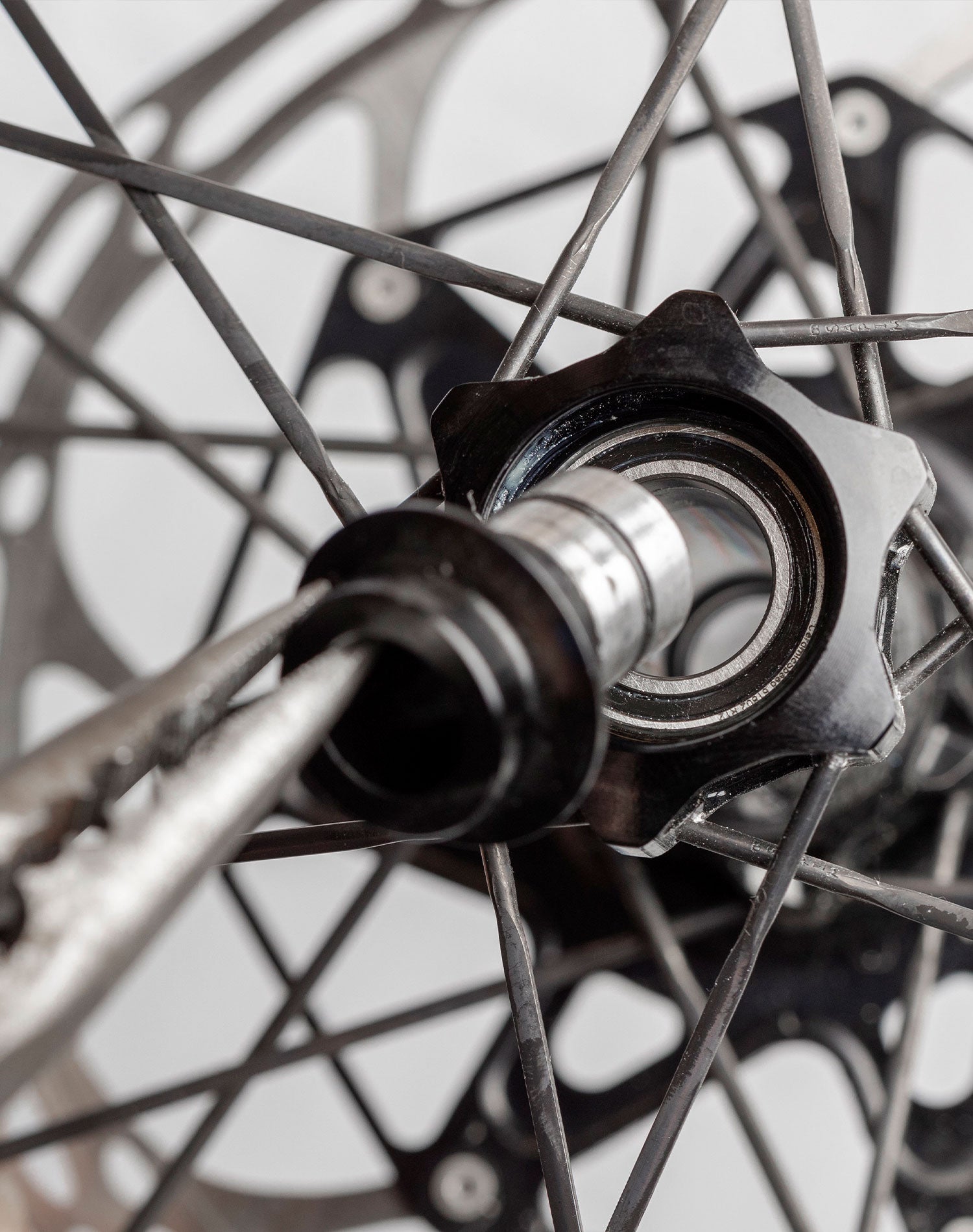
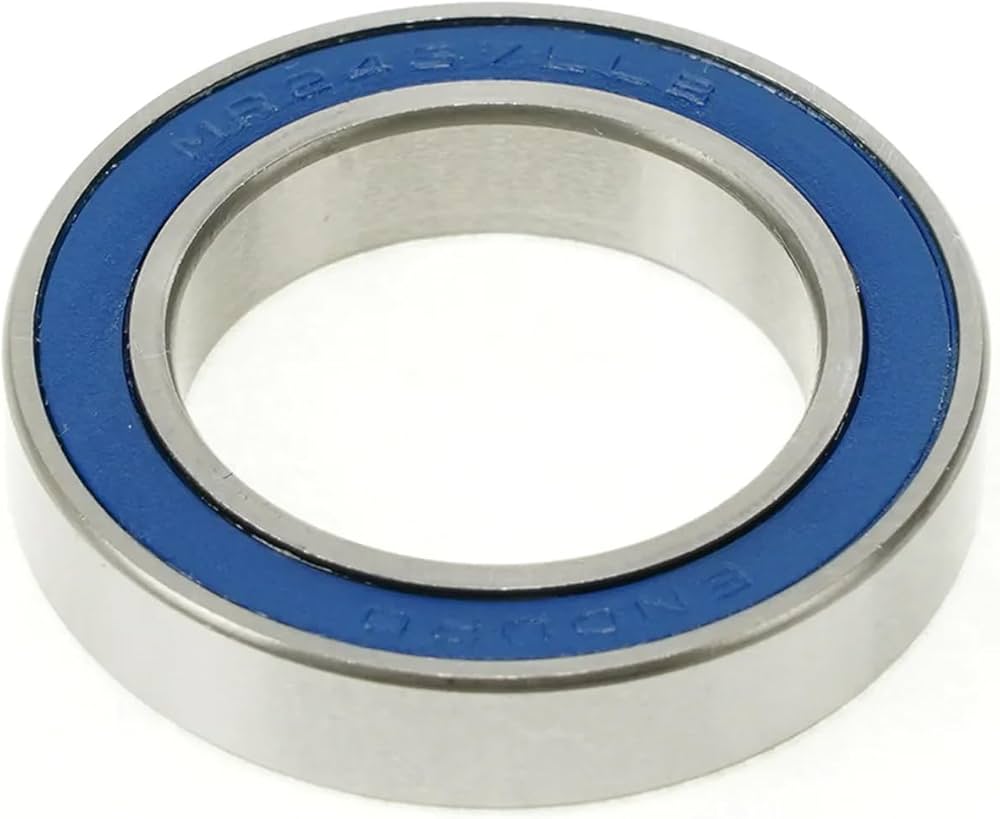
The global bicycle components market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising demand for bicycles as a sustainable mode of urban transportation, increasing health consciousness, and the rapid expansion of e-bike adoption. According to Mordor Intelligence, the global bicycle market is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 6.5% from 2023 to 2028, with component innovation playing a pivotal role in performance enhancement and durability. As critical elements in ensuring smooth wheel, pedal, and headset operation, high-quality ball bearings are essential for minimizing friction and maximizing efficiency across all bicycle types. This growing market demand has spurred advancements in bearing materials, precision engineering, and corrosion resistance, especially among leading manufacturers catering to both consumer and commercial segments. In response, we’ve identified the top 10 ball bearing manufacturers in the bicycle industry—companies that combine engineering excellence, global supply capacity, and a proven track record in delivering reliable performance under diverse riding conditions.
Top 10 Ball Bearing In Bicycles Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Enduro Bearings
Domain Est. 2004
Website: endurobearings.com
Key Highlights: Manufacturer and supplier of premium bearings and related products for industry and cycling. Enduro Industrial products click here to enter indistrial ……
#2 Chris King Hubs, with legendary made
Domain Est. 1996 | Founded: 1976
Website: chrisking.com
Key Highlights: 4-day deliveryChris King Precision Components has been domestically producing bicycle components of the highest quality since 1976. We are the manufacturer, not just a ……
#3 Bearings for bicycles – bicycle bearing
Domain Est. 2021
Website: bspdbearing.com
Key Highlights: BSPD bicycle bearings have nearly 20 years of experience in design and manufacturing, providing individual solutions for OEMs….
#4 TPI BEARINGS
Founded: 1966
Website: tpibearings.co
Key Highlights: Founded in 1966, TPI is a leading MIT (Made-in-Taiwan) manufacturer of deep groove ball and needle roller bearings….
#5 Bicycle Bearings by Boca Bearings
Domain Est. 1995
Website: bocabearings.com
Key Highlights: We offer a full line of miniature, deep groove, standard, full ceramic & ceramic hybrid bearings specifically suited to bicycles….
#6 NSK Global
Domain Est. 1996
Website: nsk.com
Key Highlights: Global leader in Motion & Control. NSK keeps the world moving with bearings, ball screws, linear guides, auto parts, and precision machinery solutions….
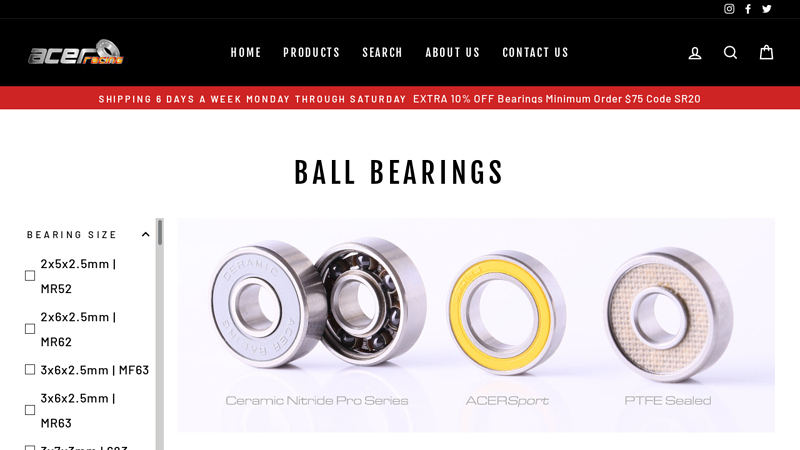
#7 Ball Bearings
Domain Est. 1998
Website: acerracing.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $40 30-day returnsNational and World Champion ceramic bearings for the hardcore racer. Superlight, extremely durable, lowest friction possible, best acceleration…
#8 CeramicSpeed
Domain Est. 2004 | Founded: 2004
Website: ceramicspeed.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $199 Free 14-day returnsCrafting the fastest bearing products for cycling and industry since 2004. Hand built in Denmark. Never Compromise….
#9 Enduro Bearings Cycling Products
Domain Est. 2004
Website: cycling.endurobearings.com
Key Highlights: An Enduro exclusive, XD15 Ceramic-Hybrid bearings utilize an advanced, nitrogen-infused stainless alloy that will never rust or corrode….
#10 The Ultimate Guide to Bicycle Pedal Bearings
Domain Est. 2019
Website: iskbearing.com
Key Highlights: Bicycle pedal bearings are crucial components that facilitate the smooth rotation of pedals. These bearings allow the pedals to spin freely ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Ball Bearing In Bicycles

H2: Market Trends for Ball Bearings in Bicycles (2026 Forecast)
The global market for ball bearings in bicycles is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by evolving consumer preferences, technological advancements, and the expansion of eco-friendly transportation. As urbanization accelerates and sustainability becomes a core priority, bicycles are increasingly viewed not just as recreational tools but as essential components of green mobility ecosystems. Ball bearings—critical for smooth wheel, pedal, and headset rotation—are benefiting from these macro trends, with several key developments shaping their market landscape.
-
Rising Demand from E-Bike Segment
One of the most influential drivers is the surge in electric bicycle (e-bike) adoption. By 2026, e-bikes are projected to account for over 35% of total bicycle sales globally, particularly in Europe, North America, and parts of Asia-Pacific. E-bikes place higher performance demands on components due to increased weight and torque, necessitating higher-grade, more durable ball bearings. This shift is pushing manufacturers toward sealed, corrosion-resistant, and low-maintenance bearing solutions, boosting both unit value and market size. -
Technological Innovations in Bearing Materials and Design
Advancements in materials science are leading to the integration of ceramic hybrid ball bearings (steel races with ceramic balls) in mid- to high-end bicycles. These bearings offer reduced friction, better heat resistance, and longer service life—critical for performance-oriented riders and e-bike users. By 2026, ceramic hybrid bearings are expected to capture a growing share of the premium segment, supported by declining production costs and improved manufacturing scalability. -
Sustainability and Lightweighting Initiatives
Bicycle OEMs are focusing on weight reduction and energy efficiency to enhance range (especially for e-bikes) and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers. This trend is driving the use of lightweight alloy cages and precision-engineered miniature ball bearings. Additionally, recyclability and reduced lubricant dependency are becoming important, with manufacturers exploring bio-based greases and dry lubrication technologies. -
Growth in Aftermarket and Replacement Demand
As the global bicycle parc expands—particularly in urban centers with bike-sharing schemes and commuter cycling—the aftermarket for replacement components, including ball bearings, is growing. DIY maintenance and the popularity of online retail platforms are making high-quality bearings more accessible. By 2026, the aftermarket is expected to represent over 40% of total ball bearing demand in the bicycle sector. -
Regional Market Dynamics
Europe remains the largest market due to strong government support for cycling infrastructure and high e-bike penetration. Asia-Pacific, led by China and India, is witnessing rapid growth in both mass-market and premium bicycles, creating opportunities for bearing suppliers. North America shows steady demand, particularly in the mountain and commuter bike segments. Localized manufacturing and supply chain resilience are becoming strategic priorities, especially post-pandemic. -
Competitive Landscape and Consolidation
The ball bearing market for bicycles is moderately consolidated, with key players like SKF, NSK, NTN, and Enduro Bearings leading in innovation and distribution. Smaller niche brands are gaining traction through customization and direct-to-consumer models. By 2026, partnerships between bearing manufacturers and e-bike OEMs are expected to increase, focusing on integrated component solutions.
Conclusion
By 2026, the ball bearing market in bicycles will be shaped by the convergence of electrification, material innovation, and sustainability. While cost-sensitive segments will continue to rely on standard steel bearings, the premium and e-bike segments will drive demand for advanced solutions. Overall, the market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 6.8% from 2023 to 2026, reaching an estimated value of USD 480 million. Success will depend on agility in R&D, alignment with OEM needs, and responsiveness to regional regulatory and consumer trends.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Ball Bearings for Bicycles (Quality, IP)
When sourcing ball bearings for bicycles, overlooking critical quality and intellectual property (IP) aspects can lead to performance issues, safety risks, and legal complications. Here are key pitfalls to avoid:
Overlooking Precision and Material Quality
Many suppliers offer ball bearings at low prices, but they may use substandard materials or poor manufacturing tolerances. Bicycle bearings require high precision to ensure smooth rotation, low friction, and durability under varying loads. Bearings made from low-grade steel or with inconsistent ball roundness and raceway finish can lead to premature failure, increased maintenance, and reduced ride quality. Always verify specifications such as ABEC (Annular Bearing Engineering Committee) ratings or ISO standards and insist on materials like chrome steel (e.g., SUJ2) or stainless steel where appropriate.
Ignoring Sealing and Ingress Protection (IP) Ratings
Bicycle bearings operate in harsh environments—exposed to water, dirt, mud, and road grime. A common mistake is sourcing bearings without proper sealing or understanding their Ingress Protection (IP) rating. Bearings with inadequate seals (e.g., non-contact rubber shields or no seals) allow contaminants to enter, accelerating wear. Opt for bearings with double-lipped rubber seals (often labeled 2RS or LLU) that offer better protection. While formal IP ratings like IP55 or IP67 are less common in small bearings, assess sealing effectiveness based on design and real-world performance data.
Failing to Verify Load and Speed Specifications
Bicycle bearings face both radial and axial loads—especially in hubs, bottom brackets, and headsets. Sourcing bearings not rated for the specific application (e.g., using light-duty bearings in high-stress areas) leads to deformation, brinelling, or spalling. Ensure the dynamic and static load capacities match the intended use. Also, consider rotational speed; while bicycles don’t spin as fast as motors, high cadence and downhill speeds still demand bearings designed for sustained performance.
Assuming All Bearings Are Interchangeable
Not all 6000-series or 6900-series bearings are created equal. Dimensions may appear standard, but subtle differences in internal clearance (C3, C0), ball complement, and cage design affect performance. Using an incorrectly specified bearing—even if it fits—can increase friction or reduce fatigue life. Always cross-check manufacturer catalogs and application requirements before substituting.
Neglecting Intellectual Property and Brand Authenticity
Reputable bearing brands (e.g., SKF, Shimano, Enduro, Chris King) invest in R&D and proprietary designs. Sourcing counterfeit or unbranded “equivalent” bearings risks IP infringement and poor quality. Some suppliers may falsely claim OEM partnerships or offer rebranded bearings without authorization. Always verify supplier legitimacy, request certification (e.g., ISO), and avoid deals that seem too good to be true—counterfeit bearings are prevalent in the market.
Skipping Lifecycle and Environmental Testing
Bicycle components must endure long-term exposure to moisture, thermal cycling, and mechanical stress. Sourcing bearings without proper testing data (e.g., salt spray resistance, life cycle testing) increases the risk of field failures. Request test reports or opt for suppliers who comply with industry standards like DIN or JIS. Bearings designed specifically for bicycles often undergo more rigorous environmental testing than generic industrial bearings.
Overlooking Packaging and Traceability
Poor packaging can damage bearings before installation—leading to pre-mature contamination or corrosion. Additionally, lack of traceability (batch numbers, manufacturing dates) complicates quality control and recall management. Ensure bearings are sealed in anti-corrosion packaging with clear labeling and traceability features.
By addressing these pitfalls, buyers can ensure reliable, high-performing bicycle bearings that meet both technical requirements and legal standards. Always partner with trusted suppliers and conduct due diligence on both quality assurance and IP compliance.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Ball Bearings in Bicycles
Overview
Ball bearings are essential components in bicycles, enabling smooth rotation in hubs, bottom brackets, headsets, and pedals. As a globally traded component, their transportation, import, and sale are subject to logistics considerations and regulatory compliance. This guide outlines key logistics and compliance requirements for ball bearings used in bicycles.
Product Classification and HS Code
Accurate classification is critical for customs clearance and duty assessment. Ball bearings are typically classified under the Harmonized System (HS) Code:
– HS Code: 8482.10 – Ball bearings, self-aligning (e.g., for hubs or headsets)
– HS Code: 8482.80 – Other ball bearings (including non-self-aligning types)
Note: The exact subheading may vary by country. Verify with local customs authorities or a customs broker.
Packaging and Transportation
- Packaging Standards: Use anti-corrosive, moisture-resistant packaging (e.g., sealed plastic bags with desiccants). Bearings should be individually wrapped or grouped in protective containers to prevent damage.
- Inner Packaging: Plastic trays or foam inserts to prevent movement during transit.
- Outer Packaging: Corrugated cardboard or wooden crates suitable for stacking and handling. Clearly label with product details, quantity, weight, and handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “Keep Dry”).
- Transport Mode: Suitable for air, sea, or land freight. For sea freight, use moisture-barrier wrapping to prevent saltwater corrosion.
- Temperature & Humidity Control: Store and transport in dry environments. Avoid extreme temperatures that may degrade lubricants.
Import/Export Documentation
Ensure the following documents are prepared and accurate:
– Commercial Invoice (with HS codes, unit prices, and total value)
– Packing List (detailing weight, dimensions, and quantity)
– Bill of Lading (for sea freight) or Air Waybill (for air freight)
– Certificate of Origin (may be required for preferential tariffs under trade agreements)
– Import/Export Licenses (if required by country; generally not needed for ball bearings, but verify locally)
Regulatory Compliance
International Standards
- ISO 15:2017 – Dimensional characteristics and tolerances for radial ball bearings
- ISO 492:2014 – Tolerance standards for radial bearings
- ABEC Standards (US-based) – Though not legally binding, ABEC ratings (e.g., ABEC-3, ABEC-5) are often used to indicate precision levels
Manufacturers and suppliers should ensure bearings meet relevant ISO standards for quality and interchangeability.
Safety and Environmental Regulations
- REACH (EU): Ensure no restricted substances (e.g., certain phthalates or heavy metals) are present in lubricants or packaging.
- RoHS (EU): Applies to electrical components, generally not to mechanical bearings, but verify if bearings are part of e-bike systems.
- Proposition 65 (California, USA): Disclose if components contain listed carcinogens or reproductive toxins (e.g., cobalt in some alloys).
Customs Duties and Trade Agreements
- Duty rates vary by country. For example:
- USA: Typically 4.1% under HTS 8482.10.5000
- EU: Usually 0% under CN code 84821000 (due to free circulation of industrial goods)
- Leverage free trade agreements (e.g., USMCA, EU-South Korea FTA) where applicable to reduce or eliminate tariffs.
Labeling and Traceability
- Product Labeling: Include bearing type, dimensions (e.g., 6000 ZZ), ABEC rating (if applicable), manufacturer logo, and batch/lot number.
- Packaging Labeling: Include country of origin, net weight, handling symbols, and importer/distributor information.
- Traceability: Maintain batch records for quality control and recall readiness.
End-of-Life and Recycling Considerations
- Ball bearings are primarily made of steel and are fully recyclable.
- Encourage take-back programs or recycling partnerships, especially in regulated markets like the EU under WEEE or ELV directives (if part of e-bikes).
Summary
To ensure smooth logistics and compliance for ball bearings in bicycles:
1. Use correct HS codes and documentation.
2. Package securely with climate protection.
3. Comply with ISO standards and regional regulations (REACH, Prop 65).
4. Monitor duty rates and leverage trade agreements.
5. Maintain traceability and support sustainable end-of-life practices.
Adhering to this guide helps avoid delays, penalties, and ensures market access worldwide.
In conclusion, sourcing ball bearings for bicycles requires careful consideration of quality, compatibility, durability, and cost. High-quality bearings made from materials such as chrome steel or ceramic significantly enhance performance, reduce friction, and extend the lifespan of bicycle components. Ensuring the correct size, precision rating (e.g., ABEC standards), and type (e.g., loose balls vs. cartridge bearings) is crucial for seamless integration with hubs, bottom brackets, headsets, and pedals. Sourcing from reputable suppliers or manufacturers that adhere to industry standards helps maintain consistency and reliability. Additionally, balancing performance needs with budget constraints allows for cost-effective procurement without sacrificing functionality. Ultimately, strategic sourcing of ball bearings contributes to smoother rides, improved efficiency, and long-term reliability in bicycles.