The global market for Bosch def (diesel exhaust fluid) system components and related manufacturing solutions has seen steady growth, driven by increasingly stringent emissions regulations and the widespread adoption of selective catalytic reduction (SCR) technology in commercial vehicles. According to Grand View Research, the global diesel exhaust fluid market was valued at USD 6.3 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.8% from 2023 to 2030. This growth trajectory, supported by environmental compliance mandates such as Euro 6 and EPA 2010 standards, has amplified demand for high-precision Bosch-compatible DEF system manufacturers capable of meeting OEM quality and scalability requirements. As Bosch remains a leading supplier of SCR dosing systems and integrated aftertreatment solutions, a select group of component manufacturers has emerged to support the production, assembly, and aftermarket servicing of these critical systems. The following analysis identifies the top six Bosch DEF manufacturers based on production capacity, technological alignment, geographic reach, and market reputation.
Top 6 Bosch Def Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Company Overview
Domain Est. 1995
Website: bosch.com
Key Highlights: Opened in 2014, this strategic site works on the development and innovation of technology, including hardware, software, AI solutions, ecommerce, and much more….
#2 Diesel Components
Domain Est. 2018
Website: boschoffhighway.com
Key Highlights: Bosch is a leading manufacturer of components for diesel engines in both the on-highway and off-highway segments and continually sets new standards with its ……
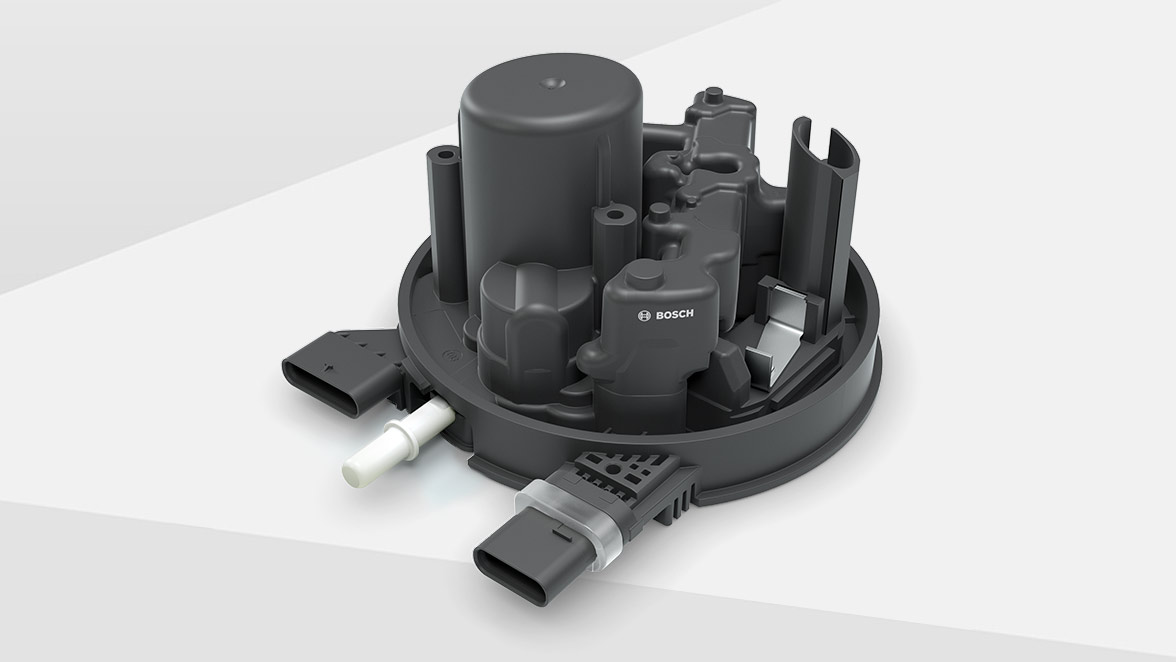
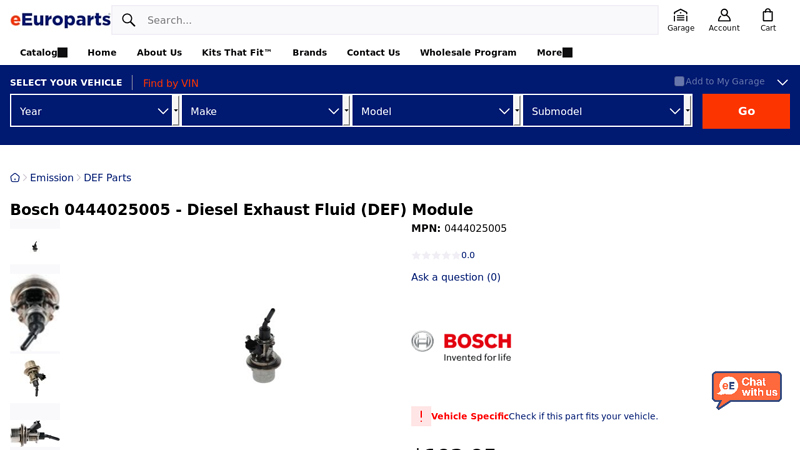
#3 Bosch 0444025005 Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF) Module
Domain Est. 2000
Website: eeuroparts.com
Key Highlights: Optimize emissions control with Bosch 0444025005 DEF Module. Enjoy seamless compatibility and expert support. Shop now….
#4 Bosch Auto Parts
Domain Est. 2004 | Founded: 1997
Website: boschautoparts.com
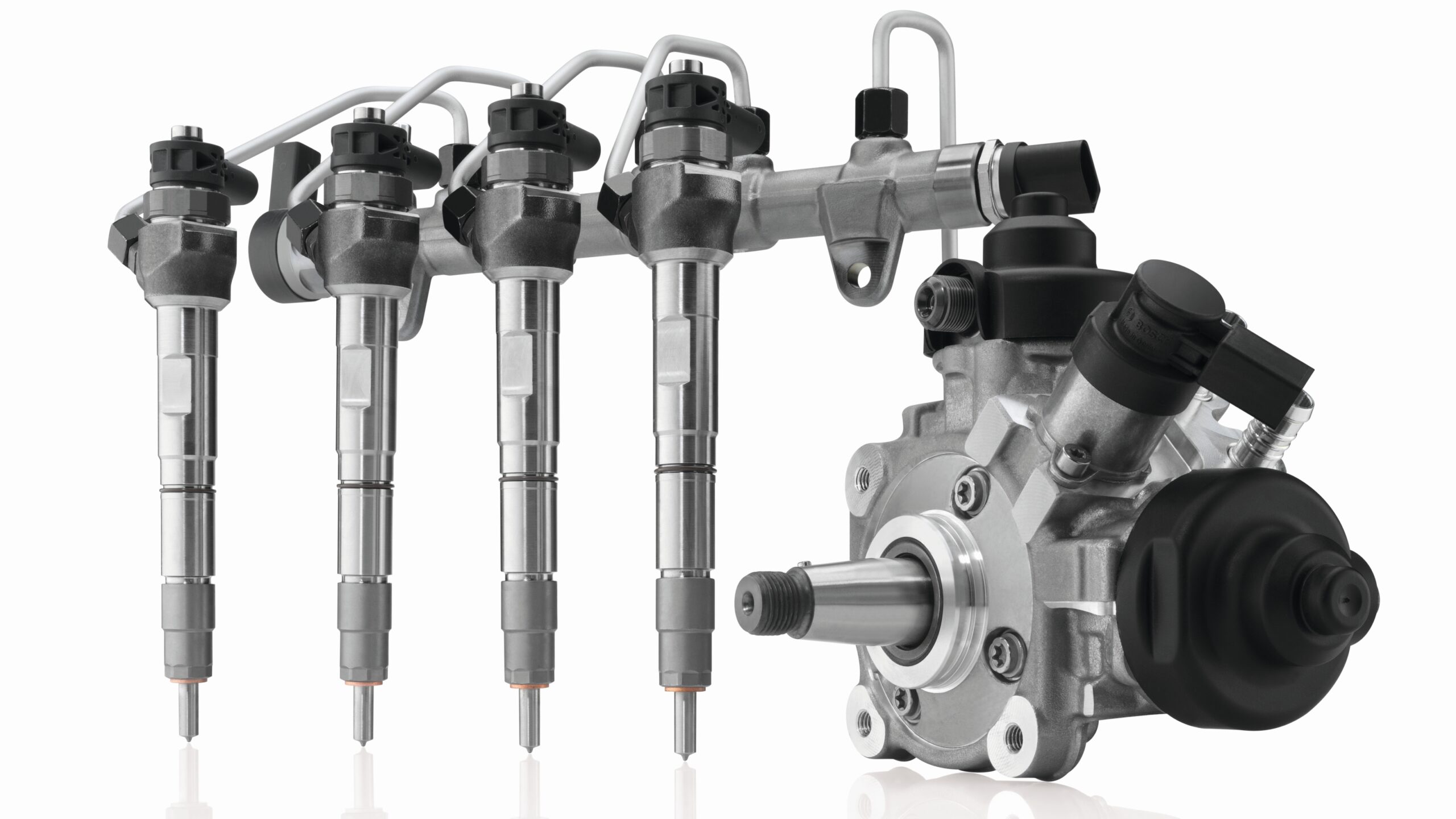
Key Highlights: World Leader and Supplier of Diesel Fuel Injection Systems. Since 1997, Bosch common rail injectors have been the industry standard for Diesel Fuel systems….
#5 The motor
Domain Est. 2010
Website: bosch-ebike.com
Key Highlights: The usual Bosch quality. Our drive units are high-quality, powerful and lightweight. They provide efficient, quiet support for a natural riding experience. They ……
#6 Denoxtronic exhaust
Domain Est. 2011
Website: bosch-mobility.com
Key Highlights: The Denoxtronic metering system injects diesel exhaust fluid (DEF), an aqueous urea solution of 32.5 %, into the exhaust gas flow….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Bosch Def
H2 2026 Market Trends Analysis for Bosch Defense (Bosch Def.)
As Bosch expands its footprint in the defense and security technology sector through its Bosch Defense Systems division—commonly referred to as Bosch Def.—the second half of 2026 (H2 2026) is expected to reflect a convergence of emerging technological capabilities, geopolitical dynamics, and evolving defense procurement strategies. This analysis outlines key market trends shaping Bosch Def.’s position and opportunities during this period.
1. Increased Demand for Integrated Security and Surveillance Solutions
Trend:
Defense and homeland security agencies are prioritizing integrated, multi-layered surveillance and command-and-control systems. The rise in hybrid threats, asymmetric warfare, and domestic security concerns is driving demand for scalable, AI-enabled surveillance platforms.
Impact on Bosch Def.:
Bosch’s expertise in intelligent video analytics, thermal imaging, and networked security systems positions it strongly. In H2 2026, Bosch is likely to benefit from contracts involving smart base installations, border monitoring, and urban security integration, especially in NATO and EU member states modernizing C4ISR (Command, Control, Communications, Computers, Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance) infrastructure.
2. Adoption of AI and Machine Learning in Defense Applications
Trend:
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is becoming mission-critical in threat detection, predictive maintenance, and real-time decision support. Defense organizations are investing heavily in AI-driven situational awareness tools.
Impact on Bosch Def.:
Bosch’s existing AI-powered video analytics, including object recognition, behavior analysis, and anomaly detection, are being adapted for military use. In H2 2026, Bosch is expected to expand AI integration into ruggedized edge devices for field deployment, particularly in forward operating bases and mobile command units.
3. Cybersecurity Integration in Physical Security Systems
Trend:
As defense systems become more connected, the convergence of cyber and physical security is a top priority. Cyber-attacks targeting surveillance networks and communication systems have increased.
Impact on Bosch Def.:
Bosch’s focus on end-to-end encryption, secure firmware updates, and compliance with military-grade cybersecurity standards (e.g., NATO SDIP-27, NIST) will be a competitive advantage. In H2 2026, Bosch Def. is likely to emphasize secure-by-design architectures in new product releases, appealing to defense clients concerned about supply chain integrity and zero-trust frameworks.
4. European Defense Autonomy and Procurement Shifts
Trend:
The European Union is accelerating defense industrial consolidation and promoting “strategic autonomy” through initiatives like the European Defense Fund (EDF) and Permanent Structured Cooperation (PESCO).
Impact on Bosch Def.:
As a German-based technology leader, Bosch is well-positioned to participate in EU-led defense projects. In H2 2026, Bosch may see increased collaboration with European defense primes (e.g., Rheinmetall, Thales, Leonardo) on joint bids for surveillance, base security, and electronic warfare support systems.
5. Sustainability and Energy-Efficient Defense Technologies
Trend:
Military organizations are adopting greener technologies to reduce logistical burdens and meet national carbon goals. This includes energy-efficient sensors, solar-powered surveillance nodes, and reduced thermal signatures.
Impact on Bosch Def.:
Bosch’s heritage in energy-efficient electronics and sensor miniaturization supports the development of low-power, long-endurance surveillance systems. In H2 2026, Bosch Def. is expected to market its energy-smart solutions—such as solar-integrated camera systems—for forward-deployed and remote monitoring applications.
6. Expansion into Allied Defense Markets (Indo-Pacific, Middle East)
Trend:
Geopolitical tensions are driving defense spending in regions like the Indo-Pacific and the Gulf. Countries are investing in border security, critical infrastructure protection, and urban surveillance.
Impact on Bosch Def.:
Bosch is likely to leverage its global distribution network and partnerships to expand into allied markets. H2 2026 may see Bosch Def. securing contracts for smart city defense integration, port security, and military base modernization in countries like Japan, South Korea, UAE, and Saudi Arabia.
7. Supply Chain Resilience and Localization
Trend:
Defense clients are demanding greater transparency and resilience in supply chains, reducing reliance on non-allied semiconductor and component sources.
Impact on Bosch Def.:
Bosch’s significant in-house R&D and manufacturing capabilities—especially in semiconductors through Bosch Sensortec and its wafer fabs—provide a strategic advantage. In H2 2026, Bosch Def. is expected to highlight its “trusted supplier” status, appealing to defense ministries prioritizing supply chain sovereignty.
Strategic Outlook for Bosch Def. in H2 2026:
- Growth Drivers: AI-enhanced surveillance, EU defense collaboration, cybersecurity integration, and global expansion.
- Challenges: Intensifying competition from U.S. defense tech firms (e.g., Raytheon, L3Harris), export control regulations (e.g., ITAR), and the need for continuous innovation.
- Opportunities: Leadership in hybrid security systems (civil-military dual-use), participation in EU defense projects, and leveraging Bosch Group’s R&D ecosystem.
Conclusion:
H2 2026 will be a pivotal period for Bosch Defense as global defense markets embrace digital transformation and strategic autonomy. Bosch Def. is poised to capitalize on its technological strengths in intelligent sensing, secure networking, and energy efficiency. By aligning with European defense initiatives and expanding into high-growth regions, Bosch can solidify its role as a key enabler of next-generation defense and security infrastructure.
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Bosch DEF (Quality, IP)
Sourcing Bosch Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF) — or any DEF marketed under the Bosch brand — requires careful attention to avoid quality and intellectual property (IP) issues. Below are common pitfalls to watch for:
1. Counterfeit or Non-Approved Products
One of the most significant risks is purchasing counterfeit DEF that falsely claims to be Bosch-branded or Bosch-approved. These products may:
– Fail to meet ISO 22241 standards for DEF purity
– Contain contaminants that damage SCR (Selective Catalytic Reduction) systems
– Lead to reduced fuel efficiency, increased emissions, or engine derates
Always verify packaging authenticity, batch numbers, and purchase only from Bosch-authorized distributors.
2. Unauthorized Use of Bosch Branding (IP Infringement)
Third-party suppliers may misuse the Bosch name, logo, or trademarks to imply endorsement or affiliation. This constitutes intellectual property infringement and may mislead buyers into believing they are purchasing genuine Bosch products.
– Look for official Bosch certification or partnership documentation
– Confirm distributor authorization through Bosch’s official channels
3. Inconsistent Product Quality from Unverified Suppliers
Even if DEF is not counterfeit, suppliers not approved by Bosch may offer inferior formulations. Issues include:
– Improper urea concentration (not 32.5% urea in deionized water)
– Use of substandard raw materials or poor storage conditions
– Lack of traceability and quality control documentation
This compromises emissions compliance and risks costly repairs.
4. Lack of Traceability and Certification
Genuine Bosch DEF should come with full traceability, including:
– ISO 22241 certification
– Batch-specific test reports
– Proper labeling with expiration dates and handling instructions
Sourcing from non-transparent suppliers often means missing documentation, increasing compliance and warranty risks.
5. Misleading Marketing Claims
Some vendors advertise “Bosch-compatible” or “OEM-spec” DEF without proof. While the fluid may meet basic standards, it is not the same as authentic Bosch-branded product.
– Avoid vague claims without third-party verification
– Request test data and certification to back performance claims
6. Inadequate Storage and Handling Practices
DEF quality degrades if not stored properly. Unauthorized resellers may lack climate-controlled facilities, leading to:
– Urea crystallization
– Contamination from improper containers (non-DEF-rated materials)
– Reduced shelf life and effectiveness
Ensure suppliers follow Bosch-recommended storage protocols (temperature, container material, shelf life).
Best Practices to Avoid Pitfalls
- Purchase only from Bosch-authorized distributors
- Verify product authenticity via Bosch’s official verification tools or customer service
- Request and retain quality certifications and batch documentation
- Audit supplier storage and handling processes
- Report suspected IP violations or counterfeit goods to Bosch immediately
By remaining vigilant and sourcing through official channels, you ensure both product quality and compliance with intellectual property standards.

It appears you’re seeking a Logistics & Compliance Guide for Bosch Defense Use, possibly referencing a product or system with “H2” designation (e.g., hydrogen-powered technology, Part H2, or a project codename). However, as of now, there is no publicly known Bosch product line or program officially titled “Bosch Def. Use H2” in the defense sector involving hydrogen (H2) that is widely documented.
That said, I can provide a generalized Logistics & Compliance Guide tailored to Bosch defense-related applications, especially if they involve hydrogen technologies (H2)—a growing area in clean energy for military use. This guide covers key logistics, regulatory, and compliance considerations.
Logistics & Compliance Guide: Bosch Defense Applications Involving H2 Technologies
Applicable to defense and government contracts, especially where Bosch supplies hydrogen (H2)-enabled systems (e.g., fuel cells, sensors, power units, or hybrid systems).
1. Overview
This guide outlines logistics and compliance requirements for the deployment, transportation, maintenance, and use of Bosch-developed or supplied technologies involving hydrogen (H2) in defense or military applications.
Whether Bosch is providing hydrogen fuel cell systems, H2 sensors, or integrated power solutions for defense platforms (e.g., vehicles, drones, or base power), strict adherence to international, national, and military standards is required.
2. Regulatory & Compliance Framework
A. International Regulations
- UN Recommendations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods (UN TDG)
H2 is classified as UN 1049 (Hydrogen, compressed), hazard Class 2.1 (Flammable Gas). - Packaging, labeling, and documentation requirements apply.
- ADR/RID/ADN (Europe)
For road, rail, and inland water transport of dangerous goods, including H2. - IMDG Code (Maritime)
Required for sea transport of H2-powered systems or pressurized storage. - ICAO/IATA (Air Transport)
Highly restricted; H2 systems typically prohibited unless specially approved.
B. U.S. Department of Defense (DoD) Requirements
- DFARS (Defense Federal Acquisition Regulation Supplement)
- Compliance with ITAR/EAR (see below).
- Flow-down clauses to subcontractors.
- DoD-STD-2167 / MIL-STD-461 / MIL-STD-810
Environmental, EMI, and reliability testing for defense systems. - Supply Chain Risk Management (SCRM)
Requirement for trusted sources; Bosch must certify origin of H2 components.
C. Export Controls
- ITAR (International Traffic in Arms Regulations)
If the H2 system is on the U.S. Munitions List (USML), export requires State Department approval. - EAR (Export Administration Regulations)
For dual-use items (e.g., fuel cells); check ECCN (Export Control Classification Number). - Example: Fuel cells may fall under ECCN 9A991.d.
✅ Action: Confirm whether Bosch H2 components are ITAR-controlled or EAR99.
D. Safety & Environmental Standards
- NFPA 2: Hydrogen Technologies Code
U.S. standard for H2 storage, piping, ventilation, and safety systems. - ISO 19880 (Gaseous Hydrogen Fueling Stations)
Applies if Bosch systems interface with H2 refueling infrastructure. - OSHA 29 CFR 1910.103
Hydrogen safety in workplaces.
3. Logistics Planning
A. Transportation
| Mode | Requirements |
|——|————–|
| Road | ADR-compliant vehicles; certified drivers; placarded H2 tanks. |
| Sea | IMDG packaging; proper stowage away from oxidizers. |
| Air | Generally prohibited unless approved as “Dangerous Goods” under IATA DGR. |
| Military Convoys | Coordination with defense logistics commands (e.g., DLA, TRANSCOM). |
⚠️ Note: Hydrogen cylinders must be secured, vented, and protected from impact.
B. Storage
- Store H2 systems in well-ventilated, non-occupied areas.
- Separate from oxidizers and ignition sources.
- Use H2 gas detectors and explosion-proof equipment.
- Follow turnover inventory (FIFO) for compressed gas.
C. Maintenance & Handling
- Only trained personnel may service H2 systems.
- Use intrinsically safe tools.
- Conduct leak testing after assembly (bubble test or H2 sensor).
- Bosch-provided service manuals must be followed exactly.
4. Bosch-Specific Requirements
A. Bosch Quality & Traceability
- IATF 16949 compliance for automotive/defense systems.
- Serial number tracking for all components (especially H2 fuel cells).
- Software/Firmware Updates: Must follow Bosch cybersecurity protocols.
B. Technical Documentation
Bosch must supply:
– Safety Data Sheets (SDS) for H2 components
– Technical Manuals (installation, operation, maintenance)
– Compliance Certificates (CE, UL, ATEX if applicable)
– DoD DD Form 250 (Material Inspection and Receiving Report) for U.S. contracts
5. Cybersecurity & Data Compliance (if applicable)
If H2 systems include IoT sensors, telemetry, or control software:
– Comply with NIST SP 800-171 (for U.S. defense contractors).
– Follow Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) if required.
– Bosch systems must support secure boot, encrypted comms, and remote disable.
6. Disposal & End-of-Life
- H2 tanks: Must be depressurized and purged before disposal.
- Fuel cells: May contain precious metals (e.g., platinum); recycle per WEEE/RoHS.
- Follow EPA and military environmental protocols for hazardous components.
7. Incident Response Plan
In case of H2 leak or fire:
1. Evacuate area; eliminate ignition sources.
2. Ventilate space; use H2 detectors to confirm levels.
3. Contact emergency response (military or civilian HAZMAT).
4. Report to Bosch Technical Support and contracting officer.
🔧 Bosch 24/7 Support: +49 711 5004-0 (Global)
📧 [email protected] (Hypothetical contact – verify actual)
8. Key Contacts & References
| Entity | Contact/Reference |
|——-|——————-|
| Bosch Defense Division | defense.bosch.com (verify official site) |
| U.S. DoD Logistics | DLA Energy, DLA Aviation |
| Regulatory | DOT PHMSA (U.S.), ECHA (EU), DGAC (France) |
| Standards | NFPA 2, ISO 19880, MIL-STD-810, ADR 2023 |
Disclaimer
This guide is generic and based on publicly available standards. Always:
– Consult the specific Bosch product manual.
– Verify contractual requirements (e.g., Statement of Work).
– Engage legal and compliance officers for export control and ITAR reviews.
If you can clarify what “Bosch Def. Use H2” refers to—such as a specific product (e.g., Bosch H2 fuel cell for defense vehicles), a project code, or a region—I can tailor this guide further (e.g., for NATO use, U.S. Army, or EU defense programs).
Conclusion for Sourcing Bosch DEF (Diesel Exhaust Fluid):
Sourcing Bosch Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF) presents a reliable and high-quality solution for meeting emissions regulations and ensuring optimal performance in modern diesel-powered vehicles and machinery. Bosch, as a globally recognized leader in automotive technology and innovation, guarantees DEF that meets or exceeds ISO 22241 standards, ensuring compatibility with Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) systems and helping reduce nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions effectively.
Procuring Bosch DEF offers several advantages, including consistent product quality, supply chain reliability, and strong technical support. Whether sourced directly from Bosch or through authorized distributors, businesses can benefit from scalable supply options, logistical support, and confidence in product integrity—critical factors for maintaining engine efficiency, minimizing downtime, and achieving environmental compliance.
In conclusion, sourcing Bosch DEF is a strategic decision for fleet operators, industrial users, and OEMs seeking a premium, dependable fluid that supports environmental sustainability, regulatory adherence, and long-term engine health. Partnering with Bosch ensures not only a superior product but also access to a trusted brand committed to innovation and environmental responsibility in the evolving landscape of clean transportation.