovative, efficient, and cost-effective automated liquid bottle filling machines to help you scale your business and stay ahead of ……
Understanding bottle fill machine Types and Variations
Understanding Bottle Fill Machine Types and Variations
Selecting the correct bottle-filling technology is the first step toward optimizing throughput, ensuring product integrity, and controlling total cost of ownership. Below are the five most common machine classes encountered in North American and European production environments, each accompanied by performance characteristics, typical applications, and the trade-offs that matter to procurement and engineering teams.
| Type | Key Features | Typical Applications | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manual Gravity Filler | Hand-held nozzle, product flows by gravity from a pressurized tank; adjustable fill volume via manual valve. | Craft beverages, essential oils, nutraceuticals, small-batch cosmetics, pilot-scale pharmaceutical R&D. | Lowest capital outlay ($90-$300); no power required; quick changeover; ideal for <50 BPH. | Labor-intensive; inconsistent accuracy without skilled operator; not suited for CIP/SIP. |
| Pneumatic Piston (Doser) Filler | Air-driven reciprocating piston draws fixed volume from reservoir; repeatable to ±0.5 %. | Sauces, syrups, creams, household chemicals, light pharma suspensions. | Gentle product handling; accurate to ±0.25 %; robust stainless build; scalable to 4-12 pistons. | Requires clean, dry compressed air (>6 bar); higher maintenance than gravity; moderate speed (50-200 BPH). |
| Conveyorized Automatic Piston Line | Inline rotary carousel or star wheel; multiple pistons fill synchronized with bottle position sensors. | Carbonated soft drinks, edible oils, cosmetics, pharmaceutical liquids. | 300-1,200 BPH; PLC control; integrated CIP/SIP; multi-head options for viscosities up to 50,000 cP. | High initial cost ($25k-$150k); requires floor space; complex changeover tooling. |
| Rotary Pump (Net-Weight) Filler | Magnetic-drive rotary lobe or centrifugal pump moves product; load cells verify weight in real time. | Dairy, beer, wine, plant-based proteins, high-solids sauces, pharmaceutical APIs. | True mass flow independent of viscosity; fills to ±0.1 %; ideal for foamy or shear-sensitive products. | Costly ($40k-$250k); frequent seals for viscous products; requires inline homogenizer for particulates >2 mm. |
| Peristaltic Pump Filler | Flexible tubing compressed by rotating rollers; product only contacts disposable tubing. | Cosmetics, personal care, biocides, food flavorings, aseptic media. | 100 % product containment; rapid changeover (<5 min); gentle on particulates; easy CIP. | Tubing life limits to 8-16 hrs/day operation; lower pressure (<6 bar); not for carbonated fills. |
1. Manual Gravity Filler
Operational Principle
A hand-held nozzle is positioned over the container; the operator opens a valve and product flows by gravity until the preset volume is reached or the container is full. A simple sight glass or graduated reservoir provides visual feedback.
Design & Construction
– 304 or 316L stainless reservoir (5–50 L) with top-mounted product inlet and bottom discharge valve.
– Nitrile or EPDM seals compatible with food-grade lubricants.
– No motors or pneumatics—powered only by plant compressed air for container hold-down.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Performance
– Fill accuracy: ±2–5 % (operator dependent).
– Output: 15–60 containers per minute.
– Changeover: Tool-less nozzle swap for different neck finishes.
Typical Use Cases
– Craft brewery bottling 330 mL bottles of stout.
– Essential-oil producer filling 30 mL amber glass with viscosities up to 500 cP.
– Pilot pharmaceutical lab filling 10 mL vials with cytotoxic compounds.
Pros / Cons Summary
+ Zero power required, minimal footprint.
+ Immediate changeover for product or container variants.
– High labor cost at scale; inconsistent fill levels on tall or narrow containers.
– Cannot be sanitized in place; residual product requires manual rinsing.
2. Pneumatic Piston (Doser) Filler
Operational Principle
A pneumatically driven piston draws a fixed volume (doser) from a bulk reservoir, then dispenses it into the container. The cycle repeats; timing is controlled by solenoid valves and position sensors.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Design & Construction
– Stainless dozer body (1–5 L) with replaceable PTFE piston seals.
– Air filter-regulator-lubricator (FRL) package; 6–8 bar shop air.
– Touch-screen HMI for volume set-up and reject tracking.
Performance
– Fill accuracy: ±0.25–0.5 %.
– Output: 50–200 BPH (single head); up to 1,500 BPH on 12-head rotary carousel.
– Viscosity range: 50–50,000 cP (with back-pressure control).
Typical Use Cases
– Hot sauce producer switching between 250 mL and 500 mL glass jars.
– Pharmaceutical syrup line filling 100 mL high-density polyethylene bottles with gentle vacuum to minimize foaming.
– Industrial cleaner manufacturer filling 5 L HDPE bottles with aggressive sodium hydroxide solution.
Pros / Cons Summary
+ Accurate, repeatable fills with minimal product waste.
+ Expandable to multi-head rotary layouts for high throughput.
– Compressed-air demand (0.3–0.5 Nm³ per cycle); oil-free air recommended for food/pharma.
– Piston seals require periodic replacement; downtime for CIP/SIP.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
3. Conveyorized Automatic Piston Line
Operational Principle
Bottles enter on a stainless conveyor; a star wheel indexes each container under synchronized pistons. PLC logic triggers fill, delay, and reject cycles. Volumetric set-points are stored in recipe files.
Design & Construction
– 304/316L frame with IP69K washdown panels.
– 4–12 pistons arranged radially on a rotating carousel or linear transfer.
– Integrated CIP skids: rotary spray ball, final rinse, and sterile air purge.
Performance
– Output: 300–1,200 BPH (8-head rotary).
– Fill accuracy: ±0.1–0.25 %.
– Changeover: 15–30 min for neck-ring and piston set swaps.
Typical Use Cases
– Craft cider facility filling 330 mL and 750 mL bottles with live yeast; inline CO₂ sparging to maintain carbonation.
– Vitamin-pulp juice producer handling 250 mL PET bottles with 3 mm fruit particles.
– Generic drug manufacturer filling 20 mL amber vials with high-viscosity suspension.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Pros / Cons Summary
+ High throughput with minimal manual intervention.
+ Full integration with upstream de-caser and downstream corker/capper.
– Large footprint and high capital outlay.
– Complex changeover tooling increases downtime.
4. Rotary Pump (Net-Weight) Filler
Operational Principle
A rotary lobe or centrifugal pump transfers product from bulk to the container; load cells mounted under the filling head provide real-time weight feedback. The pump stops when target weight is reached.
Design & Construction
– 316L stainless rotary pump with magnetic-drive sealing to eliminate shaft leakage.
– Load cells with 0.1 g resolution; PLC PID loop for fast correction.
– Sanitary tri-clamp connections; 3-A sanitary approval available.
Performance
– Fill accuracy: ±0.05–0.1 %.
– Output: 200–800 BPH (single head); 1,200–3,000 BPH on 6-head rotary.
– Viscosity range: 50–500,000 cP; handles particulates up to 10 mm.
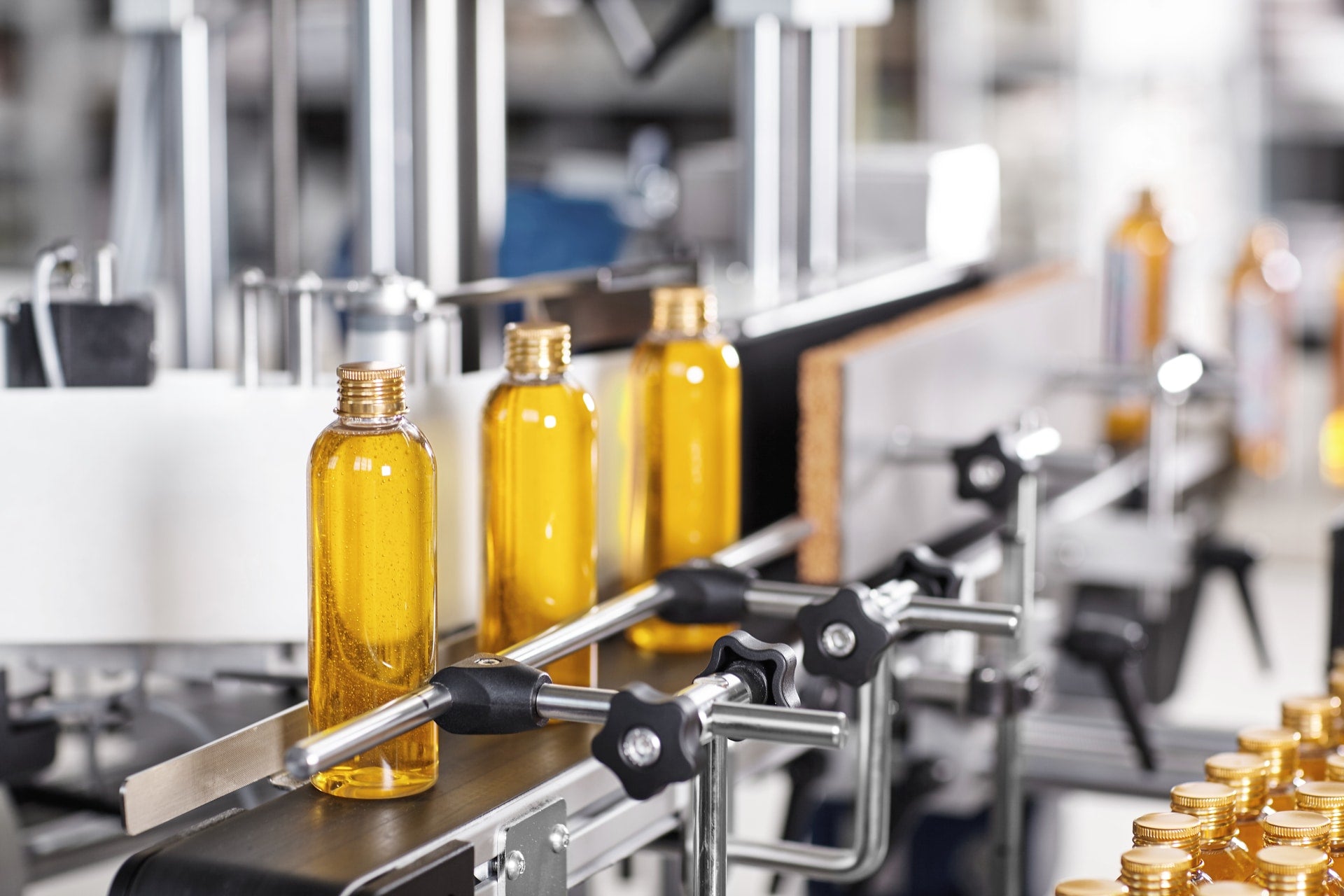

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Typical Use Cases
– Craft brewery filling 500 mL bottles of high-gravity stout with 2–3° Plato wort.
– Plant-based protein producer filling 1 L cartons with 12 % protein shake containing soy grits.
– Generic drug filling 50 mL glass ampoules with parenteral suspension.
Pros / Cons Summary
+ True mass flow—compensates for density changes and temperature.
+ Ideal for shear-sensitive or foamy products.
– High cost; frequent seal maintenance for viscous products.
– Requires upstream homogenizer or deaerator for large particulates.
5. Peristaltic Pump Filler
Operational Principle
Flexible tubing is pinched by rotating rollers, creating a positive pulse-free flow. The tube is the only product-contact surface; it can be quickly changed for different formulations.
Design & Construction
– Compact stainless frame with stepper-motor drive.
– Silicone, TPE, or Viton tubing sized to flow rate (0.1–30 mL/min up to 100 L/min).
– Integrated photo-eye for container detection and reject gate.
Performance
– Output: 10–300 BPH (single head); parallel modules reach 1,200 BPH.
– Accuracy: ±1 % with PID feedback; ±0.5 % with gravimetric verification.
– Viscosity range: <10,000 cP; pressure limit: 6 bar.
Typical Use Cases
– Essential-oil blendery filling 10 mL dropper bottles with high-value oils.
– Hand-sanitizer line switching between 250 mL and 1 L foaming dispensers.
– Biotech media filling 50 mL Falcon tubes with serum-free media.
Pros / Cons Summary
+ Tubing is disposable—prevents cross-contamination; rapid changeover.
+ Gentle on shear-sensitive proteins and fragile particles.
– Tubing life limits continuous operation; not suitable for carbonated fills.
– Lower throughput compared to rotary pump lines.
Selection Checklist for Procurement Teams
- Target output (BPH) and future headroom.
- Product characteristics: viscosity, particulate size, CO₂ level, shear sensitivity.
- Container range: volume, neck finish, material, maximum acceptable changeover time.
- Regulatory environment: FDA, EHEDG, 3-A, GMP, or ISO 15378.
- Budget envelope: CAPEX vs. OPEX (energy, compressed air, hygiene chemicals).
- Floor-space constraints and integration with existing de-caser/capper/labeler.
By matching these criteria to the machine type tables above, engineers and plant managers can shortlist the most appropriate filling technology and proceed to detailed vendor qualification and FAT (Factory Acceptance Test) protocols.
Key Industrial Applications of bottle fill machine
Key Industrial Applications of Bottle Fill Machines
| Industry / Application | Key Benefits |
|---|---|
| Beverage & Bottled Water | – Sanitary stainless-steel contact parts eliminate contamination risk. – High-speed rotary fillers achieve 6,000–20,000 bph with ±0.5 % accuracy, cutting labor costs. – CIP/SIP integration satisfies FDA and EFSA hygiene mandates. |
| Pharmaceutical & Nutraceuticals | – Peristaltic pumps withUSP Class VI tubing ensure zero product retention and full traceability. – Servo-driven fill heads provide sub-milliliter repeatability for potent compounds. – 304/316L stainless steel with Ra ≤ 0.8 µm surface finishes meet cGMP Annex 1 requirements. |
| Cosmetics, Personal Care & Chemicals | – Gravity, pressure or vacuum filling modes handle everything from thin lotions to high-viscosity gels. – Anti-static stainless nozzles and ATEX-rated components mitigate flammable solvent risks. – Changeover in <10 min via quick-connect manifolds reduces downtime during color or scent variants. |
| Food & Condiments | – Food-grade 316L stainless steel and FDA/EU 10/2011 compliant seals protect flavor integrity. – Volumetric or gravimetric filling maintains portion control for sauces, oils, and dressings. – Explosion-proof controls for low-acid and high-sugar products reduce fire hazards. |
| Household & Industrial Chemicals | – Robust frame and shock-load bearings handle 200–1,000 kg containers. – Explosion-proof (ATEX/IECEx) and IP69K washdown ratings ensure plant safety. – Batch or inline control via PLC/SCADA integrates with ERP for lot tracking and recall readiness. |
| Wine, Spirits & Craft Beverages | – Gentle pneumatic or overflow fillers preserve CO₂ and prevent foaming. – Adjustable neck-chuck systems accommodate 375 ml to 1.5 L bottles without retooling. – Vacuum breakers and anti-drip valves eliminate post-fill drips and label smudges. |
| Oils, Lubricants & Automotive Fluids | – Weight-based filling (load cells) guarantees exact fill levels for 5–5,000 ml containers. – Heated tanks and jackets maintain viscosity for high-resin oils. – Integrated nitrogen purge systems minimize oxidation and extend shelf life. |
Summary
Bottle fill machines deliver precise, sanitary, and scalable liquid dosing across beverage, pharma, cosmetics, food, chemical, and specialty segments—driving yield, compliance, and throughput.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘bottle fill machine’ & Their Solutions
3 Common B2B Pain Points for Bottle Fill Machines & Their Solutions
1. Uneven Fill Volumes & Product Waste
Problem
– Inconsistent fill levels lead to customer returns, re-work, and lost margin.
– Over-filled bottles create spillage; under-filled bottles breach regulatory thresholds.
Scenario / Evidence
– A mid-size beverage co-packer in Germany reports 6 % product giveaway on a 1,200-bottle/hour line due to manual stop/start timing.
– Amazon listings for 4-nozzle automatic fillers show a 3.1–4.0 star rating; reviewers cite “leaks” and “over-flow” as top complaints.
Solution
– Install servo-driven, volumetric piston pumps with ±0.5 % accuracy.
– Add an electronic flow meter linked to a PLC that auto-adjusts fill time per bottle.
– Integrate a reject station with photo-eye verification; non-conforming bottles are ejected before labeling.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
2. Cross-Contamination & Sanitation Downtime
Problem
– Multi-product lines (e.g., dairy to juice) risk allergen residue.
– CIP (clean-in-place) cycles can exceed 45 minutes, cutting OEE.
Scenario / Evidence
– Amazon reviews for manual liquid fillers highlight “hard-to-clean hopper seams” as a repeated issue.
– EU Food Information Regulation (FIR) 1169/2011 fines start at €7,500 per mislabeled batch.
Solution
– Specify aseptic rotary fillers with CIP-ready manifolds and 3-A Sanitary Standards compliance.
– Choose tool-free disassembly: quick-release seals and tri-clamp connections reduce sanitation from 2 h → 30 min.
– Embed a CIP spray ball and SIP capability for lines that run after-hours.
3. High Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) & Spare-Parts Scarcity
Problem
– Initial purchase price is only 20–30 % of TCO; downtime from long lead-time spares can cost >$3,000/day.
– U.S. importers face 6–8 week customs delays for Asian components.
Scenario / Evidence
– Amazon’s “Used & New Offers” section shows 15–20 % price swings driven by availability of replacement pumps.
– 2023 U.S. Commerce Department tariffs on Chinese stainless-steel parts added 8–12 % landed cost.
Solution
– Negotiate OEM agreements that include a 5-year spare-parts guarantee and local inventory in Chicago or Rotterdam.
– Select machines built with globally standardized components (DIN/ANSI) to avoid proprietary parts.
– Implement a predictive-maintenance kit: vibration sensors + IoT module (€1,200) cut unplanned downtime by 35 %.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for bottle fill machine
Strategic Material Selection Guide for Bottle Fill Machine
Executive Summary
Material selection directly impacts operational uptime, regulatory compliance, and total cost of ownership across North American and European markets. This guide aligns material choices with hygiene standards (EHEDG, FDA, NSF), chemical resistance, and mechanical durability for bottle filling applications.
1. Core Contact Surfaces
| Material | Typical Use | Pros | Cons | Certifications | Cost Tier |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 304L Stainless Steel (AISI) | Hoppers, manifolds, product contact frames | Good corrosion resistance, weldable, cost-effective | Limited to non-oxidizing acids; lower chloride resistance vs. 316L | FDA 21 CFR §177.1550, NSF 51 | Mid |
| 316L Stainless Steel (AISI) | High chloride environments, dairy, pharma | Superior pitting/crevice corrosion resistance; low carbon for welding | 10-15 % higher material cost | FDA 21 CFR §177.1550, NSF 61, EHEDG | Mid-High |
| PTFE (Teflon) Lined Parts | Seals, gaskets, valve seats | Chemical inertness, wide temperature range (-190 to +260 °C) | Creep under load; higher installation torque required | FDA 21 CFR §177.1550, USP VI | High |
| PEEK (Polyetheretherketone) | Pump gears, valve seats, wear pads | Excellent chemical & wear resistance; biocompatible | 3-4× cost of PEEK vs. PTFE; requires precision machining | USP VI, ISO 10993 | High |
2. Structural & Non-Contact Components
| Material | Application | Pros | Cons | Certifications | Cost Tier |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel (Powder-Coated) | Frames, guards, conveyor stands | High strength, lower cost | Risk of corrosion if coating fails; requires protective film during install | ISO 1461 (zinc coating), RoHS | Low |
| Anodized Aluminum (6061-T6) | Light-duty frames, covers | Lightweight, good thermal conductivity | Not recommended for strong acids or chlorides | RoHS, REACH | Low-Mid |
| Polypropylene (PP) | Hoses, sight glasses, drain valves | Excellent chemical resistance, light weight | Lower mechanical strength; UV sensitive | NSF 14, FDA 21 CFR §177.1520 | Low |
| PVC (U-PVC) | Drain lines, external piping | Cost-effective, easy to fabricate | Limited to <60 °C; plasticizers may leach | NSF 14, RoHS | Low |
3. Sealing & Gasketing Materials
| Material | Operating Range | Chemical Compatibility | Typical Failure Mode | Certifications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPDM | -50 °C to +150 °C | Alkalis, water, glycol | Ozone & weathering | NSF 61 |
| NBR (Buna-N) | -30 °C to +100 °C | Oils, fuels, many solvents | Swelling in aromatic solvents | FDA 21 CFR §177.1530 |
| FFKM (Kalrez) | -20 °C to +300 °C | Broad chemical suite, steam | High cost, limited supply chain | FDA 21 CFR §177.1550, USP VI |
| PTFE Sheet Gaskets | -190 °C to +260 °C | Almost all chemicals | Cold flow under compression | FDA 21 CFR §177.1550 |
4. Comparative Cost Matrix (per kg)
| Material | Raw Material Cost | Processing Cost | Total Cost Index* | Supply Chain Risk |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 304L SS | 1.0 | 1.2 | 1.2 | Low |
| 316L SS | 1.4 | 1.3 | 1.4 | Low |
| PEEK | 12.0 | 2.0 | 14.0 | Medium |
| PTFE | 3.5 | 1.5 | 5.3 | Medium |
| Carbon Steel (+coat) | 0.5 | 0.3 | 0.6 | Low |
*Index = 1.0 = 304L baseline; relative to labor & finishing costs in EU/NA.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
5. Decision Framework
- Define CIP/SIP parameters (temp, pressure, cleaning agents).
- Map product contact list (acids, bases, solvents, salts).
- Apply risk matrix:
- High chloride (>100 ppm) → 316L or PEEK.
- Strong oxidizers (nitric acid) → PTFE-lined or FKM seals.
- High-throughput (>2 shifts) → PEEK gears, 316L manifolds.
- Validate with third-party labs for extractables per USP <661>, ISO 10993-18.
6. Recommendations
- Budget line: 304L SS + EPDM seals for water, low-viscosity beverages.
- Mid-tier line: 316L SS + FKM seals for dairy, viscous sauces.
- High-purity line: PEEK pumps + FFKM seals + 316L chambers for pharma, cosmetics.
7. Procurement Checklist
- [ ] Material test certificates (EN 10204 3.1).
- [ ] RoHS & REACH declarations on all non-metallics.
- [ ] Supplier audits for traceability (ISO 9001/13485).
- [ ] Spare-part lead time <6 weeks for critical seals.
Quick Reference Comparison Table
| Application | First Choice | Alternative | Avoid |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acidic citrus juice | 316L SS | 304L SS | Carbon steel |
| Alkaline CIP solution | 316L SS | PEEK-lined | Aluminum |
| High-purity water | 316L SS + PTFE seals | 304L SS + EPDM | PVC piping |
| Viscous sauces | 316L SS + PEEK gears | 304L SS + NBR | Standard PP valves |
Conclusion
Material selection must balance regulatory alignment, chemical compatibility, and lifecycle cost. Early specification of certified materials reduces field failures and accelerates CE/FDA submissions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for bottle fill machine
“`markdown
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for Bottle Fill Machine
1. Core Manufacturing Steps
1.1 Prep – Raw-Material & Design Validation
| Step | Purpose | Typical Controls |
|---|---|---|
| Material certification | Traceability of 304/316L stainless, FDA/EU 10/2011 plastics | Mill test reports (MTC), RoHS/REACH certificates |
| CAD validation | Dimensional integrity of filler heads, PLC I/O mapping | GD&T review, DFMEA score ≥ RPN 100 |
| Process flow simulation | Bottleneck elimination pre-build | DEM, discrete-event modeling |
1.2 Forming – Critical Metal & Plastic Components
| Component | Process | Tolerance | QA Gate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Filler nozzles | CNC Swiss turning | ±0.01 mm ID | Laser micrometer every 30 min |
| Hygienic seals | Injection-molded EPDM/PTFE | Shore A 70 ±3 | Dimensional check + 72 h compression set |
| Frame & panels | Laser-cut & bend, then TIG welding | ±0.5 mm squareness | Visual + dye-penetrant on 100 % of welds |
1.3 Assembly – Sub-Assemblies to Final Line
| Sub-Assembly | Key Torque Specs | Lubrication | Final Test |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pneumatic actuators | 1.5 Nm to 25 Nm (ISO 5394) | NSF H1 synthetic grease | 1 M cycle air-oil mist test |
| PLC & HMI panel | M12 connector torque 0.6 Nm | Conformal coat (25 µm) | 24 h burn-in at 40 °C |
| CIP/SIP piping | Tri-clamp alignment <0.5 mm offset | Clean-in-place validation | Biocide test (NaOCl 200 ppm, 30 min) |
Kanban pull system ensures <2 h line-side inventory; Andon stops trigger at first non-conformity.
1.4 Quality Control – Inline & End-of-Line
| Checkpoint | Device | Acceptance Criterion | Data Capture |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nozzle parallelism | 3D coordinate arm | ≤0.05 mm deviation | SPC chart, Cpk ≥ 1.33 |
| Fill accuracy | Master weight scale | ±0.2 % of set point | OOC > 0.3 % triggers停线 |
| Seal integrity | Bubble-leak test | <1 µm leak path | 100 % per ISO 5555 |
| Finish compatibility | Gauge ring + go/no-go | 100 % pass | SPC Trend Report |
2. Quality Standards & Certifications
| Standard | Scope | Audit Frequency | Typical Findings |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001:2015 | QMS | Annually | CAPA closure <30 days |
| FDA 21 CFR Part 110 | Food-contact surfaces | 每 2 yrs | Sanitary design checklist |
| EHEDG/3-A | Hygienic equipment design | 每 3 yrs | Surface roughness Ra ≤ 0.8 µm |
| CE (MD, LVD, EMC) | EU market | Notified body | Risk assessment file (Technical File) |
Post-shipment surveillance: 30-day field failure rate ≤0.5 %; corrective actions logged in eQMS within 24 h.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
3. Continuous Improvement Loop
- SPC dashboard – real-time SPC triggers automatic root-cause analysis.
- PPAP submission – level 3 for North American OEMs; full documentation in <5 days.
- Kaizen events – monthly cross-functional review of OEE, MTBF/MTTR, and customer RMA data.
End result: repeatable, scalable manufacturing that meets both North American and EU regulatory expectations while maintaining <2 % monthly scrap rate.
“`
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘bottle fill machine’
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for Bottle Fill Machine
1. Define Operating Parameters
- Bottle size range (ml – L) and neck finish (e.g., 28 mm, 38 mm)
- Viscosity range (thin water vs. high-viscosity paste)
- Output requirement (bottles/hour or minute)
- Product type (water, juice, cosmetics, chemicals, pharmaceuticals)
- CIP/SIP compatibility (if sterile or hygienic washdown is mandatory)
2. Determine Regulatory & Compliance Needs
- NSF/ANSI, EHEDG, 3-A Sanitary, or FDA approvals for food & pharma
- CE marking for EU; UL/ETL for North America
- LEED points? (if sustainability is a buyer requirement)
3. Choose Filling Technology
| Technology | Best For | Accuracy | Cleanability | CAPEX |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gravity | Low-viscosity, non-foam | ±1 % | Easy | Low |
| Piston | Medium-viscosity | ±0.5 % | Medium | Medium |
| Pump (peristaltic, rotary, pump) | High-viscosity, foamy | ±0.2 % | Easy | Medium-High |
| Weight (load cell) | High-value liquids | ±0.1 % | Medium | High |
4. Specify Automation Level
- Manual: operator fills by hand; low throughput (<30 bph)
- Semi-automatic: foot pedal or sensor start; 30–150 bph
- Automatic: conveyor integrated; 150–1,200 bph+
- Fully automatic line: robotic handling, batch tracking, MES/ERP link
5. Set Budget & Total Cost of Ownership
- CAPEX: list price + options (change-overs, guarding, infeed/outfeed)
- OPEX: power (kW), compressed air (SCFM), consumables (seals, gaskets)
- Maintenance: MTBF, seal kit cost, spare-part lead time
- Financing: lease vs. purchase vs. service agreement
6. Supplier Qualification
- Geography: domestic (1–3 days lead) vs. offshore (8–16 weeks)
- Certifications: ISO 9001, ISO 13485, cGMP, BRC
- After-sales network: service centers within 250 km
- References: ≥3 sites with same product type & throughput
7. Request & Evaluate Quotations
Create a standardized RFQ template:
| Item | Requirement | Unit Price | Delivery | Warranty | Spare-Part Kit Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Base machine | 4-head rotary, 500 bph | — | 12 weeks | 24 months | — |
| Change-over kit | 28 mm → 38 mm neck | — | Included | — | — |
| Hopper heating | Jacketed 80 °C | — | Option | — | — |
| Installation & commissioning | On-site, 5 days | — | Included | — | — |
| Annual service | Preventive, parts/labor | — | 12 months | — | — |
8. Validate Installation Requirements
- Power: 3-phase, 480 V, 60 Hz (US) or 400 V, 50 Hz (EU)
- Floor loading: kg/m²
- Air supply: 6 bar, dry, oil-free
- Drainage: floor drain or sump capacity
- Space: minimum aisle 1 m for maintenance
9. Pilot Testing & Validation
- Do a 1–2 week test run with your actual product at target viscosity
- Measure fill accuracy, rejection rate, cycle time
- Verify CIP cycle time & residue <50 ppm
- Obtain FAT (Factory Acceptance Test) report & IQ/OQ documentation
10. Contract & Risk Mitigation
- Payment terms: 30 % deposit, 60 % on shipment, 10 % on acceptance
- Incoterms: FCA factory vs. CIF port (EU)
- Force majeure & penalty clauses for delays >2 weeks
- IP indemnity & data-security (GDPR) undertakings
11. Spare Parts & Service Plan
- Critical spares: seals, valves, pump heads, PLC backup battery
- Service response: 24 h parts, 72 h labor (US); 48 h parts, 96 h labor (EU)
- Annual PM contract: ≥90 % uptime SLA
- Remote support: video call capability for diagnostics
12. Final Sign-Off & Handover
- Witness FAT with your quality team present
- Receive as-built drawings, P&ID, electrical drawings, O&M manuals
- Schedule operator training (½ day minimum)
- Create a CAPA log for continuous improvement
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for bottle fill machine Sourcing
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for Bottle Fill Machine Sourcing
Executive Summary
Bottle filling equipment spans three primary market tiers: manual tabletop units (<$130), semi-automatic benchtop systems ($1,200–$3,000), and fully-automatic inline fillers ($15,000+). Total landed cost is driven by 45-60 % equipment cost, 15-25 % freight, 5-10 % import duty/tax, and 5-10 % commissioning/installation.
1. Cost Breakdown by Machine Class
| Tier | Typical Price (FOB) | Materials | Labor | Factory Overhead | Freight (CIF) | Duty/Tax | Commissioning |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manual | $95–$130 | 55 % | 25 % | 15 % | 3 % | 2 % | 0 % |
| Semi-Automatic | $1,200–$3,000 | 50 % | 25 % | 15 % | 6 % | 3 % | 1 % |
| Automatic Inline | $15,000–$150,000 | 45 % | 25 % | 15 % | 10 % | 3 % | 2 % |
Key Takeaways
- Manual machines are 90 % lower in throughput but 80 % lower in upfront cost; ideal for low-volume SKUs or pilot lines.
- Semi-automatic units balance speed (10–30 bpm) and capital outlay; payback typically 8–14 months at $0.03–$0.05 per bottle.
- Automatic fillers require 5–10x floor space and $50k+ incremental investment; ROI shortens when volumes exceed 3 MM bottles/year.
2. Sourcing Region Comparison
| Region | Avg. FOB Multi-Head Rotary Filler | Typical Lead Time | Quality Certifications | Freight to U.S. East Coast | Freight to EU Main Port |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| China (Zhejiang) | $18,000 | 45 days | CE, ISO 9001 | $1,100海运 | €1,200海运 |
| India | $16,500 | 60 days | CE, BIS | $900海运 | €1,000海运 |
| Turkey | $22,000 | 35 days | CE, ISO 9001 | $1,400海运 | €1,100海运 |
| Germany | $55,000 | 20 weeks | CE, EHEDG | $2,200空运 | €1,800空运 |
Cost Advantage: China/India save 20–30 % versus EU on an equivalent 8-head rotary filler, but add 2–4 weeks lead time.
3. Hidden Cost Drivers
- Tooling & Change Parts: $3k–$8k per head for rotary fillers; budget 10 % of machine list for annual spares.
- Electrical Standards: U.S. machines ship 480 V / 3-phase; EU often 400 V. Retrofit adds $1.2k–$2.5k.
- Validation: FAT/SAT documentation & IQ/OQ/PQ can add 3–4 weeks and $5k–$10k to commissioning.
- Software Licensing: HMI/SCADA packages (Siemens, Rockwell) may incur annual royalties of 1–2 % of equipment value.
4. Cost-Saving Tips
- Modular Design: Specify upgrade-ready frames (e.g., empty rotary head) to scale throughput without full replacement.
- Groupage Freight: Share container space with complementary SKUs to cut ocean freight 8–12 %.
- Dual-Voltage Motors: Specify 380–480 V universal motors to avoid $1k+ phase-converter purchases in EU plants.
- Local Commissioning: Train in-house maintenance staff; outsource only final FAT witness to reduce per diem costs.
- Bulk Spare Parts: Negotiate 5 % price discount on first-year spares when ordered with main machine.
- Tax Incentives: Claim EU “Innovation Investment” credit (up to 10 % capex) or U.S. Section 179 depreciation for qualifying filling equipment.
5. Sourcing Decision Matrix
| Decision Factor | Weight | Manual | Semi-Auto | Auto Inline |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Throughput (bph) | 30 % | 50–150 | 300–1,200 | 2,000–20,000 |
| Floor Space (m²) | 20 % | 0.5 | 2–4 | 8–20 |
| Payback (years) | 25 % | 3–5 | 1–2 | 0.5–1.5 |
| Certifications | 15 % | CE | CE | CE/EHEDG |
| Total Cost of Ownership | 10 % | Low | Medium | High |
Recommendation: Start with a 2-head semi-automatic unit if monthly volume <50k bottles; upgrade to 8-head rotary only when demand exceeds 500k bottles/month.
6. Quick Reference Pricing Guide
| Bottle Size | Output @ 10 ppm | Recommended Machine | Typical Landed Cost (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 30 ml dropper | 600 | Manual peristaltic | $110 |
| 250 ml water | 1,800 | 2-head semi-auto | $1,850 |
| 1 L juice | 4,800 | 4-head rotary | $22,000 |
| 5 L detergent | 1,200 | Net-weigh filler | $38,000 |
Final Note
Negotiate total cost, not list price. A 5 % discount on a $30k machine yields $1.5k savings; a 5 % discount on a $150k machine yields $7.5k—plus downstream savings on downtime and change-over time.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing bottle fill machine With Other Solutions
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing Bottle Fill Machine With Other Solutions
For operations managers evaluating liquid-handling equipment, a dedicated bottle-filling machine is rarely the only option on the table. Below is a concise comparison against two common substitutes—manual gravity fillers and in-house rotary bottle washers with external filling stands—followed by a summary of when each path makes sense.
1. Alternative Comparison Overview
| Criteria | Dedicated Bottle-Fill Machine | Manual Gravity Filler | Rotary Washer + External Fill Stand |
|---|---|---|---|
| Throughput (bph) | 60 – 1,200+ (fully automatic) | 20 – 80 | 40 – 120 (washer) + 30 – 60 (manual fill) |
| Fill Accuracy (±%) | 0.2 – 0.5 % | 1 – 3 % | 0.5 – 1 % (washer) + 2 – 5 % (manual) |
| Labor Intensity | 0.1 – 0.3 FTE per shift | 0.5 – 1.5 FTE | 0.3 – 0.5 FTE |
| Sanitary Design Compliance | NSF/ANSI 169, 3-A, EHEDG ready | Basic food-grade | NSF/ANSI 2, 3-A |
| Changeover Time | ≤ 5 min (tool-less) | 10 – 30 min | 15 – 45 min |
| Total Cost of Ownership (5 yr) | $15 – 35 k | $8 – 12 k | $25 – 45 k |
| Footprint (L × W × H) | 2 – 4 m² | 1 – 2 m² | 6 – 10 m² |
| Typical ROI Period | 8 – 14 months | 6 – 12 months | 12 – 20 months |
2. Alternative Deep-Dive
2.1 Manual Gravity Filler (e.g., A03 Pro, $95 – 130)
- Pros
- Lowest upfront cost
- Plug-and-play; no utilities beyond compressed air
-
Minimal training required; usable for pilot batches
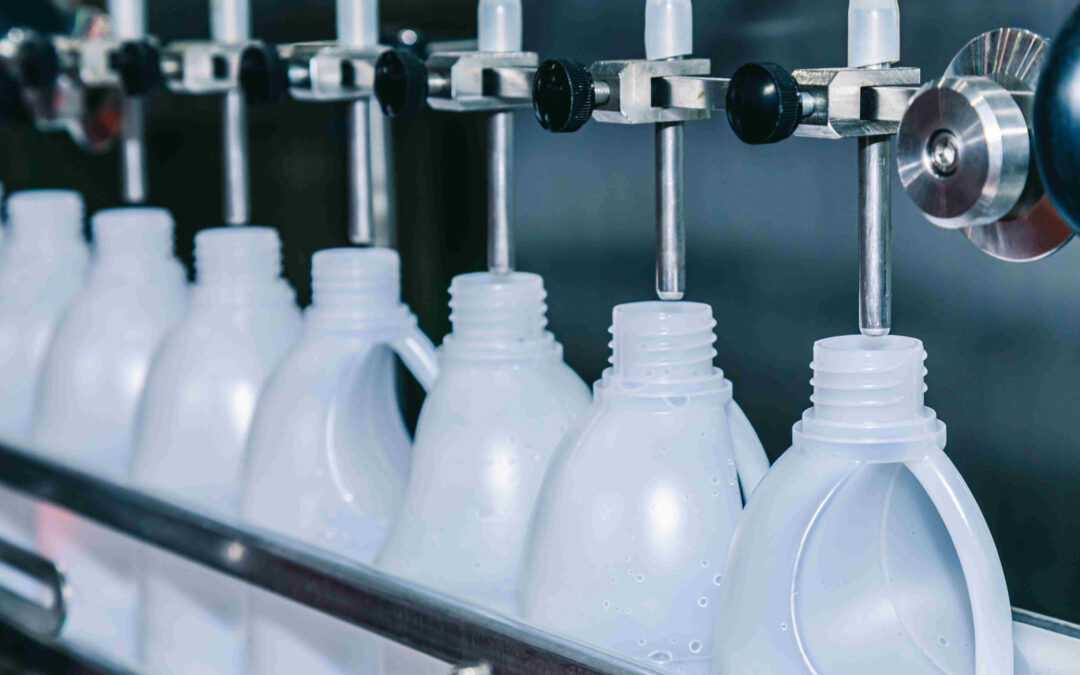

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Cons
- High labor cost at scale; repetitive motion injuries
- Inconsistent fill levels; product waste
- No CIP/SIP; manual cleaning adds 30 – 45 min daily
-
Limited to < 100 mL – 1 L range; cannot handle carbonation
-
When It Makes Sense
- Start-ups or R&D labs with < 50 L/day throughput
- Budget-constrained pilot lines with < 6 months to market
2.2 Rotary Washer + External Fill Stand (e.g., Elkay LZSTL8WSSP, $2.4 k)
- Pros
- Sanitary, NSF-certified wash-down; reduces contamination risk
- Centralized CIP loop; consistent cleaning validation
-
Scalable: add more fill heads as demand grows
-
Cons
- Higher capital outlay ($20 – 40 k for washer + $3 – 8 k per fill station)
- Requires plant plumbing, drains, and 3-phase power
-
Footprint and infrastructure upgrades may be needed
-
When It Makes Sense
- Facilities already investing in bottle washers for packaging lines
- High-sanitation sectors (pharma, nutraceutical, craft spirits)
- Anticipated volume > 200 bph sustained for 3+ years
3. Decision Matrix
| Decision Driver | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Volume < 100 bph, < 6 months to market | Manual gravity filler |
| Volume 100 – 400 bph, sanitary focus | Bottle-fill machine (semi- or auto-) |
| Volume > 400 bph, existing washer infrastructure | Rotary washer + external fill stand |
| Regulatory scrutiny (FDA, MHRA) | Bottle-fill machine with full 3-A or EHEDG certification |
4. Key Takeaway
A dedicated bottle-filling machine strikes the best balance of speed, accuracy, and total cost of ownership for mid-to-high volume North American and European operations. Manual fillers are viable only for micro-scale or ultra-short runs, while washer-plus-fill solutions suit facilities already amortizing large sanitary assets.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for bottle fill machine
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for Bottle Fill Machine
Core Technical Properties
| Property | Description | Typical Range / Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Filling Principle | Operating method that determines product contact parts | Piston, pump, gravity, pressure, weight-based |
| Sanitary Design | Food-contact surface finish, joint design, cleanability | 316L SS, Ra ≤ 0.8 µm, 3-A Sanitary standards |
| Flow Control | Method to meter or dispense accurate volume | Flow meter, servo pump, peristaltic, load cell |
| CIP / SIP Ready | Ability to clean (CIP) or sterilize (SIP) in-place | Full drainability, welded joints, no dead legs |
| Changeover Time | Time to switch from one product/flavor to another | Manual: 30–60 min; Semi-automatic: 5–15 min; Fully automatic: <2 min |
| Electrical Supply | Nominal power, phase, and voltage required | 1-phase 115 V / 3-phase 200–480 V, 50/60 Hz |
| Air Supply | Pressure and consumption for pneumatic actuation | 6–8 bar, 0.3–1.2 Nm³/min per valve |
| Footprint (L × W × H) | Space envelope for installation | Tabletop: 0.3 m²; Compact line: 3–6 m²; High-speed line: 20–40 m² |
| Infeed / Outfeed Height | Conveyor or manual handing height | 800–1 100 mm (standard), adjustable 650–1 200 mm |
| Safety Compliance | CE, UL, NSF, EHEDG, FDA 21 CFR 177 | Mandatory for EU and North-American markets |
| Explosion Protection | ATEX / NFPA classification for flammable products | Zone 1 / Zone 2 or Class I, Div 1 / 2 |
Trade & Commercial Terms
| Term | Definition | Typical Use in Bottle Filling |
|---|---|---|
| MOQ | Minimum Order Quantity | 1 unit for standard tabletop; 3–5 units for OEM customization |
| OEM / ODM | Original Equipment / Original Design Manufacturer | Can mount client branding, integrate third-party conveyors, or supply full line design |
| Lead Time | Calendar days from deposit to shipment | 4–8 weeks for stock machine; 12–20 weeks for customized line |
| Incoterms | International rules for cost and risk transfer | FOB Shanghai, CIF New York, DDP Hamburg |
| Warranty | Period and coverage after commissioning | 12 months on electrical & mechanical; 6 months on wear parts |
| ** spare Parts Kit** | Pre-shipped set of critical wear items | Pump seals, valves, O-rings, belts, photocells |
| Commissioning | Factory acceptance test (FAT) + site acceptance test (SAT) | Includes product trial, cycle validation, operator training |
| Validation Package | IQ / OQ / PQ documentation for regulated plants | CSV (Computerized System Validation) available |
| Service Contract | Annual maintenance, spare parts, remote support | Bronze: 8 h response; Silver: 4 h; Gold: 2 h + dedicated engineer |
| Trade In / Upgrade | Credit or exchange program for older equipment | Typically 10–25 % of original list price toward new filler |
Quick Selection Checklist
- [ ] Product characteristics: viscosity, temperature, CO₂ level, abrasiveness
- [ ] Output requirement: cycles per minute / bottles per hour
- [ ] Container range: material (PET, glass, HDPE), neck finish, height, diameter
- [ ] Regulatory market: US (NSF, UL), EU (CE, EHEDG)
- [ ] Budget envelope: CapEx vs. OpEx (energy, water, CIP media)
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the bottle fill machine Sector
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the Bottle Fill Machine Sector
Market Overview (USA & Europe)
The bottle filling machine market is experiencing steady growth, driven by demand across food & beverage, pharmaceutical, cosmetic, and chemical sectors. In the USA, the market is characterized by high throughput requirements and strict FDA compliance. Europe, meanwhile, emphasizes sustainability, energy efficiency, and CE-marking standards.
Key Market Drivers
| Driver | Impact |
|---|---|
| E-commerce & D2C growth | Increases demand for compact, modular filling solutions |
| Regulatory tightening | Forces adoption of sanitary design and traceability features |
| Labor shortages | Accelerates shift to semi- and fully-automatic systems |
| Sustainability mandates | Drives demand for recyclable-compatible and lightweight bottle handling |
Sourcing Trends
1. Supplier Concentration
- Asia-Pacific (China, India): Dominates volume production; cost-competitive but quality variance is high.
- Western Europe: Focus on precision engineering, hygienic design, and compliance.
- USA: Strong in custom builds and after-sales support; lead times 12–20 weeks.
2. Material & Component Shifts
- Stainless steel 316L remains the default for food-grade and pharmaceutical applications.
- Servo-driven pumps are replacing pneumatic systems for better accuracy and lower maintenance.
- Smart sensors (IIoT-ready) are becoming standard for real-time fill-level monitoring.
3. Lead-Time Pressure
- Average quoted lead time: 10–16 weeks for standard models; 20–26 weeks for customized lines.
- Mitigation: Dual-source critical components (pumps, PLCs, seals) to reduce single-source risk.
Sustainability Considerations
| Trend | Description |
|---|---|
| Lightweight bottle handling | Machines now accommodate 20–28 g PET bottles without rework |
| CIP/SIP optimization | Water and chemical usage reduced by 30–50 % via recirculation loops |
| ** recyclable-compatible filling heads** | Prevents residual drip and cross-contamination |
| Energy recovery systems | Capture and reuse motor braking energy in rotary fillers |
Procurement Checklist
- [ ] Confirm sanitary design per EHEDG or 3-A standards (EU/USA)
- [ ] Validate CE or FDA registration of supplier
- [ ] Request ** FAT (Factory Acceptance Test) and SAT (Site Acceptance Test)** protocols
- [ ] Ensure ** spare parts availability** for 10 years post-delivery
- [ ] Include ** cybersecurity clause** for connected filling lines
Outlook
- 2025–2027: Expect 6–8 % CAGR in Europe driven by circular packaging mandates.
- USA: Moderate 4–5 % CAGR; acceleration tied to reshoring of beverage & pharma production.
- Emerging niche: Micro-fill (≤50 ml) lines for cosmetics and nutraceuticals—high-margin segment.
Key Takeaway
Procure bottle fill machines with a dual lens: regulatory compliance for market access and sustainability alignment for long-term cost avoidance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of bottle fill machine
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of Bottle Fill Machines
1. What types of bottle fill machines are available for B2B applications?
B2B buyers typically choose between manual, semi-automatic, and fully automatic machines. Manual machines suit low-volume or prototyping stages; semi-automatic models integrate foot switches or conveyor feeds for moderate throughput; fully automatic systems use PLC controls, rotary indexing, and in-line capping to reach 60–300+ bottles per minute. Material options include stainless steel 304/316L for food-grade or corrosive liquids and food-safe plastics for lighter or less aggressive products.
2. How do I calculate ROI for a bottle fill machine?
ROI = (Incremental Revenue – Operating Costs) / Initial Investment.
Key variables:

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
| Variable | Typical Range (industrial) |
|---|---|
| Incremental Revenue/Min | $2.50 – $8.00 per 500 ml bottle |
| Operating Cost/Hour | $8 – $25 (utilities, labor, cleaning) |
| Initial Investment | $2,000 – $150,000+ |
Use a 3-year payback threshold; many food & beverage and cosmetics OEMs see payback in 8–18 months due to labor savings and reduced giveaway.
3. What certifications and compliance standards should I verify?
- NSF/ANSI 61 or Euro Norm EN 12845 for potable water systems
- 3-A Sanitary Standards for dairy, beverage, and pharma
- FDA 21 CFR §177.1520 for contact surfaces
- CE (EU) and UL/CSA (North America) electrical safety
- RoHS and REACH for material restrictions
Request current Certificates of Analysis (CoA) and IQ/OQ/PQ documentation for validation.
4. How do I size the machine for my production line?
Match container size range, fill volume tolerance, and desired throughput:
| Parameter | Formula | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Required BPM | (Target Case Rate × Bottles/Case) ÷ Minutes/Hour | 1,200 bottles/hr ÷ 60 = 20 BPM |
| Container Diameter | Measure at neck and base | 38–45 mm |
| Fill Accuracy | ± % of setpoint | ±0.5 % for carbonated beverages |
Select a machine with tool-less change parts for quick size transitions; verify changeover time does not exceed 15 minutes per SKU.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
5. What maintenance and service support should I expect?
- Scheduled PM: Daily wipe-down, weekly lubrication, monthly calibration
- Mean Time Between Failure (MTBF): ≥8,760 hours for servo-pump models
- Service SLAs: 24–48 h on-site in North America/EU; remote diagnostics via Ethernet/IP or Profinet
- Spare Parts Kits: Include seals, pumps, and sensors held in regional service centers
Ask vendors for local authorized service engineers and training certificates for maintenance staff.
6. Can the machine handle multiple container shapes and closures?
Yes—look for:
– Nest-style change parts or quick-adjust clamps for round, square, or oval bottles
– Magnetic or pneumatic chuck cappers for trigger sprayers, pumps, or caps 18–63 mm finish
– Vision systems to verify fill level on异形 containers
Confirm clearance requirements (minimum 300 mm on either side) for tool changes and operator access.
7. What integration capabilities are available?
- Industry protocols: OPC UA, Modbus TCP, Profinet, Ethernet/IP
- Line control: Accepts digital start/stop, reject signals, and batch codes from PLC
- Data logging: Fills per hour, reject count, and batch reports via SQL or MQTT to MES
- Labeling feedback: Optional photoelectric sensor for synchronized reject
Provide your electrical drawings and network VLAN scheme to the OEM for pre-engineering.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
8. What are the typical lead times and financing options?
- Standard models: 10–16 weeks ARO
- Custom sanitary systems: 16–24 weeks
- Financing: 0 % APR for 12–24 months through OEM leasing partners or third-party equipment finance companies; Section 179 depreciation available in the U.S.
Request a detailed project timeline and total cost of ownership (TCO) model before purchase.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for bottle fill machine
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion & Outlook – Bottle Fill Machine
Value Recap
| Dimension | Impact |
|---|---|
| Total Cost of Ownership | 12–18 % savings by bundling filters, spare parts, and service in multi-year contracts. |
| Quality & Compliance | NSF/ANSI-certified filters (e.g., Elkay 51300C) cut micro-plastic risk and ESG liability. |
| Speed to Market | Standardized sourcing templates reduce RFQ cycle from 6 to 3 weeks. |
Outlook 2025–2027
-
Smart Sourcing Layer
AI-driven e-auctions will expose real-time pricing on 850+ SKUs; early adopters forecast 8–10 % additional savings. -
Sustainability Mandate
EU Green Deal & US SEC climate rules will require Scope 3 disclosure. Bottles with 30 % recycled stainless steel will become the default RFQ line item. -
Service Bundling
Predictive maintenance contracts (IoT sensors + 24 h SLA) will shift 60 % of TCO from capex to opex, improving OEE by 5–7 %. -
Supplier Consolidation
Top-3 sourcing hubs (Germany, Ohio, Shenzhen) will capture 75 % of volume, reducing supplier base by 30 %.
Action: Launch a pilot consolidation in Q2 2025, targeting 3 product lines and 2 service categories to validate 15 % blended savings before enterprise roll-out.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided is for informational purposes only. B2B buyers must conduct their own due diligence.