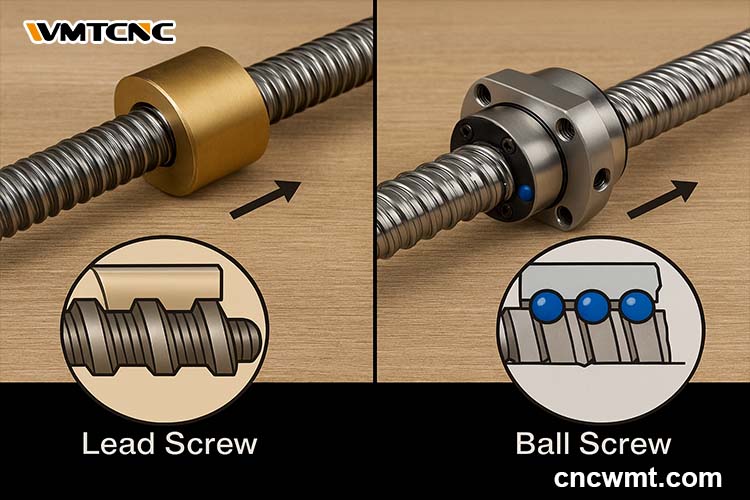
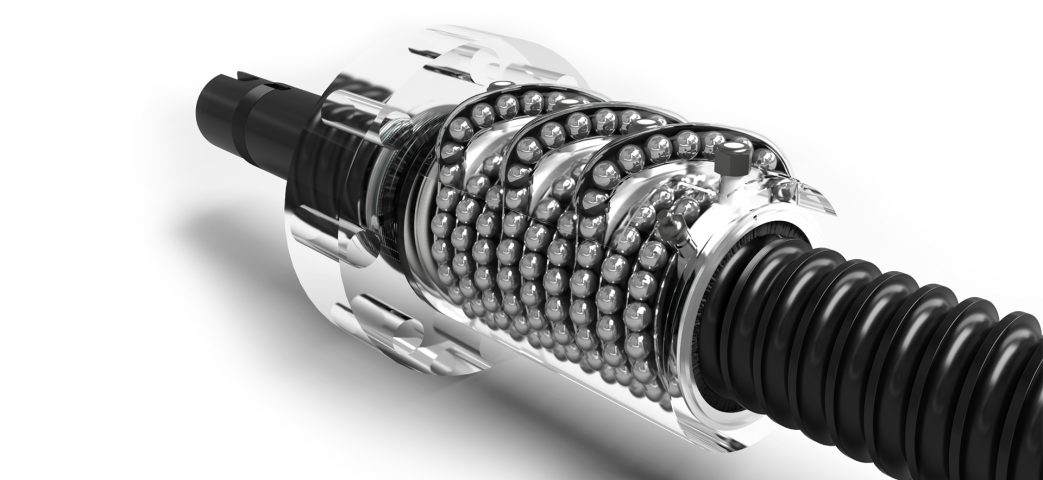
The global lead screw and ball screw market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising automation, demand for precision motion control, and expansion in industrial manufacturing and robotics. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the global ball screw market was valued at USD 2.45 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.8% from 2023 to 2028. Similarly, Grand View Research estimates that the global lead screw market size surpassed USD 1.7 billion in 2023 and is expected to expand at a CAGR of approximately 5.3% through 2030, fueled by increasing applications in aerospace, medical devices, and semiconductor equipment. As industries prioritize efficiency and accuracy, selecting high-performance components from leading manufacturers becomes critical. Below is a data-informed overview of the top 8 ball screw and lead screw manufacturers shaping this dynamic landscape.
Top 8 Ball Vs Lead Screw Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Ball Screw Manufacturers
Domain Est. 2002
Website: ball-screws.net
Key Highlights: Instantly locate the leading ball screw manufacturers and suppliers in the United States whose products are made with premium materials and are ……
#2 Ball Screw
Domain Est. 1995
Website: thk.com
Key Highlights: The Ball Screw is a high-efficiency feed screw with the ball making a rolling motion between the screw axis and the nut….
#3 Rockford Ball Screw
Domain Est. 1999
Website: rockfordballscrew.com
Key Highlights: Ball Screw vs Lead Screw: Everything You Need to Know. Rockford Ball Screw products provide our customers the ability to lift, position, hold and support ……
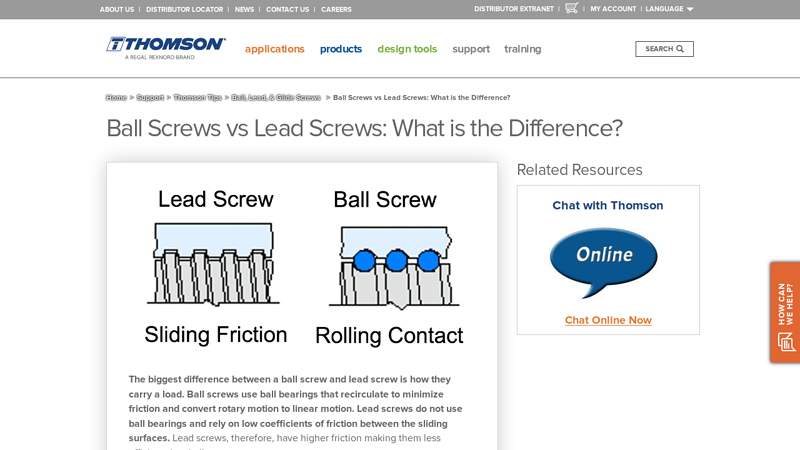
#4 Ball Screws vs Lead Screws
Domain Est. 2008
Website: thomsonlinear.com
Key Highlights: The biggest difference between a ball screw and lead screw is how they carry a load. Ball screws use ball bearings that recirculate to minimize friction….
#5 Ball Screw and Lead Screw Assemblies
Domain Est. 2008
Website: pbclinear.com
Key Highlights: Ball screws utilize recirculating steel balls within cylindrical or flanged nuts, offering superior speed, durability, and short lead times through precise ……
#6 Efficient and Effective Lead Screws
Domain Est. 2012
Website: helixlinear.com
Key Highlights: $20 delivery 30-day returnsLead screws are available in both metric and imperial sizes, with diameters ranging from 2mm to 25mm. Crafted from high-quality stainless steel or durabl…
#7 News
Domain Est. 2022
Website: kggfa.com
Key Highlights: The basic difference between a lead screw and a ball screw is that a ball screw uses a ball bearing to eliminate friction between the nut and the lead screw….
#8 Lead Screw vs Ball Screw, Which is Best for Your Project?
Domain Est. 2023
Website: johoty.com
Key Highlights: Unlike traditional lead screws, ball screws use balls to roll between the screw and nut, reducing friction. Ball screw consists of many balls in nut, and a ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Ball Vs Lead Screw

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Ball Screw vs. Lead Screw
As industrial automation, precision engineering, and energy efficiency continue to evolve, the competition between ball screws and lead screws is expected to intensify by 2026. Each technology serves distinct market segments based on performance, cost, and application requirements. Below is an analysis of the key market trends shaping the ball screw and lead screw landscape in 2026.
-
Rising Demand for High-Precision Automation
By 2026, the expansion of high-precision industries—such as semiconductor manufacturing, medical devices, and aerospace—is driving stronger demand for ball screws. Ball screws offer superior accuracy, repeatability, and efficiency (typically 90–95%) due to their rolling-element mechanism. As automation systems require tighter tolerances and faster cycle times, ball screws are becoming the preferred choice in advanced CNC machines, robotics, and electric linear actuators. -
Growth in Cost-Sensitive and Light-Duty Applications
Lead screws, despite lower efficiency (20–80%) and higher wear rates, maintain a strong foothold in cost-sensitive and light-duty applications. Their simplicity, quiet operation, and self-locking capability make them ideal for consumer electronics, 3D printers, laboratory equipment, and HVAC systems. As emerging markets expand their manufacturing base, the affordability and ease of integration of lead screws will sustain demand, particularly in applications where high speed and precision are less critical. -
Electrification and Energy Efficiency Trends
With global emphasis on energy efficiency and sustainability, ball screws are gaining an edge due to their minimal friction and high mechanical efficiency. Electrified systems—such as electric vehicles (EVs), automated guided vehicles (AGVs), and industrial exoskeletons—are increasingly adopting ball screws to reduce power consumption and improve performance. This trend is expected to accelerate through 2026, supported by advancements in miniaturized, high-load ball screw designs. -
Material and Coating Innovations
Both ball and lead screws are benefiting from material science advancements. For ball screws, innovations in corrosion-resistant coatings (e.g., DLC—Diamond-Like Carbon) and hybrid ceramic balls are enhancing lifespan and performance in harsh environments. Lead screws are seeing adoption of high-performance polymers (e.g., PEEK, acetal) that reduce friction and eliminate the need for external lubrication. These developments are blurring traditional performance gaps and expanding application possibilities. -
Regional Market Dynamics
Asia-Pacific, particularly China, Japan, and South Korea, remains the largest market for both screw types, driven by robust electronics and automotive manufacturing. However, localized production and supply chain resilience are prompting companies to diversify sourcing. In North America and Europe, re-shoring of manufacturing and stricter energy regulations are increasing adoption of ball screws in high-value automation systems. -
Integration with Smart Manufacturing and IIoT
The integration of linear motion systems into Industry 4.0 frameworks is favoring ball screws, which are more readily equipped with sensors for condition monitoring, predictive maintenance, and real-time feedback. By 2026, smart ball screw assemblies with embedded IoT capabilities are expected to gain traction in smart factories, further widening the technology gap in high-end applications.
Conclusion:
By 2026, the ball screw market is projected to grow at a faster CAGR than lead screws, driven by demand for precision, efficiency, and smart integration. However, lead screws will remain relevant in niche, low-cost, and self-locking applications. The market will increasingly segment along performance and cost lines, with ball screws dominating high-end automation and lead screws serving entry-level and specialized uses. Companies investing in hybrid solutions and advanced materials are likely to capture cross-segment opportunities.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Ball Screws vs. Lead Screws (Quality, IP)
When selecting between ball screws and lead screws for motion control applications, engineers and procurement teams must carefully evaluate quality considerations and ingress protection (IP) requirements. Overlooking these factors can lead to premature failure, reduced performance, or unsuitability for the operating environment. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Overlooking Build Quality and Material Specifications
A frequent mistake is assuming all ball or lead screws meet consistent quality standards. Ball screws, which rely on precision-ground balls and races, are highly sensitive to manufacturing tolerances. Low-quality ball screws may suffer from inconsistent preload, poor surface finishes, or dimensional inaccuracies, leading to backlash, vibration, or reduced lifespan. Similarly, lead screws—especially those with polymer nuts—can vary significantly in thread accuracy and nut composition. Sourcing from suppliers without certified quality processes (e.g., ISO 9001) increases the risk of receiving inconsistent or substandard components.
Ignoring Ingress Protection (IP) Requirements
Many applications involve exposure to dust, moisture, or other contaminants. A critical pitfall is selecting a screw type without verifying its compatibility with the required IP rating. Ball screws typically have open raceways, making them vulnerable to particulate ingress unless protected by bellows, scrapers, or seals—adding cost and complexity. In contrast, lead screws with self-lubricating nuts (e.g., PTFE-based) often perform better in dirty environments due to their inherent resistance to contamination. Failing to match the screw type and sealing solution to the IP rating can result in rapid wear, jamming, or system failure.
Mismatching Load and Duty Cycle Expectations
Ball screws offer high efficiency and load capacity but are often over-specified for light-duty or intermittent applications. Conversely, sourcing low-quality lead screws for high-load or continuous-duty use can result in excessive wear and thermal deformation. A common pitfall is focusing only on initial cost rather than total cost of ownership. Poor-quality lead screws may seem economical upfront but fail prematurely under demanding conditions, increasing downtime and replacement costs.
Neglecting Lubrication and Maintenance Needs
Ball screws require regular lubrication to maintain performance and prevent corrosion. Sourcing them for use in environments where maintenance access is limited—or where lubricant contamination is a concern—can be problematic. Lead screws, especially dry-running types, are often marketed as maintenance-free, but lower-quality versions may still degrade without proper lubrication or under high speeds. Assuming either type is universally “maintenance-free” without verifying supplier specifications is a common error.
Underestimating Environmental Compatibility
Beyond IP ratings, environmental factors such as temperature extremes, chemicals, or sterilization processes (e.g., in medical or food processing) must be considered. Low-grade materials in either screw type can corrode or degrade. For example, stainless steel ball screws may still suffer from galvanic corrosion if paired with incompatible nut materials. Similarly, lead screw nuts made with inferior polymers can swell or crack when exposed to certain solvents. Always validate material compatibility with the operating environment.
Failing to Verify Supplier Testing and Certification
Reputable suppliers provide test data for load capacity, efficiency, life expectancy (e.g., L10 life for ball screws), and IP validation. A major pitfall is sourcing from vendors who cannot supply traceable quality documentation or real-world performance data. This lack of transparency increases the risk of receiving counterfeit or non-compliant components, particularly with ball screws, which are more prone to counterfeiting due to their higher value.
By addressing these common pitfalls—focusing on certified quality, appropriate IP protection, and environmental suitability—teams can ensure reliable, long-term performance whether choosing ball screws for precision and efficiency or lead screws for cost-effectiveness and contamination resistance.

Logistics & Compliance Guide: Ball Screw vs. Lead Screw
Overview
This guide provides a comparative analysis of ball screws and lead screws in terms of logistics handling, regulatory compliance, environmental considerations, and operational safety. It is intended for procurement teams, logistics managers, engineering departments, and compliance officers involved in the selection and deployment of linear motion systems.
Material & Packaging Requirements
Ball Screws
- Materials: Typically constructed from hardened alloy steels (e.g., AISI 52100) with chrome-plated balls and precision-ground components. May include brass or polymer components in nut assemblies.
- Packaging: Require protective packaging (anti-corrosion VCI paper, foam inserts) due to high-precision surfaces. Must be sealed against moisture and particulates.
- Handling: Sensitive to impact and contamination; must be handled with clean gloves and stored in controlled environments.
Lead Screws
- Materials: Often made from stainless steel, carbon steel, or paired with polymer nuts (e.g., acetal, POM). Less surface-sensitive than ball screws.
- Packaging: Standard industrial packaging is typically sufficient. May use plastic end caps to protect thread ends.
- Handling: More robust; resistant to minor impacts and dust. Less stringent handling protocols.
Transportation & Storage
Ball Screws
- Transportation: Must be shipped horizontally to prevent internal ball misalignment. Avoid extreme temperature shifts to prevent condensation.
- Storage: Store in dry, temperature-stable environments (15–25°C, <60% RH). Use desiccants and sealed containers if stored long-term.
- Shelf Life: Limited; greased versions may degrade over 2–3 years if not re-lubricated.
Lead Screws
- Transportation: Can be shipped in any orientation. Less sensitive to vibration and temperature changes.
- Storage: Can be stored in standard warehouse conditions. Minimal degradation over time.
- Shelf Life: Indefinite if protected from rust (especially for non-stainless versions).
Regulatory & Safety Compliance
Ball Screws
- REACH & RoHS Compliance: Verify lubricants and plating materials meet EU standards. Some chrome plating may require exemptions under RoHS.
- Export Controls: High-precision ball screws may fall under ITAR or dual-use regulations (e.g., EU Dual-Use List) if used in aerospace or defense.
- Safety: High efficiency can lead to back-driving; mechanical brakes or holding systems may be required per ISO 13849 for safety-critical applications.
Lead Screws
- REACH & RoHS Compliance: Generally compliant, especially with plastic nuts (ensure polymers are halogen-free and non-toxic).
- Export Controls: Rarely subject to export restrictions due to lower precision and widespread industrial use.
- Safety: Self-locking nature reduces risk of unintended motion; typically meets functional safety standards without additional components.
Environmental & Sustainability Considerations
Ball Screws
- Lubrication: Require periodic re-lubrication with specified greases (often petroleum-based), raising concerns about maintenance waste and disposal.
- Recyclability: High metal content (steel, brass) makes them recyclable, but disassembly may be needed to separate materials.
- Carbon Footprint: Higher due to energy-intensive grinding and finishing processes.
Lead Screws
- Lubrication: Many dry-running variants available (especially with polymer nuts), reducing maintenance and environmental impact.
- Recyclability: Mixed materials (metal + polymer) may complicate recycling; check local waste classification.
- Carbon Footprint: Lower manufacturing energy; ideal for eco-conscious applications.
Maintenance & End-of-Life Disposal
Ball Screws
- Maintenance: Regular inspection and lubrication required. Contamination can lead to rapid wear.
- Disposal: Classified as industrial metal waste. Follow local regulations for used grease and metal shavings.
Lead Screws
- Maintenance: Minimal; inspect for wear, especially in high-load or continuous-duty applications.
- Disposal: Metal shafts recyclable; polymer nuts may go to general or plastic waste depending on local rules.
Conclusion
Ball screws demand higher logistics care, stricter compliance checks, and more involved maintenance due to their precision and application in regulated industries. Lead screws offer logistical simplicity, broader environmental tolerance, and easier compliance, making them suitable for cost-effective, sustainable applications. Selection should balance performance needs with logistical capacity and regulatory environment.
Conclusion: Ball Screw vs. Lead Screw – Sourcing Considerations
When sourcing between ball screws and lead screws for motion control applications, the decision should be based on a careful evaluation of performance requirements, cost constraints, and operational environment.
Ball screws are ideal for high-precision, high-efficiency, and high-load applications requiring smooth motion and long service life. They offer superior positioning accuracy, low friction, and high mechanical efficiency (typically 90% or higher), making them the preferred choice in CNC machines, industrial automation, and aerospace systems. However, their higher manufacturing complexity translates to increased cost, and they may require more sophisticated mounting and lubrication systems.
Lead screws, particularly ACME or precision ground types, are better suited for applications where cost-effectiveness, simplicity, and self-locking capabilities are priorities. They operate quietly, require minimal maintenance, and do not always need additional braking systems due to inherent friction. These traits make them suitable for light to moderate duty cycles in consumer equipment, 3D printers, and adjustable furniture.
Sourcing Recommendation:
Opt for ball screws when performance, speed, and precision are critical, and budget allows for higher initial investment with long-term reliability benefits. Choose lead screws when cost, simplicity, and moderate performance are sufficient for the application.
Ultimately, the right choice depends on balancing technical needs with economic practicality. Engaging with reputable suppliers who offer quality certifications, customization options, and technical support will ensure optimal component selection and system performance.