The global market for laser metal deposition (LMD) systems, particularly within the aviation sector, has seen robust expansion driven by the increasing demand for high-precision, cost-effective component repair and additive manufacturing solutions. According to Grand View Research, the global laser metal deposition market size was valued at USD 368.9 million in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 11.6% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by the aviation industry’s relentless pursuit of lightweight, high-performance materials and sustainable manufacturing practices. As aircraft operators and OEMs strive to extend the life of critical components such as turbine blades, landing gear, and engine parts, LMD has emerged as a key enabling technology due to its ability to deposit corrosion- and wear-resistant alloys with minimal heat input and waste. With metal additive manufacturing gaining regulatory acceptance and standardization—particularly through initiatives by bodies like SAE International—the integration of advanced laser systems into aviation production and MRO (Maintenance, Repair, and Overhaul) workflows has accelerated. In this competitive landscape, selecting the right laser system is critical: performance metrics such as deposition rate, precision, process control, and compatibility with aerospace-grade materials like Inconel, titanium, and cobalt-chrome are non-negotiable. Based on technical specifications, industry adoption, and real-world performance in certified aerospace environments, the following list highlights the top 10 laser systems currently leading innovation in metal deposition for aviation manufacturers.
Top 10 Best Laser Systems For Metal Deposition In Aviation Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Industrial Diode Laser Manufacturer
Website: laserline.com
Key Highlights: Laserline is a leading laser manufacturer in the development of custom-specific high-power lasers, with 400+ staff & in 9 nations….
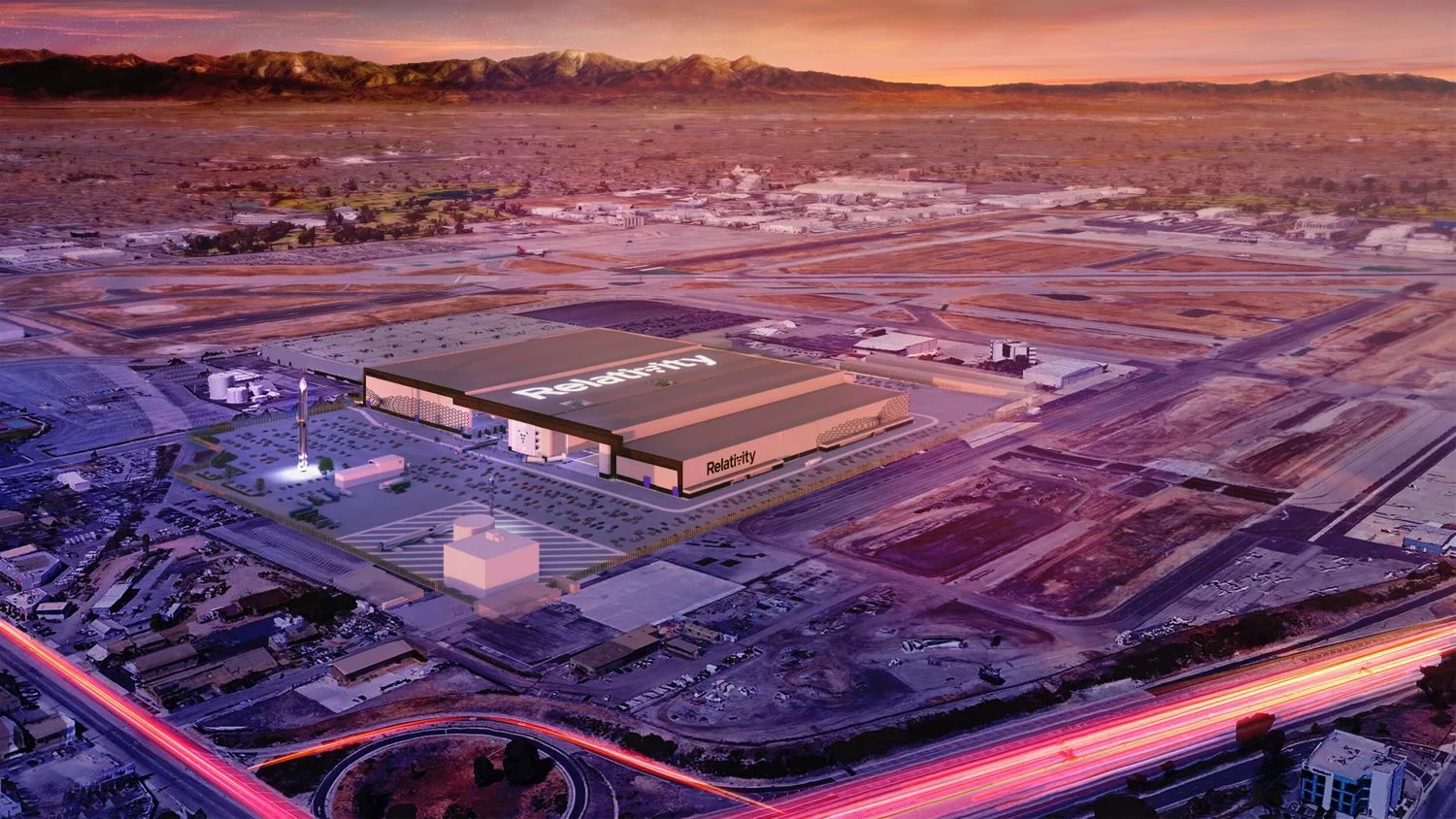
#2 Relativity Space
Website: relativityspace.com
Key Highlights: Born from Relativity’s breakthroughs in large-scale additive manufacturing, Horizon is focused on advancing the technology for aerospace, defense, and beyond….
#3 Lincoln Electric Additive Solutions
Website: lincolnelectric.com
Key Highlights: Robotic Laser Systems Laser-Pak® robotic laser systems are ideal for laser welding, cladding, feature building, joining, brazing, and additive manufacturing ……
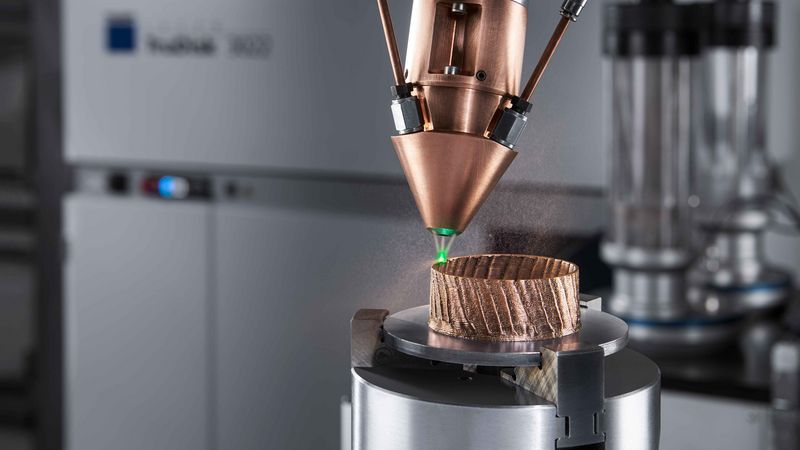
#4 Laser Metal Deposition
Website: trumpf.com
Key Highlights: Laser metal deposition is an additive manufacturing method for metals and metal-ceramic compounds. It can be used to generate or modify 3D geometries….
#5 NXG XII 600: Next
Website: nikon-slm-solutions.com
Key Highlights: With speeds 20 times faster than standard single laser systems, the NXG is meticulously crafted for serial production, revolutionizing manufacturing timelines ……
#6 Precision Laser Welders for Aerospace Manufacturing
Website: denaliweld.com
Key Highlights: Discover Denaliweld’s advanced laser welders for the aerospace industry. Achieve superior joining for critical flight components, exotic alloys, ……
#7 LAI International
Website: laico.com
Key Highlights: Direct Metal Deposition (DMD); Electron Beam Melting (EBM); Laser Powder Bed Fusion. Certified Special Processes. Assembly/Die cutting; Laser heat treating and ……
#8 KLA
Website: kla.com
Key Highlights: KLA is a leader in process control using advanced inspection tools, metrology systems, and computational analytics. Keep Looking Ahead….
#9 Best Metal Additive Manufacturing Solutions
Website: dm3dtech.com
Key Highlights: With over 25 operating DM3D systems deployed across 4 continents, we offer our customers 20+ years of tried and tested metal additive manufacturing solutions….
#10 Best Laser Systems for Aviation Metal Deposition?
Website: formalloy.com
Key Highlights: The best laser systems for metal deposition aren’t just advanced—they’re exact. Powder-fed systems give fine control. Wire-fed systems bring ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Best Laser Systems For Metal Deposition In Aviation
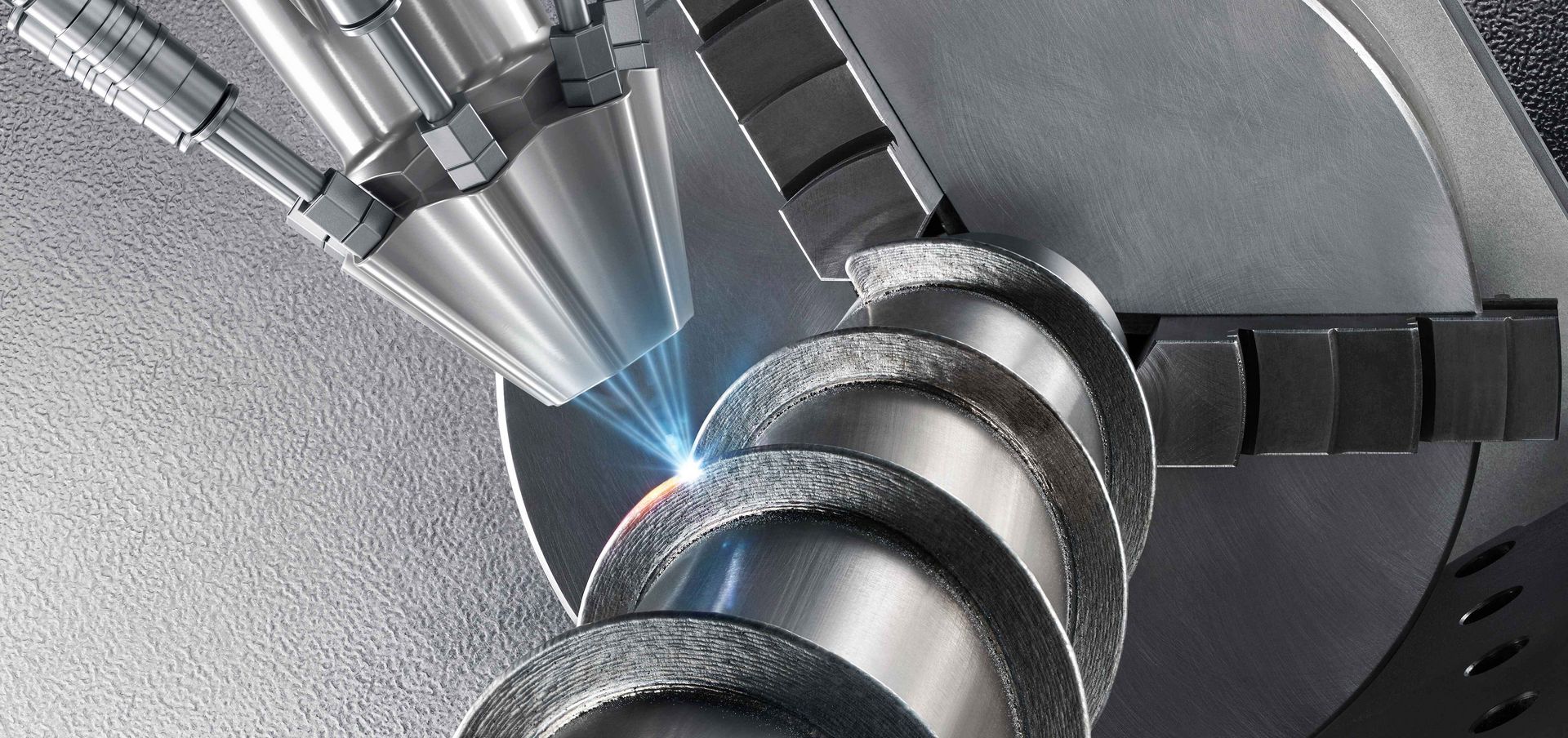

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Best Laser Systems for Metal Deposition in Aviation
As the aviation industry continues to prioritize lightweight, high-strength components and sustainable manufacturing practices, laser-based metal deposition technologies are poised to play a transformative role by 2026. Laser Metal Deposition (LMD), also known as Directed Energy Deposition (DED) using lasers, is gaining momentum as a key enabler of advanced component repair, rapid prototyping, and the production of complex aerospace-grade parts. The following analysis outlines the dominant market trends shaping the landscape for the best laser systems for metal deposition in aviation through 2026.
-
Increased Adoption of Hybrid Manufacturing Systems
By 2026, hybrid additive-subtractive laser systems are expected to dominate aerospace manufacturing floors. These systems integrate laser metal deposition with CNC machining in a single platform, enabling near-net-shape part building followed by precision finishing. This trend improves dimensional accuracy, reduces post-processing, and enhances part integrity—critical for aviation safety standards. Leading OEMs like Siemens and DMG MORI are already deploying such systems, signaling broader industry adoption. -
Growth in Engine and Turbine Component Repair
LMD is becoming the preferred method for repairing high-value components such as turbine blades, compressor vanes, and shafts. The ability to selectively deposit superalloys like Inconel 718 and Ti-6Al-4V with minimal heat-affected zones reduces material waste and extends component life. Airlines and MRO (Maintenance, Repair, and Overhaul) providers are investing heavily in LMD systems to cut costs and turnaround times, driving demand for high-precision, fiber-laser-based deposition systems. -
Advancements in High-Power, Multi-Laser Systems
To meet production demands, the market is shifting toward multi-laser heads and high-power (1–4 kW) fiber lasers that enable faster deposition rates and improved process efficiency. Systems with real-time monitoring and closed-loop control, such as those developed by Optomec and Trumpf, offer enhanced consistency in bead geometry and microstructure. These capabilities are crucial for certifying parts under stringent aviation regulations like FAA and EASA standards. -
Integration of AI and In-Process Monitoring
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are being embedded into LMD systems to predict defects, control thermal profiles, and optimize scan strategies. In 2026, the best laser deposition systems will feature integrated sensors (e.g., pyrometers, high-speed cameras) and AI-driven analytics for real-time quality assurance. This advancement supports the Industry 4.0 vision and accelerates certification of additively manufactured parts. -
Focus on Sustainable and On-Demand Manufacturing
With sustainability goals intensifying, aviation manufacturers are turning to LMD for its material efficiency and reduced scrap rates. Additionally, the ability to produce spare parts on-demand—especially for legacy aircraft—reduces inventory costs and supply chain vulnerabilities. This trend favors modular, scalable laser deposition systems that can be deployed across global maintenance hubs. -
Regulatory Push and Standardization
By 2026, regulatory bodies are expected to finalize standards for additively manufactured flight-critical components, facilitating wider acceptance of LMD parts. Organizations like SAE International and ASTM are developing specifications for process validation and material traceability, encouraging OEMs to adopt certified laser deposition systems. -
Geographic Expansion and Strategic Partnerships
North America and Europe remain leaders in LMD adoption, but Asia-Pacific, particularly China and India, is rapidly investing in laser deposition for indigenous aerospace programs. Strategic collaborations between laser system providers (e.g., Nikon SLM, GE Additive) and aviation giants (e.g., Boeing, Airbus) are accelerating technology deployment and customization for aviation-specific needs.
Conclusion:
In 2026, the best laser systems for metal deposition in aviation will be characterized by high precision, multi-laser configurations, intelligent process control, and seamless integration into digital manufacturing ecosystems. As the aviation sector embraces additive technologies to enhance performance and sustainability, LMD systems will become indispensable tools—driving innovation, reducing lifecycle costs, and supporting the next generation of air travel.
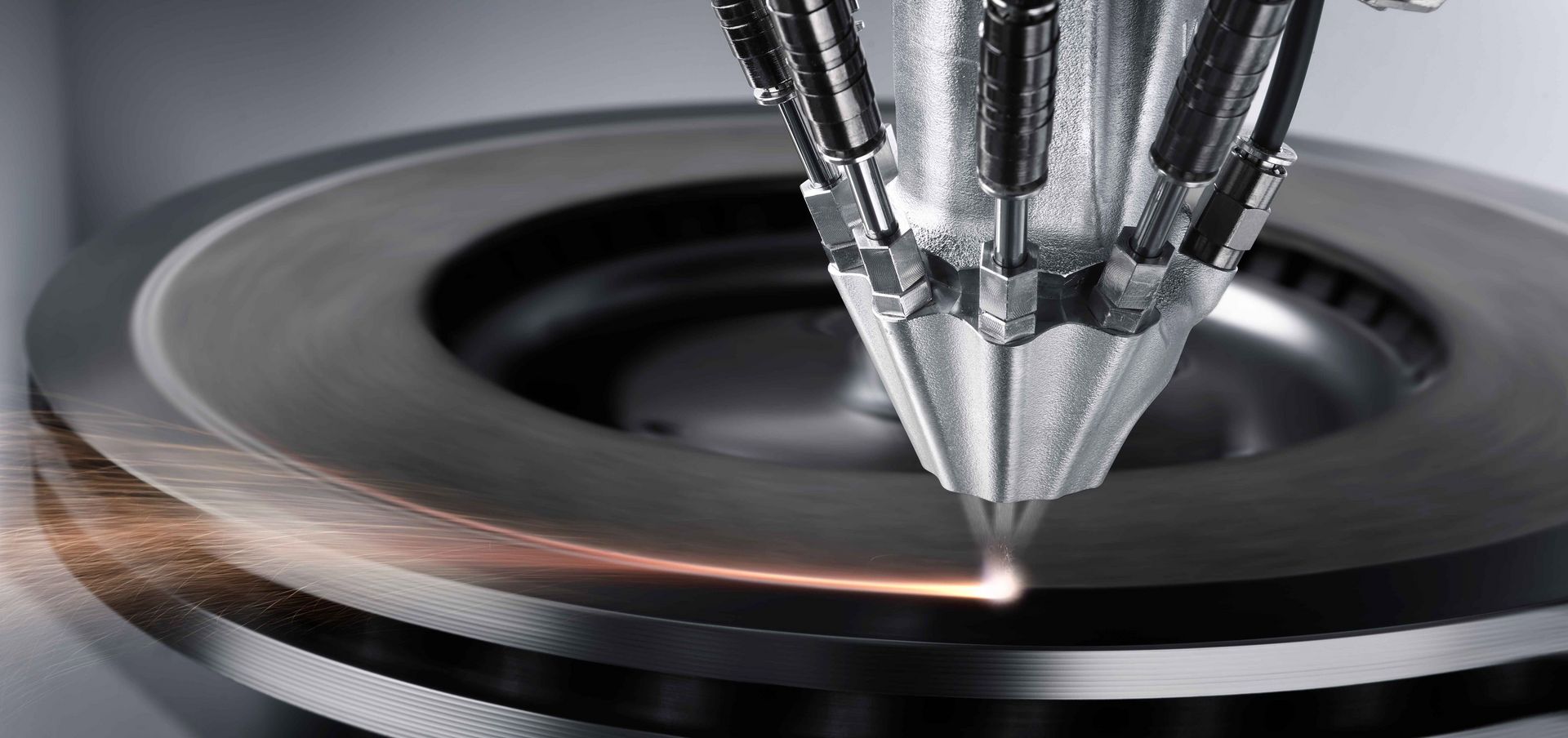

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Best Laser Systems for Metal Deposition in Aviation (Quality, IP)
Sourcing laser systems for metal deposition—such as Laser Metal Deposition (LMD) or Directed Energy Deposition (DED)—in the highly regulated aviation sector requires meticulous attention to both quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking key pitfalls can lead to project delays, compliance failures, or legal exposure. Below are critical areas to evaluate:
1. Underestimating Process Qualification and Certification Requirements
Aviation components must meet stringent standards such as AS9100, NADCAP, and OEM-specific process approvals. A common mistake is selecting a laser system based solely on technical specifications without verifying its suitability for certification.
- Pitfall: Assuming that high-power or high-precision lasers automatically comply with aerospace quality standards.
- Risk: Inability to qualify the deposition process for flight-critical parts, leading to non-compliance and costly rework.
- Best Practice: Validate that the laser system enables consistent, traceable, and repeatable results suitable for qualification under AMS standards (e.g., AMS7008). Ensure the supplier provides full documentation for process mapping, parameter control, and monitoring systems (e.g., melt pool monitoring, closed-loop feedback).
2. Inadequate Control Over Process Parameters and Data Integrity
Consistent quality in metal deposition depends on precise control over laser power, beam focus, scanning speed, shielding gas, and powder feed. Poor data management can compromise both quality and IP.
- Pitfall: Using systems with proprietary software that restrict access to real-time process data or limit customization of control algorithms.
- Risk: Inability to fully optimize the process or defend process IP during audits or disputes; reduced transparency affects repeatability and quality control.
- Best Practice: Source systems offering open or semi-open architecture with secure, auditable data logging. Ensure full access to raw sensor data and parameter logs to support First Article Inspection (FAI) and Production Part Approval Process (PPAP).
3. Overlooking Intellectual Property Ownership and Licensing
Laser deposition systems often come with embedded software, pre-defined processing strategies, or patented methodologies. Failing to clarify IP rights can restrict your freedom to operate or scale production.
- Pitfall: Assuming that purchasing a machine grants full IP rights to developed processes or deposited geometries.
- Risk: Legal disputes over ownership of process parameters, build files, or innovations derived from using the system; limitations on transferring processes to other equipment.
- Best Practice: Negotiate clear IP clauses in procurement contracts. Ensure ownership of process-specific developments and verify that the supplier’s technology does not impose royalties or usage restrictions on end products.
4. Neglecting Supplier Support and Technology Lock-In
Some laser system providers use closed ecosystems, making it difficult to switch powders, integrate third-party sensors, or modify software.
- Pitfall: Choosing a system based on upfront cost without assessing long-term support, upgrade paths, or interoperability.
- Risk: Vendor lock-in, rising maintenance costs, and inability to adapt to evolving aviation requirements or material innovations.
- Best Practice: Evaluate the supplier’s commitment to open standards, availability of SDKs (Software Development Kits), and track record in aerospace applications. Prefer modular systems that support multiple materials and future-proofing.
5. Insufficient Focus on Reproducibility and In-Process Monitoring
Aviation demands zero-defect manufacturing. Systems without robust in-situ monitoring increase the risk of undetected defects such as porosity, lack of fusion, or residual stress.
- Pitfall: Relying on post-process inspection alone, rather than real-time quality assurance.
- Risk: Late-stage rejection of expensive components, delayed certification, and potential safety issues.
- Best Practice: Source laser systems integrated with in-process monitoring (e.g., thermal imaging, coaxial cameras, acoustic sensors) and AI-driven anomaly detection. Ensure these systems are calibrated and validated for aerospace-grade materials like Ti-6Al-4V, Inconel 718, or nickel-based superalloys.
6. Overlooking Cybersecurity and Data Protection
Modern laser systems are connected and generate sensitive operational and IP-rich data. Inadequate cybersecurity exposes both quality data and proprietary processes.
- Pitfall: Connecting deposition systems to enterprise networks without assessing vulnerabilities in control software or data transmission.
- Risk: Data breaches, IP theft, or unauthorized access to process recipes used in certified aviation components.
- Best Practice: Ensure systems comply with ITAR/EAR (if applicable), use encrypted data storage, and offer role-based access control. Verify the supplier’s cybersecurity certifications and patch management policies.
By proactively addressing these pitfalls, aviation manufacturers can select laser deposition systems that not only meet technical performance criteria but also align with the industry’s uncompromising demands for quality, traceability, and IP security.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Best Laser Systems for Metal Deposition in Aviation
System Selection and Vendor Due Diligence
When selecting laser systems for metal deposition in aviation—specific as Laser Metal Deposition (LMD) or Directed Energy Deposition (DED)—it is essential to evaluate vendors not only on technical capabilities but also on compliance and logistical support. Prioritize suppliers with a proven track record in aerospace applications, ISO 9001 and AS9100 certification, and adherence to NADCAP (National Aerospace and Defense Contractors Accreditation Program) standards. Ensure documentation packages include full traceability of components, laser source calibration records, and compliance with ITAR/EAR if applicable. Conduct on-site audits of manufacturing and integration facilities to verify quality control systems and supply chain integrity.
Import/Export Regulations and International Shipments
Laser systems and associated components (e.g., high-power fiber lasers, optical sensors) may be subject to export controls under the International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR) or the Export Administration Regulations (EAR), particularly when destined for non-allied countries. Classify the laser system using the U.S. Munitions List (USML) or Commerce Control List (CCL) to determine licensing requirements. For international deployments, coordinate with legal and compliance teams to secure necessary export licenses and ensure end-user undertakings. Maintain detailed shipping records, including technical specifications, end-use statements, and end-user certificates, to comply with customs and regulatory authorities.
Transportation and Handling Protocols
Laser metal deposition systems are sensitive precision equipment requiring specialized handling during transit. Use climate-controlled, shock-monitored freight services with anti-vibration packaging. Clearly label crates with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Laser Equipment – No X-ray” warnings. Coordinate with certified logistics providers experienced in high-value aerospace machinery to minimize handling risks. For air freight, ensure compliance with IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations, especially if the system includes rechargeable lithium-ion batteries or gas cylinders (e.g., shielding gas supplies). Plan for customs clearance delays by pre-submitting technical documentation and import declarations.
Installation, Calibration, and Regulatory Compliance
Upon delivery, installation must be conducted by OEM-certified technicians in an environment meeting cleanliness (ISO Class 7 or better), EMI shielding, and temperature/humidity control standards. Perform on-site performance verification and laser safety assessments per ANSI Z136.1 and IEC 60825-1. Document all calibration procedures, beam alignment checks, and safety interlock validations. Integrate the system into the facility’s Quality Management System (QMS) and ensure compliance with FAA AC 20-107D, EASA Part 21, or other relevant airworthiness requirements for additive manufacturing. Retain all records for audit purposes, including maintenance logs and operator training certifications.
Operational Compliance and Maintenance Logistics
Establish a preventive maintenance schedule aligned with OEM recommendations and regulatory requirements. Source spare parts through authorized distributors to maintain compliance and traceability. For aviation-critical repairs or upgrades, ensure all modifications are documented and approved under the appropriate airworthiness certification process (e.g., PMA, DER approval). Maintain an inventory of critical consumables (laser optics, nozzles, feedstock) with lot traceability to support material certification for deposited components. Regularly audit system performance data to ensure consistency with deposition parameters approved in process qualification (e.g., PQR, WPS).
End-of-Life and Decommissioning Compliance
At end-of-life, decommission laser systems in accordance with environmental and safety regulations. Safely dispose of laser diodes, capacitors, and hazardous materials per EPA and OSHA guidelines. For ITAR-controlled systems, ensure physical destruction or secure data wiping of embedded controllers and proprietary software, with certification provided by a licensed disposal vendor. Document the decommissioning process for regulatory audits and update asset registers accordingly.
Conclusion: Sourcing the Best Laser Systems for Metal Deposition in Aviation
In the highly demanding field of aviation, where performance, safety, and reliability are paramount, sourcing the best laser systems for metal deposition—specifically Laser Metal Deposition (LMD) or Laser Engineered Net Shaping (LENS)—is critical for achieving high-integrity component repair, additive manufacturing, and performance enhancement. After evaluating key technical, operational, and regulatory factors, the optimal laser system must combine precision, repeatability, material compatibility, and integration capabilities with advanced monitoring and quality control systems.
Top-tier laser deposition systems for aviation applications should feature high-power fiber or disk lasers (typically 1–5 kW) with excellent beam quality for fine control over melt pools and minimal heat-affected zones. Systems that support closed-loop process monitoring—such as coaxial melt pool sensing, thermal imaging, and real-time powder flow control—are essential for meeting stringent aerospace certifications like NADCAP, AS9100, and compliance with FAA/EASA regulations.
Furthermore, vendors offering robust post-processing integration, comprehensive traceability, and proven experience in aviation OEM or MRO environments (e.g., repair of turbine blades, landing gear, or structural components) are strongly preferred. Collaborating with system providers that offer technical support, training, and scalability ensures long-term operational success and qualification within aerospace supply chains.
In conclusion, the ideal laser metal deposition system for aviation balances cutting-edge technology with regulatory compliance, process consistency, and service support. Strategic sourcing should prioritize suppliers with aerospace-specific validation, a strong track record in the field, and systems designed for repeatability and qualification under rigorous industry standards. Investing in such advanced laser systems not only enhances manufacturing and repair capabilities but also supports innovation, cost-efficiency, and sustainability in the next generation of aviation technology.