The global biofilter market is experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing environmental regulations and the rising demand for sustainable air and water treatment solutions across industrial, municipal, and agricultural sectors. According to Grand View Research, the global bioremediation market—of which biofilters are a critical component—was valued at USD 106.8 billion in 2023 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.4% from 2024 to 2030. This growth is further reinforced by Mordor Intelligence, which highlights a rising adoption of biofiltration technologies in wastewater treatment and odor control, particularly in the food and beverage, pharmaceutical, and chemical industries. As industries prioritize eco-friendly compliance and operational efficiency, the demand for high-performance biofilters continues to surge. In this evolving landscape, a select group of manufacturers have emerged as leaders, combining innovation, scalability, and proven performance. Here are the top 10 biofilter manufacturers shaping the future of biological treatment systems.
Top 10 Bio Filter Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 POLY
Domain Est. 1996
Website: poly-bio-marine.com
Key Highlights: A truly unique product, the “Poly Filter”. It was specifically designed for chemical filtration in the aquarium….
#2 BioFilter Systems
Domain Est. 1997
Website: biofilter.com
Key Highlights: BioFilter Systems has developed the most advanced, yet cost-effective, biofilter technology available today for removing nitrogenous and phosphorus waste from ……
#3
Domain Est. 1998
Website: waterloo-biofilter.com
Key Highlights: A premium manufacturer of advanced onsite sewage systems. Scientifically tested and approved septic systems….
#4 Bioteg Biofilter Systems
Domain Est. 2020
Website: bioteg.us
Key Highlights: Odor Control Made Easy! · Bioteg specializes in the planning, design and manufacturing of biofilters as an odor and air pollution control technology….
#5 BioMicrobics
Domain Est. 1996
Website: biomicrobics.com
Key Highlights: Explore SeptiTech’s cutting-edge residential and commercial trickling filter wastewater treatment systems. Dive into InTank Ballast Water’s ……
#6 Bohn Biofilter
Domain Est. 1998
Website: bohnbiofilter.com
Key Highlights: Bohn Biofilters help eliminate odors and emissions from wastewater treatment plants, landfills, food processors, petroleum facilities….
#7 BIOREM
Domain Est. 2001
Website: biorem.biz
Key Highlights: MYTILUS biotrickling filter systems feature continuous recirculation and efficiently remove compounds such as high levels of H2S or water soluble VOCs….
#8 BioAir
Domain Est. 2008
Website: bioairsolutions.com
Key Highlights: BioAir to solve air pollution and odor problems with a wide range of air treatment equipment and services….
#9 BioFiltro: Worm
Domain Est. 2012
Website: biofiltro.com
Key Highlights: BioFiltro is an international wastewater treatment company with a patented filtration system that naturally removes up to 99% of contaminants in 4 hours….
#10 Our Services for Effective Biofilter Solutions
Website: hartmann-biofilter.de
Key Highlights: Discover Hartmann Biofilter’s innovative services: customized solutions for sustainable wastewater and air purification. Learn more now!…
Expert Sourcing Insights for Bio Filter
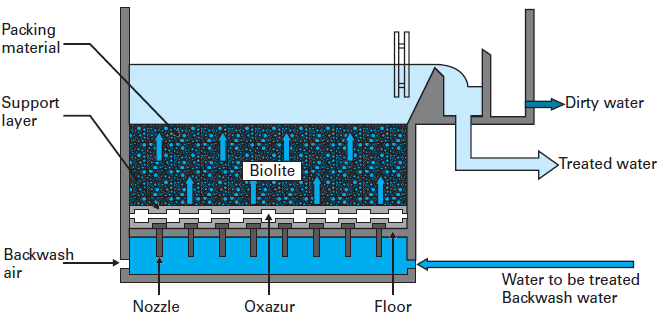
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Bio Filters
The global bio filter market is poised for significant transformation and growth by 2026, driven by increasing environmental regulations, rising industrialization, and growing emphasis on sustainable wastewater and air purification solutions. As governments and industries prioritize eco-friendly technologies, bio filters—utilizing natural microbial processes to remove pollutants—have emerged as a key player in environmental remediation. Below are the major market trends expected to shape the bio filter industry in 2026:
1. Stringent Environmental Regulations Driving Adoption
By 2026, tightening air and water quality regulations across North America, Europe, and parts of Asia-Pacific will continue to accelerate the deployment of bio filtration systems. Regulatory bodies such as the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the European Union’s Industrial Emissions Directive are enforcing lower emission thresholds for volatile organic compounds (VOCs), hydrogen sulfide, and ammonia. This compels industries—including food processing, wastewater treatment, and chemical manufacturing—to adopt bio filters as a compliant and cost-effective solution.
2. Expansion in Municipal and Industrial Wastewater Treatment
The demand for bio filters in municipal wastewater treatment plants is expected to rise significantly by 2026, especially in developing regions grappling with urbanization and water scarcity. Advanced bio filter variants such as Moving Bed Biofilm Reactors (MBBR) and Trickling Filters are being increasingly integrated into treatment processes due to their high efficiency, low energy consumption, and minimal sludge production. Industrial sectors, particularly pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals, are also investing in bio filtration to meet discharge standards.
3. Technological Advancements Enhancing Efficiency
Innovation in bio filter design and microbial media will be a key trend in 2026. Manufacturers are focusing on developing high-surface-area packing materials, such as ceramic and polymeric bio-carriers, that enhance microbial attachment and degradation rates. Integration with IoT sensors and AI-driven monitoring systems allows for real-time performance tracking, predictive maintenance, and optimization of operational parameters, boosting reliability and reducing downtime.
4. Growing Demand in Agriculture and Aquaculture
Bio filters are increasingly being adopted in closed-loop aquaculture systems and agricultural runoff treatment. By 2026, the aquaculture industry—facing pressure to reduce environmental impacts—is turning to bio filtration to manage nitrogenous waste and improve water quality. Similarly, bio filters are being deployed in greenhouse operations and hydroponic farms to treat nutrient-rich effluents sustainably.
5. Shift Toward Modular and Compact Systems
Urban space constraints and the need for decentralized treatment solutions are driving demand for compact, modular bio filter units. These systems offer scalability and ease of installation, making them ideal for small municipalities, remote facilities, and retrofitting existing infrastructure. This trend is particularly strong in Asia-Pacific and Latin America, where rapid urban development demands flexible environmental solutions.
6. Rising Investment in R&D and Public-Private Partnerships
Governments and private entities are increasing funding for bio filtration research, especially in microbial engineering and biofilm optimization. By 2026, collaborative initiatives between academic institutions, technology firms, and environmental agencies are expected to yield next-generation bio filters with enhanced contaminant removal capabilities, including emerging pollutants like microplastics and pharmaceutical residues.
7. Regional Market Growth Dynamics
While North America and Europe remain dominant due to mature regulatory frameworks and high environmental awareness, the Asia-Pacific region is projected to witness the highest growth rate by 2026. Countries like China, India, and South Korea are investing heavily in smart city projects and green infrastructure, creating substantial opportunities for bio filter deployment in both urban and industrial settings.
In conclusion, the 2026 bio filter market will be characterized by regulatory compliance, technological innovation, and expanding applications across diverse sectors. As sustainability becomes a core business imperative, bio filtration technologies are expected to play a pivotal role in achieving global environmental goals, positioning the market for sustained long-term growth.
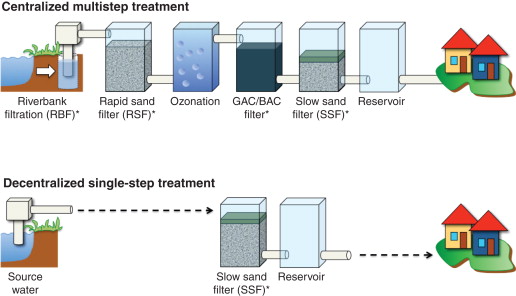
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Bio Filters (Quality, IP)
Sourcing bio filters—especially for sensitive applications like biopharmaceuticals, medical devices, or laboratory processes—requires careful attention to both product quality and intellectual property (IP) considerations. Overlooking these areas can lead to supply chain disruptions, regulatory non-compliance, or legal exposure. Below are key pitfalls to avoid.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Inadequate Filter Certification and Documentation
A common mistake is selecting suppliers who cannot provide full traceability, including lot-specific certificates of analysis (CoA), biocompatibility reports (e.g., USP Class VI), or sterilization validation data. Without proper documentation, compliance with FDA, EMA, or other regulatory bodies becomes difficult.
2. Material Incompatibility
Bio filters must be chemically compatible with the process fluid (e.g., solvents, buffers, APIs). Sourcing filters made from unsuitable materials can lead to leachables, extractables, or premature filter failure, compromising product safety and efficacy.
3. Insufficient Performance Validation
Assuming that all bio filters with similar specifications perform equally is risky. Differences in pore size distribution, protein binding characteristics, or flow rates can impact filtration efficiency. Always require performance data under conditions that mimic your actual use case.
4. Lack of Sterility Assurance
For sterile filtration, it’s critical to source filters from manufacturers with validated sterilization processes (e.g., gamma irradiation) and aseptic packaging. Poor sterility assurance can introduce contamination risks, especially in GMP environments.
5. Poor Supplier Quality Management Systems
Choosing a supplier without robust quality systems (e.g., ISO 13485, ISO 9001, or cGMP compliance) increases the risk of inconsistent product quality and limited responsiveness to deviations or audits.
Intellectual Property-Related Pitfalls
1. Infringement of Patented Filter Technologies
Many advanced bio filters (e.g., those with specific membrane chemistries or pleated designs) are protected by patents. Sourcing from a low-cost vendor may unknowingly involve IP infringement if they replicate patented technologies without licensing, exposing your company to litigation.
2. Unclear IP Ownership in Custom Designs
When co-developing or customizing a bio filter, failure to define IP ownership in the supply agreement can lead to disputes. Without clear contracts, the supplier may retain rights to the design, limiting your ability to switch vendors or scale production.
3. Use of Proprietary Manufacturing Processes
Some suppliers use proprietary methods (e.g., surface treatments, membrane casting) protected by trade secrets or patents. If your application requires specific performance tied to such processes, ensure you have the right to use the filter without violating third-party IP.
4. Inadequate Due Diligence on Supplier IP
Relying solely on a supplier’s claims about IP clearance is risky. Conduct due diligence—request IP freedom-to-operate (FTO) opinions or patent landscape analyses—to confirm that the filter does not infringe on existing patents, particularly in key markets like the US or EU.
5. Risk of Reverse Engineering and Knock-offs
Sourcing from regions with weaker IP enforcement increases the chance of receiving counterfeit or reverse-engineered products. These may appear identical but lack performance consistency or regulatory compliance, jeopardizing quality and safety.
Mitigation Strategies
- Verify Certifications: Require full regulatory documentation and audit supplier quality systems.
- Test Performance In-House: Conduct pilot testing under real-world conditions.
- Review Contracts: Include clear IP clauses, especially for custom solutions.
- Conduct IP Screening: Work with legal or IP experts to assess freedom-to-operate.
- Choose Reputable Suppliers: Prioritize vendors with proven track records and transparent IP practices.
Avoiding these pitfalls ensures reliable, compliant, and legally sound sourcing of bio filters critical to your operations.
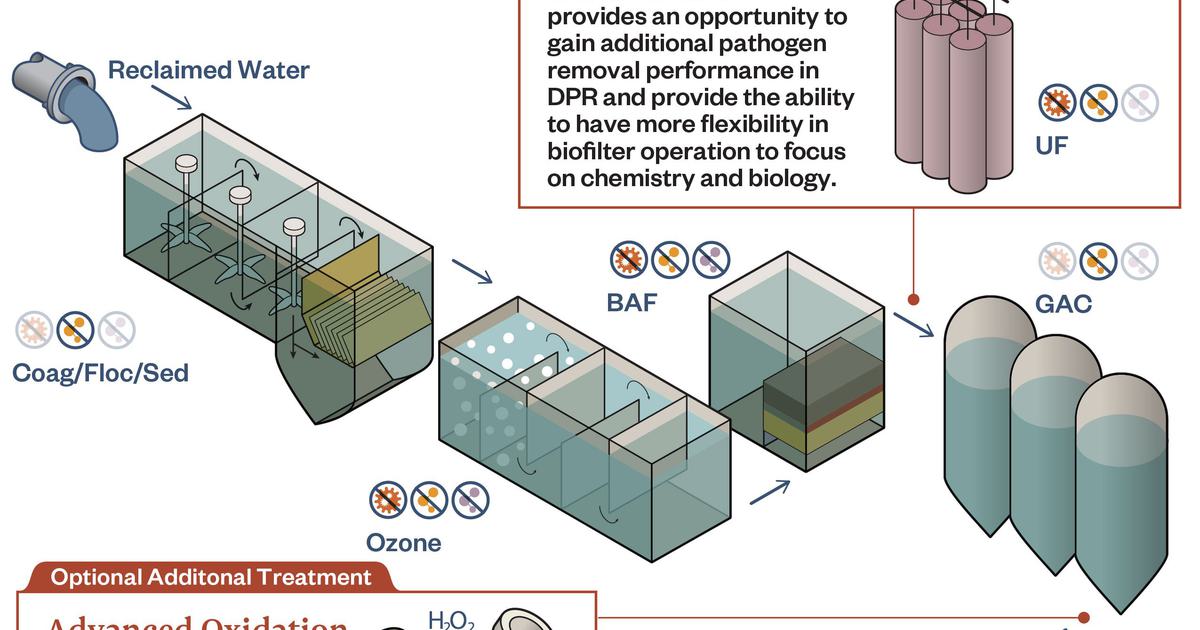
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Bio Filter
This guide outlines the key logistics considerations and regulatory compliance requirements for the transportation, handling, storage, and use of bio filters. Adhering to these guidelines ensures product integrity, environmental safety, and legal compliance.
Product Overview and Classification
Bio filters are engineered biological treatment systems used to remove contaminants from air or water streams. They typically contain living microorganisms immobilized on a support medium. Depending on design and application, bio filters may be classified as industrial equipment, environmental technology, or biological agents, impacting regulatory handling.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Bio filters must comply with environmental, health, safety, and import/export regulations depending on jurisdiction and application. Key regulatory areas include:
– Environmental Protection Regulations: Compliance with local and international standards (e.g., EPA in the U.S., REACH in the EU) for emissions control and biological treatment systems.
– Biological Safety Standards: If the bio filter contains non-native or genetically modified organisms, adherence to biosafety protocols (e.g., NIH Guidelines, EU Directive 2009/41/EC) is required.
– Waste Disposal Laws: End-of-life bio filter media may be classified as biological waste and must be disposed of according to hazardous or non-hazardous waste regulations.
– Customs and Import Controls: International shipments may require permits for biological materials (e.g., APHIS in the U.S., CITES if organic components are involved).
Packaging and Handling Procedures
Proper packaging ensures the bio filter remains functional and contained during transit:
– Use sealed, durable containers to prevent leakage of biological media.
– Label packages with biohazard symbols if live cultures are present.
– Include temperature control (e.g., insulated packaging, cold chain logistics) if microbial viability depends on stable conditions.
– Handle with care to avoid damage to support media or housing structure.
Transportation Guidelines
Transport bio filters according to applicable regulations for biological materials and industrial equipment:
– Domestic Shipments: Follow DOT (U.S.) or ADR (EU) regulations for biological substances when applicable.
– International Shipments: Comply with IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations if shipping live organisms; complete required documentation (e.g., Shipper’s Declaration for Dangerous Goods).
– Cold Chain Management: Monitor and record temperature during transit if required for microbial stability.
– Use carriers experienced in handling sensitive biological or environmental equipment.
Storage Conditions
Store bio filters in a controlled environment to maintain microbial activity and structural integrity:
– Temperature: Maintain between 4°C and 25°C unless specified otherwise by manufacturer.
– Humidity: Store in a dry, ventilated area to prevent mold or degradation of media.
– Light: Avoid direct sunlight to prevent overheating and microbial stress.
– Shelf Life: Adhere to manufacturer-recommended shelf life; inspect before deployment.
Installation and Operational Compliance
Ensure proper installation and operation to meet environmental performance standards:
– Follow manufacturer guidelines for acclimatization of microbial cultures.
– Monitor system performance (e.g., contaminant removal efficiency) and maintain records.
– Conduct regular maintenance to prevent clogging or microbial die-off.
– Report any system failures or unintended releases to relevant authorities if required.
Decommissioning and Disposal
At end-of-life, bio filters must be decommissioned safely:
– Deactivate biological components if necessary (e.g., heat treatment, biocides).
– Dispose of filter media according to local waste regulations; classify as biological waste if applicable.
– Recycle housing or structural components where possible.
– Document disposal procedures for audit and compliance purposes.
Documentation and Recordkeeping
Maintain comprehensive records to demonstrate compliance:
– Product specifications and safety data sheets (SDS)
– Shipping manifests and customs documentation
– Installation, maintenance, and performance logs
– Waste disposal certificates
– Regulatory permits and approvals
Adherence to this guide ensures safe, legal, and efficient lifecycle management of bio filter systems. Always consult local authorities and the manufacturer for application-specific requirements.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Biofilter:
Sourcing a biofilter requires a comprehensive evaluation of technical specifications, operational requirements, site conditions, and long-term maintenance needs. It is essential to select a system that aligns with the specific pollutants to be treated, required air flow rates, and regulatory compliance standards. Engaging with experienced suppliers, conducting thorough performance assessments, and considering lifecycle costs—including installation, energy consumption, and media replacement—will ensure optimal efficiency and reliability. Ultimately, investing in a well-designed, properly sized, and adequately supported biofiltration system contributes to sustainable air quality management and environmental responsibility.