The global bamboo products market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for sustainable and eco-friendly building materials. According to Grand View Research, the global bamboo market size was valued at USD 80.3 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.2% from 2023 to 2030. This surge is largely attributed to bamboo’s rapid renewability, high strength-to-weight ratio, and low environmental impact, making it an ideal alternative to traditional hardwoods and synthetic materials. As construction, interior design, and furniture industries increasingly prioritize green sourcing, bamboo slabs—known for their durability and aesthetic appeal—have emerged as a preferred choice. With Asia-Pacific leading production and North America and Europe accelerating adoption, the market for engineered bamboo slabs is more competitive than ever. Based on performance, innovation, certifications, and production capacity, here are the top 9 bamboo slab manufacturers shaping the future of sustainable building materials.
Top 9 Bamboo Slab Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Bamboo Building Materials
Domain Est. 2002
Website: nwbamboo.com
Key Highlights: Northwest Bamboo, Inc. provides bamboo building materials including bamboo lumber, micro laminates, bamboo veneer, and more to clients worldwide….
#2 Hawaiian Style Flooring
Domain Est. 1999
Website: bambooflooringhawaii.com
Key Highlights: Bamboo Flooring Hawaii is more than just bamboo! We have expanded to include our Hawaiian Style Flooring Collection of luxury vinyl tile, exotic engineered wood ……
#3 Bamboo Living
Domain Est. 2003
Website: bambooliving.com
Key Highlights: We are a full-service architecture firm creating the world’s only internationally certified, permit-ready, prefabricated bamboo buildings and home furnishings….
#4 The Bamboo Flooring Company
Domain Est. 2004
Website: bambooflooringcompany.com
Key Highlights: The Bamboo Flooring Company, suppliers of high quality bamboo flooring and bamboo flooring accessories. Order online or visit our Leicester showroom….
#5 Natural Wide Plank Solid Solid T&G Bamboo Floor
Domain Est. 2005
Website: ambientbp.com
Key Highlights: In stock Rating 4.8 18 Natural bamboo flooring in wide solid planks with tongue and groove design. Sustainable, durable, and classic….
#6 Hacienda Guadua Bamboo
Domain Est. 2007
Website: guaduabamboo.com
Key Highlights: A tropical paradise located in the heart of Colombia. Hacienda Guadua Bamboo is the new headquarters of the company Guadua Bamboo SAS….
#7 Laminated bamboo production
Domain Est. 2008
Website: moso-bamboo.com
Key Highlights: Laminated bamboo is produced from flat bamboo strips, which are horizontally or vertically placed and glued together into panels or beams as a base material ……
#8 Bambu Lab
Domain Est. 2019
Website: bambulab.com
Key Highlights: Bambu Lab builds state-of-the-art desktop 3D printers that break the barriers between the digital and physical worlds. Explore High performance 3D printers ……
#9 Modern Bamboo
Website: modernbamboo.ph
Key Highlights: Modern Bamboo is the leading supplier of high-quality bamboo products in the Philippines. With a focus on sustainability and eco-friendliness….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Bamboo Slab

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Bamboo Slab
The bamboo slab market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by intensifying sustainability demands, technological advancements, and evolving consumer preferences. Here’s a breakdown of key trends shaping the landscape:
1. Surge in Sustainable & Circular Economy Alignment:
* Core Driver: Heightened global focus on decarbonization, deforestation concerns, and ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) reporting will make bamboo’s rapid renewability (harvestable in 3-5 years vs. decades for hardwoods) a primary selling proposition.
* Trend: Increased demand from eco-conscious consumers, architects (LEED/WELL certification seekers), and corporations with net-zero commitments. Expect stronger emphasis on certifications (FSC, PEFC) and transparent supply chains to combat greenwashing.
* Circularity: Growth in recycled/reclaimed bamboo slab products and improved end-of-life recyclability or biodegradability options will gain traction.
2. Technological Innovation in Manufacturing & Product Performance:
* Advanced Processing: Wider adoption of high-density compression (HDC) and strand-woven techniques will yield slabs with significantly enhanced hardness (surpassing many hardwoods), moisture resistance, and dimensional stability, expanding applications beyond flooring/countertops.
* Hybrid Materials: Development of bamboo-composite slabs (e.g., bamboo-polymer or bamboo-mineral blends) will improve durability for high-moisture areas (bathrooms, kitchens) and outdoor use, while potentially reducing costs.
* Precision Engineering: CNC machining and digital templating will enable more complex, customized slab designs (curves, intricate patterns) for architectural features and luxury interiors.
3. Expansion into New Applications & Markets:
* Beyond Flooring & Countertops: Bamboo slabs will increasingly penetrate furniture manufacturing (tables, cabinetry, wall panels), cladding (interior/exterior), acoustic panels, and automotive interiors (luxury EVs).
* Architectural Integration: Growing use in modular construction and prefabricated elements due to dimensional stability and prefabrication ease.
* Geographic Growth: Strongest growth expected in North America (driven by sustainability regulations and design trends) and Europe (Green Deal influence), with rising adoption in Asia-Pacific beyond traditional markets.
4. Design Evolution & Aesthetic Diversification:
* Beyond “Natural Look”: Expansion of color infusion (rich charcoals, warm grays, natural tones), texturing (wire-brushed, hand-scraped), and finishes (matte, satin, high-gloss) to compete with stone and engineered quartz.
* Customization & Size: Larger format slabs (reducing seams) and greater availability of custom sizes/colors for high-end residential and commercial projects.
* Emphasis on Authenticity: Continued demand for clear, straight grain patterns and “carbonized” (heat-treated) options, but balanced with innovative aesthetic choices.
5. Supply Chain Resilience & Sourcing Challenges:
* Vertical Integration: Major players will invest in securing sustainable bamboo plantations and controlling more of the supply chain to ensure quality, ethical labor practices, and mitigate price volatility.
* Geopolitical Factors: Trade dynamics (e.g., US-China relations) and regional environmental policies will impact raw material costs and logistics. Diversification of sourcing regions (e.g., India, Southeast Asia, Latin America) will increase.
* Labor & Expertise: Scaling production while maintaining quality requires investment in skilled labor and automation, potentially impacting costs.
6. Competitive Landscape & Price Positioning:
* Increased Competition: Entry of more manufacturers, especially from Asia, will intensify competition, potentially driving down prices for standard products but increasing innovation.
* Premium Positioning: High-end, certified, technologically advanced bamboo slabs will command premium prices, competing directly with mid-to-high-end hardwoods and engineered stone.
* Cost-Effectiveness: For basic applications, bamboo will remain a cost-competitive sustainable alternative to hardwoods.
Conclusion for 2026:
By 2026, the bamboo slab market will be characterized by sophistication and diversification. It will move beyond a niche “eco-alternative” to become a mainstream, high-performance material choice. Success will depend on proven sustainability credentials, technological innovation in durability and design, supply chain transparency, and the ability to meet the specific performance demands of expanding applications. The market will cater to both cost-sensitive builders seeking sustainable options and luxury segments demanding premium, customizable, and architecturally significant materials. H2 2026 is likely to see the consolidation of these trends, with clear winners emerging based on innovation and sustainable practices.
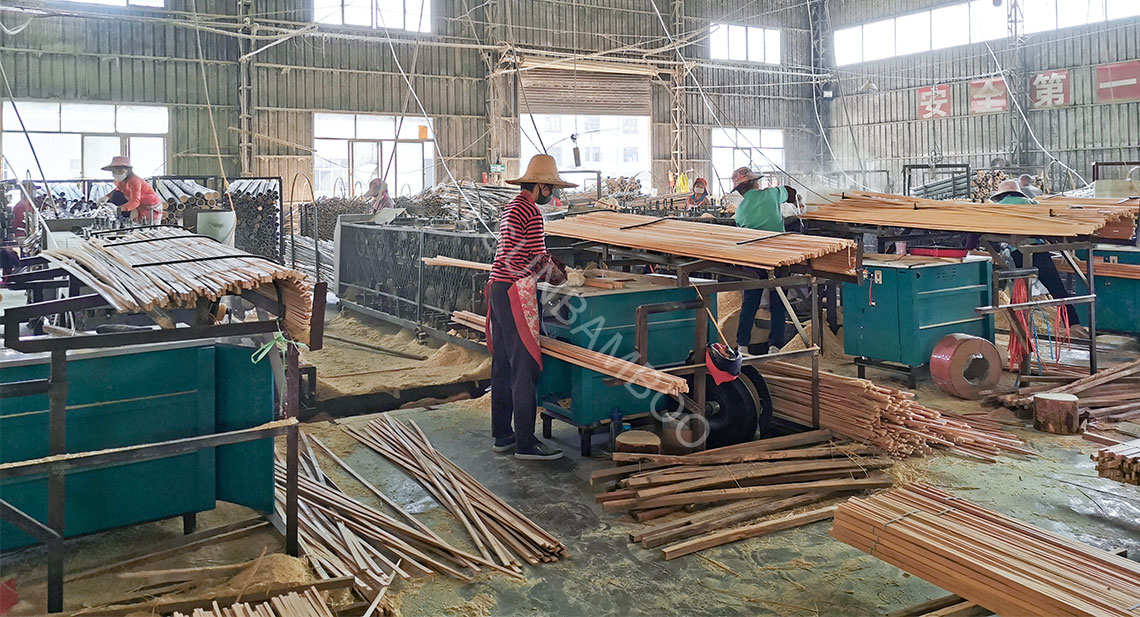

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Bamboo Slab (Quality, IP)
Inconsistent Material Quality
Bamboo slabs can vary significantly in density, color, and grain pattern due to differences in species, harvest time, and processing methods. Buyers often encounter inconsistent quality across batches, including warping, cracking, or voids in the material. This inconsistency can stem from inadequate drying processes or low-grade adhesives used in lamination, compromising structural integrity and aesthetic appeal.
Misrepresentation of “Solid” Bamboo
Many suppliers market engineered bamboo slabs as “solid,” leading to confusion. True solid bamboo is rare; most products are laminated strand or pressed bamboo. Without clear specifications, buyers may receive lower-density, less durable materials that don’t meet project requirements, especially for high-wear applications.
Lack of Sustainable Certification and Traceability
Bamboo is often touted as eco-friendly, but unsustainable harvesting practices can negate environmental benefits. Sourcing without verified certifications (e.g., FSC, PEFC) risks supporting deforestation or unethical labor practices. Additionally, unclear supply chains make it difficult to confirm responsible sourcing and environmental claims.
Intellectual Property (IP) Infringement Risks
Designers and manufacturers may unknowingly source bamboo slabs that replicate patented patterns, finishes, or engineered structures. Especially with mass-produced or imported slabs, there’s a risk of using materials that infringe on existing IP rights, potentially leading to legal disputes or project delays.
Inadequate Documentation for Compliance and Warranty
Suppliers may fail to provide proper technical data sheets, warranties, or compliance documentation (e.g., for formaldehyde emissions like CARB2 or EPA TSCA Title VI). This lack of transparency can create liability issues, especially in commercial or residential construction where regulatory compliance is mandatory.
Currency and Logistics Volatility
Sourcing bamboo slabs—often from Asia—involves exposure to fluctuating shipping costs, import tariffs, and lead times. Delays or cost overruns due to logistics issues can disrupt project timelines, particularly when suppliers don’t offer reliable delivery guarantees or inventory transparency.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Bamboo Slab
This guide outlines essential logistics and compliance considerations for the transportation, handling, and regulatory adherence related to Bamboo Slab products. Adhering to these guidelines ensures smooth operations, regulatory compliance, and product integrity throughout the supply chain.
Product Classification and Documentation
Bamboo Slabs are classified as wood products under international trade regulations. Ensure all shipments are accompanied by accurate documentation, including commercial invoices, packing lists, and bills of lading. Clearly specify the product as “Bamboo Slab” with a detailed description of dimensions, volume, and intended use. Proper classification under the Harmonized System (HS) Code 4409.29 (for planed or sanded bamboo in the round or square) or applicable local codes is critical for customs clearance.
Phytosanitary and ISPM-15 Compliance
Bamboo is subject to phytosanitary regulations to prevent the spread of pests and diseases. For international shipments, a Phytosanitary Certificate issued by the national plant protection organization (e.g., USDA APHIS, EU NPPO) is required. If wooden packaging (e.g., pallets, crates) is used, it must comply with International Standards for Phytosanitary Measures No. 15 (ISPM-15). Packaging must be heat-treated and marked with the official IPPC stamp.
Customs Clearance and Import Regulations
Check destination country regulations before shipment. Some countries have specific restrictions or require pre-arrival notifications for bamboo products. Ensure compliance with local environmental laws, such as the U.S. Lacey Act or EU Timber Regulation (EUTR), which prohibit trade in illegally sourced wood. Maintain documentation proving legal harvest and sustainable sourcing, including chain-of-custody certification if applicable (e.g., FSC or PEFC).
Packaging and Handling Requirements
Bamboo Slabs must be securely packaged to prevent damage during transit. Use moisture-resistant wrapping and sturdy wooden or metal crating where necessary. Protect slab edges with corner guards and separate layers with spacers to avoid scratching. Clearly label packages with handling instructions, including “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and moisture-sensitive warnings.
Transportation and Storage Conditions
Transport Bamboo Slabs in dry, ventilated, and covered environments to prevent moisture absorption and warping. Avoid direct exposure to rain, humidity, or temperature extremes. Ideal storage conditions are between 10°C and 25°C with relative humidity of 40–60%. Slabs should be stored flat on level surfaces with adequate support to prevent bending or cracking.
Restricted Substances and Emissions Compliance
Ensure Bamboo Slabs comply with formaldehyde emission standards such as CARB Phase 2 (California Air Resources Board) and EPA TSCA Title VI in the U.S., or E1/E0 standards in the EU. Provide test reports or certifications upon request. Avoid use of prohibited adhesives or treatments containing restricted chemicals (e.g., certain biocides or heavy metals).
Sustainability and Certification Requirements
Source Bamboo Slabs from suppliers adhering to sustainable forestry practices. Preference should be given to products with recognized certifications such as FSC (Forest Stewardship Council) or PEFC (Programme for the Endorsement of Forest Certification). Maintain documentation to support sustainability claims for compliance with green building standards (e.g., LEED) or corporate ESG policies.
Return and Disposal Procedures
Establish protocols for handling damaged or rejected shipments. Non-compliant or contaminated products must be quarantined and reported to relevant authorities as needed. Follow local regulations for disposal or recycling of bamboo waste. Do not return non-conforming products without prior approval and phytosanitary evaluation.
Recordkeeping and Audit Readiness
Maintain records of all compliance documentation, including certificates of origin, phytosanitary certificates, test reports, and chain-of-custody records, for a minimum of five years. Ensure systems are audit-ready for customs, environmental, or certification body inspections.
Conclusion for Sourcing Bamboo Slab:
Sourcing bamboo slabs presents a sustainable, eco-friendly, and economically viable alternative to traditional hardwood materials. With its rapid renewability, high strength-to-weight ratio, and aesthetic appeal, bamboo offers numerous advantages for applications in construction, furniture, and interior design. However, successful sourcing requires due diligence in selecting reputable suppliers who adhere to ethical harvesting practices, proper treatment processes, and quality certifications such as FSC or PEFC.
Challenges such as variability in quality, potential for inconsistent processing, and the need for proper moisture resistance treatments must be carefully managed through clear specifications and quality control measures. Additionally, considering transportation logistics and environmental impact is essential to maintaining the overall sustainability benefits of bamboo.
In conclusion, when sourced responsibly and processed correctly, bamboo slabs are a durable, attractive, and environmentally sound material choice. By partnering with reliable suppliers and prioritizing sustainable practices, businesses can leverage bamboo’s unique properties to meet both performance requirements and sustainability goals.