The global ventilation equipment market is experiencing steady expansion, driven by increasing awareness of indoor air quality, stringent building regulations, and rising construction activities. According to Grand View Research, the global HVAC market size was valued at USD 176.8 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.2% from 2023 to 2030. A key segment within this market is basement exhaust systems, essential for moisture control, odor removal, and maintaining healthy living environments in below-grade spaces. With the growing demand for energy-efficient and smart ventilation solutions, manufacturers are innovating rapidly to meet evolving consumer and regulatory needs. As the residential and commercial construction sectors continue to expand—particularly in North America and Europe—the need for reliable basement exhaust systems has never been more critical. In this landscape, eight manufacturers have emerged as industry leaders, combining technological innovation, performance reliability, and strong market presence to lead the basement ventilation segment.
Top 8 Basement Exhaust Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Tjernlund Products, Inc.
Domain Est. 1997
Website: tjernlund.com
Key Highlights: Tjernlund Products is a premier manufacturer of mechanical ventilation and exhaust solutions tailored for both residential and commercial applications….
#2 Vent
Domain Est. 1996 | Founded: 1936
Website: vent-axia.com
Key Highlights: Since 1936, Vent-Axia has been manufacturing a large range of efficient ventilation products helping improve indoor air quality in homes and commercial ……
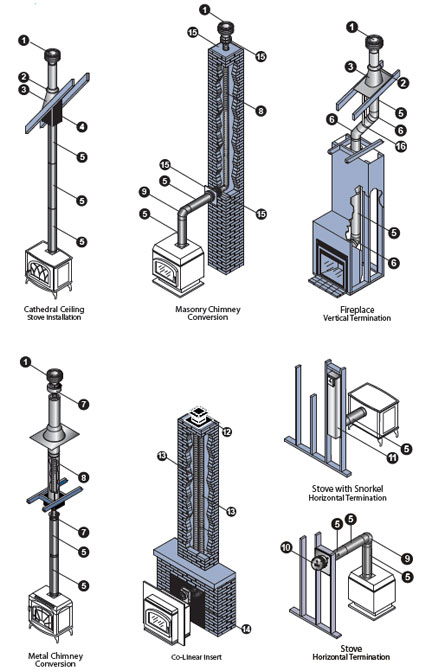
#3 Duravent
Domain Est. 1996
Website: duravent.com
Key Highlights: Consistently the first to market with new innovations in venting systems, Duravent has captured a leadership position in emerging markets….
#4 Sustainable, energy
Domain Est. 1998
Website: systemair.com
Key Highlights: Our mission is to bring fresh, clean, and healthy air to your spaces, with Fans, Air Handling Units, Residential Ventilation Systems and more….
#5 Broan-NuTone
Domain Est. 1999
Website: broan-nutone.com
Key Highlights: Broan-NuTone headquartered in the US, produces Range Hoods, Bath Exhaust Ventilation Fans, and Balanced Ventilation/Fresh Air Systems to improve the air you ……
#6 Air King Homepage
Domain Est. 2000
Website: airkinglimited.com
Key Highlights: At Air King we pride ourselves in the expert knowledge of exhaust fans, range hoods, fresh air intake, and air circulator fans….
#7 Basement Ventilation System
Domain Est. 2002
Website: ezbreathe.com
Key Highlights: EZ Breathe Ventilation System creates a much-needed path of escape for the dirty basement air and introduces the existing clean, dry air from upstairs….
#8 Crawlspace Exhaust Fan
Domain Est. 2012
Expert Sourcing Insights for Basement Exhaust

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Basement Exhaust Systems
As we approach 2026, the basement exhaust systems market is undergoing significant transformation driven by advancements in smart home technology, increasing awareness of indoor air quality (IAQ), and evolving building regulations. Below are the key trends shaping the industry:
1. Integration with Smart Home Ecosystems
Basement exhaust systems are becoming increasingly integrated with smart home platforms such as Google Home, Amazon Alexa, and Apple HomeKit. By 2026, manufacturers are prioritizing Wi-Fi-enabled and app-controlled ventilation units that allow homeowners to monitor humidity levels, control fan speeds remotely, and receive maintenance alerts. This trend is fueled by consumer demand for convenience, energy efficiency, and real-time environmental monitoring.
2. Focus on Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
With global emphasis on reducing carbon emissions and advancing green building standards (e.g., LEED, ENERGY STAR), basement exhaust systems are being redesigned for lower energy consumption. Energy recovery ventilators (ERVs) and heat recovery ventilators (HRVs) are gaining traction, especially in regions with extreme climates. These systems recover heat or coolness from exhaust air, reducing the load on HVAC systems and lowering utility costs.
3. Rising Demand for Mold and Moisture Prevention
Basements are particularly prone to moisture accumulation, leading to mold growth and structural damage. In 2026, consumers and contractors are placing greater emphasis on proactive ventilation solutions. Advanced basement exhaust systems now come with built-in humidity sensors and automatic activation triggers, ensuring consistent moisture control without manual intervention.
4. Regulatory Push for Improved Indoor Air Quality
Governments and building code authorities in North America, Europe, and parts of Asia are tightening IAQ requirements. New construction and renovation projects are increasingly mandated to include mechanical ventilation in basements, especially when used as living spaces (e.g., home gyms, offices, or bedrooms). These regulations are driving market growth and encouraging innovation in quieter, more efficient exhaust technologies.
5. Growth in DIY and Retrofit Markets
The rise of DIY home improvement culture, supported by online tutorials and e-commerce platforms, is expanding the market for easy-to-install basement exhaust systems. Compact, modular units designed for retrofit applications are gaining popularity, allowing homeowners to upgrade ventilation without major renovations. This trend is particularly strong in aging housing stock in the U.S. and Western Europe.
6. Advancements in Noise Reduction Technology
Consumer expectations for quieter home environments are pushing manufacturers to develop ultra-quiet exhaust fans. By 2026, leading brands are incorporating sound-dampening materials, optimized fan blade designs, and variable speed motors to minimize operational noise—critical for basement living areas used as entertainment rooms or guest suites.
7. Regional Market Divergence
North America and Western Europe lead in market adoption due to stringent building codes and high homeownership rates. Meanwhile, emerging markets in Asia-Pacific and the Middle East are beginning to see growth, driven by urbanization, rising disposable incomes, and increased awareness of healthy living environments.
Conclusion
By 2026, the basement exhaust market will be defined by intelligence, efficiency, and health-conscious design. Companies that prioritize smart integration, energy savings, and IAQ performance will be best positioned to capture growing consumer and regulatory demand. As basements evolve into functional living spaces, effective ventilation will no longer be optional—it will be a cornerstone of modern home design.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Basement Exhaust Systems (Quality and IP)
Sourcing basement exhaust systems requires careful attention to both quality and Ingress Protection (IP) ratings to ensure long-term performance, safety, and compliance. Overlooking key factors can lead to premature failures, safety hazards, or ineffective ventilation. Below are common pitfalls to avoid:
1. Ignoring IP Rating Requirements for the Environment
One of the most frequent mistakes is selecting an exhaust fan without verifying the appropriate IP rating for the basement environment. Basements are prone to moisture, dust, and occasional water exposure (e.g., minor flooding or condensation).
- Pitfall: Using a fan with too low an IP rating (e.g., IP20) in a damp or humid basement, leading to corrosion, short circuits, or motor failure.
- Best Practice: Opt for a minimum of IP44 (protected against solid objects >1mm and splashing water from any direction) for most basements. In areas prone to flooding or high humidity, consider IP55 or higher.
2. Prioritizing Cost Over Build Quality
Choosing the cheapest available option often results in subpar materials and construction, especially with motors, housings, and fan blades.
- Pitfall: Low-cost fans may use plastic components that degrade quickly, underpowered motors that fail under continuous use, or poorly balanced impellers that cause excessive noise and vibration.
- Best Practice: Evaluate material quality (e.g., corrosion-resistant housings, sealed motors), motor durability (e.g., ball bearings vs. sleeve bearings), and manufacturer reputation. Invest in commercial-grade units for critical applications.
3. Overlooking Continuous Duty Rating
Basement exhaust systems often need to run for extended periods to manage humidity and air quality.
- Pitfall: Selecting a fan not rated for continuous operation, which can overheat and fail prematurely.
- Best Practice: Ensure the unit is explicitly rated for continuous duty (24/7 operation) and has thermal protection to prevent burnout.
4. Mismatched Airflow Capacity (CFM)
Undersizing or oversizing the exhaust fan leads to inefficiency and poor air quality.
- Pitfall: An undersized fan fails to remove sufficient moisture and contaminants; an oversized fan can create negative pressure, backdrafting issues, or excessive noise.
- Best Practice: Calculate required airflow based on basement size, usage, and ventilation needs (typically 0.5–1 air changes per hour). Use formulas or consult HVAC guidelines to match CFM (cubic feet per minute) to the space.
5. Neglecting Noise Levels (Sones)
Basements may be used as living spaces, home offices, or recreational areas where noise matters.
- Pitfall: Installing a high-CFM fan with high sone ratings, leading to disruptive noise.
- Best Practice: Balance airflow needs with acoustics. Look for fans rated below 1.0 sone for habitable basement areas, especially if used during waking hours.
6. Skipping Compliance and Certification Checks
Using uncertified equipment can violate building codes and compromise safety.
- Pitfall: Installing non-certified fans that don’t meet regional electrical or fire safety standards (e.g., UL, CE, ETL).
- Best Practice: Verify that the exhaust system is certified for residential or commercial use in your region and complies with local building codes.
7. Poor Ducting and Installation Planning
Even a high-quality fan will underperform with improper installation.
- Pitfall: Using undersized, poorly insulated, or excessively long duct runs, which restrict airflow and reduce efficiency.
- Best Practice: Design ducting with minimal bends, use rigid or semi-rigid ducts, insulate if passing through cold zones, and ensure proper termination outside (away from air intakes).
8. Forgetting Maintenance Access and Cleanability
Over time, dust and moisture accumulation can reduce performance.
- Pitfall: Installing a fan in an inaccessible location or with no provision for cleaning, leading to clogged grilles and reduced airflow.
- Best Practice: Choose models with easy-access filters or cleanable housings and ensure installation allows for routine maintenance.
By avoiding these common pitfalls—especially those related to IP rating suitability and overall build quality—organizations and property managers can ensure reliable, safe, and efficient basement ventilation for years to come.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Basement Exhaust
Overview
This guide outlines the logistics and compliance requirements for the installation, operation, and maintenance of basement exhaust systems. These systems are critical for ensuring indoor air quality, occupant safety, and adherence to building codes and environmental regulations. Proper planning, documentation, and coordination are essential to meet all legal and operational standards.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
All basement exhaust systems must comply with applicable local, state, and federal regulations. Key compliance standards include:
– International Mechanical Code (IMC): Governs design, installation, and inspection of mechanical systems, including ventilation.
– International Building Code (IBC): Addresses structural and fire safety considerations related to exhaust ductwork.
– National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) Standards: Specifically NFPA 90A for HVAC systems in commercial and industrial buildings.
– ASHRAE Standard 62.1: Provides ventilation rates and air quality requirements for acceptable indoor air.
– Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) Guidelines: Relevant when exhaust includes contaminants such as radon, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), or hazardous fumes.
– Local Building Department Permits: Required before installation or modification; inspections may be mandated at various project stages.
Permitting and Documentation
Prior to installation, obtain all necessary permits from the local authority having jurisdiction (AHJ). Required documentation typically includes:
– Detailed mechanical drawings and system schematics
– Load calculations and airflow specifications
– Equipment submittals and product data sheets
– Fire damper and smoke control plans (if applicable)
– Radon mitigation plans (in high-risk zones)
Maintain records of permits, inspections, and approvals for audit and compliance verification.
Equipment and Material Standards
Exhaust components must meet recognized safety and performance standards:
– Ductwork: UL 181 listed for fire resistance; galvanized steel or equivalent material
– Fans: Certified by AMCA for airflow and efficiency; suitable for continuous duty
– Dampers: UL 555 listed for fire resistance if penetrating fire-rated assemblies
– Motors: NEMA-rated; appropriate for environmental conditions (e.g., moisture-resistant)
All equipment must be installed per manufacturer specifications and code requirements.
Installation Logistics
Coordinate with general contractors, electricians, plumbers, and fire protection specialists during construction. Key logistical considerations:
– Schedule exhaust system rough-in before wall and ceiling enclosures
– Ensure structural support for duct runs and fan units
– Provide clear access for maintenance and inspection points
– Protect ductwork during construction to prevent debris or moisture ingress
– Align exhaust outlets with exterior building envelope per local setback and discharge regulations
Inspection and Testing
After installation, conduct comprehensive testing to ensure compliance and functionality:
– Airflow verification using calibrated anemometers or flow hoods
– Static pressure testing of duct system
– Operational testing of fans, controls, and interlocks
– Smoke testing for leakage in duct joints (if required)
– Final inspection and sign-off by AHJ or certified third-party inspector
Operational and Maintenance Compliance
To remain compliant, implement a documented maintenance program including:
– Quarterly visual inspections of fans, ducts, and dampers
– Semi-annual cleaning of ductwork and exhaust outlets
– Annual performance testing and calibration of sensors/controls
– Recordkeeping of all maintenance, repairs, and component replacements
– Immediate reporting and correction of system failures affecting air quality or safety
Environmental and Safety Considerations
- Ensure exhaust discharge is directed away from air intakes, windows, and pedestrian areas
- Install carbon monoxide (CO) and/or radon monitors if risk is present
- Label all components with safety warnings and operational data
- Comply with hazardous material exhaust regulations if handling fumes from labs, garages, or industrial processes
Emergency Procedures
Establish protocols for system failure or hazardous air events:
– Post emergency contact numbers and shutdown procedures near main control panels
– Integrate exhaust failure alarms with building management systems (BMS)
– Train facility staff on response actions and evacuation routes if air quality is compromised
Record Retention and Audits
Maintain a compliance file containing:
– As-built drawings and equipment manuals
– Permits, inspection reports, and test results
– Maintenance logs and service contracts
– Incident reports and corrective actions
Files must be retained for minimum periods as required by local regulations (typically 5–10 years).
Conclusion
Adherence to logistics and compliance standards for basement exhaust systems ensures the health, safety, and legal protection of building occupants and owners. Proactive planning, documentation, and maintenance are critical to long-term system performance and regulatory compliance.
Conclusion for Sourcing Basement Exhaust System:
Sourcing an appropriate basement exhaust system is a critical step in maintaining indoor air quality, controlling moisture levels, and ensuring a healthy, safe, and comfortable basement environment. After evaluating various options—including fan types (e.g., inline duct fans, centrifugal blowers), ventilation requirements, energy efficiency, noise levels, and installation considerations—it is evident that selecting the right system depends on the specific needs of the space, such as basement size, intended use (e.g., living area, storage, workshop), and local building codes.
Ducted exhaust systems with moisture and humidity sensors offer optimal performance, particularly in regions prone to high humidity or basement flooding. Energy recovery ventilators (ERVs) or heat recovery ventilators (HRVs) may also be considered for balanced ventilation with minimal energy loss. Prioritizing energy-efficient, durable, and low-maintenance units from reputable suppliers ensures long-term reliability and cost savings.
In conclusion, a well-sourced basement exhaust system not only mitigates mold and mildew risks but also enhances air circulation and overall indoor environmental quality. Proper research, professional consultation, and adherence to local regulations are essential to make an informed decision that supports both comfort and structural integrity.