The global metal lathe market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising demand for precision machining in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and industrial manufacturing. According to Grand View Research, the global CNC machine tools market—of which benchtop metal lathes are a key segment—was valued at USD 74.6 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by the increasing adoption of compact, high-precision machines in small to mid-sized workshops and educational institutions. Benchtop metal lathes, in particular, are gaining traction due to their space efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and adaptability for prototyping and light industrial applications. As automation and smart manufacturing continue to reshape the sector, manufacturers are investing in advanced features like digital readouts, improved spindle accuracy, and CNC integration even in smaller models. Against this backdrop, identifying the leading benchtop metal lathe manufacturers provides valuable insight into innovation, reliability, and performance in a competitive and evolving marketplace.
Top 10 Bench Top Metal Lathe Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Sherline
Domain Est. 1995
Website: sherline.com
Key Highlights: Sherline Products are suppliers of precision mini-benchtop lathes, milling machines, CNC machine accessories for industrial and home use….
#2 South Bend Lathe Co.
Domain Est. 2000
Website: southbendlathe.com
Key Highlights: South Bend Lathe Works became the largest manufacturer of precision metalworking lathes in the world with customers in more than 88 countries….
#3 Metal Lathes
Domain Est. 2001
#4 EMCO lathes & milling machines manufacturer, CNC training …
Domain Est. 2007
Website: emco-world.com
Key Highlights: The machine tool manufacturer EMCO is your expert for high-quality lathes, milling machines and CNC training. Discover our training courses, ……
#5 9″X20″ Bench Top Lathe
Domain Est. 1996
Website: palmgren.com
Key Highlights: In stock Free deliveryHeavy cast iron construction, smooth power transmission, precision thrust and ball bearings in the head stock and spindle, hardened and ground ways all design…
#6 Monarch Lathes
Domain Est. 1998 | Founded: 1909
Website: monarchlathe.com
Key Highlights: Over 100 Years of Unmatched Craftsmanship. Monarch Lathes has been supplying the world with high quality, manual metal cutting equipment since 1909….
#7 TAIG Tools
Domain Est. 1999
Website: taigtools.com
Key Highlights: At TAIG Tools we manufacture precision desktop Milling Machines, Lathes (otherwise known as Micro Mills and Micro Lathes) and a complete line of accessories….
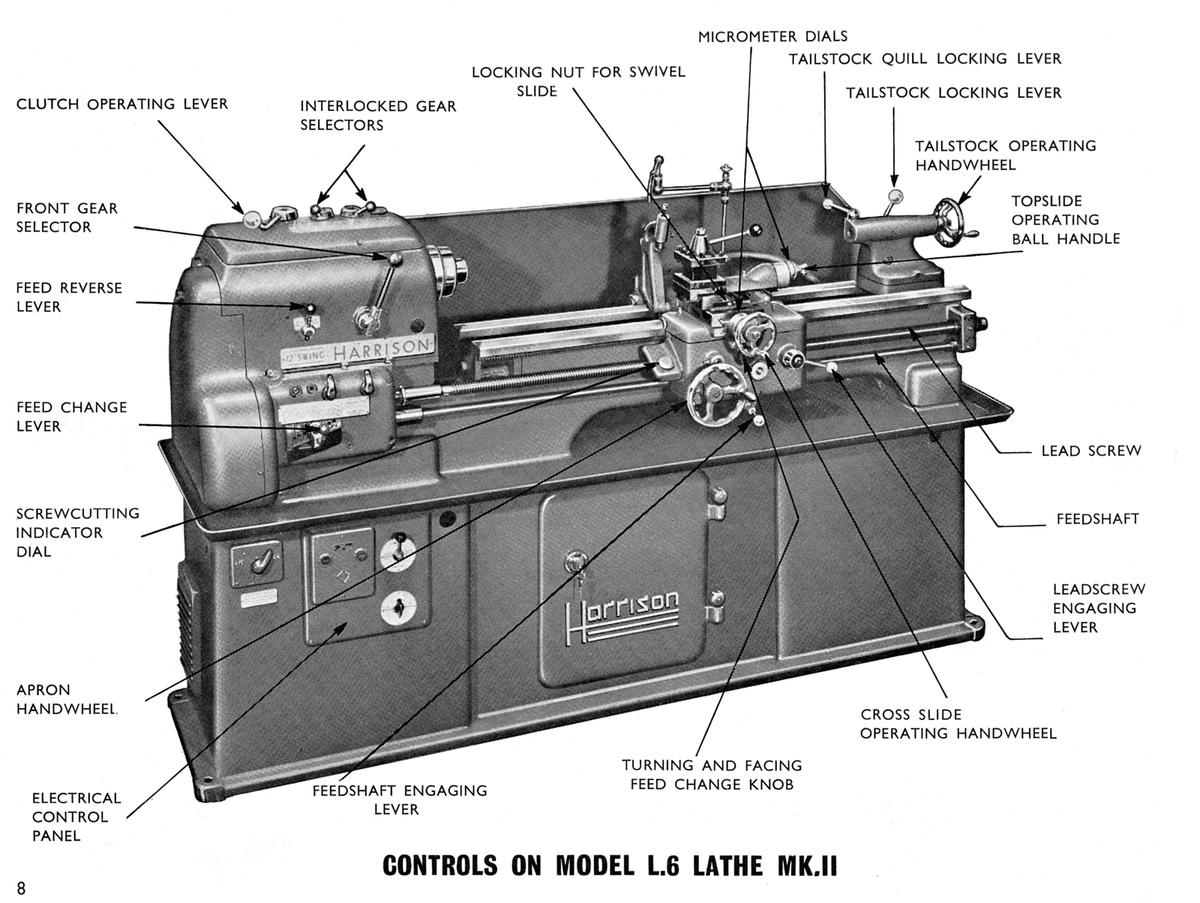
#8 Harrison Lathe Official Sales, Parts, Accessories, Manuals Repair …
Domain Est. 2009
Website: harrisonlathe.com
Key Highlights: Harrison Lathes built 1898 recognized worldwide reputation for super precision quality, long term reliability, and universal serviceability….
#9 Workbench lathes
Domain Est. 2018
Website: weiss-machines.com
Key Highlights: WBL210 VARIABLE SPEED BENCH LATHE. From 1 285€ HT · WBL-250. WBL250 BENCH LATHE · WBM-250G. WM250G GEAR-DRIVEN BENCH LATHE · WBL-250f. WBL250F VARIABLE SPEED BENCH ……
#10 Weiss Bench Lathe
Domain Est. 2023
Expert Sourcing Insights for Bench Top Metal Lathe

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Bench Top Metal Lathes
The global market for bench top metal lathes is expected to undergo significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological advancements, shifting manufacturing demands, and evolving industrial automation. These compact, precision-focused machines continue to serve critical roles in prototyping, small-scale production, education, and maintenance workshops. Below are key trends shaping the bench top metal lathe market in 2026:
-
Increased Adoption of CNC Integration
By 2026, Computer Numerical Control (CNC) bench top lathes are projected to dominate market growth. The integration of CNC technology enhances precision, repeatability, and ease of use, making these machines attractive to small and medium enterprises (SMEs), educational institutions, and hobbyists. Improvements in user-friendly interfaces and affordable CNC retrofit kits are further accelerating adoption. -
Growing Demand from Educational and Training Institutions
Vocational training centers, technical schools, and engineering colleges are investing in bench top lathes to provide hands-on experience in machining. The compact size, safety features, and lower operational cost make these lathes ideal for educational environments. Government initiatives promoting skill development in advanced manufacturing are expected to boost demand. -
Rise of Smart Manufacturing and Industry 4.0
Bench top lathes are increasingly being equipped with IoT-enabled features such as remote monitoring, predictive maintenance, and data logging. This connectivity supports integration into smart factories, even at smaller scales. By 2026, manufacturers are expected to offer lathes with plug-and-play compatibility with digital manufacturing ecosystems. -
Expansion in Emerging Economies
Countries in Asia-Pacific (especially India, Vietnam, and Indonesia), Latin America, and Africa are witnessing increased industrialization and growth in micro-manufacturing. The affordability and versatility of bench top lathes make them a preferred choice for startups and local workshops, driving market expansion in these regions. -
Focus on Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
Manufacturers are prioritizing energy-efficient motors, low-noise operation, and recyclable materials in lathe design. With growing emphasis on sustainable manufacturing, eco-conscious consumers and businesses are favoring models that reduce environmental impact. -
Customization and Modular Designs
There is a rising trend toward modular bench top lathes that allow users to upgrade components (e.g., digital readouts, tool holders, spindle speeds) based on application needs. This flexibility enhances product lifecycle and appeals to a broader customer base, from DIY enthusiasts to professional machinists. -
Competitive Pricing and Online Distribution
The proliferation of e-commerce platforms has made bench top lathes more accessible globally. Direct-to-consumer sales, bundled accessories, and competitive pricing are intensifying market competition. Brands are leveraging online tutorials and virtual support to enhance customer experience. -
Challenges from 3D Printing and Alternative Technologies
While additive manufacturing poses a competitive threat for prototyping, bench top lathes maintain irreplaceable value in producing high-tolerance metal components. The market is adapting by positioning lathes as complementary tools within hybrid manufacturing setups.
In conclusion, the 2026 bench top metal lathe market is characterized by innovation, digital integration, and broader accessibility. As industries embrace precision and flexibility at smaller scales, bench top lathes are poised to remain essential tools across diverse sectors. Manufacturers who invest in smart features, sustainability, and user-centric design will likely lead the evolving landscape.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing a Bench Top Metal Lathe (Quality & IP Considerations)
Sourcing a bench top metal lathe requires careful evaluation to avoid compromising on quality and inadvertently infringing on intellectual property (IP). Below are key pitfalls to watch for:
Overlooking Build Quality and Material Standards
Many low-cost bench top lathes, especially those from less-regulated manufacturers, use substandard materials such as soft cast iron or inadequate steel alloys. This results in poor vibration damping, reduced accuracy, and shorter machine life. Always verify the grade of cast iron used (e.g., Meehanite or equivalent) and inspect spindle and ways construction.
Ignoring Spindle and Bearing Quality
Low-quality lathes often use undersized or poorly rated bearings, leading to premature wear and runout issues. Ensure the lathe uses precision-ground spindles with high-grade ABEC-rated bearings. Avoid models with sealed bearings that cannot be replaced or adjusted.
Assuming Brand Names Reflect Authenticity
Some suppliers clone reputable brand designs (e.g., mini versions of Sherline or Taig) and sell them under misleading names or logos. These clones may infringe on design patents or trademarks. Verify the manufacturer’s legitimacy and check for IP compliance, especially if the lathe bears a logo similar to a known brand.
Falling for Inflated Specifications
Spec sheets may list exaggerated performance metrics such as speed ranges, precision tolerances, or horsepower. Cross-check with independent reviews and user feedback. For example, a “0.001-inch accuracy” claim without thermal stability or rigidity to support it is likely misleading.
Neglecting IP and Design Infringement Risks
Cloned or counterfeit lathes often replicate patented features like quick-change tool posts, collet systems, or headstock designs. Purchasing such equipment may expose your workshop or business to legal risks if used commercially, especially in regulated industries. Always source from authorized distributors or manufacturers with transparent IP policies.
Skipping Due Diligence on Supplier Reputation
Unverified suppliers, particularly on online marketplaces, may offer lathes with inconsistent quality control and no technical support. Research the supplier’s history, customer service responsiveness, and warranty terms. Look for certifications like ISO 9001 as a sign of quality management.
Undervaluing After-Sales Support and Spare Parts
Even high-quality lathes require maintenance. Sourcing from manufacturers with poor spare parts availability or no local service support can render the machine unusable over time. Confirm the availability of replacement components like belts, gears, and tooling before purchase.
By addressing these pitfalls proactively, you can ensure a durable, reliable bench top lathe that meets both quality standards and legal requirements.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Bench Top Metal Lathe
Product Classification and HS Code
Identify the Harmonized System (HS) code for your bench top metal lathe to ensure accurate customs clearance. Typical classifications fall under HS Code 8458 (Metal-cutting lathes), but variations exist based on features (e.g., CNC vs. manual, turning diameter). Confirm the exact code with your manufacturer or a customs broker to avoid delays or penalties.
Import/Export Regulations
Comply with import/export controls specific to your destination country. Some regions require permits or notifications for machinery imports. Check for export restrictions in the country of origin, especially if the lathe contains components subject to dual-use regulations (e.g., advanced control systems). Maintain proper export documentation, including commercial invoices and packing lists.
Safety and Electrical Compliance
Ensure the lathe meets regional safety standards such as:
– CE Marking (EU): Compliance with Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC and Low Voltage Directive 2014/35/EU.
– UL/CSA (North America): Certification to applicable ANSI/UL or CSA standards for industrial machinery.
– UKCA (UK): Required for sale in Great Britain post-Brexit, aligning with UK supply regulations.
Verify voltage compatibility (e.g., 110V vs. 220V) and include appropriate power adapters or transformers if needed.
Packaging and Transportation Requirements
Use robust, skid-resistant packaging with internal bracing to protect precision components during shipping. Clearly label packages with:
– Handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “Do Not Invert”)
– Weight and center of gravity indicators
– Proper shipping names and UN numbers if lubricants or coolants are included
Ship via freight carriers experienced in handling industrial machinery to minimize damage risk.
Documentation Checklist
Prepare and retain the following for logistics and customs:
– Commercial Invoice
– Packing List
– Bill of Lading or Air Waybill
– Certificate of Conformity (CE, UKCA, etc.)
– User Manual and Safety Instructions (in local language, if required)
– Warranty and Technical Specifications
Environmental and Disposal Compliance
Adhere to environmental regulations such as RoHS (EU) and WEEE directives, which may apply to electrical components. Provide information on proper disposal of machine parts, coolants, and packaging materials per local waste management laws.
End-User Certification and Due Diligence
For certain markets, an end-user statement may be required to confirm the lathe will be used for civilian, non-military purposes. Conduct due diligence to ensure the buyer is not on any restricted party lists (e.g., U.S. OFAC, EU sanctions lists).
After-Sales Support and Warranty Logistics
Outline warranty terms, spare parts availability, and technical support channels. Establish procedures for handling returns, repairs, or recalls in compliance with consumer protection laws in the target market.
In conclusion, sourcing a benchtop metal lathe requires careful consideration of several key factors including precision, build quality, motor power, spindle speed range, swing capacity, and compatibility with intended applications. Evaluating reputable suppliers, comparing warranties and after-sales support, and balancing cost against long-term durability and performance are essential steps in making an informed decision. Additionally, ensuring that the lathe meets safety standards and integrates well within the available workspace will contribute to efficient and reliable operation. By prioritizing requirements based on specific machining needs and conducting thorough research, buyers can select a benchtop metal lathe that offers optimal value, enhances productivity, and supports both current and future projects in a workshop or educational environment.