The global battery wires market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand in the automotive, renewable energy, and consumer electronics sectors. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the battery cables market was valued at USD 3.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 5.6 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of over 6.5% during the forecast period. This expansion is largely fueled by the accelerating adoption of electric vehicles (EVs), increasing deployment of energy storage systems, and stringent regulatory standards for fuel efficiency and emissions. As automakers and energy providers intensify their focus on reliable, high-performance electrical connections, the role of specialized battery wire manufacturers has become increasingly critical. In this rapidly evolving landscape, a select group of manufacturers are leading innovation in conductivity, durability, and thermal resistance. Below are the top 10 battery wires manufacturers shaping the industry’s future.
Top 10 Battery Wires Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
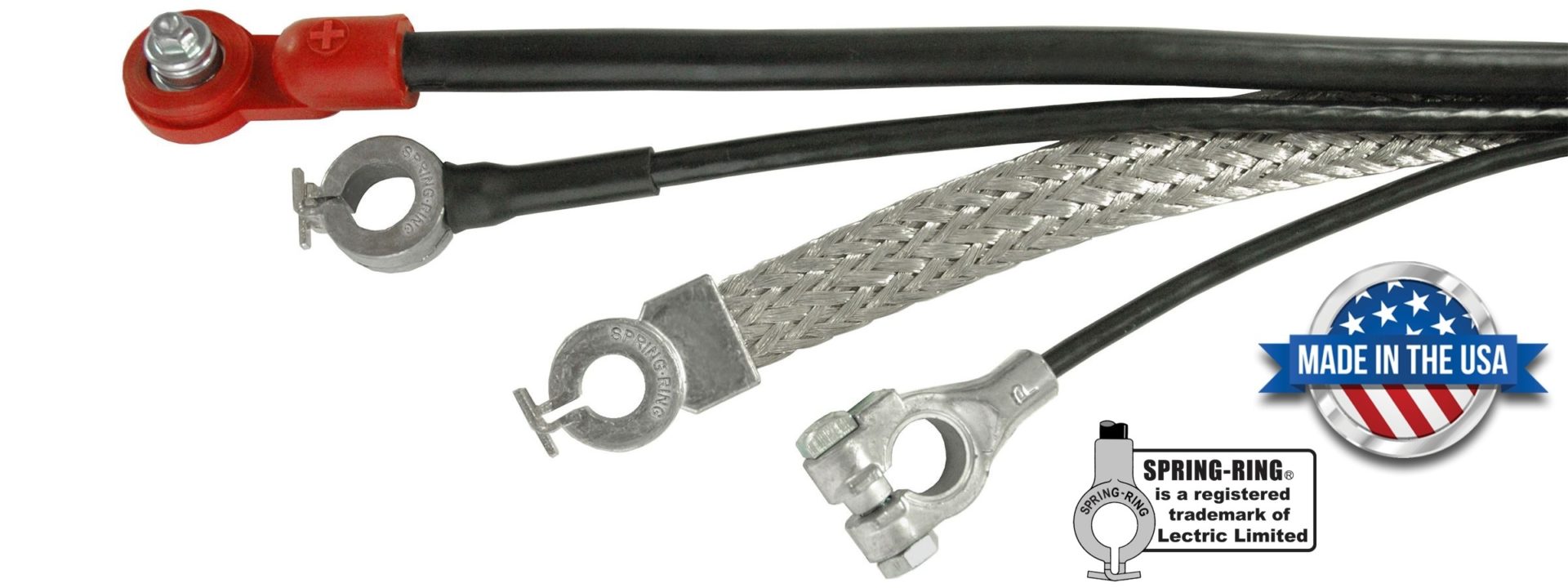
#1 Wire and Cable Manufacturers
Domain Est. 1996
Website: encorewire.com
Key Highlights: Encore Wire is the leading manufacturer of copper and aluminum for residential, commercial and industrial wire needs. We’re unlike any other wire company….
#2 EnerSys
Domain Est. 1997
Website: enersys.com
Key Highlights: Discover EnerSys, the global leader in stored energy solutions, delivering innovative batteries, chargers, and power systems for industrial and ……
#3 East Penn Manufacturing
Domain Est. 2002
Website: eastpennmanufacturing.com
Key Highlights: Wire, Cable & Battery Accessories … A private, family-owned company operating the largest single-site, lead battery manufacturing facility in the world….
#4 Pacer Group
Domain Est. 2008
Website: pacergroup.net
Key Highlights: Pacer is a top US wire and cable manufacturer with products ranging from 18 AWG primary marine wire to 4/0 marine battery cable….
#5 Battery and Power Cables in Wire & Cable
Domain Est. 1992
Website: te.com
Key Highlights: TE’s battery and power cables are designed for in-vehicle power distribution in high temperature applications. The cables carry several hundred Amps….
#6 Southwire
Domain Est. 1994
Website: southwire.com
Key Highlights: Choose Southwire for your wire and cable needs – we offer high-performance products that are built to last….
#7 Power-Sonic
Domain Est. 1995
Website: power-sonic.com
Key Highlights: Power-Sonic delivers innovative battery solutions with sealed lead acid and lithium batteries, energy storage systems, and EV chargers….
#8 Battery Wire & Cable
Domain Est. 1998
Website: waytekwire.com
Key Highlights: 4-day delivery · 30-day returnsWaytek Wire is your source for all your battery cable and battery wire needs, with battery cable available in sizes ranging from a 4/0 gauge to 8 AW…
#9 Quality Copper Battery Cables Made in the USA!
Domain Est. 2014
Website: batterycablesusa.com
Key Highlights: $3.97 delivery 30-day returnsBattery Cables USA is proud to offer the highest quality pure copper battery cables delivering maximum power where and when you need it!…
#10 Custom Cable and Wire
Domain Est. 2022
Website: customcableusa.com
Key Highlights: Custom Cable and Wire is home to custom made battery cables and the best quality US made UL 1426 marine grade wire products for your boat, rv, trailer, ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Battery Wires

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Battery Wires
The global battery wires market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by the accelerating shift toward electrification, advancements in energy storage technologies, and stringent environmental regulations. Battery wires—critical components that ensure safe and efficient electrical connectivity in battery systems—are becoming increasingly vital across industries such as electric vehicles (EVs), renewable energy storage, consumer electronics, and industrial applications. Below is an analysis of the key market trends expected to shape the battery wires landscape in 2026.
-
Surge in Electric Vehicle (EV) Adoption
The most influential driver for battery wire demand is the rapid expansion of the EV market. Governments worldwide are enforcing stricter carbon emission standards and offering incentives for EV adoption. By 2026, global EV sales are projected to exceed 40 million units annually. This growth will directly boost demand for high-performance battery wires capable of handling high currents, thermal fluctuations, and vibration resistance. Automakers are increasingly prioritizing lightweight, high-conductivity wires made from tinned copper or aluminum alloys to improve vehicle efficiency and range. -
Advancements in Battery Technology
Next-generation battery chemistries such as solid-state, lithium-sulfur, and sodium-ion are expected to gain commercial traction by 2026. These technologies often operate under different voltage, temperature, and current conditions than traditional lithium-ion batteries, necessitating specialized wire solutions. Battery wire manufacturers are investing in R&D to develop insulation materials with enhanced thermal stability (e.g., cross-linked polyethylene, silicone rubber) and improved resistance to chemical degradation. -
Growth in Renewable Energy Storage Systems
As solar and wind energy installations expand, so does the need for large-scale energy storage systems (ESS). Battery-based storage projects—especially grid-scale and residential ESS—are proliferating. These systems require robust, long-lasting battery interconnects and wiring to ensure reliability and safety. The trend toward modular battery systems further increases the volume of wiring needed per installation, creating sustained demand for standardized, fire-resistant battery wire solutions. -
Stringent Safety and Regulatory Standards
Safety concerns related to battery thermal runaway and electrical faults are prompting regulators to enforce stricter standards for wiring components. By 2026, compliance with international standards such as UL 457, ISO 6722, and IEC 62196 will be mandatory in most markets. This is pushing manufacturers to adopt flame-retardant, low-smoke, and halogen-free insulation materials. Additionally, traceability and durability testing are becoming prerequisites in high-risk applications, especially in transportation and aerospace. -
Regional Market Shifts
Asia-Pacific, led by China, Japan, and South Korea, will remain the dominant hub for both battery and battery wire production due to strong government support and established supply chains. However, North America and Europe are rapidly expanding domestic EV and battery manufacturing capacities under initiatives like the U.S. Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) and the European Battery Alliance. This regional reshoring is fostering local battery wire production, reducing dependency on imports and encouraging innovation in material sourcing and manufacturing processes. -
Sustainability and Recycling Initiatives
Environmental sustainability is gaining importance across the battery value chain. By 2026, there will be increased emphasis on recyclable and eco-friendly battery wiring materials. Manufacturers are exploring biodegradable insulation options and closed-loop recycling systems for copper and other conductive materials. Regulatory pressure and corporate ESG goals are accelerating this shift. -
Integration of Smart Wiring and Monitoring
Emerging trends include the integration of sensors and smart monitoring capabilities into battery wires. These “intelligent” wires can detect temperature anomalies, current imbalances, or insulation wear in real time, improving system safety and predictive maintenance. While still in early adoption, this technology is expected to become more prevalent in premium EVs and critical infrastructure by 2026.
Conclusion
By 2026, the battery wires market will be characterized by heightened demand, technological innovation, and a focus on safety, sustainability, and performance. Companies that adapt to evolving battery technologies, regional regulations, and smart integration opportunities will be best positioned to capture market share. As electrification continues to accelerate across sectors, battery wires will remain a foundational yet increasingly sophisticated component of the global energy transition.
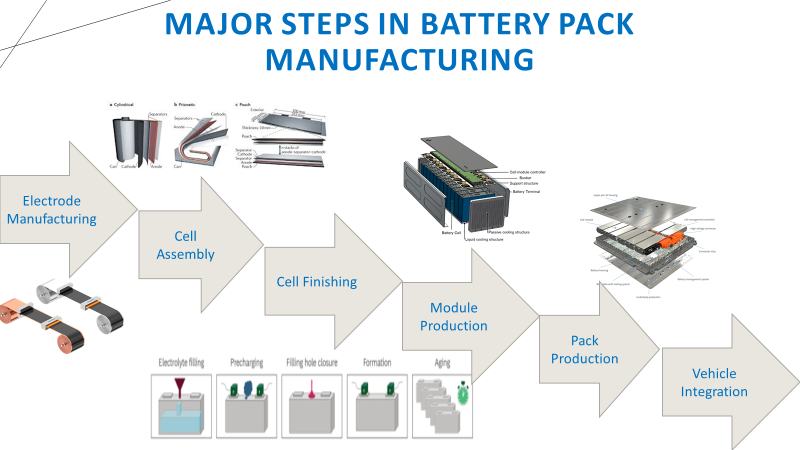
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Battery Wires: Quality and Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
Sourcing battery wires—critical components in electric vehicles, renewable energy systems, and consumer electronics—requires careful attention to both quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these aspects can lead to safety hazards, product failures, legal disputes, and reputational damage. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Inadequate Material Specifications
A common mistake is failing to define precise material requirements such as conductor purity (e.g., oxygen-free copper), insulation type (e.g., cross-linked polyethylene, XLPE), and temperature ratings. Sourcing wires with substandard materials can result in increased resistance, overheating, or premature insulation breakdown.
2. Lack of Compliance with Industry Standards
Battery wires must meet rigorous standards like UL, ISO, IEC, or automotive-specific norms (e.g., ISO 6722). Procuring components without proper certification increases the risk of non-compliance, product recalls, and safety incidents—especially under high-voltage or high-temperature conditions.
3. Inconsistent Manufacturing Processes
Suppliers with poor process controls may deliver inconsistent wire gauge, insulation thickness, or shielding integrity. Without regular audits or production line inspections, such inconsistencies may go undetected until failure occurs in the field.
4. Insufficient Testing and Validation
Relying solely on supplier-provided test reports without third-party validation or in-house testing (e.g., dielectric strength, thermal cycling, abrasion resistance) can mask latent defects. Battery systems demand rigorous qualification protocols to ensure long-term reliability.
5. Counterfeit or Gray Market Components
Purchasing from unauthorized distributors or low-cost suppliers increases exposure to counterfeit wires that mimic specifications but fail under real-world conditions. These components often lack traceability and quality documentation.
Intellectual Property (IP)-Related Pitfalls
1. Unlicensed Use of Proprietary Designs
Some battery wire designs—especially those with unique geometries, shielding configurations, or connector integrations—are patented. Sourcing generic equivalents without verifying freedom to operate can lead to infringement claims, litigation, or forced redesigns.
2. Supplier Confidentiality Breaches
Sharing detailed technical requirements or schematics with potential suppliers without robust Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs) risks exposure of proprietary system designs. This is especially critical in competitive markets like EVs or energy storage.
3. Lack of IP Ownership Clauses in Contracts
Contracts that fail to clarify IP ownership—particularly for custom-designed wires—can result in disputes. For instance, if a supplier develops a tailored solution, they may claim rights to the design, limiting your ability to switch manufacturers or scale production.
4. Reverse Engineering Risks
Engaging suppliers in regions with weak IP enforcement increases the risk that your wire specifications or assembly methods could be reverse-engineered and sold to competitors. Due diligence on supplier locations and legal environments is essential.
5. Inadequate Documentation and Traceability
Poor record-keeping of sourcing decisions, design iterations, and supplier communications can weaken your position in IP disputes. Maintaining a clear audit trail supports defense against infringement allegations and ensures design integrity.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls, implement a structured sourcing strategy including:
– Rigorous supplier qualification and on-site audits
– Clear technical specifications and compliance requirements
– Third-party testing and batch validation
– Comprehensive contracts with IP clauses and NDAs
– Ongoing monitoring of supply chain integrity and IP landscape
By proactively addressing both quality and IP concerns, companies can ensure reliable performance, regulatory compliance, and protection of their innovations when sourcing battery wires.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Battery Wires
Overview
Battery wires are critical components in energy storage, automotive, industrial, and consumer electronics systems. Due to their conductive nature and frequent integration with batteries—especially lithium-based systems—they are subject to stringent logistics and regulatory compliance requirements. This guide outlines key considerations for the safe and compliant transportation, storage, handling, and documentation of battery wires.
Classification and Regulatory Framework
Battery wires themselves are typically not classified as hazardous materials unless they are part of or attached to batteries. However, when shipped with or integrated into battery systems, they may fall under hazardous goods regulations. Key regulatory standards include:
– UN Recommendations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods (UN Model Regulations)
– IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations (for air transport)
– IMDG Code (for sea transport)
– 49 CFR (U.S. Department of Transportation for domestic and international ground transport)
– REACH and RoHS (for material compliance in the EU)
Ensure battery wires comply with substance restrictions, especially concerning lead, cadmium, and other restricted materials.
Packaging and Labeling Requirements
Proper packaging is essential to prevent short circuits, physical damage, and environmental exposure:
– Use non-conductive, durable packaging materials to insulate wire ends.
– Seal terminals with tape or protective caps to prevent accidental contact.
– Clearly label packages with:
– Product identification (e.g., part number, voltage rating)
– Manufacturer information
– RoHS/REACH compliance marks (if applicable)
– If bundled with batteries, apply appropriate UN hazard labels (e.g., Class 9 for lithium batteries)
Transportation Considerations
- Air Freight: Battery wires alone are generally not restricted. However, if integrated into battery packs or shipped with batteries, IATA regulations apply. Lithium battery shipments require special packaging, documentation, and labeling.
- Sea Freight: Follow IMDG Code requirements for hazardous cargo if batteries are included. Ensure proper stowage and segregation from incompatible materials.
- Ground Transport (e.g., truck, rail): Comply with 49 CFR or ADR (Europe) as applicable. Even non-hazardous wires should be secured to prevent shifting or damage.
Storage and Handling
- Store in a dry, temperature-controlled environment to prevent insulation degradation.
- Keep away from corrosive substances, sharp objects, and sources of heat or ignition.
- Handle with clean gloves to avoid contamination, especially in cleanroom or OEM assembly environments.
- Use proper lifting equipment for bulk shipments to avoid strain or cable damage.
Documentation and Traceability
Maintain accurate records for compliance and quality assurance:
– Material Declarations: Provide RoHS, REACH, and Conflict Minerals compliance statements.
– Certificates of Conformance (CoC): Include electrical specifications, insulation type, and temperature ratings.
– Safety Data Sheets (SDS): Required if hazardous materials are present (e.g., PVC insulation with flame retardants).
– Bill of Lading and Packing Lists: Clearly describe contents, quantities, and handling instructions.
Environmental and Disposal Compliance
- Recycle scrap wires through certified e-waste programs.
- Comply with WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) directives in applicable regions.
- Avoid landfill disposal due to metal content (copper, aluminum) and potential environmental impact.
Key Best Practices
- Segregate battery wires from live batteries during shipping unless pre-assembled and properly protected.
- Train personnel on hazardous materials handling if shipping with batteries.
- Conduct regular audits of suppliers to ensure ongoing compliance with environmental and safety standards.
- Use serialization or barcoding for traceability throughout the supply chain.
Conclusion
While battery wires are not inherently hazardous, their integration with power systems and regulatory frameworks demands careful attention to logistics and compliance. Adhering to international standards, proper packaging, and thorough documentation ensures safe delivery, regulatory compliance, and supply chain integrity. Always consult the latest versions of transport regulations and engage certified dangerous goods safety officers when applicable.
Conclusion for Sourcing Battery Wires:
Sourcing battery wires requires a careful evaluation of quality, specifications, cost, and reliability to ensure optimal performance and safety in the intended application. It is essential to select wires that meet industry standards for conductivity, temperature resistance, insulation, and durability—particularly in demanding environments such as automotive, renewable energy systems, or industrial equipment. Partnering with reputable suppliers who provide consistent quality, traceable materials, and compliance with certifications (such as UL, CSA, or RoHS) helps mitigate risks associated with failures or inefficiencies. Additionally, considering long-term cost factors—like maintenance, lifespan, and energy efficiency—rather than focusing solely on upfront pricing contributes to a more sustainable and cost-effective solution. Ultimately, a strategic sourcing approach that balances technical requirements with supply chain reliability ensures the performance, safety, and longevity of battery-powered systems.