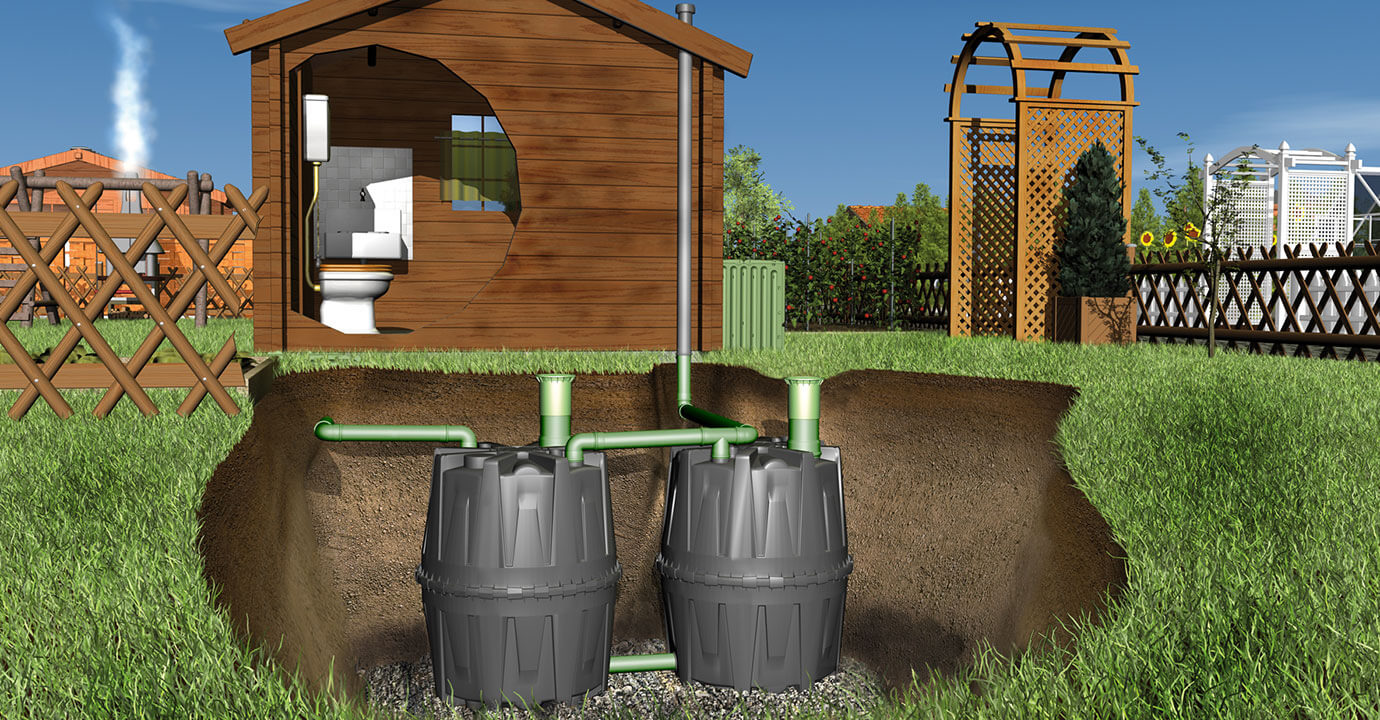
The global septic tank market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising sanitation needs, population expansion in rural and off-grid areas, and increasing investments in decentralized wastewater treatment solutions. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the septic tank market was valued at approximately USD 7.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.2% from 2024 to 2029. This growth is further supported by regulatory mandates promoting safe wastewater disposal and advancements in durable, low-maintenance tank designs such as those made from polyethylene and fiberglass. Among the various types, barrel septic tanks—compact, prefabricated units often repurposed or designed for small-scale use—have gained traction in residential, agricultural, and remote applications due to their ease of installation and cost-efficiency. As demand rises, a select group of manufacturers has emerged as leaders in innovation, quality, and market reach. Here are the top nine barrel septic tank manufacturers shaping the industry today.
Top 9 Barrel Septic Tank Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Premier Plastics Tanks
Domain Est. 1997
Website: premierplastics.com
Key Highlights: Premier Plastics Inc. has over 20 years of experience manufacturing light weight, high strength, and corrosion free polyethylene plastic septic tanks, water ……
#2 Water Tanks, Rain Barrels, Septic Tanks, Chemical Tanks
Domain Est. 2007
Website: jtisupply.com
Key Highlights: PRODUCTS. Liquid Storage Tanks & Septic … JTI Supply, Inc. 31989 Cinema Way Tangent, OR 97309. Phone: (541) 928-2937. Email: [email protected]. Site Map. Home ……
#3 Septic Tank Suppliers
Website: plastictankcompanies.com
Key Highlights: Easily contact the top septic tank manufacturers and suppliers. These companies have a wide range of products, custom items, discount prices and a huge ……
#4 Septic Tanks – Steel & Polyethylene
Domain Est. 1997
Website: greertank.com
Key Highlights: Greer manufactures quality septic tanks in both steel and durable polyethylene. Our septic tanks are rigorously tested and are built to last….
#5 Ace Roto Mold
Domain Est. 1999
Website: denhartogindustries.com
Key Highlights: Ace Roto-Mold’s Septic/Cistern line leads the industry in strength and durability. Plastic Septic tanks are the future of wastewater management. Plastic Cistern ……
#6 Plastic-Mart Homepage
Domain Est. 2004
Website: plastic-mart.com
Key Highlights: Plastic-Mart.com is the nation’s largest supply of above ground & underground plastic tank sizes. From plastic septic tanks to rainwater tanks, RV tanks to boat ……
#7 Storage Tanks, Septic Tanks, & Barrels
Domain Est. 2009
Website: smithsupplycompany.com
Key Highlights: Come to one of the three locations for Smith Supply Co in Texas today for your storage tanks, septic tanks, and barrel needs….
#8 FIBERGLASS SEPTIC TANKS
Domain Est. 2010
Website: thetanksource.com
Key Highlights: All FIBERGLASS SEPTIC TANKS. Home » » FIBERGLASS SEPTIC TANKS. GBF0500. GALLONS: 500 gallon. DIAMETER: 72″. OVERALL HEIGHT: 55″. CHAMBERS: 2. $900.00….
#9 Septic tanks
Website: graf.info
Key Highlights: Mechanical septic tanks retain floating solids and solids that will settle in domestic wastewater. This is a purely mechanical form of treatment….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Barrel Septic Tank

H2: Projected 2026 Market Trends for Barrel Septic Tanks
The market for barrel septic tanks is expected to undergo notable shifts by 2026, influenced by evolving environmental regulations, increasing demand for affordable wastewater solutions, and advancements in alternative septic technologies. While traditional barrel septic tanks—typically repurposed steel or plastic drums used in rudimentary septic systems—have long served off-grid and rural populations, their role is being reevaluated amid growing sustainability and regulatory standards.
-
Decline in Traditional Use Due to Regulatory Pressures
By 2026, stricter environmental and public health regulations in North America, Europe, and parts of Asia-Pacific are expected to limit the use of improvised barrel septic systems. Regulatory bodies are increasingly enforcing codes that require engineered, durable, and leak-proof septic solutions. As a result, the use of recycled or non-compliant barrel tanks is likely to diminish, especially in regions aiming to reduce groundwater contamination. -
Shift Toward Sustainable and Pre-Fabricated Alternatives
The market trend is shifting toward pre-fabricated, code-compliant plastic and concrete septic tanks. Innovations in polyethylene and fiberglass tank designs offer longer lifespans, better sealing, and easier installation than makeshift barrel systems. By 2026, these modern alternatives are expected to dominate new installations, particularly in developing regions undergoing rural sanitation upgrades. -
Niche Applications and DIY Market Persistence
Despite declining mainstream usage, barrel septic tanks may retain a niche presence in remote or low-income areas where access to standardized systems is limited. The DIY (do-it-yourself) housing and off-grid living movements, particularly in the U.S. and Canada, will continue to support limited demand. However, this segment will remain small and largely unregulated, posing ongoing environmental concerns. -
Environmental and Health Concerns Driving Change
Barrel septic tanks are associated with high failure rates, soil contamination, and health risks due to leakage and inadequate treatment. By 2026, increased public awareness and government-led sanitation campaigns are projected to further discourage their use. NGOs and development programs are more likely to promote eco-san toilets or compact treatment units over barrel-based systems. -
Regional Market Variability
In Sub-Saharan Africa and parts of Southeast Asia, where informal wastewater solutions are still common, repurposed barrel systems may persist due to affordability and lack of infrastructure. However, international aid and green financing initiatives are expected to accelerate the adoption of safer, scalable alternatives by the mid-2020s.
In conclusion, while barrel septic tanks may continue to serve isolated or underserved communities in 2026, the overall market trend points toward a steady decline in favor of compliant, sustainable, and technologically advanced septic solutions. The future of decentralized wastewater treatment lies in innovation and regulation—not improvisation.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Barrel Septic Tanks (Quality, IP)
When sourcing barrel septic tanks—often repurposed or makeshift solutions for wastewater treatment—several critical pitfalls related to quality and intellectual property (IP) can compromise performance, safety, and legal compliance. Understanding these risks is essential for contractors, municipalities, and homeowners.
Poor Material Quality and Structural Integrity
One of the most frequent issues with barrel septic tanks is the use of substandard or inappropriate materials. Many barrels are originally designed for transporting liquids like chemicals or food products, not for long-term burial and sewage treatment. Over time, exposure to soil pressure, moisture, and biological agents can cause degradation, leading to cracks, leaks, or collapse. Polyethylene or steel drums not rated for below-ground use may fail prematurely, resulting in environmental contamination and costly remediation.
Lack of Compliance with Environmental and Health Standards
Barrel septic tanks often do not meet local or national regulatory requirements for septic systems. Unlike certified prefabricated tanks, repurposed barrels typically lack proper baffles, ventilation, and inlet/outlet configurations needed for effective wastewater separation and treatment. This can lead to system failure, groundwater pollution, and violations of environmental protection laws.
Inadequate Treatment Capacity and System Design
Barrel setups are frequently undersized or poorly configured for the intended load. Without proper hydraulic retention time and multi-chamber design, they fail to adequately separate solids, break down organic matter, or treat effluent. This results in frequent maintenance, odor issues, and potential health hazards.
Intellectual Property (IP) and Design Infringement Risks
When sourcing or replicating barrel-based septic solutions marketed as “innovative” or “patented,” there is a risk of infringing on existing IP. Some manufacturers hold patents on specific septic tank designs, filtration systems, or modular configurations. Using similar designs—especially if reverse-engineered from a proprietary product—without proper licensing can lead to legal action, fines, or forced discontinuation of use.
Additionally, selling or promoting a barrel septic system based on a patented design, even with modifications, may still constitute infringement if the core innovation is copied.
Absence of Manufacturer Warranty and Technical Support
Unlike commercial septic tanks, repurposed barrels come with no warranty, installation guidance, or technical support. This lack of accountability increases the risk of improper installation and long-term failure. Should issues arise, there is no recourse for repairs or replacements.
Conclusion
While barrel septic tanks may appear to be a low-cost or expedient solution, the risks related to material quality, regulatory compliance, system performance, and potential IP violations make them a problematic choice. Investing in certified, code-compliant septic systems ensures long-term reliability, environmental safety, and legal protection.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Barrel Septic Tank
This guide outlines key considerations for the logistics and regulatory compliance associated with the use, transport, and installation of barrel septic tanks. These systems, typically made from repurposed 55-gallon drums, are generally not compliant with modern septic regulations and are strongly discouraged. However, understanding the logistical and legal implications is essential.
Regulatory Compliance
Barrel septic tanks do not meet the standards set forth by most local, state, and federal environmental and health authorities. Compliance is a major concern:
- Prohibited by Code: Most jurisdictions prohibit the use of barrel septic tanks due to inadequate containment, risk of leakage, and failure to meet minimum treatment standards.
- Health Department Regulations: Health departments require septic systems to be designed, installed, and maintained according to engineered specifications. Barrel systems fail to provide proper effluent treatment and pose contamination risks to groundwater.
- Environmental Protection Standards: The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and state environmental agencies regulate on-site wastewater systems to protect water quality. Barrel tanks are not approved due to their high failure rate and pollution potential.
- Permit Requirements: Installation of any septic system typically requires a permit. Barrel tanks will not be approved during site evaluation or permitting processes.
Transportation Logistics
If transporting barrel septic tanks (e.g., for removal or disposal), follow proper logistics procedures:
- Hazardous Material Handling: Assume the barrel contains residual wastewater or sludge. Treat it as a potentially hazardous material. Use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE).
- Secure Loading: Transport barrels upright and secured to prevent tipping or leakage during transit. Use spill containment trays if necessary.
- Vehicle Requirements: Use vehicles equipped to handle waste materials. Open-bed trucks should have tarps to prevent spillage.
- Disposal Regulations: Barrels contaminated with sewage must be disposed of at approved waste facilities. Confirm acceptance policies with local waste management authorities.
Installation & Site Considerations
While not compliant, understanding site logistics highlights why barrel tanks are inadequate:
- Improper Sizing: 55-gallon barrels are vastly undersized for household wastewater needs, leading to immediate overflow.
- Lack of Drain Field Integration: Proper septic systems require a leach field for effluent dispersal. Barrel tanks cannot support this function.
- Soil and Site Evaluation: Legal installations require percolation (perc) tests and site evaluations. Barrel systems bypass these critical steps.
- Setback Requirements: Regulations mandate minimum distances from wells, property lines, and water bodies. Barrel installations often violate these.
Environmental & Legal Risks
Using barrel septic tanks exposes property owners to significant risks:
- Fines and Penalties: Authorities may impose fines for illegal wastewater disposal or non-compliant systems.
- Remediation Costs: Property owners may be required to remove the barrel system and install a compliant septic system at their own expense.
- Property Devaluation: Non-compliant systems can hinder property sales and financing.
- Groundwater Contamination: Leaching from barrel tanks can pollute drinking water sources, leading to public health concerns.
Recommended Alternatives
To remain compliant and environmentally responsible:
- Conventional Septic Systems: Install a properly designed and permitted septic tank and drain field.
- Aerobic Treatment Units (ATUs): For sites with space or soil limitations, ATUs provide advanced treatment.
- Municipal Sewer Connection: Where available, connecting to public sewer is the most compliant and low-maintenance option.
Conclusion
Barrel septic tanks are not compliant with modern environmental and public health standards. Logistics surrounding their use involve significant legal, environmental, and financial risks. Property owners should consult local health and environmental authorities to design and install an approved on-site wastewater system. Always obtain permits and professional inspections to ensure compliance and protect public health.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Barrel Septic Tank
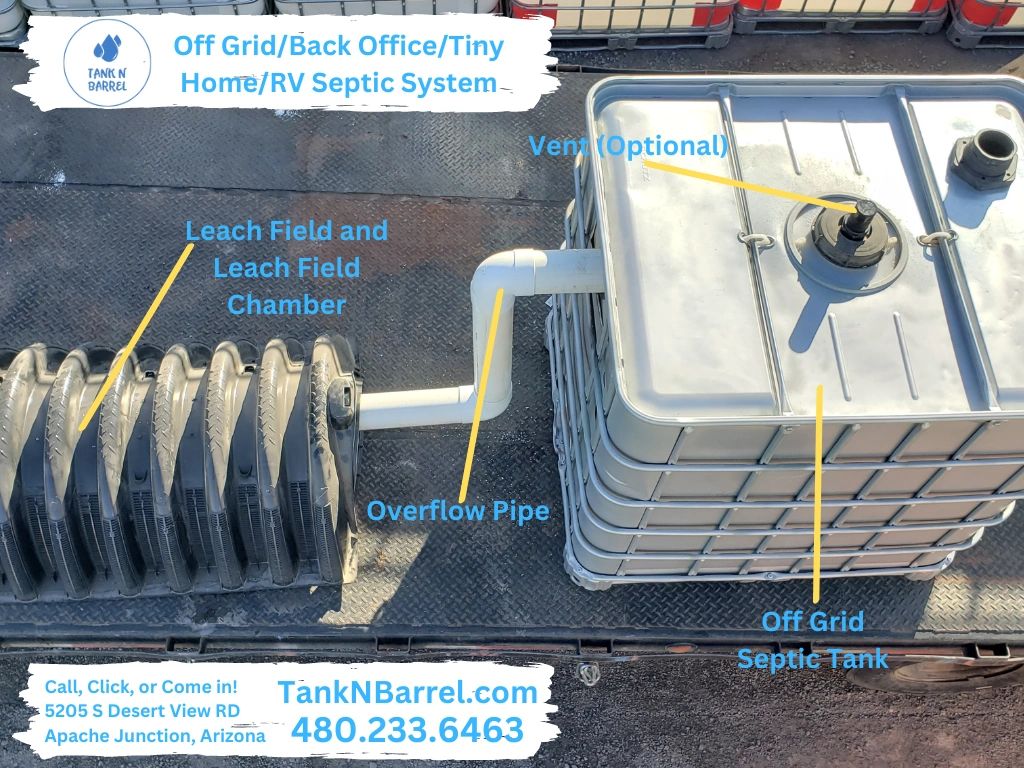
In conclusion, sourcing a barrel septic tank can be a cost-effective and practical solution for small-scale or temporary wastewater management needs, such as in remote cabins, off-grid homes, or construction sites. However, careful consideration must be given to local regulations, environmental impact, and long-term functionality. While repurposed barrels offer affordability and ease of installation, they may not meet health and safety standards in many jurisdictions and can pose risks of leakage, contamination, and inadequate treatment if not properly designed and maintained.
For sustainable and compliant waste management, it is essential to evaluate alternatives such as prefabricated septic tanks or approved on-site sewage systems that adhere to environmental and public health codes. If proceeding with a barrel-based system, ensure it is installed correctly, inspected regularly, and used only as a short-term solution. Ultimately, responsible sourcing and adherence to local guidelines are crucial to ensuring both effectiveness and environmental safety.