The global belt manufacturing industry has experienced steady growth, driven by rising demand in the fashion, automotive, and industrial sectors. According to Grand View Research, the global belts and hoses market size was valued at USD 24.3 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by increasing automotive production, particularly in emerging economies, and growing consumer preference for durable, style-forward accessories. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence projects the global conveyor belt market alone to grow at a CAGR of over 4.5% during the forecast period of 2023–2028, supported by rising industrial automation and infrastructure development. With such momentum, identifying the top-performing manufacturers—those combining innovation, scalability, and sustainability—has become essential for sourcing executives and supply chain stakeholders. The following list highlights the top 10 belt manufacturers shaping the industry across multiple sectors.
Top 10 Belt Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Mitsuboshi Belting Ltd.
Domain Est. 1998
Website: mitsuboshi.com
Key Highlights: We are a comprehensive manufacturer of rubber and plastics, including transmission belts used in automobiles, precision equipment, agricultural machinery, ……
#2 V
Domain Est. 1999
Website: web.optibelt.com
Key Highlights: High-quality V-belts and timing belts from the german manufacturer Optibelt. We have been setting standards in drive systems with first-class system ……
#3 MBL (USA) Corporation
Domain Est. 2000
Website: mblusa.com
Key Highlights: As the North American division of Mitsuboshi Belting Ltd., we proudly manufacture and distribute premium power transmission belts….
#4 About Us
Domain Est. 2015
Website: timkenbelts.com
Key Highlights: A manufacturer of premium performance power transmission belts, Timken Belts’ associates and products help keep industry in motion and the world more ……
#5 Beltservice Corporation
Domain Est. 1996
Website: beltservice.com
Key Highlights: Beltservice Corporation is a leading fabricator of custom conveyor belting. Every day, we stake our reputation on the durability, variety, and performance….
#6 Conveyor Belting
Domain Est. 1998
Website: beltpower.com
Key Highlights: Investing in high-quality conveyor belting is essential for maximizing operational efficiency and minimizing downtime….
#7 Ammeraal Beltech
Domain Est. 1999
Website: ammeraalbeltech.com
Key Highlights: Ammeraal Beltech: global market leader in the design, manufacturing, fabrication & servicing of high-quality, high-performance process & conveyor belts….
#8 B&B Manufacturing
Domain Est. 1999
Website: bbman.com
Key Highlights: Our expertly engineered belted drive solutions are trusted across industries like 3D Printing, Air-Cooled Heat Exchangers, CNC Machinery, and Oil & Gas, ……
#9 Volta Belting
Domain Est. 1999
Website: voltabelting.com
Key Highlights: Elevate your poultry processing operations with Volta Belting’s innovative conveyor belt solutions, designed for superior hygiene and efficiency….
#10 D&D Global Best Power Transmission Belts
Domain Est. 2011
Website: ddglobal.com
Key Highlights: D&D is a leading manufacturer of top-tier power transmission belts for various industries. Fast access to 35000+ SKUs with personalized service….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Belt

H2: Market Trends for Belts in 2026
As we approach 2026, the global belt market is undergoing significant transformation driven by evolving consumer preferences, technological advancements, and sustainability imperatives. The market—encompassing fashion belts, industrial belts (such as conveyor and timing belts), and specialty belts (including fitness and safety belts)—is witnessing divergent yet interconnected trends across segments.
-
Rising Demand for Sustainable and Ethical Fashion Belts
In the fashion accessories sector, sustainability is a dominant driver. Consumers, especially in North America and Europe, are increasingly demanding eco-friendly materials such as recycled leather, plant-based alternatives (e.g., Piñatex, mushroom leather), and traceable supply chains. Brands are responding by launching “circular” belt lines that support repair, resale, and recycling. By 2026, it is projected that over 40% of premium fashion belts will incorporate sustainable materials, with certifications like B Corp and Leather Working Group becoming key differentiators. -
Smart and Functional Wearable Belts Gaining Traction
The integration of technology into everyday wearables is expanding into the belt category. Smart belts equipped with health monitoring (e.g., posture correction, activity tracking, and waist circumference measurement) are gaining popularity, particularly among health-conscious consumers and aging populations. Companies like Withings and Lumo BodyTech are pioneering this space. By 2026, the smart belt segment is expected to grow at a CAGR of 18%, driven by advancements in flexible sensors and miniaturized electronics. -
Industrial Belts: Focus on Efficiency and Durability
In the industrial sector, demand for high-performance belts—especially in automotive, manufacturing, and logistics—is rising due to automation and supply chain optimization. Polyurethane and reinforced rubber belts with extended lifespans and reduced energy loss are in high demand. The electric vehicle (EV) revolution is also influencing timing belt design, with quieter, lighter, and more heat-resistant materials being developed. By 2026, the industrial belt market is projected to exceed $25 billion, with Asia-Pacific leading in consumption due to rapid industrialization. -
Customization and Personalization in Fashion
Mass customization is becoming a key competitive edge in the fashion belt industry. Online platforms now offer personalized engraving, adjustable sizing, modular buckles, and made-to-order production, reducing waste and enhancing customer loyalty. Brands leveraging AI-driven design tools and 3D printing for prototyping are gaining market share. This trend is especially strong among Gen Z and millennial consumers who value individuality and brand authenticity. -
Supply Chain Resilience and Regionalization
Geopolitical uncertainties and post-pandemic supply chain disruptions have prompted companies to regionalize production. By 2026, nearshoring of belt manufacturing—particularly in fashion belts—is increasing in regions like Eastern Europe, Mexico, and Vietnam. This shift not only reduces lead times but also supports sustainability goals by cutting transportation emissions. -
E-commerce and DTC Models Dominate Sales
The direct-to-consumer (DTC) model continues to reshape belt retail. Online channels now account for over 60% of fashion belt sales in developed markets. Augmented reality (AR) try-on tools and AI-powered size recommendations are improving online shopping experiences, reducing return rates, and driving conversion.
Conclusion
The belt market in 2026 is characterized by innovation, sustainability, and digital integration. While fashion belts evolve toward personalization and eco-consciousness, industrial belts advance in performance and efficiency. Cross-sector trends such as smart technology and supply chain resilience underscore a market that is both diverse and dynamically adapting to global challenges and opportunities. Companies that embrace agility, transparency, and technological integration will be best positioned to lead in this evolving landscape.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Belts (Quality, IP)
Sourcing belts—whether timing belts, conveyor belts, V-belts, or other types—exposes buyers to several critical risks related to quality control and intellectual property (IP). Overlooking these pitfalls can lead to product failures, supply chain disruptions, legal liabilities, and reputational damage. Below are key challenges to consider:
Poor Quality Control and Inconsistent Manufacturing Standards
Many suppliers, particularly in low-cost regions, lack rigorous quality management systems. This can result in inconsistent materials, improper curing processes, dimensional inaccuracies, and premature belt failure. Without proper certifications (e.g., ISO 9001) or on-site audits, buyers risk receiving substandard products that don’t meet performance or durability requirements.
Use of Substandard or Non-Specified Materials
Low-cost suppliers may substitute high-performance materials (e.g., EPDM, neoprene, or polyurethane) with cheaper, inferior alternatives that degrade faster under heat, oil, or UV exposure. This compromises belt life and safety, especially in industrial or automotive applications where failure can lead to costly downtime.
Counterfeit or IP-Infringing Products
Original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) often hold patents, trademarks, and design rights for proprietary belt designs (e.g., specific tooth profiles, reinforcement cords). Sourcing from unauthorized suppliers increases the risk of receiving counterfeit or IP-infringing belts, which can expose the buyer to legal action, customs seizures, and liability claims.
Lack of Traceability and Documentation
Reputable belt manufacturers provide material certifications, test reports, and batch traceability. Many low-tier suppliers fail to deliver proper documentation, making it difficult to verify compliance with industry standards (e.g., DIN, ANSI, RMA) or conduct root-cause analysis during failures.
Misrepresentation of OEM Compatibility
Some suppliers claim their belts are “compatible” with OEM parts without proper engineering validation. While dimensions may match, differences in tensile strength, flexibility, or noise performance can reduce efficiency and increase wear on pulleys and other components.
Inadequate Testing and Performance Validation
Belts must undergo rigorous testing for tensile strength, elongation, heat resistance, and fatigue life. Suppliers without proper testing labs may skip or falsify test results, leading to undetected weaknesses that manifest only after deployment.
Supply Chain Vulnerability and Lead Time Instability
Over-reliance on a single, low-cost supplier—especially one with weak IP practices—can create supply chain risks. If the supplier faces legal action for IP infringement or quality recalls, production can halt abruptly, disrupting operations.
Failure to Audit or Verify Supplier Claims
Buyers often rely on supplier-provided data without independent verification. Without third-party audits, factory inspections, or sample performance testing, it is difficult to confirm both quality and IP legitimacy.
Mitigating these pitfalls requires due diligence: vetting suppliers thoroughly, demanding documentation, conducting audits, and where applicable, working with legal counsel to ensure IP compliance. Investing in reputable suppliers—even at a higher initial cost—can prevent far greater losses down the line.
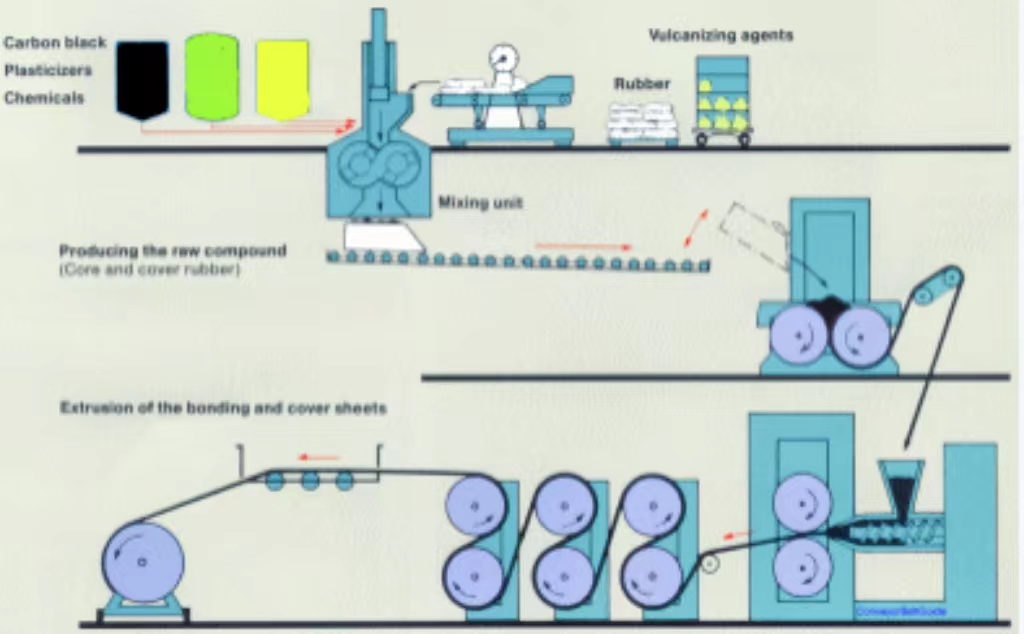
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Belt
Proper logistics planning and adherence to compliance regulations are essential for ensuring the efficient and legal transportation of goods along the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) corridors. This guide outlines key considerations for businesses engaged in cross-border trade via land, rail, and multimodal routes.
Understanding the Belt and Road Logistics Network
The Belt component of the BRI primarily refers to overland transport corridors connecting China with Central Asia, the Middle East, and Europe. Key routes include the China-Europe Railway Express (CERE), which links major industrial hubs through countries such as Kazakhstan, Russia, Belarus, Poland, and Germany. Logistics operations along these corridors involve coordination between multiple rail operators, customs authorities, and freight forwarders.
Key Logistics Considerations
- Route Planning: Choose optimal routes based on transit time, cost, infrastructure capabilities, and geopolitical stability. Rail transit from eastern China to Western Europe typically takes 12–18 days, significantly faster than sea freight.
- Multimodal Integration: Combine rail with road and, where applicable, inland waterways to achieve first- and last-mile connectivity. Intermodal terminals are critical for efficient cargo transfers.
- Cargo Packaging and Handling: Ensure goods are securely packed to withstand rail vibrations and multiple handling operations. Use ISO-standard containers where possible.
- Tracking and Visibility: Implement real-time tracking systems (e.g., GPS, IoT sensors) to monitor cargo location, temperature, and security throughout the journey.
- Partner Selection: Work with experienced freight forwarders and logistics providers familiar with BRI routes, local regulations, and rail operators.
Compliance Requirements
Compliance with international, regional, and national regulations is mandatory for seamless cross-border operations.
Customs Documentation
- Commercial Invoice: Must include detailed descriptions, values, and terms of sale (preferably Incoterms® 2020).
- Packing List: Itemize contents, weights, and dimensions of each package or container.
- Bill of Lading or CMR (for road): Contract of carriage; for rail, the CIM/SMGS waybill is used across different rail networks.
- Certificate of Origin: Required for tariff preferences; may need to be verified by a chamber of commerce.
- Customs Declarations: Accurate Harmonized System (HS) codes are essential for duty calculation and trade statistics.
Regulatory Compliance
- Transit Permits: Required in countries such as Russia and Kazakhstan for goods transiting their territory. TIR Carnets may be used for road segments under the TIR Convention.
- Sanitary and Phytosanitary (SPS) Standards: Applicable to agricultural, food, and plant-based products. Pre-shipment inspections may be required.
- Product Certification: Certain goods (e.g., electronics, machinery) may require conformity assessments (e.g., CE, GOST, KC) depending on destination markets.
- Restricted and Prohibited Goods: Be aware of national restrictions on items such as batteries, chemicals, and dual-use technologies.
Security and Safety
- Container Security Initiative (CSI): High-risk containers may be subject to pre-screening.
- Authorized Economic Operator (AEO): Obtain AEO status in your home country to benefit from expedited processing and reduced inspections.
- Cargo Screening: Comply with security screening requirements imposed by rail operators and border agencies.
Harmonizing Across Jurisdictions
Due to the involvement of multiple countries, logistics must account for varying:
– Rail Gauges: Breaks of gauge occur (e.g., China/CIS vs. Europe), requiring transloading or variable-gauge axles.
– Customs Procedures: Use of digital platforms like the Single Window system where available; pre-clearance can reduce delays.
– Language and Documentation: Provide documents in local languages or with certified translations as required.
Best Practices for Success
- Leverage Digital Tools: Use electronic data interchange (EDI) and blockchain platforms (e.g., TradeLens) to streamline documentation and reduce fraud.
- Engage Local Experts: Employ local customs brokers and legal advisors to navigate complex regulatory environments.
- Maintain Accurate Records: Retain shipping documents for at least five years for audit and compliance verification.
- Monitor Geopolitical Developments: Stay informed about changes in trade policies, sanctions, or infrastructure disruptions along the route.
By aligning logistics operations with compliance standards and leveraging regional cooperation mechanisms, businesses can optimize supply chain performance and minimize risks across the Belt corridors.
In conclusion, sourcing belt manufacturers requires a strategic approach that balances quality, cost, reliability, and scalability. A thorough evaluation of potential suppliers—including their production capabilities, material sourcing, compliance with industry standards, and track record for on-time delivery—is essential to ensure long-term success. Visiting manufacturing facilities, requesting product samples, and conducting due diligence on certifications can significantly reduce risks. Additionally, fostering strong communication and building lasting partnerships with manufacturers contributes to consistent product quality and operational efficiency. Whether sourcing locally or internationally, prioritizing transparency, sustainability, and responsiveness will ultimately support a resilient supply chain and enhance competitiveness in the marketplace.