The global blood bank refrigerator market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising blood transfusion demands, increasing healthcare infrastructure development, and stringent regulatory requirements for safe blood storage. According to Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at approximately USD 480 million in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.8% from 2024 to 2029. Similarly, Grand View Research estimates that the market size surpassed USD 500 million in 2023 and is expected to expand significantly, fueled by technological advancements such as IoT-enabled monitoring, precise temperature control systems, and energy-efficient designs. As hospitals, blood banks, and diagnostic centers prioritize the integrity of blood components, the need for reliable cold chain solutions has become critical. This growing demand has led to increased competition and innovation among manufacturers, shaping a landscape where performance, compliance, and reliability are paramount. The following list highlights the top 10 blood bank refrigerator manufacturers leading this evolution through advanced engineering, global reach, and adherence to international quality standards.
Top 10 Blood Bank Refrigerator Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Haier Biomedical, the complete cold chain manufacturer covering …
Domain Est. 2005
Website: haiermedical.com
Key Highlights: Haier Biomedical is the world’s complete cold chain manufacturer and solution provider covering the full range of -196°C to +8°C….
#2 Blood Bank Refrigerators
Domain Est. 2009
Website: bsilab.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery 15-day returnsBlood bank refrigerators are purposefully designed to preserve whole blood, blood components, and reagents at a constant temperature of +4°C….
#3 Blood Bank Refrigerators
Domain Est. 2012
Website: kirsch-medical.com
Key Highlights: KIRSCH is a manufacturer, which enables us to consistently develop our blood bank refrigerators. Each unit consists of a robust housing and high-quality ……
#4 B Medical Systems
Domain Est. 2015
Website: bmedicalsystems.com
Key Highlights: Global manufacturer and distributor of medical-grade devices: vaccine refrigerators, laboratory freezers and refrigerators, ULT freezers, blood bank ……
#5 Blood Bank Refrigerators (MBR)
Domain Est. 2017
Website: phchd.com
Key Highlights: Our Blood Bank Refrigerator MBR series ensures stable and reliable temperature control utilizing PHCbi original technology cultivated in Japan manufacturing ……
#6 Blood Bank Refrigeration
Domain Est. 1998
Website: follettice.com
Key Highlights: High-performance double door blood bank refrigerators are engineered for precise temperature control. Powerful forced air refrigeration system….
#7 Blood Bank Refrigerators
Domain Est. 2000
Website: helmerinc.com
Key Highlights: GX Solutions blood bank refrigerators provide an optimal storage environment, fewer noise distractions for staff, and increased energy efficiency….
#8 Blood Bank Refrigerators
Domain Est. 2006
Website: thermofisher.com
Key Highlights: Meet stringent AABB, ANRC and FDA requirements with Thermo Scientific™ Revco™ Blood Bank Refrigerators to store whole blood and blood components. Voltage….
#9 ABS
Domain Est. 2007
Website: americanbiotechsupply.com
Key Highlights: Your trusted source for medical, lab & pharmaceutical cold storage solutions. 25+ years expertise in reliable, temperature-controlled equipment….
#10 Blood Bank Refrigerator & Plasma Storage Solutions
Domain Est. 2021
Website: corepointscientific.com
Key Highlights: Explore high-performance blood bank refrigerators designed to meet AABB and FDA standards with precise temperature control and reliable alarms—ideal for ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Blood Bank Refrigerator

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Blood Bank Refrigerators
The global market for blood bank refrigerators is poised for substantial evolution by 2026, driven by technological advancements, increasing demand for safe blood storage, regulatory requirements, and expanding healthcare infrastructure. These trends reflect a growing emphasis on temperature precision, energy efficiency, digital integration, and compliance with international standards.
-
Increased Demand for Temperature Precision and Stability
By 2026, blood bank refrigerators are expected to feature enhanced temperature control systems, maintaining the critical +2°C to +6°C range with minimal fluctuations. Manufacturers are integrating dual evaporators, advanced sensors, and real-time monitoring to ensure blood component integrity. This trend is fueled by rising awareness of the sensitivity of blood products—especially platelets and plasma—to temperature deviations. -
Adoption of Smart and Connected Refrigeration Systems
The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) technology is a dominant trend. Smart blood bank refrigerators equipped with remote monitoring, cloud-based data logging, and automated alert systems allow hospitals and blood banks to reduce human error and ensure continuous oversight. By 2026, predictive maintenance and AI-driven diagnostics are expected to become standard in premium models, improving uptime and reducing operational risks. -
Focus on Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
With global emphasis on reducing carbon footprints, manufacturers are transitioning to eco-friendly refrigerants (e.g., hydrocarbons) and energy-efficient compressors. Models compliant with ENERGY STAR and other green certifications are gaining preference, particularly in Europe and North America. This trend aligns with healthcare sustainability goals and reduces long-term operational costs for blood storage facilities. -
Expansion in Emerging Markets
Developing regions such as Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Africa are witnessing increased investments in blood transfusion services and blood bank infrastructure. Governments and NGOs are supporting the establishment of regional blood centers, driving demand for reliable and affordable blood bank refrigerators. By 2026, localized manufacturing and cost-optimized models are expected to capture significant market share in these regions. -
Stringent Regulatory Compliance and Standardization
Regulatory bodies such as the FDA, AABB, and WHO are enforcing stricter guidelines for blood storage equipment. Blood bank refrigerators will need to meet higher standards for validation, documentation, and traceability. Features like audit trails, tamper-proof logs, and compliance with ISO 13485 are becoming essential, especially in public healthcare systems and accredited blood banks. -
Growth in Mobile and Field Blood Storage Solutions
The need for blood in remote areas and disaster response scenarios is spurring innovation in portable and solar-powered blood bank refrigerators. By 2026, these units are expected to offer improved battery life, rugged designs, and GPS-enabled tracking, ensuring safe transport and storage during emergencies and outreach programs. -
Consolidation and Innovation Among Key Players
Major manufacturers such as Haier Biomedical, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Helmer Scientific, and Arrows GmbH are investing heavily in R&D to differentiate their offerings. Strategic partnerships, mergers, and acquisitions are likely to shape the competitive landscape, with a focus on scalable, modular refrigeration systems tailored to various blood bank sizes.
In summary, the 2026 blood bank refrigerator market will be defined by smarter, greener, and more reliable storage solutions. The convergence of digital health, regulatory rigor, and global health equity initiatives will drive innovation, making blood storage safer and more accessible worldwide.
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Blood Bank Refrigerators (Quality & Intellectual Property)
Sourcing blood bank refrigerators requires careful attention to both technical performance and intellectual property (IP) considerations. Overlooking key aspects can compromise blood safety, regulatory compliance, and organizational liability. Below are common pitfalls in these two critical areas:
Quality-Related Pitfalls
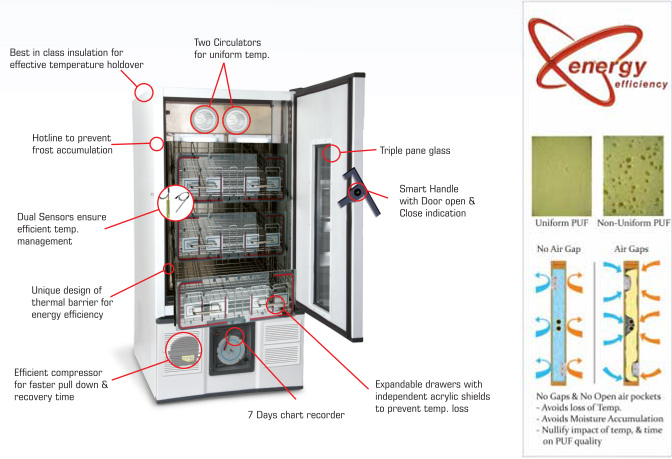
1. Inadequate Temperature Stability and Uniformity
One of the most critical quality failures is selecting a refrigerator that cannot maintain the strict temperature range of +2°C to +6°C throughout the entire storage area. Poor internal airflow design or insufficient insulation can lead to temperature gradients, risking blood component viability. Always verify third-party validation reports and mapping studies.
2. Insufficient Alarms and Monitoring Systems
Refrigerators lacking real-time remote monitoring, audible/visual alarms, and battery backup for power failures can result in undetected temperature excursions. Failing to ensure continuous data logging and alarm notification capabilities increases the risk of blood spoilage and patient safety incidents.
3. Use of Non-Compliant or Substandard Materials
Units constructed with materials that are not corrosion-resistant or not suitable for frequent decontamination can harbor pathogens and shorten equipment life. Ensure interiors are made of medical-grade stainless steel and that all components meet biocompatibility standards.
4. Lack of Regulatory Certification
Procuring units without proper certifications (e.g., CE, FDA 510(k), ISO 13485, or local regulatory approvals) poses compliance risks. Always confirm that the device is cleared specifically for blood storage and meets relevant standards like AABB, CLIA, or WHO guidelines.
5. Poor Maintenance and Service Support
Even high-quality units degrade without proper service. Sourcing from suppliers without local technical support, readily available spare parts, or qualified service technicians can lead to prolonged downtimes and compromised blood inventory.
Intellectual Property-Related Pitfalls
1. Procuring Counterfeit or Clone Devices
Some suppliers offer low-cost refrigerators that mimic branded models but infringe on patented designs, control systems, or software. These clones often lack rigorous testing and can have undetected flaws, exposing the buyer to IP litigation and safety risks.
2. Unauthorized Software or Firmware Use
Blood bank refrigerators often include proprietary monitoring software protected by copyright and licensing agreements. Using unlicensed or pirated software—not only violates IP law but may also disable critical updates, security patches, or audit trail functions required for compliance.
3. Inadequate Due Diligence on Supplier IP Rights
Failing to verify that the supplier owns or has proper licensing rights to the technology they sell can result in legal liability. This is especially critical when sourcing from third-party distributors or overseas manufacturers with unclear IP ownership.
4. Lack of Warranty and IP Indemnification
Contracts that do not include IP indemnification clauses leave the buyer vulnerable if the equipment is later found to infringe on third-party patents. Always ensure procurement agreements explicitly state that the supplier assumes liability for IP violations.
5. Ignoring Design and Utility Patents
Key features such as door seals, airflow systems, or alarm logic may be protected by utility or design patents. Using a device that incorporates such protected technology without authorization—even unknowingly—can lead to enforcement actions from patent holders.
Conclusion
To avoid these pitfalls, organizations must implement a rigorous sourcing process that includes technical validation, regulatory verification, and legal review of IP status. Engaging qualified biomedical engineers, legal counsel, and procurement specialists ensures both the quality and IP integrity of blood bank refrigerators.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Blood Bank Refrigerator
Introduction
Blood bank refrigerators are critical components in the safe storage and handling of blood and blood components. Proper logistics and compliance with regulatory standards ensure the integrity, safety, and efficacy of blood products. This guide outlines key logistical considerations and compliance requirements essential for the operation of blood bank refrigerators in healthcare and transfusion settings.
Regulatory Standards and Guidelines
Blood bank refrigerators must comply with national and international regulations to maintain blood product safety. Key standards include:
- FDA 21 CFR Part 606 (Current Good Manufacturing Practice): Governs the storage conditions for blood and blood components in the U.S.
- AABB (Association for the Advancement of Blood & Biotherapies) Standards: Provides detailed requirements for temperature monitoring, equipment validation, and inventory management.
- CAP (College of American Pathologists) Guidelines: Recommends protocols for temperature control and documentation.
- ISBT (International Society of Blood Transfusion): Offers global best practices for blood storage and transportation.
Facilities must adhere to these standards to maintain accreditation and ensure patient safety.
Temperature Requirements
Blood products must be stored within a tightly controlled temperature range to maintain viability:
- Whole Blood and Red Blood Cells: 1°C to 6°C (33.8°F to 42.8°F)
- Platelets: Room temperature (20°C to 24°C) with agitation—stored in specialized platelet incubators, not blood bank refrigerators
- Plasma and Cryoprecipitate: Frozen at ≤ -18°C or colder; stored in dedicated freezers
Blood bank refrigerators must maintain a consistent temperature within the 1°C to 6°C range at all times.
Equipment Specifications
Blood bank refrigerators must meet specific technical and operational criteria:
- Dedicated Use: Used exclusively for blood and blood components; no storage of food, medications, or other lab materials.
- Temperature Monitoring: Equipped with continuous digital data loggers (DDLs) that record temperatures at least every 4 hours.
- Alarms: Audible and visual high/low temperature alarms must be functional and tested regularly.
- Airflow and Design: Designed for uniform temperature distribution with forced air circulation and internal fans.
- Backup Power: Connection to an emergency power supply (e.g., generator or UPS) to maintain temperature during outages.
Installation and Validation
Prior to operation, blood bank refrigerators must undergo:
- Installation Qualification (IQ): Confirming proper setup and location (away from sunlight, heat sources, and high-traffic areas).
- Operational Qualification (OQ): Testing temperature performance across all shelves and door positions.
- Performance Qualification (PQ): Ongoing verification under full-load conditions, including door-opening studies.
Validation must be documented and repeated annually or after major repairs or relocation.
Temperature Monitoring and Documentation
Continuous monitoring and accurate record-keeping are essential:
- Digital Data Loggers (DDLs): Must be calibrated annually and store at least 30 days of data.
- Manual Checks: Temperatures must be checked and recorded at least twice daily (per AABB).
- Alarm Response: Written procedures for responding to temperature excursions, including investigation, documentation, and reporting.
All records must be retained for a minimum of 5 years or per institutional policy.
Inventory Management and Labeling
Efficient logistics include proper inventory controls:
- First-Expired, First-Out (FEFO): Blood units must be rotated to use the nearest expiry dates first.
- Labeling: Each unit must be clearly labeled with blood type, component, collection date, expiry date, and unique identifier.
- Segregation: Group blood components by type and expiration date; separate incompatible types (e.g., Rh-negative from Rh-positive if required).
- Barcoding and Tracking: Use of barcode or RFID systems to track inventory and reduce transfusion errors.
Maintenance and Servicing
Regular maintenance ensures equipment reliability:
- Scheduled Servicing: Biannual preventive maintenance by qualified technicians.
- Cleaning: Interior and exterior cleaned weekly with hospital-grade disinfectants; gaskets and seals inspected for integrity.
- Filter and Coil Maintenance: Condenser coils cleaned quarterly to ensure efficient operation.
- Service Logs: All maintenance, repairs, and calibrations must be documented.
Emergency Preparedness
Contingency plans are required for potential failures:
- Power Outage Response: Include transfer protocols to backup refrigerators or validated coolers with cold packs.
- Temperature Excursion Protocol: Define actions for out-of-range temperatures, including quarantine, assessment of blood unit viability, and reporting to regulatory bodies if necessary.
- Backup Equipment: Availability of secondary blood bank refrigerators or validated transport containers.
Staff Training and Competency
Personnel must be trained on:
- Proper handling and storage procedures
- Temperature monitoring and documentation
- Alarm response and emergency protocols
- Inventory rotation and labeling standards
Competency assessments should be conducted annually or upon role changes.
Audits and Compliance Checks
Regular internal and external audits ensure ongoing compliance:
- Internal Audits: Conducted quarterly to review temperature logs, maintenance records, and staff practices.
- External Inspections: Preparedness for inspections by AABB, CAP, FDA, or other regulatory bodies.
- Corrective Actions: Documented response to audit findings with root cause analysis and preventive measures.
Conclusion
Maintaining a compliant and efficient blood bank refrigerator system is essential for patient safety and regulatory adherence. By following established logistics protocols and compliance standards, healthcare facilities can ensure the integrity of blood products from storage to transfusion. Regular training, documentation, and quality assurance practices are the foundation of a reliable blood bank operation.
Conclusion on Sourcing a Blood Bank Refrigerator
Sourcing a blood bank refrigerator is a critical step in ensuring the safe and effective storage of blood and blood components, which are highly sensitive to temperature fluctuations. After evaluating key factors such as temperature accuracy and stability (typically 2–6°C), compliance with regulatory standards (e.g., AABB, FDA, WHO), alarm systems, redundancy features, energy efficiency, storage capacity, and ease of maintenance, it is evident that selecting a reliable and validated unit is essential for patient safety and regulatory compliance.
Prioritizing refrigerators specifically designed for blood bank use—equipped with digital temperature monitoring, data logging, and remote alarm capabilities—ensures continuous surveillance and minimizes the risk of product spoilage. Additionally, considering vendor reputation, post-purchase service support, warranty, and training enhances long-term operational efficiency.
In conclusion, a well-informed procurement process that balances technical specifications, regulatory requirements, and total cost of ownership will ensure the acquisition of a blood bank refrigerator that supports uninterrupted, safe, and compliant blood storage, ultimately contributing to improved transfusion outcomes and patient care.