The global bentonite market is experiencing steady expansion, driven by rising demand across industries such as drilling, foundry, construction, and environmental management. According to Grand View Research, the global bentonite market size was valued at USD 2.8 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.6% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by increasing infrastructure development, particularly in emerging economies, and the expanding use of bentonite in oil & gas drilling operations. Additionally, Mordor Intelligence projects continued market momentum, with growing applications in cat litter, agriculture, and wastewater treatment further boosting demand. As the need for high-quality bentonite powder rises, a select group of manufacturers has emerged as industry leaders, combining technological expertise, large-scale production, and global distribution networks to meet evolving market needs. Here are the top 10 bentonite powder manufacturers shaping the market today.
Top 10 Bentonite Powder Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
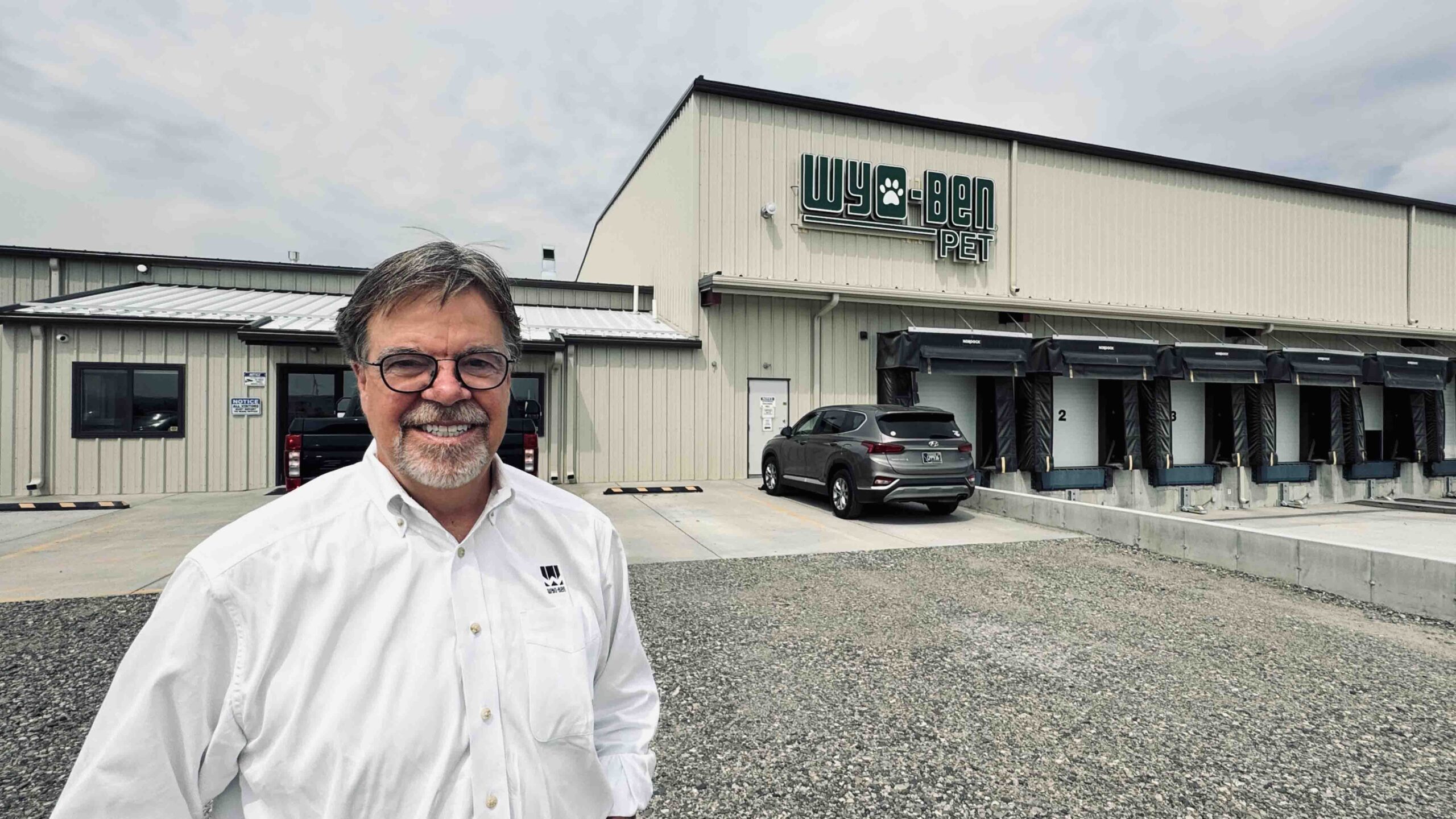
#1 Wyo-Ben
Domain Est. 1996 | Founded: 1951
Website: wyoben.com
Key Highlights: Wyo-Ben has been in business since 1951, and is a leading producer of Wyoming Bentonite Clay based products. Our materials are used globally….
#2 Bentonite
Domain Est. 1997 | Founded: 1960
Website: bentonite.ashapura.com
Key Highlights: World’s 3rd Largest Producer of Bentonite · Touching lives since 1960 · Over 3,500 acres of land of Bentonite mines in India · Exports to more than 70 countries ……
#3 Black Hills Bentonite
Domain Est. 1998 | Founded: 1947
Website: bhbentonite.com
Key Highlights: Since 1947, Black Hills Bentonite has provided high-quality Wyoming Sodium Bentonite for a diverse range of industrial and commercial applications….
#4 Bentonite Manufacturer, Bentonite Exporter & Bentonite Supplier …
Domain Est. 2018
Website: kutchbentoclay.com
Key Highlights: Leading Bentonite Manufacturers, Exporters & Suppliers Our premium bentonite is widely used in oil and gas drilling, foundry casting, iron ore pelletization, ……
#5 Bentonite Performance Minerals
Domain Est. 1996
Website: bentonite.com
Key Highlights: An integrated Wyoming sodium bentonite company. Collaborating with our customers for over 90 years. Leave it better than we find it….
#6 Bentonite
Domain Est. 1999
Website: imerys.com
Key Highlights: Bentonite is a highly absorbent, viscous plastic clay which is a valuable binding, sealing, absorbing and lubricating agent in a huge variety of industries ……
#7 Bentonite Group of Companies
Domain Est. 2000
Website: bentonit.ru
Key Highlights: Bentonite Company LLC is a managing company of Bentonite Group of Companies engaged in mining and processing of bentonite clay….
#8
Domain Est. 2000 | Founded: 1973
Website: westernclay.com
Key Highlights: Western Clay has been supplying high quality bentonite into various industries since 1973. Our products have been used in many different applications….
#9 Texas Sodium Bentonite
Domain Est. 2000
Website: texassodiumbentonite.com
Key Highlights: We are a sodium bentonite supplier providing premium materials for a variety of industries. Buy our sodium bentonite in bulk at competitive prices….
#10 Lonestar Minerals
Domain Est. 2012
Website: lonestarbarite.com
Key Highlights: We supply high quality bentonite for Pond sealing, wastewater treatment, cat litter and drilling mud wherever you need it in the United States….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Bentonite Powder

H2: Projected Market Trends for Bentonite Powder in 2026
The global bentonite powder market is poised for steady growth by 2026, driven by expanding industrial applications, rising infrastructure development, and increasing demand across key sectors such as construction, foundry, drilling, and environmental management. Several macroeconomic and technological trends are expected to shape the market landscape in the coming years.
1. Rising Demand in Construction and Civil Engineering
Bentonite powder is widely used in civil engineering projects, particularly in slurry walls, tunnel boring, and foundation stabilization due to its excellent swelling and sealing properties. With increasing urbanization and infrastructure investments—especially in Asia-Pacific, the Middle East, and Africa—the demand for bentonite in construction applications is expected to grow significantly by 2026. Governments’ focus on sustainable and resilient infrastructure will further boost utilization.
2. Growth in Oil & Gas Drilling Activities
The oil and gas industry remains a major consumer of bentonite powder, primarily as a key component in drilling muds. As exploration and offshore drilling activities rebound or stabilize post-pandemic, especially with renewed energy security concerns, demand for high-performance bentonite in drilling fluids is projected to rise. Innovations in drilling technologies and deeper exploration projects will drive demand for premium-grade sodium bentonite.
3. Environmental and Geosynthetic Applications
Environmental regulations promoting landfill liners, waste containment, and groundwater protection are accelerating the adoption of bentonite in geosynthetic clay liners (GCLs). By 2026, stricter environmental compliance standards globally are expected to increase the use of bentonite-based sealing solutions in mining, waste management, and water conservation projects.
4. Technological Advancements and Product Differentiation
Manufacturers are investing in processing technologies to enhance the purity, consistency, and functional performance of bentonite powder. Surface modification and activation techniques are enabling tailored solutions for niche applications in catalysis, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals. This trend toward value-added bentonite products will support market diversification and higher profit margins.
5. Regional Market Dynamics
Asia-Pacific is expected to dominate the bentonite powder market by 2026, led by China, India, and Southeast Asian countries due to rapid industrialization and construction booms. North America and Europe will maintain steady demand, driven by environmental applications and foundry operations. Latin America and Africa offer emerging opportunities, particularly in mining and infrastructure.
6. Supply Chain and Sustainability Pressures
Sustainability concerns and the push for responsible mining practices are influencing bentonite sourcing. Producers are increasingly adopting eco-friendly extraction methods and exploring recycling of used bentonite in foundry and drilling applications. Supply chain resilience, particularly after recent global disruptions, will be critical, with regional self-sufficiency becoming a strategic priority.
7. Price Volatility and Raw Material Constraints
While demand grows, price fluctuations due to raw material scarcity, energy costs, and geopolitical factors may impact market stability. Countries with abundant bentonite reserves—such as the U.S., Turkey, India, and Greece—will play a crucial role in ensuring supply stability. Investments in mine development and processing facilities are expected to mitigate potential bottlenecks.
Conclusion
By 2026, the bentonite powder market is projected to experience robust growth, supported by structural demand across multiple industries and ongoing innovation. Companies that focus on sustainable sourcing, product differentiation, and geographic expansion are likely to gain a competitive edge. With increasing regulatory support for environmental protection and infrastructure development, bentonite powder will remain a critical industrial mineral in the global economy.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Bentonite Powder (Quality & IP)
Sourcing Bentonite Powder requires careful attention to both quality consistency and intellectual property (IP) considerations. Overlooking these factors can lead to product failures, supply disruptions, legal disputes, and reputational damage. Below are common pitfalls to avoid:
Inadequate Quality Verification
One of the most frequent issues is failing to implement rigorous quality control measures. Bentonite properties vary significantly based on source, mineral composition (especially sodium vs. calcium types), and processing methods. Buyers often assume consistency across suppliers or batches without proper testing, leading to performance problems in applications like drilling muds, foundry sands, or cat litter.
Pitfalls include:
– Relying solely on supplier-provided certificates of analysis (CoA) without independent lab verification.
– Not specifying critical parameters such as swelling capacity, rheology, moisture content, grain size distribution, and cation exchange capacity (CEC).
– Ignoring the impact of impurities (e.g., quartz, feldspar) that can affect safety and performance.
Poor Supply Chain Transparency
Lack of visibility into the origin and processing of bentonite increases risks related to quality drift and ethical sourcing. Some suppliers may blend material from multiple mines or use undisclosed additives to cut costs, which can alter performance characteristics.
Pitfalls include:
– Not auditing supplier mining and processing facilities.
– Accepting vague or untraceable material origin information.
– Overlooking environmental, health, and safety (EHS) compliance in the supply chain.
Intellectual Property (IP) Risks in Custom Formulations
When sourcing bentonite for specialized applications (e.g., in cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, or advanced composites), companies may develop proprietary blends or treatment processes. Failure to safeguard IP can result in misappropriation or reverse engineering by suppliers.
Pitfalls include:
– Sharing detailed formulations or processing methods without non-disclosure agreements (NDAs).
– Allowing toll manufacturers or suppliers to claim ownership of process improvements.
– Failing to secure IP rights in contracts, especially when co-developing products.
Regulatory and Compliance Gaps
Bentonite used in regulated industries (e.g., food contact, pharmaceuticals, organic agriculture) must meet specific standards (e.g., FDA, EU REACH, USDA Organic). Sourcing without verifying compliance can lead to product recalls or import denials.
Pitfalls include:
– Assuming all bentonite is food or pharma grade without documentation.
– Not checking for heavy metal content (e.g., lead, arsenic) or radioactivity levels.
– Overlooking country-specific import regulations or labeling requirements.
Overlooking Long-Term Supply Risks
Bentonite is a naturally occurring mineral with finite, geographically concentrated deposits. Relying on a single source or region without contingency planning exposes buyers to geopolitical, environmental, or logistical disruptions.
Pitfalls include:
– Not diversifying suppliers or sourcing regions.
– Failing to assess the sustainability and longevity of the supplier’s mine.
– Ignoring the impact of transportation costs and carbon footprint in sourcing decisions.
Conclusion
To mitigate these pitfalls, buyers should establish clear quality specifications, conduct due diligence on suppliers, enforce robust IP protections, and maintain regulatory compliance. Regular audits, batch testing, and strong contractual agreements are essential for reliable and secure bentonite sourcing.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Bentonite Powder
Overview of Bentonite Powder
Bentonite powder is a naturally occurring clay primarily composed of montmorillonite, widely used in industrial, construction, drilling, environmental, and consumer applications. Due to its absorbent properties and regulatory status, proper logistics and compliance management are essential for safe and legal transportation and handling.
Classification and Regulatory Status
Bentonite powder is generally classified as a non-hazardous material under major international transport regulations. However, classification can vary based on specific composition, additives, and regional regulations.
- UN Number: Not assigned (typically exempt from hazardous classification)
- IMO/IMDG Code: Not regulated as dangerous goods (Class 9 may apply if in dust form with inhalation risk, but generally excluded)
- IATA DGR: Not classified as dangerous goods for air transport
- ADR/RID (Road/Rail in Europe): Usually not classified as hazardous; may fall under UN3260 (Corrosive solid, inorganic, n.o.s.) if alkaline, but pure bentonite typically does not
- OSHA/GHS (USA): Not classified as a hazardous chemical under GHS, though nuisance dust may require hazard communication
Note: Always verify with a current Safety Data Sheet (SDS) and competent authority if the bentonite contains additives, chemical treatments, or crystalline silica above threshold limits.
Packaging Requirements
Proper packaging ensures product integrity and prevents dust emissions during transport.
- Primary Packaging: Multi-wall paper bags (typically 25 kg or 50 lbs), poly-lined woven polypropylene bags, or moisture-resistant packaging
- Intermediate/Unit Load: Palletized loads stretch-wrapped; use slip sheets if needed
- Bulk Options: Flexi-bulk bags (1,000 kg), tanker trucks, railcars, or containerized bulk (Big Bags)
- Moisture Protection: Include moisture barrier liners if shipping to humid environments or for long durations
Storage Guidelines
- Location: Store in a dry, well-ventilated, covered area away from moisture and direct weather exposure
- Stacking: Limit stack height to prevent bag compression and damage (typically no more than 10 bags high)
- Segregation: Keep separate from foodstuffs, oxidizing agents, and incompatible chemicals
- Shelf Life: Indefinite if kept dry; monitor for clumping or moisture absorption
Transportation Modes and Considerations
Road Transport
- Use covered trucks or containers to prevent moisture ingress
- Secure loads to prevent shifting
- Comply with local weight and dimension regulations
Rail Transport
- Utilize covered hopper cars or enclosed boxcars
- Ensure proper loading/unloading procedures to minimize dust
Sea Freight
- Pack in containers with desiccants if necessary
- Use jumbo bags or palletized cargo; avoid moisture-sensitive routes
- Declare as “Non-Hazardous Cargo” unless otherwise classified
Air Freight
- Permitted as non-dangerous cargo
- Use dust-tight packaging to meet airline requirements
- May be subject to additional carrier-specific rules
Handling and Safety Precautions
- Dust Control: Use local exhaust ventilation; wear NIOSH-approved dust masks (N95 or equivalent) in high-exposure areas
- PPE: Wear gloves, safety goggles, and protective clothing to avoid skin and eye irritation
- Hygiene: Wash hands after handling; avoid eating, drinking, or smoking in handling areas
- Spill Management: Sweep or vacuum spills; avoid dry sweeping that generates dust. Do not flush into drains
Regulatory Compliance
United States
- OSHA: Comply with Permissible Exposure Limits (PEL) for inert or nuisance dust (15 mg/m³ total, 5 mg/m³ respirable)
- EPA: No major restrictions for natural bentonite; reporting not required under TSCA for unmodified forms
- DOT: Not regulated as hazardous material under 49 CFR when transported in non-bulk form and meeting criteria
European Union
- REACH: Bentonite is registered; ensure supplier provides current registration number
- CLP Regulation: Typically not classified as hazardous; label as “Not Classified” with SDS section 2 confirmation
- Transport: Follow ADR guidelines; usually transported as non-dangerous goods
Other Regions
- Canada: Comply with WHMIS 2015; typically not classified as hazardous
- Australia: Listed on AICS; no significant restrictions for natural bentonite
- China: Subject to customs inspection; ensure accurate HS code declaration
Documentation Requirements
- Commercial Invoice: Clearly describe as “Natural Bentonite Powder, Non-Hazardous”
- Packing List: Include net/gross weights, packaging type, and quantity
- Bill of Lading/Air Waybill: Mark as non-dangerous cargo
- Safety Data Sheet (SDS): Provide up-to-date SDS (preferably within last 3 years), compliant with local regulations (e.g., GHS, CLP)
- Certificate of Analysis (COA): Optional but recommended for quality assurance
Environmental and Disposal Considerations
- Disposal: Non-hazardous waste; dispose of in accordance with local landfill regulations
- Environmental Impact: Generally inert; low toxicity to aquatic life
- Spill Response: Contain and collect; no special environmental hazard unless mixed with contaminants
Key Compliance Reminders
- Always obtain and review the current SDS before shipping or handling
- Confirm classification with your supplier or laboratory if bentonite is modified or blended
- Label packages appropriately—“Keep Dry,” “Fragile,” or “This Way Up” as needed
- Train personnel on safe handling and emergency procedures
- Verify import/export requirements in destination countries (e.g., phytosanitary certificates not typically needed)
By following this guide, businesses can ensure the safe, compliant, and efficient logistics of bentonite powder across global supply chains.
Conclusion for Sourcing Bentonite Powder:
Sourcing high-quality bentonite powder requires a strategic approach that balances purity, consistency, cost-effectiveness, and reliable supply chain logistics. After evaluating multiple suppliers and market options, it is essential to prioritize vendors with proven quality control measures, relevant certifications (such as ISO or MSDS compliance), and the capacity to meet volume demands without compromising on specifications. Factors such as particle size, swelling capacity, pH level, and intended application—whether for drilling, foundry, cat litter, or cosmetics—must align with project or production requirements.
Moreover, establishing long-term relationships with suppliers who offer transparency in sourcing, sustainable mining practices, and responsive customer service can significantly enhance operational efficiency and reduce downtime. Conducting regular quality audits, requesting sample testing, and comparing total cost of ownership—not just unit price—will ensure optimal value and performance.
In conclusion, successful sourcing of bentonite powder hinges on thorough due diligence, clear specification alignment, and a partnership-oriented approach with suppliers to ensure consistent quality, timely delivery, and scalability for future needs.