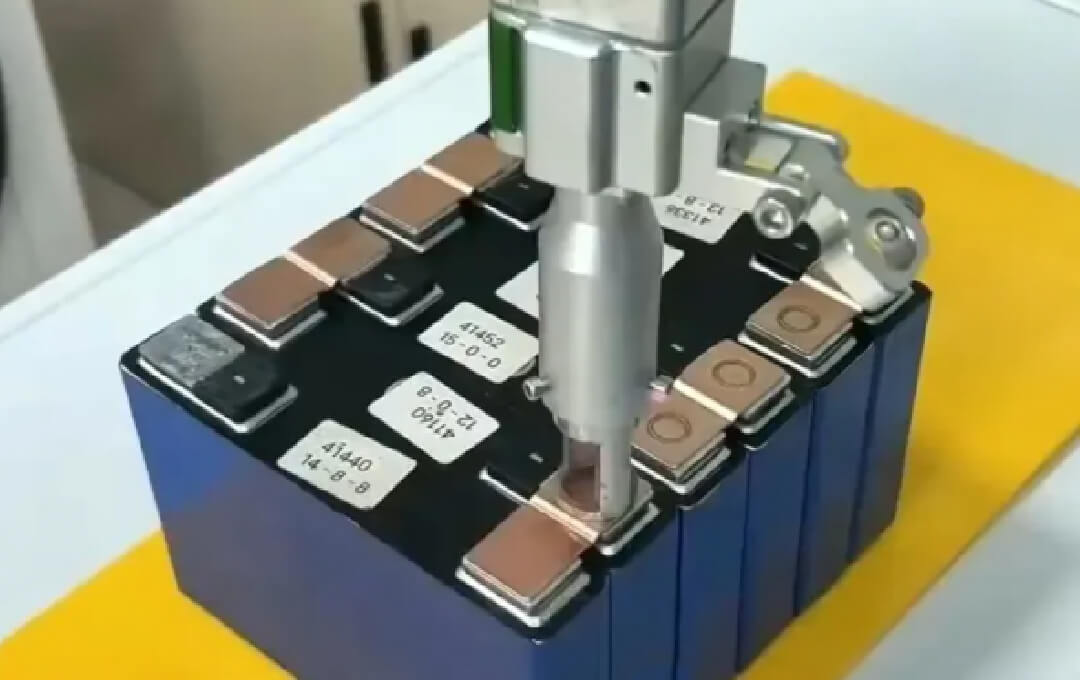
The global battery laser welding market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by the rising demand for high-precision, high-speed joining solutions in lithium-ion battery manufacturing for electric vehicles (EVs), consumer electronics, and energy storage systems. According to Grand View Research, the global laser welding market size was valued at USD 4.5 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.7% from 2023 to 2030. A significant portion of this growth is attributed to the surging production of EVs and the need for reliable, hermetic sealing in battery pack assembly—processes where laser welding outperforms traditional methods in accuracy and efficiency. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence projects the battery manufacturing equipment market to expand at a CAGR of over 15% during the forecast period (2023–2028), with laser welding systems playing a pivotal role due to their compatibility with thin foils, high conductivity metals, and automated production lines. As demand for safer, longer-lasting, and faster-charging batteries intensifies, manufacturers are turning to advanced laser welding technologies, placing leading equipment suppliers at the heart of the electrification revolution. This growing reliance on precision welding has elevated the prominence of specialized battery laser welding manufacturers worldwide—here are ten at the forefront.
Top 10 Battery Laser Welding Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Laser Welding
Website: huiyaolaser.com
Key Highlights: Huiyao Laser is a leading battery laser welding machine manufacturer offering professional battery pack and battery module welding solutions for many fields, ……
#2 LaserStar Technologies
Website: laserstar.net
Key Highlights: LaserStar Technologies designs and manufactures high-performance laser welding, marking, and cutting systems for industrial, jewelry, ……
#3 China Battery Welding Machine Factory
Website: heltec-energy.com
Key Highlights: This is a Lithium Battery Special Handheld Galvanometer-Type Laser Welding Machine, supporting welding 0.3mm-2.5mm copper/aluminum. Main applications: spot ……
#4 EV Battery Welding & Battery Manufacturing
Website: laserax.com
Key Highlights: We offer a laser welding service to weld complete battery packs. This is ideal if you need to start welding while are waiting for a machine order, if you need ……
#5 RMA Battery Laser Welder
Website: laserbatterywelder.com
Key Highlights: At RMA #LaserExperts, we lead in Battery Laser Welding, offering advanced, tailored solutions for the US and Europe battery industry….
#6 IPG Photonics
Website: ipgphotonics.com
Key Highlights: IPG Photonics manufactures high-performance fiber lasers, amplifiers, and laser systems for diverse applications and industries. Discover your solution….
#7 Laser systems for e
Website: fivesgroup.com
Key Highlights: High precision laser welding solutions for lightweight e-mobility applications · Effectively joining dissimilar materials such as aluminium and copper ……
#8 Unique, Safe, Efficient
Website: boschmanufacturingsolutions.com
Key Highlights: InFly Laser Welding stands for intelligent, optically guided, on-the-fly laser welding of battery cell connectors….
#9 Battery Industry
Website: amadaweldtech.com
Key Highlights: AMADA WELD TECH offers a production solution: resistance welding, laser welding, laser marking, laser surface cleaning or laser cutting….
#10 EV Battery Manufacturing
Website: coherent.com
Key Highlights: Learn how Coherent fiber lasers deliver the best and most economical solution for the precise and demanding welding tasks of EV battery production….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Battery Laser Welding
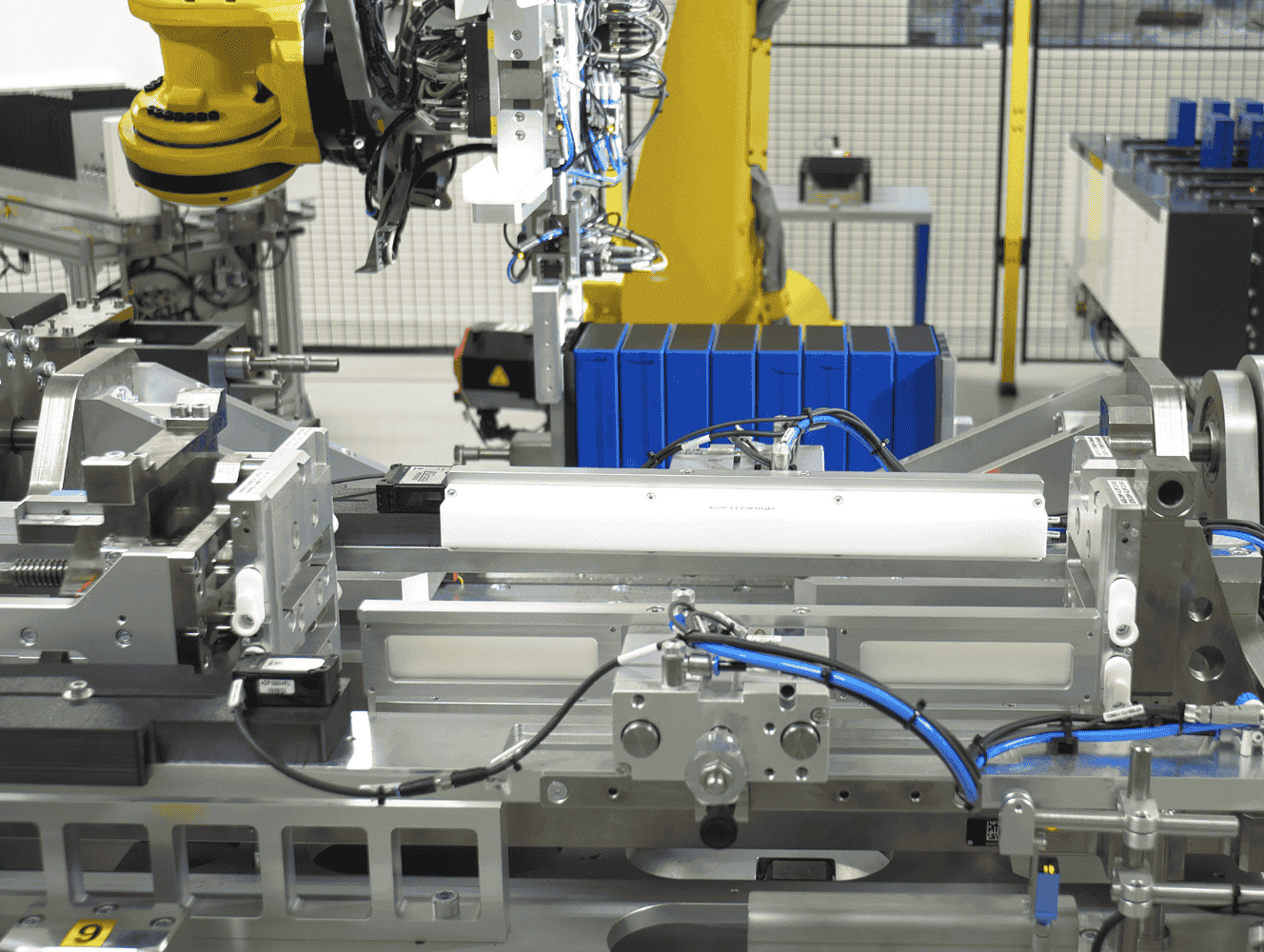
H2: 2026 Market Trends in Battery Laser Welding
The battery laser welding market is poised for substantial transformation by 2026, driven by the rapid expansion of the electric vehicle (EV) industry, advancements in battery technology, and increasing demand for high-precision, efficient manufacturing processes. This analysis outlines key market trends expected to shape the battery laser welding sector in 2026.
-
Rising Demand from Electric Vehicle Manufacturers
By 2026, the global push toward electrification of transportation will continue to be the primary growth driver for battery laser welding. As EV adoption accelerates—supported by government regulations, consumer preferences, and declining battery costs—automakers will expand production capacity. This growth will increase the need for high-speed, reliable laser welding systems to assemble battery cells, modules, and packs. Manufacturers will prioritize laser welding for its precision, minimal heat distortion, and ability to join dissimilar materials such as copper and aluminum. -
Adoption of High-Power and Ultrashort Pulse Lasers
Technological advancements in laser sources will play a pivotal role in 2026. High-power fiber lasers (3 kW and above) will become standard in high-throughput battery production lines, enabling faster welding speeds and deeper penetration. Additionally, ultrashort pulse (USP) lasers will gain traction for micro-welding applications in prismatic and pouch cells, where minimal thermal impact is critical to battery safety and longevity. -
Integration of Automation and Smart Manufacturing
The battery laser welding market will see deeper integration with Industry 4.0 technologies. By 2026, welding systems will increasingly feature real-time monitoring, AI-driven process optimization, and closed-loop feedback systems for quality assurance. Automated guided vehicles (AGVs), robotic arms, and digital twin technologies will streamline production, reducing downtime and improving yield rates across gigafactories. -
Focus on Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
Sustainability will become a competitive differentiator. Laser welding systems will be evaluated not only on performance but also on energy consumption and recyclability. Equipment manufacturers will emphasize energy-efficient designs and low-emission operations to align with ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) goals of battery producers. -
Geopolitical and Supply Chain Dynamics
Regionalization of battery production—especially in North America, Europe, and Southeast Asia—will influence laser welding equipment demand. In response to trade policies and supply chain resilience concerns, OEMs and tier suppliers will localize manufacturing, driving investment in domestic laser welding infrastructure. This shift will benefit regional laser technology providers and foster partnerships between laser system integrators and battery gigafactories. -
Growth in Solid-State and Next-Gen Battery Production
As solid-state and sodium-ion batteries move toward commercialization by 2026, new welding challenges will emerge. These next-generation batteries often require hermetic sealing and delicate joining processes, where laser welding’s non-contact, clean joining capability will be crucial. Innovations in beam shaping, wavelength selection (e.g., green and blue lasers for copper welding), and hybrid welding techniques will address these evolving needs. -
Consolidation and Strategic Partnerships
The market will likely witness increased consolidation among laser technology providers and strategic alliances with battery manufacturers. Key players will expand their portfolios through mergers and acquisitions to offer turnkey welding solutions. Collaborations between laser OEMs and battery cell producers will accelerate co-development of customized welding processes optimized for specific cell formats and chemistries.
In conclusion, the 2026 battery laser welding market will be characterized by technological innovation, automation, and alignment with broader trends in clean energy and advanced manufacturing. Companies that invest in scalable, intelligent, and sustainable laser welding solutions will be best positioned to capture growth in this high-potential sector.
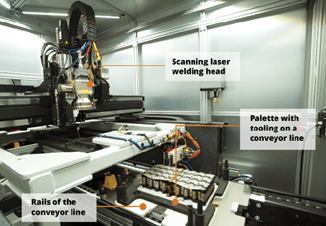
Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Battery Laser Welding Equipment: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing battery laser welding equipment is critical for ensuring the performance, safety, and longevity of battery cells and packs. However, organizations often encounter significant challenges related to quality inconsistencies and intellectual property (IP) vulnerabilities. Overlooking these pitfalls can result in production delays, safety hazards, legal disputes, and compromised product integrity.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inadequate Process Validation and Repeatability
Many suppliers offer laser welding systems without comprehensive validation under real-world battery manufacturing conditions. A common issue is inconsistent weld penetration, spatter formation, or porosity—defects that compromise weld strength and electrical conductivity. Without rigorous statistical process control (SPC) data and proven repeatability across batch runs, buyers risk integrating unreliable equipment. Always demand documented weld quality metrics (e.g., tensile strength, hermeticity test results) and insist on on-site process validation using your specific cell formats and materials.
Substandard Component Selection
Lower-cost suppliers may cut corners by using inferior optics, cooling systems, or motion stages. These components directly impact long-term reliability and maintenance frequency. For example, non-industrial-grade lasers or poorly calibrated galvanometers can lead to beam instability and weld defects. Scrutinize the bill of materials (BOM), request component certifications, and verify compatibility with high-volume, 24/7 production environments.
Lack of Industry-Specific Expertise
Battery welding demands specialized knowledge—such as managing reflective materials (copper, aluminum), controlling heat input to avoid thermal runaway, and meeting stringent cleanliness standards. Generic laser welding suppliers without battery sector experience may not understand these nuances, leading to inadequate system design. Prioritize suppliers with a proven track record in lithium-ion or solid-state battery production.
Intellectual Property-Related Pitfalls
Ambiguous IP Ownership in Custom Solutions
When co-developing or customizing laser welding systems (e.g., unique fixturing, control algorithms), unclear contractual terms can result in disputes over IP ownership. Suppliers may retain rights to process innovations, limiting your ability to scale or transfer technology. Always define IP ownership, licensing terms, and field-of-use rights in writing before project initiation. Ensure your proprietary welding parameters and process data remain exclusively yours.
Reverse Engineering and Technology Leakage
Working with suppliers—especially in regions with weaker IP enforcement—poses risks of design replication or unauthorized use of know-how. Suppliers might leverage insights from your project to develop competing solutions. Mitigate this by using non-disclosure agreements (NDAs), limiting technical disclosure to essential personnel, and conducting IP audits of supplier facilities when feasible.
Dependency on Proprietary Software and Controls
Many laser systems rely on closed-source software for monitoring, diagnostics, and process optimization. This creates vendor lock-in and hinders your ability to integrate with existing Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) or perform independent data analysis. Demand open APIs, source code escrow agreements, or access to software development kits (SDKs) to maintain control over your production data and workflows.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP pitfalls during the sourcing process—through rigorous due diligence, clear contractual agreements, and supplier vetting—organizations can secure reliable, scalable, and legally protected laser welding solutions for advanced battery manufacturing.
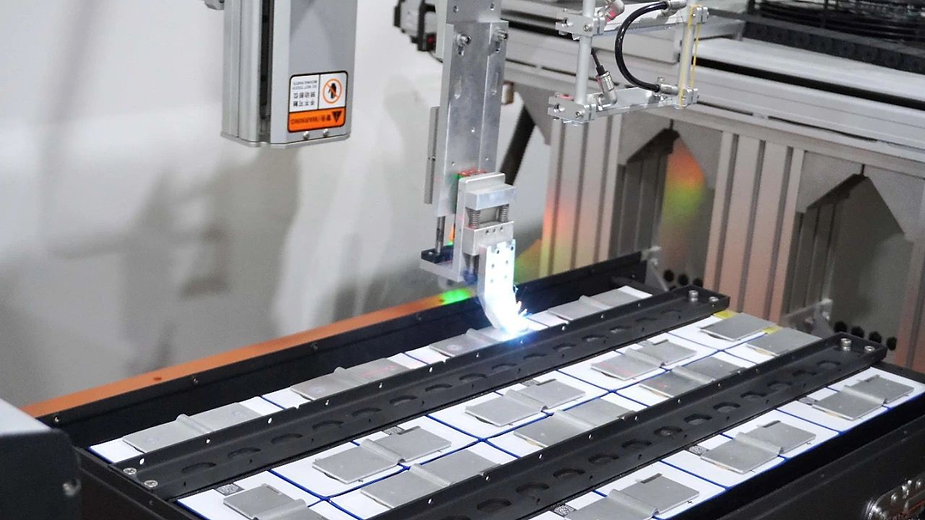

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Battery Laser Welding
Overview of Battery Laser Welding in Manufacturing
Battery laser welding is a precision joining process critical in the production of lithium-ion and other advanced battery cells and packs used in electric vehicles, consumer electronics, and energy storage systems. Due to the high energy density of batteries and the sensitive nature of laser equipment, proper logistics and compliance protocols are essential to ensure safety, product quality, and regulatory adherence throughout the supply chain and manufacturing lifecycle.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
International and National Standards
Battery laser welding operations must comply with a range of international and national regulations, including:
- IEC 61400-23 / ISO 13849: For machinery safety, including laser systems.
- ANSI Z136.1 (USA): Safe use of lasers, covering classification, controls, and protective measures.
- IEC 60825: International standard for laser product safety.
- UN 38.3: Required for the transportation of lithium batteries, ensuring they pass vibration, shock, and thermal tests.
- RoHS and REACH (EU): Restriction of hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment.
- OSHA 29 CFR 1910 (USA): Workplace safety standards, particularly for laser operations and hazardous energy control.
Industry-Specific Compliance
- Automotive (IATF 16949): Quality management system specific to automotive production, including traceability and process control for battery welding.
- UL 1973 / UL 9540A: Safety standards for battery energy storage systems, often requiring verified welding integrity.
- AQAP 2000 (NATO): May apply for defense-related battery systems.
Hazardous Material Handling and Transportation
Classification of Battery Components
Lithium-ion battery cells and packs are classified as Class 9 hazardous materials under the UN Model Regulations (UN 3480, UN 3481). Pre-weld components such as nickel, copper, and aluminum foils are generally non-hazardous but must be stored and handled to prevent contamination.
Packaging and Labeling Requirements
- Batteries intended for integration must be packaged to prevent short circuits, physical damage, and thermal runaway.
- Use of non-conductive inner packaging, rigid outer containers, and proper UN-certified packaging.
- Required labels: Class 9 hazard label, lithium battery handling mark, and orientation arrows.
- Documentation: Shipper’s Declaration for Dangerous Goods, Safety Data Sheets (SDS).
Transport Modes and Restrictions
- Air (IATA DGR): Strict limits on state of charge (typically ≤30%), quantity per package, and crew notification.
- Sea (IMDG Code): Stowage segregation, temperature monitoring, and ventilation requirements.
- Ground (ADR in Europe, 49 CFR in USA): Driver training, placarding, and emergency response plans.
Laser Safety and Operational Compliance
Laser Classification and Control Measures
- Most industrial laser welders used in battery manufacturing are Class 4 lasers, requiring strict engineering and administrative controls.
- Mandatory use of laser safety enclosures, interlocks, and beam shutters.
- Installation of warning signs and lights indicating laser operation.
- Use of laser protective eyewear with appropriate optical density (OD) for the laser wavelength (commonly 1,064 nm for fiber lasers).
Workplace Safety Protocols
- Conduct laser safety audits and appoint a Laser Safety Officer (LSO).
- Implement lockout/tagout (LOTO) procedures during maintenance.
- Train all personnel on emergency shutdown procedures and first aid for laser exposure.
- Install fume extraction systems to manage metal vapor and particulate byproducts from welding.
Environmental, Health, and Safety (EHS) Considerations
Air Quality and Emissions Control
- Laser welding generates metal fumes (e.g., nickel, chromium, manganese) and nanoparticles, requiring local exhaust ventilation (LEV) and high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filtration.
- Regular testing of workplace air quality to comply with OSHA PELs or ACGIH TLVs.
- Monitor for ozone and nitrogen oxides if using high-power pulsed lasers in ambient air.
Waste Management
- Collect and dispose of contaminated filters, weld spatter, and scrap electrodes as hazardous waste if they contain regulated metals.
- Recycle copper, nickel, and aluminum scraps through certified e-waste or metal reclamation facilities.
- Maintain records for waste manifests and disposal compliance.
Supply Chain and Inventory Management
Component Traceability
- Implement barcoding or RFID tracking for battery cells, foils, and welded assemblies to support full traceability.
- Maintain logs of welding parameters (power, speed, pulse duration) for quality audits and failure analysis.
Just-in-Time (JIT) Logistics
- Coordinate delivery schedules to minimize on-site storage of lithium batteries, reducing fire risk.
- Use climate-controlled storage areas (typically 20–25°C, 40–60% RH) to preserve battery performance and safety.
- Validate supplier compliance with conflict minerals regulations (e.g., Dodd-Frank Section 1502) and carbon footprint reporting (e.g., GHG Protocol).
Quality Assurance and Process Validation
Welding Process Controls
- Follow validated welding procedures (WPS) with documented acceptance criteria.
- Use in-process monitoring such as weld seam cameras, pyrometers, and acoustic sensors.
- Perform destructive testing (e.g., peel tests, micro-sectioning) and non-destructive testing (e.g., X-ray, ultrasonic) on sample welds.
Calibration and Maintenance
- Calibrate laser power meters, beam profilers, and motion systems according to manufacturer and ISO 9001 requirements.
- Maintain logs of preventive maintenance and corrective actions.
Emergency Preparedness and Response
Fire Safety
- Install lithium battery fire suppression systems (e.g., water mist, aerosol, or specialized dry chemical agents).
- Provide fire-resistant storage cabinets for batteries and charged cells.
- Train staff in lithium battery fire response, including the use of thermal runaway propagation barriers.
Spill and Exposure Response
- Equip work areas with spill kits for electrolyte leaks (often flammable and toxic).
- Establish eye wash stations and safety showers within 10 seconds’ reach of laser and battery handling zones.
- Develop and practice emergency evacuation plans specific to fire, toxic release, or laser incidents.
Documentation and Audit Readiness
Required Records
- Laser safety program documentation
- Employee training records (laser safety, hazardous materials, emergency response)
- Equipment maintenance and calibration logs
- Batch records with welding parameters and QA results
- SDS for all chemicals and materials
- Shipping documentation and transport compliance records
Internal and External Audits
- Conduct quarterly internal audits to verify compliance with EHS, quality, and logistics standards.
- Prepare for third-party audits by certification bodies (e.g., TÜV, UL, Bureau Veritas) with up-to-date documentation and facility walkthroughs.
Conclusion
Successful logistics and compliance in battery laser welding require an integrated approach that spans regulatory adherence, safety engineering, environmental protection, and supply chain integrity. By implementing robust controls and documentation practices, manufacturers can ensure safe, efficient, and legally compliant operations in this high-precision, high-risk domain.
Conclusion for Sourcing Battery Laser Welding Systems:
Sourcing laser welding technology for battery manufacturing is a strategic decision that directly impacts production quality, efficiency, and long-term scalability. As the demand for high-performance batteries—particularly for electric vehicles and energy storage systems—continues to rise, precision joining methods like laser welding have become critical to ensuring reliability, safety, and consistency in cell assembly.
When sourcing laser welding systems, key factors must be carefully evaluated, including welding precision, process speed, system integration capabilities, maintenance requirements, and total cost of ownership. Fiber lasers with pulsed or continuous-wave (CW) modes have proven effective for various battery welding applications, such as tab-to-terminal, busbar, and cell-to-module connections, due to their minimal heat input, high repeatability, and compatibility with reflective materials like copper and aluminum.
Additionally, supplier expertise, technical support, and compliance with industry standards (e.g., ISO, UL, or IATF) are essential for ensuring long-term success. Investing in automated, modular, and scalable laser welding solutions not only enhances manufacturing yield but also supports future technology upgrades and shifts in battery formats.
In conclusion, sourcing the right laser welding solution requires a holistic evaluation of technology, supplier capability, and alignment with production goals. A well-chosen system will enhance battery performance, improve production throughput, and position the manufacturer competitively in the rapidly evolving energy and mobility markets.