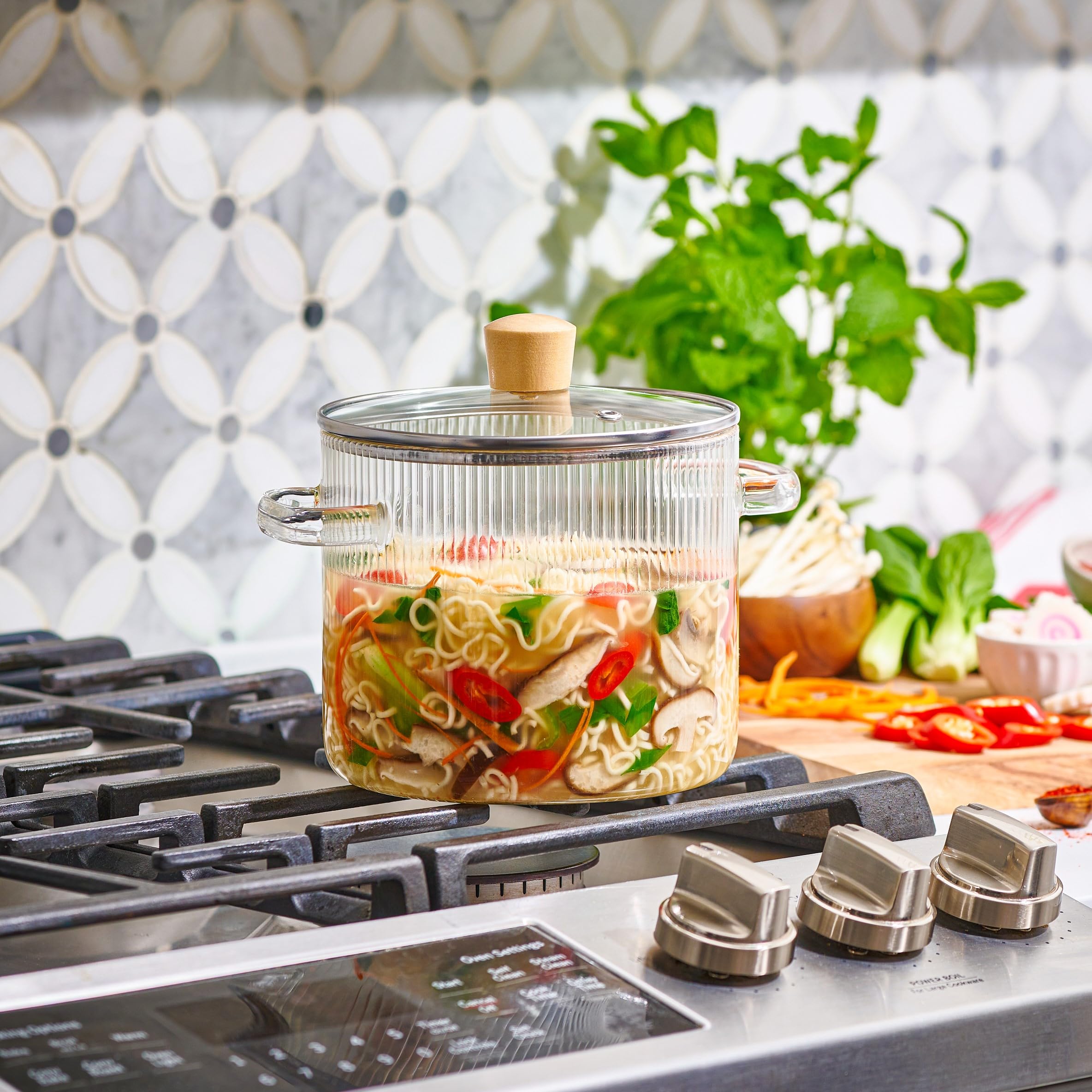
The global borosilicate glass cookware market is witnessing steady growth, driven by increasing consumer preference for durable, non-toxic, and heat-resistant kitchenware. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the global glassware market – which includes borosilicate cooking pots – is projected to grow at a CAGR of approximately 5.2% from 2023 to 2028. This growth is supported by rising health awareness and a shift toward chemical-free, eco-friendly cooking materials. Borosilicate glass, known for its thermal shock resistance and longevity, has become a preferred choice over traditional materials like aluminum and non-stick coatings. As demand surges across North America, Europe, and the Asia-Pacific region, manufacturers are scaling production and investing in innovative designs to capture market share. In this evolving landscape, seven leading companies stand out for their product quality, global distribution, and technological advancements in borosilicate glass manufacturing.
Top 7 Borosilicate Glass Cooking Pots Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 PYREX® Brand Glass Products
Domain Est. 1991
Website: corning.com
Key Highlights: Made from Type 1, Class A low expansion borosilicate glass, PYREX glassware has become the accepted standard in chemistry labs across the globe. Unlike common ……
#2 BOROSIL
Domain Est. 1997
Website: borosil.com
Key Highlights: Borosil Scientific Limited is a pioneering solution provider in the scientific field, offering over 4000 specialized products….
#3 Ecolution Cookware
Domain Est. 2009
Website: ecolutionhome.com
Key Highlights: Ecolution believes cookware should be easy to use, safe, healthy, and make your life easier. Shop our full range of non stick pots, pan, cookware, bakeware, ……
#4 Ocuisine® ∙ borosilicate glass cooking dishes
Domain Est. 2013
Website: ocuisine.fr
Key Highlights: Our glass withstands extreme temperatures without cracking. Shock-Resistant. Made from fully tempered borosilicate glass, strong and resistant to impacts….
#5 A unique glass
Domain Est. 2020
Website: pyrex.co.uk
Key Highlights: *Thermal and mechanical resistance compared to competing products made of borosilicate glass. MADE IN FRANCE. Unique expertise for products of the highest ……
#6 Borosilicate Glass Cookware
Domain Est. 2023
Website: boro-glass-supplier.com
Key Highlights: Superior Heat Resistance: Our Borosilicate Glass Cookware can withstand extreme temperatures, making it perfect for baking, roasting, and stovetop cooking….
#7 Commitment
Website: pyrex.eu
Key Highlights: At Pyrex®, we’ve been committed for over 100 years to healthy, gourmet cooking that’s ever more respectful of the planet….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Borosilicate Glass Cooking Pots
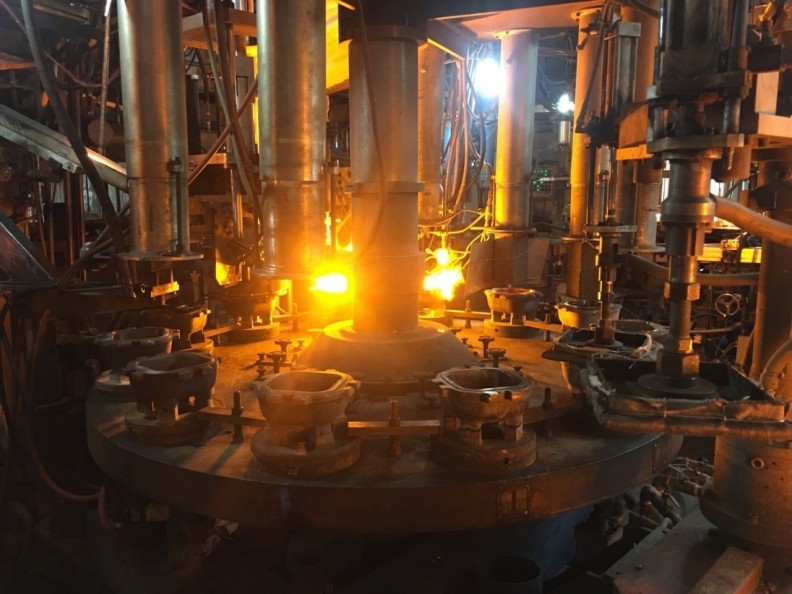

H2: Market Trends for Borosilicate Glass Cooking Pots in 2026
In 2026, the market for borosilicate glass cooking pots is expected to experience sustained growth, driven by evolving consumer preferences, technological advancements, and increasing awareness of health and sustainability. Several key trends are shaping the industry:
-
Rising Demand for Healthy and Non-Toxic Cookware
Consumers are increasingly prioritizing non-toxic, chemical-free kitchenware. Borosilicate glass, known for its inert composition and resistance to leaching harmful substances, aligns well with this trend. As awareness grows about the potential risks of non-stick coatings and metal-based pots, demand for borosilicate alternatives is accelerating, particularly among health-conscious households and eco-aware millennials and Gen Z consumers. -
Sustainability and Circular Economy Influence
With global emphasis on reducing plastic and single-use materials, borosilicate glass is gaining favor due to its durability, recyclability, and long product lifecycle. Brands are responding by highlighting sustainable sourcing, energy-efficient manufacturing, and recyclable packaging. In 2026, eco-certifications and carbon footprint disclosures are becoming key differentiators in marketing strategies. -
Innovation in Design and Functionality
Manufacturers are enhancing borosilicate glass pots with ergonomic handles, tempered lids, and compatibility with multiple heat sources (oven, stovetop, induction with proper bases). Hybrid designs that combine borosilicate bodies with stainless steel or silicone components are gaining popularity, improving safety and usability without compromising transparency or chemical resistance. -
E-Commerce and Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) Growth
Online retail continues to dominate cookware sales, enabling niche brands to reach global audiences. In 2026, targeted digital marketing, influencer collaborations, and user-generated content on platforms like Instagram and TikTok are instrumental in driving brand visibility and consumer trust. Subscription models and bundled kitchen sets are also becoming common in e-commerce strategies. -
Expansion in Emerging Markets
Rising disposable incomes and urbanization in regions such as Southeast Asia, India, and Latin America are fueling demand for premium kitchenware. Educational campaigns about the benefits of borosilicate glass—especially its thermal shock resistance and transparency for monitoring cooking—are helping penetrate these markets. -
Competition and Price Sensitivity
While premium pricing reflects quality, increased competition from alternative materials (e.g., ceramic-coated metals) pressures brands to justify cost through added value—such as lifetime warranties, modular designs, or smart integration features. Entry-level borosilicate lines are emerging to capture price-sensitive segments without diluting brand reputation. -
Regulatory and Safety Standards
Stricter global regulations on food contact materials are reinforcing consumer confidence in borosilicate glass. Compliance with standards such as FDA, LFGB, and REACH is now a baseline expectation, with third-party testing and transparency becoming standard practice among leading manufacturers.
In summary, the 2026 market for borosilicate glass cooking pots is characterized by innovation, health-driven demand, and sustainability focus. As consumers seek safer, longer-lasting, and environmentally responsible kitchen solutions, borosilicate glass is well-positioned to capture a growing share of the global cookware market.
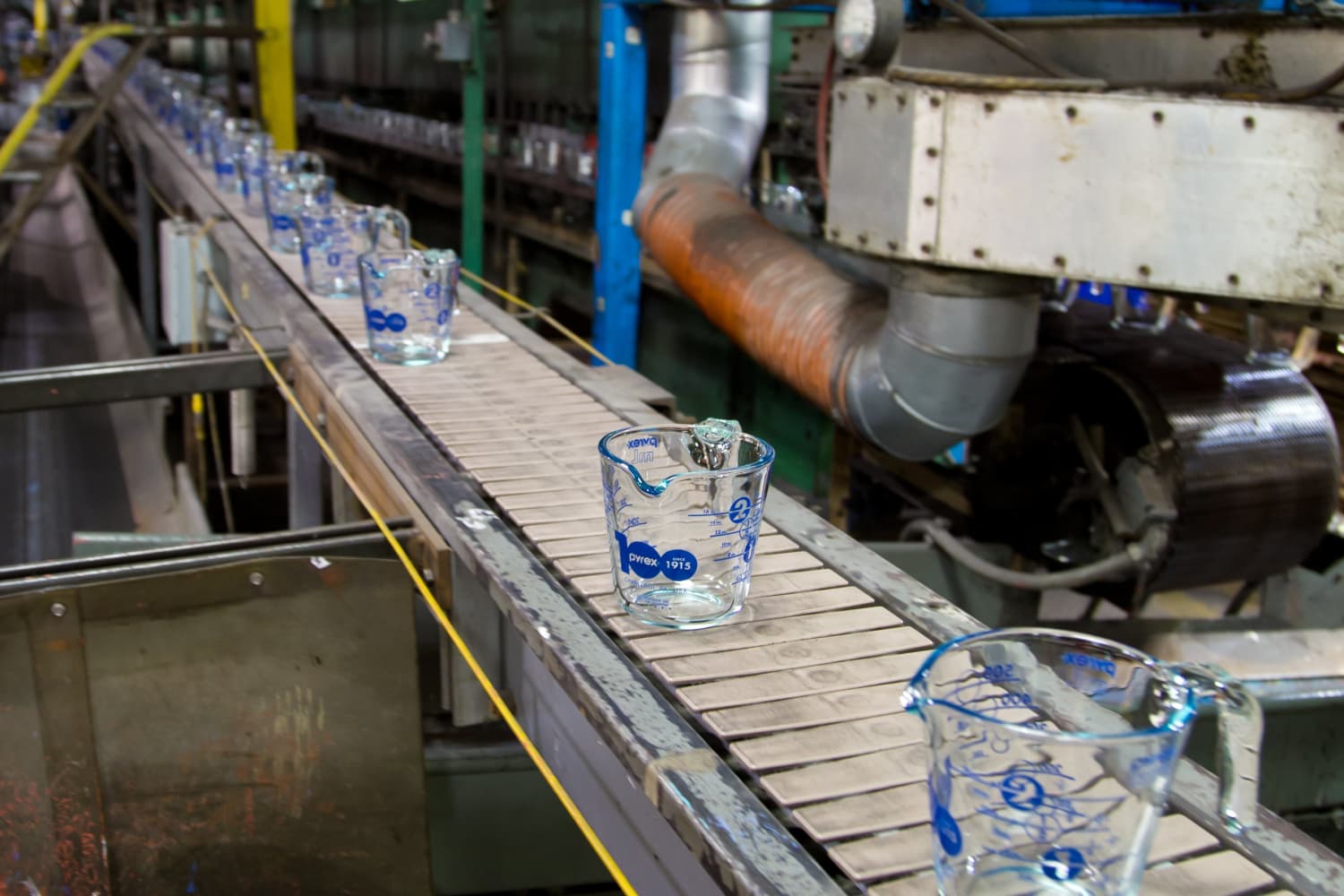

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Borosilicate Glass Cooking Pots (Quality & IP)
Sourcing borosilicate glass cooking pots offers benefits like thermal shock resistance and clarity, but several critical pitfalls related to quality and intellectual property (IP) can undermine your product’s success and expose your business to risk.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Misrepresentation of Borosilicate Content or Type
Suppliers may falsely claim their glass is borosilicate when it is actually soda-lime or low-borosilicate glass. Some may use inferior grades (e.g., 3.3 expansion coefficient vs. the standard 5.0) that do not offer the same thermal durability, leading to cracking under temperature changes.
2. Inconsistent Thermal Shock Resistance
Even genuine borosilicate can fail if manufacturing processes are substandard. Poor annealing or uneven wall thickness can create stress points, reducing resistance to sudden temperature changes—a key selling point for consumers.
3. Subpar Manufacturing Defects
Look for issues like bubbles, striations, uneven rims, or weak seals on lids. These defects not only affect aesthetics but can compromise safety and performance, increasing the risk of breakage during use.
4. Use of Non-Food-Grade Materials
Some suppliers may use glass or coatings that are not certified as food-safe (e.g., lacking FDA or EU 1935/2004 compliance). This poses health risks and can lead to product recalls or legal liabilities.
5. Inadequate Packaging and Handling
Borosilicate glass is durable but still fragile. Poor packaging can result in damage during shipping. Ensure suppliers use reinforced packaging with adequate cushioning to protect edges and corners.
Intellectual Property (IP) Pitfalls
1. Copying Protected Designs
Many popular borosilicate cookware designs are protected by design patents or registered外观 designs. Sourcing near-identical products from generic suppliers risks infringing on these rights, potentially leading to cease-and-desist orders, lawsuits, or customs seizures.
2. Unauthorized Use of Brand Logos or Trademarks
Some manufacturers may offer products with engraved or printed logos that mimic established brands. Using these—even if unintentionally—exposes you to trademark infringement claims and brand dilution.
3. Lack of IP Clearance from Suppliers
Suppliers often disclaim responsibility for IP issues. Without a contractual guarantee or warranty that the product doesn’t infringe third-party rights, you, as the buyer, bear full liability.
4. Difficulty in Proving Originality
If challenged, you may struggle to prove your design is original or independently created. Without proper documentation or IP searches prior to sourcing, defending against infringement claims becomes costly and complex.
5. Grey Market or Diverted Goods
Some suppliers offer “genuine” branded borosilicate cookware at suspiciously low prices. These may be grey market goods or counterfeits, violating brand IP and potentially damaging your reputation with consumers.
Mitigation Strategies
- Verify Material Authenticity: Request material certifications (e.g., ISO 9001, SGS reports) and conduct independent lab testing for boron oxide content and thermal resistance.
- Audit Manufacturing Processes: Visit factories or hire third-party inspectors to assess quality control, annealing procedures, and safety compliance.
- Conduct IP Due Diligence: Perform design and trademark searches before finalizing designs. Require suppliers to sign IP indemnity clauses.
- Develop Unique Designs: Invest in original product development to avoid infringement and build brand equity.
- Secure Proper Documentation: Obtain compliance certificates (FDA, LFGB, etc.) and written assurances of IP non-infringement from suppliers.
Avoiding these pitfalls ensures not only a durable, safe product but also protects your brand from legal and reputational harm.
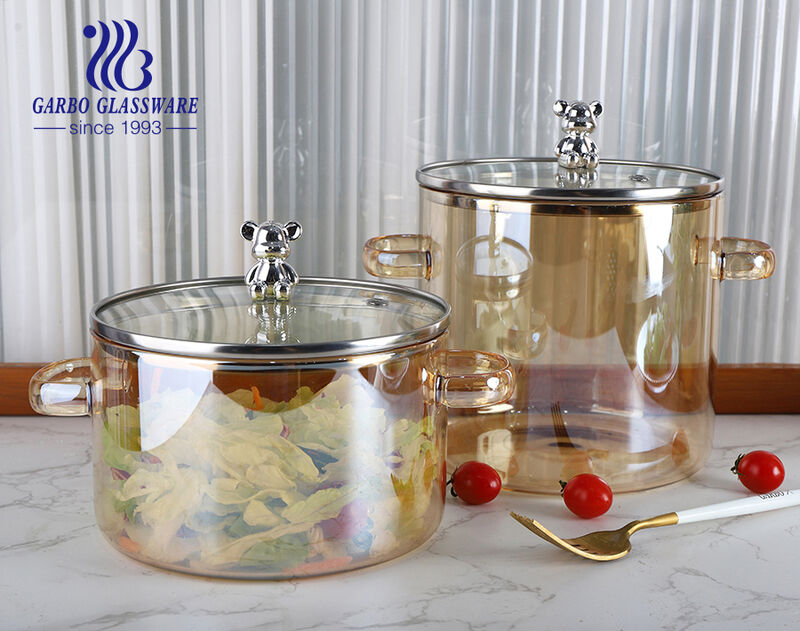

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Borosilicate Glass Cooking Pots
Product Classification and Regulatory Overview
Borosilicate glass cooking pots are classified under specific Harmonized System (HS) codes for international trade and customs purposes. Typically, these products fall under HS Code 7013.37 (Glassware of a kind used for table, kitchen, toilet, office, indoor decoration or similar purposes, of glass other than glass having lead content by weight exceeding 8%, not optically worked: Other: Other). However, classification may vary slightly by country, so verification with local customs authorities is recommended.
These products must comply with food contact material (FCM) regulations in the target market. In the European Union, compliance with Regulation (EC) No 1935/2004 and Commission Regulation (EU) No 2023/2006 on good manufacturing practice is mandatory. The glass must not transfer harmful substances to food under normal or foreseeable use conditions.
In the United States, borosilicate glass cookware must meet FDA 21 CFR Part 179, which governs the use of glass and glass-like materials in food packaging and cookware. The material must be safe for repeated use in contact with food and resistant to thermal shock.
Packaging and Labeling Requirements
Proper packaging is essential to prevent breakage during transit. Use double-wall corrugated boxes with internal dividers or molded pulp inserts to secure each pot. Wrap individual units in bubble wrap or foam sleeves for additional protection. Clearly label outer packaging with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Do Not Stack” warnings.
Labeling on the product or packaging must include:
– Manufacturer’s name and address
– Country of origin
– Product capacity and dimensions
– Care and usage instructions
– Heat resistance range (e.g., “Oven-safe up to 500°F / 260°C”)
– Dishwasher and microwave safety statements (if applicable)
– Compliance marks (e.g., FDA, CE, LFGB)
In the EU, products must also carry the CE mark if required by applicable directives, and include traceability information per EU FCM regulations.
Transportation and Handling
Due to the fragile nature of glass, use temperature-controlled and humidity-stable transport to prevent thermal stress or condensation damage. Avoid exposure to extreme temperatures, especially during air freight.
Ship via reputable carriers with experience in handling fragile goods. For international shipments, ensure compliance with International Air Transport Association (IATA) and International Maritime Organization (IMO) regulations for packaging and labeling.
Implement strict handling procedures at warehouses and distribution centers. Train staff to avoid dropping, stacking, or compressing packages. Store inventory in dry, climate-controlled facilities away from direct sunlight and vibration sources.
Import and Customs Compliance
Before shipping, obtain all required import permits or notifications based on destination country regulations. Provide complete documentation, including:
– Commercial invoice
– Packing list
– Bill of lading or air waybill
– Certificate of Origin
– Product compliance certificates (e.g., FDA letter of non-objection, EU Declaration of Conformity)
– Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS), if requested
Ensure accurate country-of-origin marking on both product and packaging. Mislabeling may result in customs delays, fines, or rejection of goods.
Quality Assurance and Testing
Conduct regular third-party testing to verify compliance with relevant standards:
– Thermal shock resistance (e.g., EN 1183, ASTM C336)
– Leaching tests for heavy metals (e.g., lead, cadmium) under food simulants
– Physical durability and strength tests
Maintain a Quality Management System (QMS) compliant with ISO 9001. Keep records of all material sourcing, manufacturing processes, inspections, and test results for traceability and audit readiness.
Environmental and Sustainability Considerations
Borosilicate glass is fully recyclable. Provide end-of-life disposal information to consumers. Consider using recycled packaging materials and minimizing plastic content in packaging to meet sustainability goals and comply with regulations such as the EU Packaging and Packaging Waste Directive (94/62/EC).
Monitor evolving regulations on extended producer responsibility (EPR) in target markets, especially in the EU and Canada, where producers may be required to contribute to recycling programs.
In conclusion, sourcing borosilicate glass cooking pots offers a compelling combination of durability, thermal resistance, and health-safe cooking properties. Their ability to withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking makes them ideal for versatile kitchen use—from stovetop to oven to refrigerator. Additionally, borosilicate glass is non-reactive, preserving the flavor and integrity of food while avoiding the leaching of harmful chemicals often associated with other cookware materials.
When sourcing these products, it is essential to verify manufacturer credentials, material authenticity, and compliance with international safety standards such as FDA or LFGB. Considering reputable suppliers, evaluating product thickness and design, and assessing cost versus long-term value are critical steps in ensuring quality and performance.
Overall, investing in genuine borosilicate glass cookware supports sustainable, safe, and efficient cooking practices, making it a wise choice for both home and professional kitchens. Proper sourcing enhances product reliability and user satisfaction, reinforcing the value of this innovative material in modern culinary applications.