The global berberine market has experienced significant growth due to increasing consumer interest in natural health supplements and rising scientific validation of its metabolic and cardiovascular benefits. According to Grand View Research, the global berberine market was valued at USD 218.6 million in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.8% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is driven by rising demand for plant-based therapeutics, expanding applications in managing blood sugar and cholesterol levels, and growing awareness of gut health. With increasing regulatory scrutiny and quality variation among suppliers, identifying reliable manufacturers has become critical for brands and distributors. Based on production capacity, ISO/GMP certifications, export footprint, and ingredient purity testing data, the following eight companies have emerged as leading berberine manufacturers globally.
Top 8 Berberine Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1
Domain Est. 1997
Website: sabinsa.com
Key Highlights: Sabinsa Corporation is a manufacturer, supplier and marketer of herbal extracts, cosmeceuticals, minerals, dietary supplements and specialty fine chemicals ……
#2 Berberine Extract Suppliers Exporters
Domain Est. 2013
Website: botanichealthcare.net
Key Highlights: Botanic Healthcare is one of the largest Berberine Extract manufacturers in India, offering a diverse range of herbal and organic extracts….
#3 Berberine hydrochloride
Domain Est. 2014
Website: pharmacompass.com
Key Highlights: PharmaCompass offers a list of Berberine Hydrochloride GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API ……
#4 Thorne Berberine 500 Mg
Domain Est. 1997
Website: store.mayoclinic.com
Key Highlights: Each bottle of Thorne Berberine contains 60 capsules, with a recommended dose of 1-2 capsules daily. Benefits. Promotes heart function; Supports a healthy ……
#5 Berberine Supplier
Domain Est. 2000
Website: vivion.com
Key Highlights: Vivion has earned its stature in the industry as a reputable wholesale distributor of Berberine and numerous other ingredients and chemicals….
#6 Berberine HCl
Domain Est. 2012
Website: adooq.com
Key Highlights: In stock Rating 5.0 (3) Berberine hydrochloride was novelly found that it has various beneficial effects on the cardiovascular system and significant anti-inflammatory activities…
#7 Berberine HCL Extracts Supplier in United States
Domain Est. 2017
Website: herbal-creations.com
Key Highlights: Rating 9.5/10 (50) Your trusted source for premium Berberine HCL extracts. Our transparent supply chain, quality commitment, and tailored solutions set us apart as the go-to ……
#8 Berberine Extract • Rafbrix Extracts
Domain Est. 2023
Website: rafbrixextracts.com
Key Highlights: At Rafbrix Extracts, our Berberine Extract is produced from the wildcrafted Berberis Aristata, thriving in the pristine Himalayan foothills….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Berberine
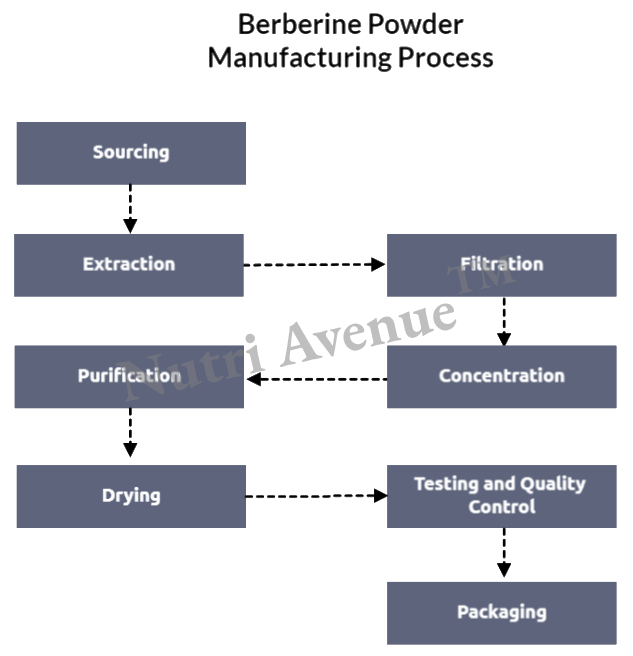
H2: Market Trends for Berberine in 2026
By 2026, the global berberine market is projected for significant expansion, driven by a convergence of consumer health trends, scientific validation, and evolving regulatory landscapes. Key trends shaping the market include:
1. Accelerated Demand in Metabolic Health:
Berberine’s established role in supporting healthy blood glucose levels and metabolic function will remain a primary growth driver. With rising global rates of prediabetes and metabolic syndrome, consumers and healthcare practitioners are increasingly turning to evidence-based supplements like berberine as part of integrative health strategies. This trend is amplified by growing awareness of its potential insulin-sensitizing effects, positioning berberine as a natural alternative or complement to pharmaceutical interventions.
2. Expansion into Cardiovascular and Gut Health Applications:
While metabolic health dominates, clinical research highlighting berberine’s benefits for lipid profile management (reducing LDL and triglycerides) and gut microbiome modulation will expand its use cases. By 2026, product formulations are expected to increasingly target heart health and digestive wellness, appealing to a broader demographic concerned with long-term preventive care.
3. Growth of Premium and Enhanced Formulations:
Bioavailability has historically been a limitation of berberine. In response, the market will see a surge in advanced delivery systems—such as liposomal encapsulation, nanoparticle technology, and combination formulas (e.g., with milk thistle or probiotics)—designed to improve absorption and efficacy. These premium products will command higher price points and differentiate brands in a competitive landscape.
4. Increased Regulatory Scrutiny and Standardization:
As berberine gains mainstream attention, regulatory bodies in key markets (e.g., U.S. FDA, EU EFSA) will likely intensify oversight regarding labeling claims, purity, and safety. This will drive demand for third-party testing, GMP-certified manufacturing, and transparent sourcing—particularly from sustainable, traceable botanical origins. Standardization of berberine content (typically 97%) will become a market expectation.
5. E-Commerce and DTC Dominance:
Direct-to-consumer (DTC) brands leveraging digital marketing, personalized health platforms, and subscription models will capture significant market share. Online channels will facilitate consumer education and access, particularly in North America and Europe, where demand for natural health products is robust.
6. Asian Market Maturation and Global Supply Dynamics:
China remains the primary source of raw berberine (derived from Coptis chinensis and Berberis spp.). By 2026, sustainability concerns and fluctuating crop yields may lead to price volatility, prompting investment in cultivation optimization and alternative sourcing. Meanwhile, domestic markets in China and India will see increased use of berberine in traditional and modern wellness formulations.
In summary, the 2026 berberine market will be characterized by scientific credibility, product innovation, and heightened regulatory standards, transforming it from a niche supplement into a cornerstone of evidence-based natural health. Companies that invest in clinical research, bioavailability enhancement, and consumer trust will lead the market.

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Berberine: Quality and Intellectual Property Concerns
Sourcing berberine, a popular natural alkaloid used in dietary supplements and traditional medicine, presents several challenges—particularly regarding product quality and intellectual property (IP) risks. Being aware of these pitfalls is essential for manufacturers, supplement brands, and distributors aiming to ensure safety, efficacy, and legal compliance.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inconsistent Purity and Potency
One of the most prevalent issues in berberine sourcing is variability in purity and active compound concentration. Suppliers, especially those from regions with less stringent regulatory oversight, may offer berberine with purity levels below the advertised 97–98%. Contaminants such as heavy metals, residual solvents, or other alkaloids (e.g., palmatine) can compromise safety and reduce effectiveness.
Unverified Botanical Sources
Berberine is typically extracted from plants like Berberis aristata, Coptis chinensis, or Phellodendron amurense. However, some suppliers may use unapproved or misidentified plant material due to cost or availability. Without proper botanical authentication (e.g., via HPLC or DNA barcoding), this can lead to inconsistent product profiles and potential regulatory non-compliance.
Adulteration and Dilution
To cut costs, some suppliers may adulterate berberine with fillers like maltodextrin or synthetic analogs. Others may dilute high-concentration batches, resulting in sub-potent products. Without rigorous third-party testing (e.g., from ISO 17025-accredited labs), such adulteration can go undetected until it affects end-product quality.
Lack of GMP and Regulatory Compliance
Suppliers not adhering to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) or lacking certifications (e.g., FDA registration, ISO, or EU-GMP) pose significant risks. Non-compliant facilities may not maintain proper hygiene, documentation, or traceability, increasing contamination risks and limiting auditability.
Intellectual Property-Related Pitfalls
Infringement of Patented Formulations
While berberine itself is a natural compound and not patentable, specific formulations, delivery systems (e.g., berberine combined with bioavailability enhancers), or extraction methods may be protected by patents. Sourcing berberine for use in proprietary blends without conducting freedom-to-operate (FTO) analyses can expose companies to infringement claims, especially in markets like the U.S. or Europe.
Use of Trademarked Brand Names
Some suppliers market berberine under branded names (e.g., “Berberine-97®” or “Glucotrust+”) that are trademarked. Using such names without authorization—even if the underlying material is the same—can lead to legal disputes. Buyers must verify trademark status and ensure labeling complies with brand usage guidelines.
Misrepresentation of Exclusive Rights
Suppliers may falsely claim exclusive rights to supply berberine or assert that their material is “patent-protected,” creating confusion. These claims can mislead buyers into believing they are obtaining a unique or legally protected ingredient, when in fact, they may be exposed to IP risks or paying a premium for unverified exclusivity.
Lack of Transparency in Supply Chain
Opaque sourcing chains make it difficult to trace the origin of berberine and assess potential IP entanglements. If raw material passes through multiple intermediaries without clear documentation, downstream users may inadvertently incorporate patented processes or infringe third-party rights without knowledge.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls, buyers should:
– Require Certificates of Analysis (CoA) and conduct independent lab testing.
– Source from GMP-certified suppliers with transparent supply chains.
– Perform due diligence on IP status, including patent and trademark searches.
– Use supply agreements that include warranties for quality and IP indemnification.
– Engage legal counsel for FTO assessments before launching new berberine-based products.
By proactively addressing quality and IP concerns, companies can minimize risks and ensure the integrity and legality of their berberine-containing products.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Berberine
Overview of Berberine
Berberine is a naturally occurring alkaloid compound found in several plants, including Berberis vulgaris (barberry), Coptis chinensis (goldthread), and Hydrastis canadensis (goldenseal). It is commonly used as a dietary supplement for its potential metabolic, cardiovascular, and antimicrobial benefits. Due to its pharmacological activity, the transportation, import/export, and sale of berberine are subject to regulatory oversight in many jurisdictions.
Regulatory Classification
The legal status of berberine varies significantly by country. Understanding its classification is essential for compliance.
United States (FDA)
- Berberine is classified as a dietary supplement ingredient under the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA).
- It is not approved as a drug by the FDA for the treatment of any disease.
- Manufacturers must ensure compliance with Current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMPs) for dietary supplements (21 CFR Part 111).
- Structure/function claims are permitted, but disease treatment claims are prohibited without drug approval.
European Union (EFSA & EMA)
- Berberine is evaluated by the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA).
- It is not approved as a novel food in all EU member states; some countries restrict its use in supplements.
- The European Commission has raised concerns about berberine’s safety, particularly regarding blood glucose and drug interactions.
- Importers must ensure compliance with the EU Novel Foods Regulation (EU) 2015/2283.
Canada (Health Canada)
- Berberine is regulated as a Natural Health Product (NHP).
- Requires a Product Licence (NPN) before sale.
- Must comply with the Natural Health Products Regulations (NHPR), including safety, efficacy, and quality standards.
China (NMPA)
- Berberine is approved as an over-the-counter (OTC) drug for gastrointestinal infections.
- As a traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) ingredient, it is subject to strict quality control under NMPA regulations.
- Export for pharmaceutical use requires proper documentation, including a Certificate of Pharmaceutical Product (CPP).
Other Regions
- Australia (TGA): Listed as a complementary medicine; requires inclusion in the Australian Register of Therapeutic Goods (ARTG).
- India (AYUSH): Regulated as an Ayurvedic or herbal ingredient; must meet Ayurvedic Pharmacopoeia standards.
- Japan (MHLW): Permitted in supplements under the Foods with Function Claims (FFC) system if approved.
Import and Export Requirements
International trade of berberine requires adherence to specific documentation and regulatory standards.
Key Documentation
- Certificate of Analysis (CoA): Must include purity, heavy metals, microbial contamination, and solvent residues.
- Certificate of Free Sale (CFS): Often required by importing countries to confirm the product is legally marketed in the country of origin.
- Customs Declarations: Accurate Harmonized System (HS) code classification (e.g., 2939.91 for alkaloids).
- CITES Compliance: Not applicable, as berberine-producing plants are generally not CITES-listed.
Quality and Testing Standards
- Comply with pharmacopoeial standards (e.g., USP, EP, or ChP).
- Products must be tested for:
- Berberine content (typically 85–98% purity)
- Heavy metals (lead, arsenic, cadmium, mercury)
- Microbial limits (total aerobic count, E. coli, Salmonella)
- Residual solvents (if applicable)
Labeling and Packaging Compliance
Labeling must align with destination country regulations.
Required Information
- Product name and berberine content per serving
- Supplement facts panel (U.S.) or nutrition information (EU)
- Manufacturer or distributor details
- Batch number and expiration date
- Usage instructions and safety warnings (e.g., “Consult a healthcare provider if taking medication”)
Prohibited Claims
- Avoid disease treatment claims (e.g., “lowers cholesterol” or “treats diabetes”) unless approved as a drug.
- Claims must be supported by scientific evidence and comply with local advertising laws.
Storage and Transportation
Proper handling ensures product integrity.
Storage Conditions
- Store in a cool, dry place away from light and moisture.
- Ideal temperature: 15–25°C (59–77°F).
- Avoid exposure to extreme temperatures during transit.
Transportation
- Use sealed, tamper-evident packaging.
- Maintain a documented cold chain if required (rare for berberine).
- Comply with IATA regulations if shipping by air (non-hazardous for berberine powder).
Risk Management and Due Diligence
Mitigate compliance risks through proactive measures.
Supplier Vetting
- Source from GMP-certified manufacturers.
- Require third-party testing reports and traceability documentation.
- Audit suppliers periodically for quality and ethical practices.
Regulatory Monitoring
- Stay updated on regulatory changes (e.g., EFSA safety re-evaluations, FDA warning letters).
- Subscribe to alerts from agencies like FDA, Health Canada, and TGA.
Legal Consultation
- Engage legal experts familiar with food, supplement, and pharmaceutical regulations in target markets.
- Ensure contracts with suppliers and distributors include compliance clauses.
Conclusion
Successfully navigating the logistics and compliance landscape for berberine requires a thorough understanding of international regulatory frameworks, meticulous documentation, and commitment to quality. Proactive due diligence, transparent labeling, and adherence to GMP standards are essential for lawful distribution and consumer safety. Always verify requirements with local authorities before importing or selling berberine in any jurisdiction.
Conclusion: Sourcing Berberine Suppliers
Sourcing high-quality berberine requires a strategic and diligent approach to ensure product safety, efficacy, and regulatory compliance. After evaluating multiple suppliers, key factors such as purity (preferably ≥97%), third-party testing, certifications (e.g., GMP, ISO, NSF), transparent sourcing of raw materials (typically from Berberis aristata or Coptis chinensis), and reliable supply chain logistics emerge as critical criteria.
Suppliers from regions with strong manufacturing standards—particularly China, India, and Europe—offer competitive pricing and scalability, but due diligence is essential to verify quality and avoid adulterated or substandard products. Establishing long-term relationships with vetted suppliers, conducting regular audits, and requesting batch-specific Certificates of Analysis (CoA) can mitigate risks and ensure consistency.
Ultimately, the ideal berberine supplier balances quality, compliance, and cost-effectiveness while aligning with your brand’s standards and regulatory requirements. Prioritizing transparency, sustainability, and scientific backing will support the development of trustworthy, high-performance products in the competitive nutraceutical market.