The global bone grinder market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising demand across the pet food, animal feed, and organic fertilizer industries. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the animal feed processing equipment market—which includes bone grinding machinery—is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.2% from 2023 to 2028. This expansion is fueled by increasing livestock production, stricter feed safety regulations, and a growing preference for processed by-products rich in calcium and protein. As sustainability and circular economy practices gain traction, bone grinding has emerged as a critical step in waste valorization, further amplifying the need for efficient and durable grinding equipment. With North America and Europe leading in technological adoption and Asia-Pacific witnessing rapid industrialization in meat processing, the demand for high-performance bone grinders is on the rise. In this competitive landscape, a select group of manufacturers stand out for innovation, reliability, and global reach—shaping the future of the industry.
Top 8 Bone Grinder Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Speco
Domain Est. 1996
Website: speco.com
Key Highlights: One of the largest manufacturers of Grinder Plates and Knives in the world. From meat grinder plates and knives to bone collector systems and insert blades….
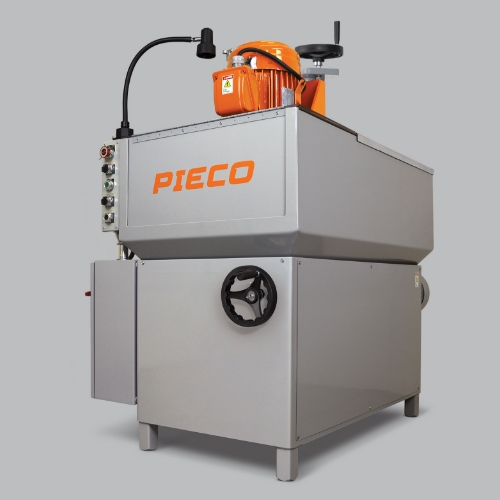
#2 PIECO
Domain Est. 1996
Website: pieco.com
Key Highlights: PIECO is a manufacturer and supplier of meat grinding products, safety equipment, and specialized tools for the commercial meat processing industry….
#3 Shop all
Domain Est. 1999
Website: cislak.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $559Bone Grinder. Sort By: Featured Items, Newest Items, Best Selling, A to Z ……
#4 Bone Shredder Machine
Domain Est. 2015
Website: gemsmachine.com
Key Highlights: Professional Beef Bone Grinder manufacturer is located in China, including Bone Mill Machine,Beef Bone Grinding Machine, Bone Meal Crusher, etc….
#5 High-Performance Industrial Grinders
Domain Est. 2016
Website: romegrindingsolutions.com
Key Highlights: Rome manufactures a wide range of industrial food grinders designed to safely meet the needs of the food production industry….
#6 China Bone Grinder Suppliers Factory
Domain Est. 2022
Website: lffoodmachine.com
Key Highlights: As one of the leading bone grinder suppliers in China, we warmly welcome you to buy high-grade bone grinder for sale here from our factory….
#7 Stainless Steel Bone Grinder Machine, Almond Butter Machine …
Domain Est. 2019
Website: hnmiracle.com
Key Highlights: Cow bone crusher, also named bones grinder machine, it can be used for processing fresh and dry ox bone, cow bone, pig bone, goat bone, donkey bone, chicken ……
#8 SHREDDERS AND GRINDERS
Domain Est. 2021
Website: ancoeas.com
Key Highlights: Duracut Crusher and Bone Shredder. The ANCO Duracut Crusher is designed specifically for bone or whole carcass crushing. The Duracut unit has a one-pass design ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Bone Grinder

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Bone Grinder
The global market for bone grinders—machinery used primarily in the meat processing, pet food, and agricultural industries to pulverize animal bones into fine meal or powder—is poised for notable transformation by 2026. Driven by shifts in consumer behavior, regulatory developments, and technological innovation, the following trends are expected to shape the industry landscape:
-
Increased Demand from the Pet Food Industry
By 2026, the premium and raw pet food sectors are projected to grow significantly, particularly in North America, Europe, and parts of Asia-Pacific. As pet owners increasingly opt for natural, high-protein diets for their animals, demand for bone meal as a key ingredient will rise. This will drive investments in high-efficiency, hygienic bone grinding systems capable of producing consistent, pathogen-free output. -
Sustainability and Circular Economy Imperatives
With growing emphasis on waste reduction and resource recovery in food processing, bone grinders are becoming essential tools for upcycling animal by-products. Regulatory support for zero-waste initiatives in slaughterhouses and rendering plants will encourage adoption of advanced bone grinding technologies that maximize yield and minimize environmental impact. -
Technological Advancements and Automation
The integration of IoT-enabled sensors, predictive maintenance systems, and automated feed controls in bone grinders is expected to accelerate by 2026. These innovations will enhance operational efficiency, reduce downtime, and ensure compliance with food safety standards (e.g., HACCP, FDA, and EU regulations). Manufacturers will focus on modular, scalable designs to serve both large industrial processors and small-to-medium enterprises (SMEs). -
Stringent Food Safety and Hygiene Standards
Global regulatory bodies are tightening controls on animal by-product processing to prevent contamination and disease transmission (e.g., BSE). As a result, bone grinder manufacturers will need to prioritize materials like food-grade stainless steel, seamless designs, and CIP (Clean-in-Place) compatibility to meet evolving compliance requirements. -
Regional Market Diversification
While North America and Europe remain dominant markets due to established meat processing infrastructures, Asia-Pacific—particularly China, India, and Southeast Asia—is expected to witness the fastest growth. Rising meat consumption, urbanization, and investments in food processing infrastructure will fuel demand for reliable bone grinding equipment. -
Expansion into Alternative Applications
Beyond traditional uses, bone meal derived from grinding is gaining traction as an organic fertilizer and calcium supplement in agriculture and nutraceuticals. This diversification of end-use applications will open new revenue streams and encourage innovation in particle size control and sterilization technologies. -
Consolidation and Strategic Partnerships
By 2026, the bone grinder market may see increased consolidation as key players acquire niche technology firms or form partnerships with meat processors and waste management companies. These alliances will aim to offer integrated solutions that include equipment, maintenance, and by-product valorization services.
In conclusion, the 2026 bone grinder market will be characterized by technological sophistication, regulatory compliance, and expanding applications. Companies that innovate in efficiency, sustainability, and adaptability will be best positioned to capture growth amid rising global demand for value-added animal by-product utilization.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing a Bone Grinder: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing a bone grinder—especially for industrial, food processing, or research applications—can present significant challenges related to both product quality and intellectual property (IP). Being aware of common pitfalls helps avoid operational inefficiencies, legal complications, and safety concerns.
Poor Build Quality and Material Selection
One of the most frequent issues when sourcing bone grinders is receiving equipment constructed from substandard materials. Low-grade stainless steel or inadequate motors may lead to rapid wear, contamination risks, or even equipment failure. Inferior components compromise grinding efficiency, increase maintenance costs, and may not meet food safety or hygiene standards (e.g., FDA, CE, or NSF compliance).
Inaccurate Performance Specifications
Suppliers, particularly from less-regulated markets, may exaggerate machine capabilities—such as throughput, particle size output, or durability. These misleading claims can result in a bone grinder that underperforms in real-world conditions, disrupting production schedules and requiring costly replacements or retrofits.
Lack of Safety Features and Regulatory Compliance
Some imported or low-cost models may lack essential safety mechanisms like emergency stop buttons, protective guards, or overload protection. Additionally, they might not comply with regional safety and sanitation standards, leading to legal liabilities, workplace hazards, or rejection by regulatory bodies during inspections.
Inadequate After-Sales Support and Spare Parts Availability
Sourcing from distant or unverified suppliers often means limited access to technical support, maintenance training, or spare parts. A breakdown in a critical component can halt operations for extended periods if replacements are not readily available or take weeks to arrive.
Intellectual Property Infringement
A significant but often overlooked risk is sourcing equipment that violates intellectual property rights. Some manufacturers may replicate patented designs, control systems, or proprietary grinding mechanisms without authorization. Purchasing such equipment—even unknowingly—can expose your organization to legal action, especially if the original IP holder discovers infringement in your supply chain.
Risk of Counterfeit or “Knock-Off” Equipment
In high-demand markets, counterfeit bone grinders mimicking reputable brands are increasingly common. These units often use inferior engineering, lack proper documentation, and may bear falsified certifications. Using counterfeit equipment can void warranties, compromise safety, and damage your brand reputation.
Insufficient Documentation and Technical Transparency
Many suppliers fail to provide comprehensive technical documentation, including CAD drawings, material certifications, or maintenance manuals. This lack of transparency makes integration into existing systems difficult and can complicate quality audits or regulatory approvals.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls, conduct thorough due diligence: verify supplier credentials, request third-party quality certifications, perform factory audits if possible, and consult legal experts to ensure IP compliance. Prioritize suppliers with proven track records, transparent manufacturing practices, and strong after-sales support.
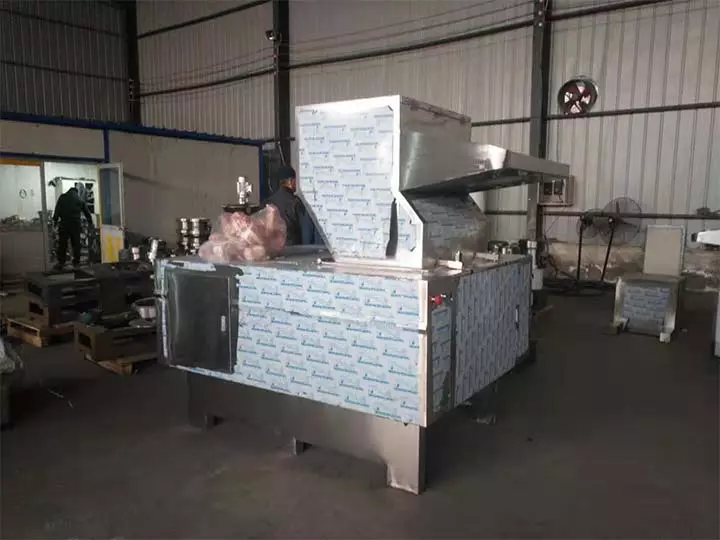

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Bone Grinder
Overview
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for the safe, legal, and efficient handling, transportation, storage, and operation of a bone grinder. Whether used in food processing, rendering, waste management, or agricultural operations, adherence to regulatory standards and best practices is critical.
Equipment Classification and Regulatory Framework
Bone grinders are typically classified under industrial machinery or food processing equipment, depending on their application. Key regulatory bodies include:
– OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) – Workplace safety and machine guarding
– FDA (Food and Drug Administration) – If used in food production (e.g., pet food, animal feed)
– USDA (U.S. Department of Agriculture) – For meat processing and rendering facilities
– EPA (Environmental Protection Agency) – Waste disposal and environmental emissions
– Local Health Departments – Sanitation and operational permits
Operators must verify jurisdiction-specific requirements and ensure compliance with all applicable regulations.
Transportation and Shipping
When transporting a bone grinder:
– Use secure, flatbed or enclosed trailers with proper tie-downs to prevent shifting.
– Ensure weight limits comply with DOT (Department of Transportation) regulations.
– Label heavy equipment with visible “Heavy Machinery” and “Fragile Components” warnings.
– Protect electrical components and blades from moisture and impact during transit.
– Maintain shipping documentation, including bills of lading and equipment specifications.
Storage Requirements
Store bone grinders in a dry, secure, and well-ventilated area:
– Elevate equipment off the floor to prevent moisture damage.
– Cover with breathable tarps to minimize dust accumulation.
– Lock out and tag out (LOTO) power sources when not in use.
– Store spare blades and parts in labeled, organized containers.
– Maintain a clean, clutter-free environment to reduce slip, trip, and fire hazards.
Installation and Operational Safety
Prior to operation:
– Install the grinder on a stable, level surface with vibration dampening if needed.
– Connect to appropriate power sources per manufacturer specifications (voltage, phase, grounding).
– Install required machine guards, emergency stop buttons, and interlock systems.
– Conduct a pre-operational inspection of blades, belts, motors, and safety features.
– Train all personnel on startup, shutdown, and emergency procedures.
Sanitation and Cleaning Protocols
For food-grade or biohazard applications:
– Follow a documented Sanitation Standard Operating Procedure (SSOP).
– Disassemble and clean grinder components regularly using food-safe or industrial-grade cleaners.
– Sanitize with approved agents (e.g., quaternary ammonia, peracetic acid) to prevent microbial growth.
– Maintain cleaning logs and conduct periodic ATP swab testing for verification.
– Prevent cross-contamination by dedicating equipment to specific materials when possible.
Waste Management and Disposal
- Collect bone dust and offal in sealed, leak-proof containers.
- Comply with local regulations for organic waste disposal or rendering.
- Document waste quantities and disposal methods to support traceability.
- If grinding hazardous animal material (e.g., SRM – Specified Risk Materials), follow USDA/APHIS protocols.
- Minimize airborne particulates using dust collection systems and PPE.
Personnel Training and Documentation
- Train operators on hazards (pinch points, entanglement, noise, dust), PPE, and emergency response.
- Require certification for high-risk operations.
- Maintain records of:
- Equipment maintenance and repairs
- Employee training and certifications
- Sanitation logs
- Incident and near-miss reports
- Regulatory inspections and compliance audits
Maintenance and Calibration
- Follow manufacturer-recommended maintenance schedules.
- Inspect blades, bearings, motors, and safety systems monthly.
- Replace worn or damaged parts immediately.
- Keep a maintenance log with dates, actions taken, and technician signatures.
- Calibrate feed rates and motor performance as needed for consistent output.
Emergency Preparedness
- Post emergency contact numbers and shutdown procedures near the equipment.
- Equip the area with fire extinguishers (Class C for electrical), eyewash stations, and first aid kits.
- Conduct regular drills for equipment jam response, power failure, and medical emergencies.
- Establish lockout/tagout (LOTO) procedures and verify compliance during audits.
Compliance Audits and Recordkeeping
- Schedule internal and third-party audits annually.
- Verify documentation meets FDA, USDA, OSHA, or other relevant standards.
- Retain records for a minimum of 2–5 years, depending on jurisdiction.
- Correct non-conformances promptly and document corrective actions.
Conclusion
Proper logistics and compliance management for a bone grinder ensure operational efficiency, worker safety, and regulatory adherence. By following this guide, facilities can minimize risk, maintain product integrity, and demonstrate due diligence in all aspects of bone grinder use.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Bone Grinder:
Sourcing a bone grinder requires careful consideration of several key factors including the intended application, production capacity, bone type and size, durability of materials, ease of cleaning and maintenance, compliance with food safety or industry standards, and overall cost-effectiveness. After evaluating various suppliers, models, and technologies, it is essential to select a bone grinder that balances performance, reliability, and value for money. Prioritizing machines made from food-grade stainless steel with strong motors and safety features ensures long-term operational efficiency and compliance with hygiene regulations. Additionally, choosing a supplier with strong after-sales support, warranties, and spare parts availability minimizes downtime and supports sustained operations. Ultimately, a well-researched procurement decision will enhance processing capabilities, improve product quality, and contribute to operational success in industries such as meat processing, pet food manufacturing, or organic fertilizer production.