The global organic fertilizer market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising awareness of sustainable agriculture and increasing demand for high-yield, eco-friendly farming practices. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the organic fertilizers market was valued at USD 11.36 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 12.5% from 2024 to 2029. Bloodmeal fertilizer, a nitrogen-rich byproduct of the meat processing industry, has emerged as a key player in this segment due to its ability to promote vigorous plant growth and improve soil health. With nitrogen content typically ranging from 12% to 14%, bloodmeal is one of the fastest-acting natural nitrogen sources available, making it a preferred choice among organic farmers and commercial growers alike. As regulatory support for organic farming intensifies and consumer demand for chemical-free produce climbs, the demand for high-quality bloodmeal fertilizers is poised for continued expansion—fueling innovation and competition among leading manufacturers worldwide.
Top 6 Bloodmeal Fertilizer Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
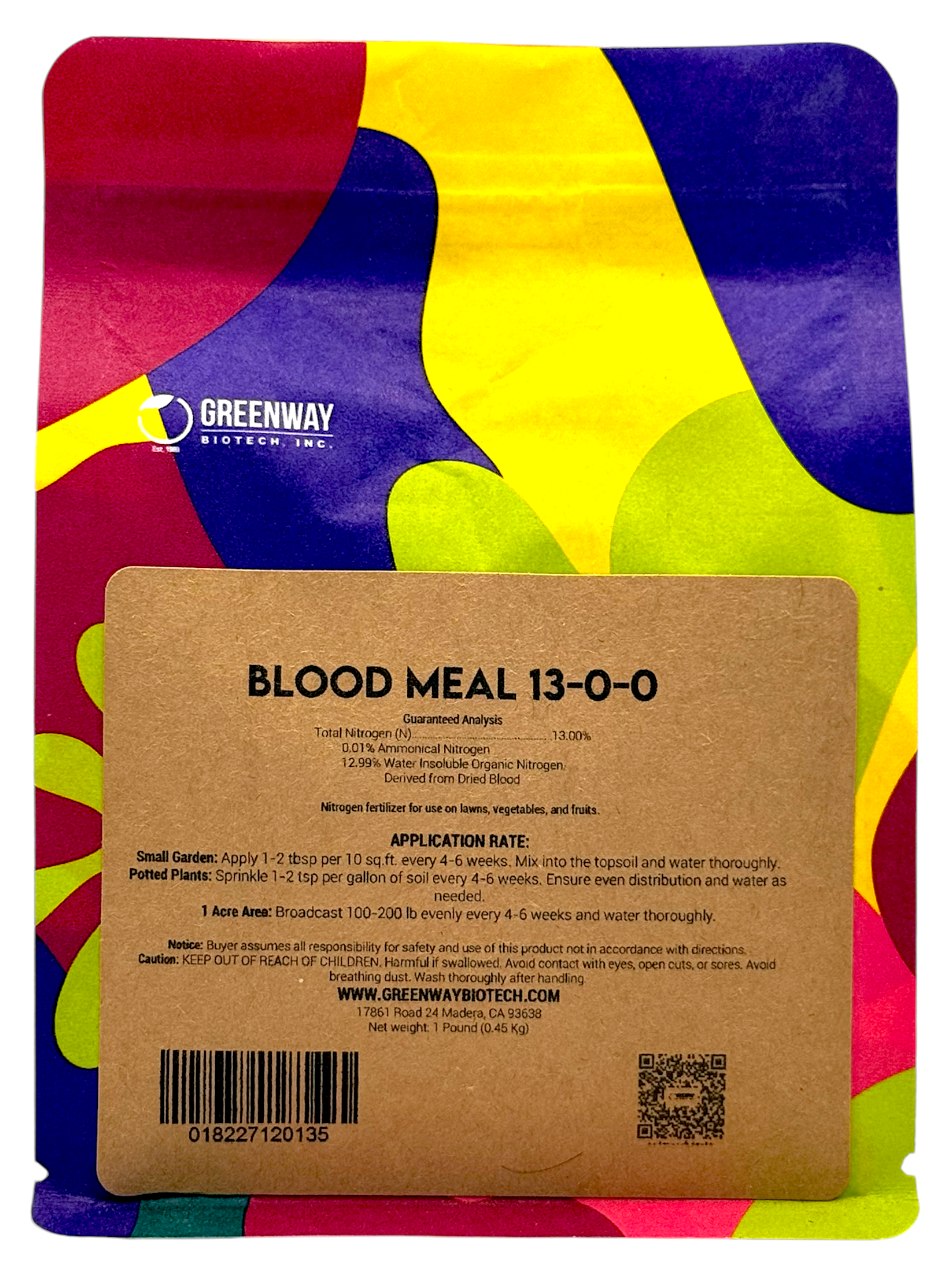
#1 Blood Meal 13
Domain Est. 2003
Website: concentratesnw.com
Key Highlights: Blood Meal 13-0-0 provides a potent source of nitrogen to your soil and is ideal for heavy feeders like corn, broccoli, tomatoes, and leafy greens….
#2 Blood Meal
Domain Est. 2005
Website: boyervalley.com
Key Highlights: Our Blood Meal is a dry, inert powder made from poultry blood and can be used as a high quality protein animal feed and as a high-nitrogen fertilizer….
#3 Blood Meal
Domain Est. 1996
Website: norganics.com
Key Highlights: Blood meal is ideal for nitrogen hungry plants such as lettuce or corn and can also help hasten the composting of highly carbonaceous material such as leaves or ……
#4 Blood Meal 12
Domain Est. 1997
Website: fertrell.com
Key Highlights: Blood Meal 12-0-0. A fast release source of organic nitrogen. It should only be used on plants that have a high nitrogen requirement….
#5 Blood Meal
Domain Est. 1999
Website: fedcoseeds.com
Key Highlights: In stock $21 deliveryOne of the fastest release times of all organic nitrogen sources. Highly recommended for corn. The smell (understandably) freaks out deer….
#6 Organic Blood Meal Fertilizer 13-0-0
Domain Est. 2010
Expert Sourcing Insights for Bloodmeal Fertilizer

H2: Market Trends in Bloodmeal Fertilizer for 2026
The global bloodmeal fertilizer market is poised for notable growth and transformation by 2026, driven by rising demand for organic farming, increasing awareness of soil health, and regulatory support for sustainable agriculture. Bloodmeal, a high-nitrogen organic fertilizer derived from dried animal blood, is gaining renewed attention as a natural alternative to synthetic nitrogen sources. Below are key market trends shaping the bloodmeal fertilizer landscape in 2026:
-
Increased Adoption in Organic Farming
With consumer demand for organically grown food on the rise, farmers worldwide are transitioning to certified organic practices. Bloodmeal, approved for use in organic farming by organizations such as the USDA Organic and EU Organic Certification, is becoming a preferred nitrogen source. Its slow-release properties support long-term soil fertility, making it particularly attractive for organic vegetable, fruit, and specialty crop production. -
Sustainability and Circular Economy Initiatives
The meat processing industry generates significant quantities of animal by-products, including blood. Converting this waste stream into bloodmeal aligns with circular economy principles, reducing environmental impact and adding value to waste. By 2026, enhanced processing technologies and stricter waste management regulations are expected to boost the supply and quality of bloodmeal fertilizer, particularly in North America and Europe. -
Regulatory Support and Environmental Concerns
Governments and environmental agencies are promoting reduced reliance on synthetic fertilizers due to their contribution to greenhouse gas emissions, water pollution, and soil degradation. Incentives for bio-based fertilizers and stricter nitrogen runoff regulations are encouraging agricultural producers to adopt organic options like bloodmeal. The European Green Deal and similar policies in North America and parts of Asia are accelerating this shift. -
Innovation in Formulation and Application
By 2026, manufacturers are expected to invest in product innovation, including pelleted or granulated bloodmeal formulations for easier handling and more controlled nutrient release. Blending bloodmeal with other organic materials (e.g., bone meal, feather meal) to create balanced NPK (nitrogen-phosphorus-potassium) fertilizers is another emerging trend, broadening its application across diverse crop types. -
Growing Demand in Horticulture and Home Gardening
The expansion of urban agriculture and the popularity of home gardening—fueled by pandemic-era habits and sustainability awareness—are driving retail demand for organic soil amendments. Bloodmeal is increasingly available in consumer-friendly packaging through garden centers and e-commerce platforms, boosting market penetration in residential segments. -
Supply Chain Challenges and Price Volatility
Despite growth, the bloodmeal market faces challenges related to raw material availability, animal health regulations (e.g., BSE concerns), and transportation logistics. Fluctuations in livestock slaughter rates can impact blood supply, leading to price volatility. However, improved traceability systems and regional processing hubs are helping stabilize supply chains. -
Regional Market Dynamics
North America and Europe lead in bloodmeal fertilizer adoption due to strong organic certification frameworks and advanced processing infrastructure. Meanwhile, Asia-Pacific—particularly India and China—is expected to see rapid growth as sustainable agriculture initiatives gain momentum. Latin America and Africa present emerging opportunities, though market development is hindered by limited processing capacity and regulatory hurdles.
In summary, the bloodmeal fertilizer market in 2026 reflects a convergence of environmental consciousness, regulatory support, and agronomic innovation. As organic and regenerative agriculture continue to expand, bloodmeal is positioned to play a critical role in sustainable nutrient management strategies worldwide.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Bloodmeal Fertilizer (Quality, IP)
Sourcing bloodmeal fertilizer—while beneficial as a high-nitrogen organic input—comes with several potential pitfalls, particularly concerning quality consistency and intellectual property (IP) issues. Being aware of these challenges helps ensure effective and compliant use in agricultural or horticultural applications.
Quality Inconsistency and Adulteration
One of the most significant risks when sourcing bloodmeal is variability in nutrient content and potential adulteration. Bloodmeal should contain approximately 12–14% nitrogen, but poor processing or dilution with fillers (such as feathers, bone, or other low-nitrogen animal byproducts) can reduce its efficacy. Improper drying methods may also lead to inconsistent particle size, poor solubility, or microbial contamination. Buyers should request third-party lab analysis (e.g., guaranteed analysis for N-P-K, moisture content, and pathogen screening) and verify supplier certifications (e.g., OMRI listing for organic use) to ensure product integrity.
Risk of Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy (BSE) and Regulatory Non-Compliance
Bloodmeal derived from ruminant sources, especially cattle, carries potential biosecurity risks, including the theoretical transmission of prion diseases like BSE (mad cow disease). Many countries regulate or prohibit the use of ruminant-based blood products in agriculture, particularly in feeds or fertilizers applied to grazing lands. Importers and users must confirm the animal source (e.g., porcine or avian blood is often safer and permitted) and ensure compliance with local, national, and international regulations (e.g., EU TSE regulations, USDA guidelines). Failure to verify sourcing can result in shipment rejections or legal liability.
Intellectual Property and Brand Protection Issues
While less common in commodity fertilizers, IP concerns may arise when sourcing branded or proprietary formulations of bloodmeal. Some manufacturers may trademark specific processing methods (e.g., “flash-dried” or “pathogen-free” bloodmeal) or blend bloodmeal into patented organic fertilizer mixes. Unauthorized replication or mislabeling of such formulations could lead to infringement claims. Additionally, suppliers may restrict distribution channels or geographic usage rights in licensing agreements. Buyers should review contractual terms carefully and avoid reverse-engineering or rebranding protected products without permission.
Supply Chain Transparency and Traceability Gaps
Lack of transparency in the supply chain increases the risk of receiving substandard or mislabeled bloodmeal. Without clear traceability from slaughterhouse to bag, it is difficult to verify ethical sourcing, animal welfare standards, or processing conditions. This opacity can also hinder compliance with sustainability certifications or organic standards. Prioritizing suppliers with full traceability systems and auditable records mitigates these risks and supports responsible sourcing.
By addressing these pitfalls proactively—through rigorous vetting, testing, and legal due diligence—buyers can secure high-quality, compliant bloodmeal fertilizer while minimizing operational and reputational risks.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Bloodmeal Fertilizer
Overview of Bloodmeal Fertilizer
Bloodmeal fertilizer is an organic, high-nitrogen soil amendment derived from dried and powdered animal blood, typically collected during slaughterhouse operations. It is widely used in organic farming and gardening to promote lush, green plant growth. Due to its animal origin, bloodmeal is subject to specific regulatory, handling, and transportation requirements to ensure safety, prevent disease transmission, and maintain product integrity.
Regulatory Classification and Compliance
Bloodmeal is classified as a Category 3 animal by-product under the European Union’s Animal By-Products Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009, meaning it poses a low health risk but still requires approved processing and use conditions. In the United States, bloodmeal is regulated by the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA), the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), and state departments of agriculture. Key compliance areas include:
– Organic Certification: Bloodmeal must be processed without chemical defluorination or synthetic additives to qualify under the National Organic Program (NOP).
– Labeling Requirements: Products must include guaranteed analysis (N-P-K values), origin (bovine, porcine, etc.), and usage instructions.
– Import/Export Regulations: International shipments require health certificates and compliance with destination country standards (e.g., APHIS permits for U.S. imports).
Handling and Storage Guidelines
Proper handling and storage are critical to maintain efficacy and prevent contamination:
– Storage Conditions: Store in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area away from direct sunlight. Moisture can cause clumping and microbial growth.
– Containment: Use sealed, pest-proof containers to prevent insect or rodent infestation.
– Segregation: Keep separate from food, feed, and incompatible substances (e.g., strong oxidizers).
– Worker Safety: Handlers should wear gloves and masks to avoid inhalation of dust, which may cause respiratory irritation.
Transportation and Shipping Requirements
Bloodmeal is generally not classified as hazardous under DOT or IATA regulations when properly packaged, but attention to detail is essential:
– Packaging: Use moisture-resistant, durable bags (e.g., multi-wall paper or poly-lined sacks) sealed to prevent leakage. Bulk transport in closed trailers is acceptable.
– Labeling: Include product name, net weight, manufacturer details, and organic certification (if applicable).
– Temperature Control: While not required, avoid extreme heat or freezing during transit to prevent degradation.
– Documentation: Maintain bills of lading, certificates of analysis, and organic transaction certificates (OTCs) for traceability.
Biosecurity and Environmental Considerations
Due to its animal origin, bloodmeal presents biosecurity risks if not managed properly:
– Disease Prevention: Ensure bloodmeal is derived from healthy animals processed in certified facilities to minimize risk of pathogens (e.g., BSE, foot-and-mouth disease).
– Application Restrictions: Do not apply near water sources to prevent nutrient runoff. Follow recommended rates to avoid nitrogen leaching.
– Composting Use: Bloodmeal can be used in composting systems but must be incorporated promptly to reduce odor and pest attraction.
Recordkeeping and Traceability
Robust documentation supports compliance and facilitates recalls if needed:
– Maintain records of sourcing (supplier, dates, batch numbers), processing, testing, and distribution.
– Track organic certification status and ensure renewal.
– Retain copies of import/export permits, inspection reports, and customer transaction records for a minimum of 3–5 years, as required by organic and animal by-product regulations.
Conclusion
Bloodmeal fertilizer is a valuable organic input, but its animal origin necessitates strict adherence to logistics and compliance protocols. By following regulatory requirements, implementing proper handling and storage practices, and maintaining thorough documentation, producers and distributors can ensure safe, lawful, and effective use of bloodmeal in agricultural systems.
In conclusion, sourcing blood meal fertilizer offers a highly effective, organic solution for enhancing soil nitrogen content and promoting robust plant growth. As a byproduct of the meat industry, blood meal is a sustainable option that supports circular economy principles when responsibly sourced. Its high nitrogen content makes it particularly valuable for leafy greens, lawns, and plants with elevated nitrogen demands. However, careful consideration must be given to sourcing practices—prioritizing suppliers that adhere to ethical, sanitary, and environmentally sound processing methods is essential. Additionally, due to its potential to burn plants if overapplied and its possible attraction to pests, blood meal should be used according to recommended guidelines. Overall, when sourced responsibly and applied correctly, blood meal fertilizer is a powerful tool in organic and sustainable gardening and agriculture.