The global haunted attractions market, including specialty manufacturers of immersive horror experiences like Bhoot Jhalokia setups, is witnessing robust growth driven by rising consumer demand for experiential entertainment. According to Grand View Research, the global haunted house market was valued at USD 542.3 million in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.7% from 2023 to 2030. This surge is fueled by increasing urbanization, the popularity of seasonal events such as Halloween, and the growing integration of advanced technologies like animatronics, augmented reality, and AI-driven special effects in Indian and international horror attractions. As demand climbs, a niche ecosystem of specialized Bhoot Jhalokia manufacturers has emerged, particularly in India, catering to regional festivals, theme parks, and pop-up haunted experiences. These manufacturers combine cultural storytelling with cutting-edge engineering to deliver spine-chilling realism. Based on market presence, innovation, and customer reach, here are the top 6 Bhoot Jhalokia manufacturers shaping the future of fear-based entertainment in South Asia.
Top 6 Bhoot Jhalokia Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
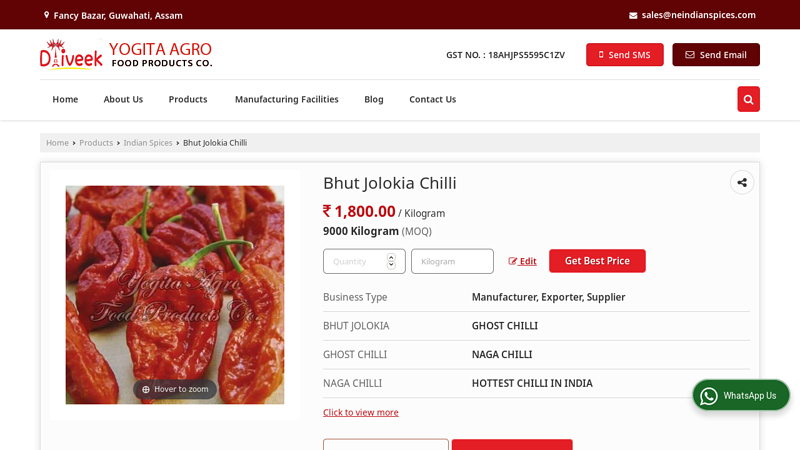
#1 Bhut Jolokia Chilli
Domain Est. 2014
Website: neindianspices.com
Key Highlights: We are the noted Manufacturer, Exporter and Supplier of high quality Bhut Jolokia Chilli cultivated using organic means. It is used in both fresh and dried ……
#2 Mango Bhoot Jolokia
Domain Est. 2019
Website: kazeliving.com
Key Highlights: 1-day returnsMango Bhoot Jolokia … Super versatile sauces that add a punch of flavour to indian and western cuisines. MRP Rs. 249.Missing: jhalokia manufacturer…
#3 Bhut Jolokia (Ghost Pepper) Manufacturer & Wholesaler In India
Domain Est. 2021
Website: agroyardz.com
Key Highlights: We are a leading ghost pepper manufacturer and supplier in India at wholesale pricing. We supply pan India and export to several countries….
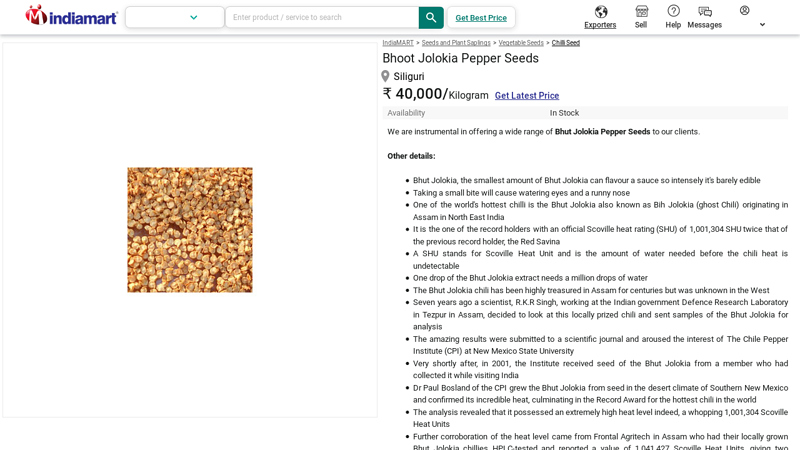
#4 Bhoot Jolokia Pepper Seeds
Domain Est. 1996
Website: indiamart.com
Key Highlights: Maa Impex – Offering Bhoot Jolokia Pepper Seeds,Arunim Chilli Seeds in Siliguri, West Bengal. Also get Chilli Seed price list from verified companies | ID: ……
#5 KING CHILLI
Domain Est. 2005
Website: momamanipur.mn.gov.in
Key Highlights: King Chilli also known as ghost pepper, ghost chilli, naga jolokia and bhoot jolokia is among one of the hottest chilli in the world….
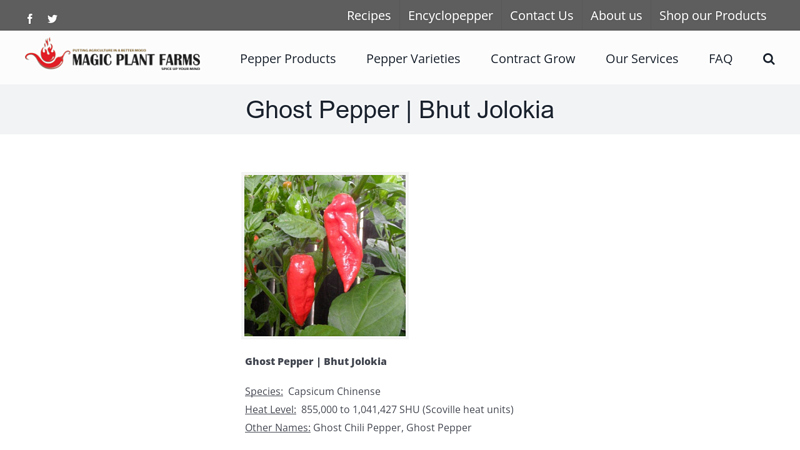
#6 Bhut Jolokia Ghost Pepper
Domain Est. 2014
Website: magicplantfarms.com
Key Highlights: The Bhut Jolokia or Ghost Chili, named for its ghostly bite, is the hottest chili pepper in the world. Also known as the Naga Jolokia and Bih Jolokia, or ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Bhoot Jhalokia

H2: Market Trends Analysis for Bhoot Jhalokia in 2026
As of 2026, Bhoot Jhalokia—commonly known as the Bhoot Jalokia or Ghost Chili—continues to demonstrate a distinctive trajectory in both domestic and international markets, driven by evolving consumer preferences, agricultural innovation, and heightened global interest in ultra-spicy food experiences.
-
Increased Global Demand for Specialty Chilies
The Bhoot Jhalokia, once primarily cultivated in Northeast India (particularly in Assam, Nagaland, and Manipur), has seen expanded cultivation and export demand. In 2026, gourmet food markets in North America, Europe, and Southeast Asia are increasingly incorporating Bhoot Jhalokia into specialty sauces, spice blends, and culinary challenges. This surge is partly fueled by the rising popularity of extreme heat food trends and social media-driven “chili challenges.” -
Commercialization and Value-Added Products
A key trend in 2026 is the shift from raw chili sales to value-added products. Local cooperatives and agri-startups in India are producing Bhoot Jhalokia-infused oils, dried powders, ready-to-eat spicy snacks, and even medicinal balms (leveraging capsaicin’s analgesic properties). These products command premium pricing, improving farmer incomes and enabling brand differentiation in export markets. -
Sustainable and Organic Farming Practices
With growing consumer awareness around sustainability, many Bhoot Jhalokia farmers have adopted organic farming methods. Certification programs supported by state governments and NGOs are helping smallholders access premium export channels. In 2026, certified organic Bhoot Jhalokia is gaining traction in eco-conscious markets, particularly in the EU and Canada. -
Climate-Resilient Cultivation Techniques
Climate variability has impacted traditional chili yields, prompting investment in greenhouse farming and micro-irrigation systems. In 2026, several pilot projects using IoT-enabled monitoring and drought-resistant variants of Bhoot Jhalokia are showing promising results, improving yield consistency and quality. -
Regulatory and Safety Considerations
Due to its extreme Scoville rating (often exceeding 1 million SHU), regulatory scrutiny on labeling and consumer safety has increased. In 2026, export markets require clear heat warnings and child-resistant packaging for Bhoot Jhalokia products, influencing packaging design and marketing strategies. -
Cultural and Tourism Integration
The chili has become a cultural symbol in Northeast India. In 2026, “spice tourism” is on the rise, with festivals like the “Bhoot Jalokia Festival” in Nagaland attracting international visitors, food bloggers, and culinary investors, further boosting regional visibility and economic opportunities. -
Competition from Other Super-Hot Varieties
While Bhoot Jhalokia remains iconic, it faces competition from newer super-hot chilies like the Carolina Reaper and Pepper X. However, its unique smoky, fruity flavor profile and geographical indication (GI) tag help maintain its niche in gourmet and artisanal segments.
Conclusion
By 2026, the Bhoot Jhalokia market is transitioning from a regional agricultural product to a globally recognized specialty spice. Strategic branding, value addition, and sustainable practices are key drivers of growth. With continued support for farmers, innovation in product development, and targeted international marketing, Bhoot Jhalokia is poised for sustained market expansion in the coming years.
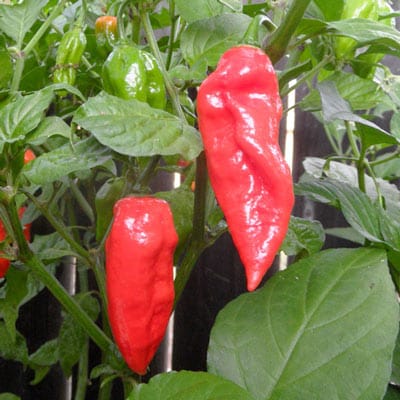

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Bhoot Jhalokia (Quality, IP)
Sourcing Bhoot Jhalokia—also known as Ghost Pepper or Bhut Jolokia—can present significant challenges, especially when quality consistency and intellectual property (IP) considerations are involved. Being aware of these pitfalls is crucial for importers, food manufacturers, and agricultural businesses.
Inconsistent Quality and Purity
One of the most prevalent issues in sourcing Bhoot Jhalokia is variability in quality. Peppers may differ in heat level (Scoville rating), moisture content, color, and size due to differences in cultivation practices, soil conditions, and post-harvest handling. Adulteration with other chili varieties or improper drying techniques can further degrade product integrity, leading to unreliable performance in food products or extracts.
Lack of Standardized Certification
There is often a lack of standardized certification for authentic Bhoot Jhalokia, particularly from smallholder farmers or informal supply chains. Without proper third-party testing or geographical indication (GI) certification, buyers risk purchasing mislabeled or substandard products. This undermines brand credibility and can lead to customer dissatisfaction.
Intellectual Property and Geographical Indication (GI) Risks
Bhoot Jhalokia holds a registered Geographical Indication tag in India, specifically associated with the northeastern states of Assam, Nagaland, and Manipur. Sourcing from outside these regions—or from suppliers falsely claiming GI authenticity—can lead to legal and reputational risks. Unauthorized use of the Bhoot Jhalokia name or branding may infringe on GI rights, exposing businesses to potential litigation or trade barriers.
Supply Chain Transparency Issues
Opaque supply chains make it difficult to trace the origin of the peppers. Intermediaries may mix GI-protected produce with non-certified chilies, diluting authenticity. Without traceability systems, verifying claims about origin, cultivation methods, or fair trade practices becomes nearly impossible.
Counterfeit and Mislabeling
Due to its high demand and premium pricing, Bhoot Jhalokia is frequently counterfeited. Inferior or less pungent chili varieties are often sold under the Ghost Pepper name. This not only affects product performance but also erodes consumer trust and could lead to regulatory non-compliance in export markets.
Inadequate Handling and Storage
Poor post-harvest practices, such as improper drying, storage in humid conditions, or lack of pest control, can result in mold, aflatoxin contamination, or loss of capsaicin content. These factors compromise both safety and efficacy, especially for use in pharmaceuticals or high-end culinary applications.
Conclusion
To mitigate these risks, buyers should partner with certified suppliers, demand verifiable documentation (e.g., GI tags, lab test reports), and invest in supply chain transparency. Conducting due diligence on IP rights and ensuring compliance with regional protections will safeguard both product quality and legal integrity.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Bhoot Jhalokia
Note: As of current geographical and political knowledge, “Bhoot Jhalokia” does not correspond to any recognized country, region, or jurisdiction. It may be a fictional, mythical, or misspelled location. The following guide is therefore a hypothetical framework designed for a fictional or illustrative purpose. If you intended a real location (e.g., a region in India, Nepal, or Bhutan), please clarify for accurate guidance.
Overview of the Region
Bhoot Jhalokia is portrayed as a remote, mountainous region with limited infrastructure and a mystical cultural heritage. Logistics operations must account for difficult terrain, seasonal weather disruptions, and unique local customs. Regulatory frameworks are presumed to be community-based with spiritual oversight, blending traditional practices with emerging national compliance standards.
Transportation & Infrastructure
Road networks are narrow and unpaved, suitable only for 4×4 vehicles and pack animals during monsoon and winter months. Air transport via small charter helicopters is available for urgent shipments. No rail connectivity exists. All vehicles must obtain a “Spirit Passage Permit” from the Council of Elders before entering sacred valleys.
Import & Export Regulations
All goods entering Bhoot Jhalokia require clearance through the Border Shrine of Acceptance. Prohibited items include synthetic plastics, loud machinery, and materials deemed spiritually disruptive (e.g., artificial colors, electronic toys). Export of cultural artifacts, medicinal herbs, and ritual objects requires certification from the Temple Compliance Office.
Customs Procedures
Customs inspections are conducted by designated Shamans who assess both physical contents and “energetic resonance” of shipments. A ritual cleansing fee (in local currency or barter goods) applies. Documentation must include a handwritten Manifest of Intent signed by the sender and blessed by a local priest.
Regulatory Compliance
Businesses operating in Bhoot Jhalokia must adhere to the Code of Harmonious Trade, which emphasizes environmental balance, community benefit, and respect for ancestral traditions. Enterprises must appoint a Local Spirit Liaison and conduct quarterly harmony audits. Violations may result in trade bans or mandatory purification ceremonies.
Labor & Safety Standards
Workers must undergo spiritual orientation and wear protective amulets provided by the Labor Guardian. Overtime is limited during lunar eclipses. Safety protocols include daily chanting sessions and avoidance of red-colored packaging, believed to attract mischievous spirits.
Environmental & Cultural Preservation
All packaging must be biodegradable or reusable. Plastic, Styrofoam, and non-native materials are banned. Logistics hubs must be camouflaged into the landscape and located away from sacred groves. Noise pollution is regulated under the Silence Ordinance, enforced after sunset.
Emergency & Risk Management
Due to frequent fog and spectral activity, GPS systems are unreliable. All transport teams must include a guide familiar with spirit paths. Emergency supply caches are maintained at temple outposts. In case of possession or supernatural delay, notify the Regional Exorcist Office immediately.
Conclusion
Operating in Bhoot Jhalokia demands more than logistical planning—it requires cultural sensitivity, spiritual awareness, and adaptive compliance. Success hinges on collaboration with local custodians and adherence to both visible and invisible laws. Always consult the current Moon Calendar and seek blessing before shipment.
Conclusion on Sourcing Bhoot Jhalokia (Ghost Chili)
Sourcing Bhoot Jhalokia, one of the world’s hottest chili peppers, requires careful consideration of origin, quality, safety, and sustainability. Indigenous to Northeast India—particularly Assam, Nagaland, and Manipur—the most authentic and potent Bhoot Jhalokia is traditionally cultivated by local farmers using indigenous methods. To ensure authenticity and superior quality, sourcing directly from certified organic farms or cooperatives in the region is recommended, with proper verification through GI (Geographical Indication) tags, which protect the identity and origin of this unique chili.
Buyers should prioritize suppliers who adhere to ethical farming practices, fair trade principles, and safe post-harvest handling to preserve the chili’s heat (measured in Scoville Heat Units) and flavor profile. Due to its extreme pungency, proper labeling, handling protocols, and safety certifications are essential when sourcing for commercial use in food, pharmaceutical, or defense applications.
In conclusion, sustainable and responsible sourcing of Bhoot Jhalokia not only supports local communities and preserves traditional agricultural knowledge but also ensures the delivery of a premium, authentic product to global markets. Building long-term partnerships with regional producers, investing in traceability systems, and promoting value-added processing locally can further enhance economic and social benefits while meeting growing international demand.