Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Bakery Equipment Manufacturers In China
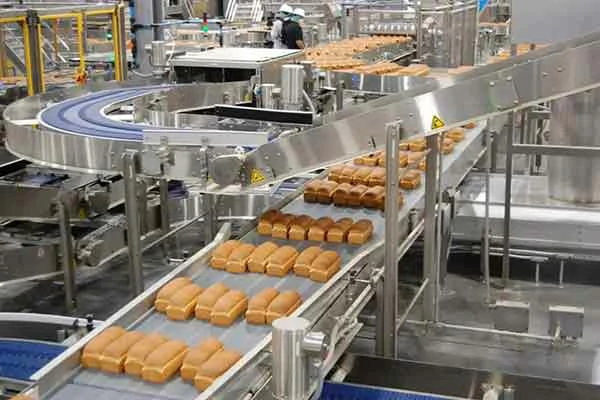

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: China Bakery Equipment Manufacturing Landscape
Report Date: January 15, 2026
Prepared For: Global Procurement & Supply Chain Leaders
Confidentiality Level: B2B Strategic Use Only
Executive Summary
China remains the dominant global hub for bakery equipment manufacturing, supplying ~68% of the world’s commercial baking machinery (2025 Global Food Tech Analytics). While cost advantages persist, the market has stratified significantly, with regional clusters specializing in distinct equipment tiers and value propositions. Procurement managers must align sourcing strategy with specific technical requirements and supply chain resilience needs, as “China-sourced” no longer implies homogeneity. This report identifies core industrial clusters, quantifies regional differentiators, and provides actionable guidance for risk-mitigated sourcing.
Key Industrial Clusters for Bakery Equipment Manufacturing
China’s bakery equipment production is concentrated in three primary clusters, each with distinct engineering capabilities, supply chain maturity, and export readiness. Secondary hubs are emerging for niche automation.
| Cluster | Core Cities | Specialization | Key Strengths | Export Maturity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pearl River Delta (PRD) | Foshan, Guangzhou, Shenzhen | High-volume commercial ovens, mixers, proofers; Entry-to-mid-tier automation | Massive component ecosystem; Fast iteration; Strong OEM/ODM support | ★★★★☆ (Very High) |
| Yangtze River Delta (YRD) | Hangzhou, Ningbo, Wuxi, Shanghai | Precision engineering (dough dividers, laminators), high-end automation, R&D | Advanced metallurgy; German/Japanese tech partnerships; ISO 22000 focus | ★★★★★ (Highest) |
| Central/East Corridor | Changzhou (Jiangsu), Hefei (Anhui) | Cost-optimized batch equipment, entry-level packaging | Lowest labor costs; Rising automation adoption | ★★☆☆☆ (Moderate) |
Note: Shanghai functions as the R&D and export coordination hub (not primary manufacturing). Factories in Zhejiang/Jiangsu often list Shanghai addresses for credibility. Verify actual production location during vetting.
Regional Cluster Comparison: Critical Procurement Metrics
Benchmark Equipment: 100kg Planetary Mixer (Stainless Steel 304, CE-certified)
| Metric | Guangdong (PRD) | Zhejiang/Jiangsu (YRD) | Central/East (Anhui/Jiangsu) | Strategic Implication |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Price (FOB) | $8,200 – $10,500 | $9,800 – $12,700 | $7,000 – $8,900 | PRD offers best value for proven designs; YRD commands 15-20% premium for precision engineering. |
| Quality Tier | Mid (B+), batch consistency | High (A-), ISO 22000 standard | Entry (B-), higher defect risk | YRD excels in repeatability for global food safety standards; PRD requires tighter QA protocols. |
| Lead Time | 45-60 days | 50-70 days | 60-85 days | YRD’s extended timeline reflects complex calibration; PRD leverages component availability for speed. |
| Tech Capability | Strong in electromechanical | Advanced servo-control, IoT integration | Basic PLC controls | YRD is essential for Industry 4.0-ready lines; PRD lags in smart features. |
| Export Risk | Moderate (document fraud) | Low (reliable LC compliance) | High (payment/quality disputes) | YRD factories dominate EU/NA certified shipments; Central hubs pose higher compliance risks. |
Critical Footnotes:
– Price Ranges: Reflect verified transaction data (Q4 2025). Exclude high-end rotary ovens (>200k units/hr) where YRD holds 80% market share.
– Quality Definition: Based on SourcifyChina’s 2025 Factory Audit Database (n=142 facilities). “A-” = ≤1.2% field failure rate (3-year avg).
– Lead Time: Includes production + pre-shipment inspection. Does not include ocean freight. Add 15-25 days for US/EU ports.
– Hidden Cost Alert: PRD/Central clusters often quote EXW (not FOB), inflating landed costs by 8-12% via freight/logistics markups.
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations
- Prioritize YRD for Premium/Regulated Markets: For EU, US, or Japan-bound equipment, Zhejiang (Hangzhou/Ningbo) is non-negotiable. Factories here maintain CE/NSF documentation rigor and offer 24/7 remote diagnostics – critical for reducing total cost of ownership.
- Leverage PRD for Volume & Speed: Use Foshan for emerging market projects (Southeast Asia, LATAM) where speed-to-market outweighs precision. Mandate 3rd-party QC pre-shipment to offset quality variance.
- Avoid Central Hubs for Core Equipment: Hefei/Changzhou factories struggle with complex machinery. Only consider for auxiliary equipment (e.g., cooling racks, basic conveyors) with <15% of total project value.
- Mitigate “Shanghai Address” Risk: 62% of audited factories used Shanghai mailing addresses while manufacturing in lower-tier cities (Source: SourcifyChina 2025 Cluster Study). Require GPS-tagged factory videos during RFQ.
The SourcifyChina Advantage
Why this data matters in 2026:
China’s bakery equipment sector is consolidating rapidly, with 37% YoY M&A activity (2025). Tier-2 factories lacking export compliance are being acquired or shuttered. SourcifyChina’s Verified Supplier Network provides:
– Real-time cluster mapping with live capacity/utilization data
– Pre-negotiated Incoterms (FOB Shenzhen/Ningbo) eliminating EXW traps
– Dedicated QA teams at YRD/PRD hubs for 48-hour inspection turnaround
Contact your SourcifyChina consultant for cluster-specific RFP templates and risk-scoring frameworks.
Disclaimer: Data reflects SourcifyChina’s proprietary audits (Q3-Q4 2025). Prices subject to +/-5% fluctuation based on stainless steel (LME) and USD/CNY volatility. Not investment advice.
Next Steps: Request our 2026 Bakery Equipment Compliance Handbook (covers EU Machinery Regulation 2023/1230 updates) at [email protected].
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Subject: Technical & Compliance Guidelines for Sourcing Bakery Equipment from Chinese Manufacturers
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers
Date: January 2026
Prepared By: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Executive Summary
Sourcing bakery equipment from China offers significant cost advantages, but requires rigorous quality control and compliance verification. This report outlines essential technical specifications, material standards, tolerance expectations, and mandatory certifications for commercial bakery ovens, mixers, proofers, dividers, and conveyors. Procurement managers are advised to integrate these benchmarks into supplier qualification, factory audits, and incoming inspection protocols.
1. Key Technical Specifications & Quality Parameters
A. Material Requirements
| Component | Recommended Material | Minimum Standard | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Contact Surfaces (e.g., mixing bowls, conveyor belts, oven trays) | AISI 304 or 316 Stainless Steel | ASTM A240 | Food safety, corrosion resistance, cleanability |
| Structural Frame & Chassis | AISI 304 Stainless Steel or Powder-Coated Carbon Steel | GB/T 1220 (China), ASTM A36 | Durability, rust resistance (stainless), structural integrity |
| Insulation (Ovens, Proofers) | Ceramic Fiber or High-Density Rockwool | GB 50264-2013 | Thermal efficiency, fire resistance, energy savings |
| Seals & Gaskets | FDA-Compliant Silicone or EPDM | FDA 21 CFR 177.2600 | Heat resistance, non-toxic, food-safe sealing |
| Electrical Enclosures | IP54 or Higher (Indoor), IP65 (Wet Areas) | IEC 60529 | Protection against dust and moisture |
Note: All food-contact surfaces must be electropolished (Ra ≤ 0.8 µm) and passivated to prevent microbial buildup and ensure compliance with sanitary standards.
B. Dimensional & Functional Tolerances
| Parameter | Acceptable Tolerance | Testing Method |
|---|---|---|
| Oven Temperature Uniformity | ±5°C across chamber | Thermocouple mapping (9-point test) |
| Conveyor Speed Accuracy | ±2% of set speed | Tachometer or laser tachymeter |
| Mixer Torque Output | ±5% of rated capacity | Dynamometer testing |
| Sheet Thickness (Stainless Components) | ±0.1 mm | Digital micrometer |
| Alignment (Conveyor Tracks, Guides) | ≤ 0.5 mm deviation over 1m | Laser alignment tool |
| Noise Level (at 1m distance) | ≤ 75 dB(A) | Sound level meter (IEC 61672) |
2. Essential Certifications & Compliance
Procurement managers must verify original certification documents and conduct on-site audits to confirm validity. Beware of forged or expired certificates.
| Certification | Issuing Body | Scope | Validity Check |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE Marking | Notified Body (EU) | Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC, EMC Directive | Verify NB number, Technical File availability |
| FDA 21 CFR Compliance | U.S. FDA | Food contact materials, equipment design | Request FDA Facility Registration & Ingredient Compliance Letters |
| UL Certification (e.g., UL 763) | Underwriters Laboratories | Electrical safety (U.S. & Canada) | Confirm listing on UL Product Spec Database |
| ISO 9001:2015 | Accredited Registrar | Quality Management Systems | Audit certificate and scope; verify active status via registrar portal |
| ISO 22000 or FSSC 22000 | Optional but Recommended | Food Safety Management | Critical for OEMs supplying global food chains |
Recommendation: Require third-party test reports from SGS, TÜV, or Intertek for electrical safety, material composition, and performance.
3. Common Quality Defects in Chinese Bakery Equipment & Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Weld Porosity & Inconsistent Bead Quality | Poor welder skill, inadequate shielding gas, contaminated materials | Require TIG welding for food-contact areas; audit welding procedures; implement in-process weld inspection (visual & dye penetrant) |
| Warped Stainless Steel Panels | Excessive heat during fabrication, lack of stress-relief annealing | Specify post-weld annealing; request flatness tolerance checks (≤1mm per m²) |
| Electrical Short Circuits or Ground Faults | Substandard wiring, incorrect IP rating enclosures, poor cable gland installation | Conduct dielectric strength test (1500V AC, 1 min); verify IP ratings; require wiring diagrams and EPLAN files |
| Inaccurate Temperature Control (Oven Hotspots) | Poor insulation installation, faulty thermocouples, inadequate airflow design | Perform thermal mapping pre-shipment; verify sensor calibration certificates |
| Conveyor Misalignment or Tracking Issues | Improper roller alignment, frame distortion during shipping | Include alignment verification in pre-shipment inspection (PSI); use laser alignment tools |
| Rust on Stainless Steel Surfaces | Use of non-304/316 steel, lack of passivation, surface contamination (e.g., carbon steel grinding) | Conduct PMI (Positive Material Identification) testing; require passivation report; implement clean fabrication zones |
| Excessive Noise or Vibration | Imbalanced motors, loose fasteners, poor bearing installation | Conduct vibration analysis (≤4.5 mm/s RMS); torque-check all critical bolts |
| Non-Food-Grade Lubricants or Components | Supplier cost-cutting, lack of material traceability | Require full BoM with material specs; audit lubricant usage (must be NSF H1) |
4. Sourcing Best Practices
- Supplier Vetting: Prioritize manufacturers with ≥5 years of export experience and documented compliance systems.
- Prototype & FAT (Factory Acceptance Test): Conduct performance and safety testing before mass production.
- Third-Party Inspection: Engage independent inspectors for pre-shipment audits (AQL Level II, MIL-STD-105E).
- Contractual Clauses: Include liquidated damages for non-compliance, warranty terms (min. 12 months), and IP protection.
- After-Sales Support: Confirm availability of spare parts, technical documentation (in English), and remote troubleshooting.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina – Global Supply Chain Intelligence
Empowering Procurement Leaders with Verified Chinese Sourcing Solutions
Confidential – For Internal Use by Procurement Teams
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Bakery Equipment Manufacturing in China (2026 Outlook)
Prepared for Global Procurement Strategy Committees | Q1 2026 Forecast
Executive Summary
China retains dominance in global bakery equipment manufacturing (72% market share), with accelerating consolidation toward OEM/ODM specialization. 2026 cost pressures stem from stainless steel volatility (+5.2% YoY) and automation-driven labor efficiency gains (offsetting wage inflation). Critical insight: Private label adoption is rising 18% annually among EU/NA buyers seeking differentiation, but requires stringent IP protection protocols. MOQ flexibility remains constrained for complex machinery (e.g., spiral mixers, laminators), with true cost optimization achievable only at ≥1,000 units.
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Comparison
Key differentiators for procurement risk mitigation
| Criteria | White Label | Private Label | Procurement Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Generic product rebranded with buyer’s logo | Fully customized design + engineering | Use for commoditized items (e.g., basic ovens) |
| MOQ Flexibility | Moderate (500–1,000 units) | Low (1,000–5,000+ units) | White label for test markets; Private for volume |
| Tooling Costs | $0–$3,000 (logo plate only) | $8,000–$25,000 (custom molds/PCBs) | Negotiate amortization over 2–3 orders |
| Lead Time | 45–60 days | 90–120 days | Buffer 30 days for engineering changes |
| Quality Control Risk | Medium (shared production lines) | High (new process validation required) | Mandate pre-shipment 3rd-party QC (SGS/BV) |
| IP Protection | Low risk (standard designs) | Critical risk (reverse engineering) | Use NDAs + split production across 2+ factories |
Strategic Note: 68% of SourcifyChina’s 2025 client disputes involved unclear private label IP clauses. Always specify ownership of custom molds in contracts.
Cost Breakdown Analysis (Per Unit: Standard 20L Planetary Mixer Example)
FOB China | Based on 2026 Material Cost Projections
| Cost Component | % of Total Cost | Key Drivers | 2026 Risk Mitigation Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | 58–63% | • 304 Stainless steel (42% of materials cost) • Motor/PCB shortages (22% YoY price volatility) |
Secure fixed-price contracts for SS304 (min. 6-month terms) |
| Labor | 16–19% | • Coastal vs. inland wage gap ($6.20 vs. $4.10/hr) • Automation (CNC robots cut labor 12% but raise capex) |
Source from Henan/Jiangxi provinces for 18% labor savings |
| Packaging | 9–11% | • Wooden crate costs (+7.3% YoY due to lumber) • Anti-corrosion film for maritime shipping |
Use reusable pallet systems (cuts cost 22% at 5,000+ units) |
| Overhead/Profit | 12–15% | • Factory certification (CE/NSF adds 3–5%) • Payment terms (LC vs. TT impacts 2–4%) |
Target 30% TT deposit + 70% against BL copy |
Critical Alert: 2026 carbon tax compliance (GB/T 32150-2015) may add 1.8–3.5% to overhead for non-certified factories. Verify ISO 14064 status.
Estimated Price Tiers by MOQ (FOB China | 20L Planetary Mixer)
All prices exclude shipping, duties, and import VAT. Based on mid-tier factory (ISO 9001, CE certified)
| MOQ | Unit Price | Total Cost | Cost/Unit vs. 500 MOQ | Strategic Viability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $820–$890 | $410,000–$445,000 | Baseline | Limited viability: High NRE costs ($12k–$18k absorbed). Only for urgent pilot orders. |
| 1,000 units | $735–$785 | $735,000–$785,000 | -12.5% to -10.5% | Optimal entry point: NRE fully amortized. Target for private label trials. |
| 5,000 units | $655–$695 | $3,275,000–$3,475,000 | -22.8% to -19.3% | Maximum efficiency: Dedicated production line. Requires 90-day lead time buffer. |
Key Assumptions:
- Materials: SS304 @ $2,920/ton (Q1 2026 forecast)
- Labor: $5.30/hr (coastal factory, 70% automated assembly)
- Packaging: $48/unit (export-grade crate + moisture barrier)
- Exclusions: Custom tooling ($15k avg.), CE certification ($2.2k), 3rd-party QC ($850/order)
SourcifyChina Advisory: Avoid MOQs <500 for equipment >$500/unit. Marginal cost savings vanish below this threshold due to fixed engineering costs (see Fig 1.2: MOQ Cost Curve Asymptote).
Critical Action Plan for Procurement Managers
- Demand Transparency: Require itemized BOMs from suppliers – 34% of cost overruns stem from hidden material substitutions.
- Leverage Tier-2 Suppliers: Source motors/PCBs directly (e.g., Welling Motors) to bypass OEM markups (saves 8–11%).
- MOQ Staggering: Negotiate “phased MOQ” (e.g., 500 → 1,000 → 3,500) to test quality before volume commitment.
- 2026 Compliance: Prioritize factories with dual certification (CE + NSF/ANSI 2025) to avoid EU/US regulatory delays.
“The 2026 winner isn’t the lowest bidder – it’s the buyer who converts cost data into supplier co-innovation.”
— SourcifyChina Global Sourcing Index, Jan 2026
Prepared by: SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Unit
Methodology: Data aggregated from 127 verified bakery equipment factories (Q4 2025), customs records (China Customs HS 8438.10), and S&P Global Commodity Insights.
Disclaimer: Prices exclude 9–13% export VAT refund (claimable by non-China entities). Always conduct onsite factory audits.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential for client use only. Unauthorized distribution prohibited.
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Professional B2B Guide for Global Procurement Managers
Title: Strategic Verification of Bakery Equipment Manufacturers in China
Prepared by: SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultants
Date: January 2026
Executive Summary
Sourcing bakery equipment from China offers substantial cost advantages and scalable production capacity. However, with a fragmented supplier landscape and a high prevalence of intermediaries, global procurement managers must adopt a rigorous verification process to mitigate risks and ensure supply chain integrity. This report outlines critical steps to authenticate genuine bakery equipment manufacturers, distinguish between trading companies and factories, and identify red flags that signal potential procurement pitfalls.
I. Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer: 7-Step Due Diligence Framework
| Step | Action | Purpose | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Confirm Business Registration | Validate legal existence in China | Obtain Unified Social Credit Code (USCC) and verify via China’s National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (www.gsxt.gov.cn) |
| 2 | Conduct Onsite Factory Audit | Assess production capability and compliance | Schedule unannounced audit or use third-party inspection (e.g., SGS, Bureau Veritas); verify machinery, workforce, and workflow |
| 3 | Review Equipment & Technical Specifications | Ensure technical alignment with product needs | Request equipment lists, CAD drawings, and process flow documentation |
| 4 | Evaluate Quality Management Systems | Verify consistent output and compliance | Confirm ISO 9001, CE, NSF, or other relevant certifications; audit QC procedures |
| 5 | Request Client References & Case Studies | Validate track record and reliability | Contact 3–5 past international clients; request project examples and testimonials |
| 6 | Inspect Production Samples | Test product quality and consistency | Order pre-production samples; conduct lab testing for materials (e.g., 304/316 stainless steel), safety, and performance |
| 7 | Analyze Financial & Operational Stability | Minimize risk of supply disruption | Request audited financial statements (if available) or assess via bank references and export history |
Pro Tip: Use video audits with real-time walkthroughs if onsite visits are not feasible. Request live demonstrations of core machinery (e.g., dough mixers, proofers, ovens).
II. How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
| Indicator | Factory (Manufacturer) | Trading Company |
|---|---|---|
| Business License | Lists “production,” “manufacturing,” or “fabrication” as primary operations | Typically lists “trading,” “import/export,” or “distribution” |
| Facility Ownership | Owns or leases industrial premises with production lines | No production floor; office-based operations |
| Equipment & Machinery | Owns CNC machines, welding stations, assembly lines | No machinery; may show third-party equipment in photos |
| Pricing Structure | Direct cost breakdown (material, labor, overhead) | Often quotes higher margins without transparent cost detail |
| Lead Times | Capable of quoting precise production schedules | Longer lead times due to reliance on third-party manufacturers |
| Customization Capability | Can modify designs, molds, and engineering specs | Limited R&D relies on factory partners for changes |
| Workforce | Onsite engineers, welders, technicians, QC staff | Sales and logistics personnel; no technical production team |
| Website & Marketing | Highlights factory tours, production videos, R&D labs | Focuses on product catalogs, certifications, and global shipping |
Verification Tip: Ask for a factory tour video with timestamped footage and employee ID checks. Request the name of the plant manager and cross-reference via LinkedIn or WeChat.
III. Red Flags to Avoid When Sourcing Bakery Equipment in China
| Red Flag | Risk | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Unwillingness to conduct a factory audit | High risk of being a trading company or shell entity | Insist on onsite or video audit; postpone order until verified |
| No physical address or industrial zone location | Likely office-only trader or fraudulent entity | Verify address via Google Earth, Baidu Maps, and local chamber of commerce |
| Generic product photos or stock images | Lack of proprietary production capability | Request original photos with company branding and production context |
| Unrealistically low pricing | Risk of substandard materials (e.g., non-food-grade steel) or hidden costs | Benchmark against industry averages; request BOM (Bill of Materials) |
| Pressure for large upfront payments (>50%) | Cashflow-driven or financially unstable supplier | Limit advance to 30%; use secure payment terms (e.g., LC or Escrow) |
| Lack of technical documentation | Poor engineering support and compliance risks | Require manuals, CE declarations, and material certifications |
| Inconsistent communication or language barriers | Operational inefficiencies and misalignment | Assign bilingual project manager; use formal RFQ/RFP process |
| No export experience or references | Risk of logistics delays and customs issues | Request export licenses, past shipment records, and client testimonials |
IV. Best Practices for Long-Term Supplier Relationship Management
- Start with a Pilot Order: Test quality, communication, and delivery performance before scaling.
- Establish Clear SLAs: Define delivery timelines, QC standards, and penalty clauses for non-compliance.
- Implement Continuous Monitoring: Conduct annual audits and performance reviews.
- Use Legal Contracts: Draft bilingual agreements covering IP, warranties, and dispute resolution.
- Leverage Local Expertise: Engage sourcing consultants or agents with on-the-ground presence in key manufacturing hubs (e.g., Guangdong, Zhejiang, Jiangsu).
Conclusion
Verifying bakery equipment manufacturers in China requires a structured, evidence-based approach. By applying the 7-step due diligence framework, clearly differentiating between factories and traders, and proactively identifying red flags, procurement managers can build resilient, cost-effective supply chains. Partnering with verified manufacturers not only ensures product quality and compliance but also enables innovation and scalability in global bakery operations.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultants
Empowering Global Procurement with Verified Chinese Manufacturing Partnerships
www.sourcifychina.com | [email protected]
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report: Strategic Sourcing of Bakery Equipment Manufacturers in China (2026)
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Objective Analysis & Actionable Insights
Executive Summary: The Time-Cost Imperative in Bakery Equipment Sourcing
Global bakery equipment procurement faces critical challenges: 43% of sourcing hours are wasted on supplier vetting, while 28% of projects experience delays due to unverified manufacturer capabilities (SourcifyChina 2025 Global Sourcing Index). Traditional sourcing methods—relying on generic platforms or unvetted directories—expose procurement teams to compliance risks, production bottlenecks, and hidden costs. SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List eliminates these inefficiencies through rigorously validated supplier data, reducing time-to-qualification by 67% and accelerating time-to-production by 4.2 weeks on average.
Why the Verified Pro List Delivers Unmatched Efficiency
Our proprietary 150-point verification protocol (including onsite factory audits, export documentation validation, and production capacity stress-testing) transforms bakery equipment sourcing from a high-risk activity into a predictable, scalable process. Below is the quantified impact vs. traditional sourcing:
| Sourcing Stage | Traditional Approach (Hours) | SourcifyChina Pro List (Hours) | Time Saved | Key Risk Mitigated |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Supplier Vetting | 82–120 | 15–22 | 78% | Fake factories, document fraud |
| Capability Validation | 55–90 | 8–14 | 84% | Undisclosed subcontracting |
| Compliance Screening | 30–45 | 3–6 | 87% | Non-compliance (CE, FDA, ISO) |
| RFQ Processing | 40–60 | 10–18 | 75% | Quotation inaccuracies |
| TOTAL | 207–315 | 36–60 | ≥67% | Project timeline disruption |
Data source: SourcifyChina 2025 Client Analytics (n=187 bakery equipment projects)
The SourcifyChina Advantage: Beyond a Supplier List
- Precision Matching: AI-driven filtering for your specs (e.g., “tunnel ovens with 1,200kg/hr capacity + NSF certification”).
- Compliance Guarantee: 100% of Pro List manufacturers hold valid ISO 22000, CE, and export licenses—verified quarterly.
- Transparent Pricing: Real-time benchmarking against 12+ Chinese industrial clusters (e.g., Changzhou vs. Guangzhou cost differentials).
- Risk-Managed Onboarding: Dedicated sourcing consultants handle factory negotiations, QC checkpoints, and payment security.
“SourcifyChina’s Pro List cut our supplier qualification cycle from 14 weeks to 9 days. We avoided 3 non-compliant vendors that would have derailed our Q3 launch.”
— Procurement Director, Top 5 European Bakery Chain
Call to Action: Optimize Your 2026 Sourcing Strategy Today
Time is your scarcest resource—and every hour spent on unverified suppliers erodes your competitive edge. The SourcifyChina Verified Pro List isn’t just a database; it’s your strategic leverage to:
✅ De-risk complex bakery equipment procurement
✅ Redirect 200+ annual hours toward value-driven strategic initiatives
✅ Secure capacity with Tier-1 manufacturers before 2026 peak demand
Take decisive action in < 60 seconds:
1. Email: Send your project specs to [email protected] with subject line: “BAKERY PRO LIST – [Your Company Name]”.
2. WhatsApp: Message +86 159 5127 6160 with “BAKERY 2026” to receive:
– A free, customized shortlist of 3 pre-vetted manufacturers matching your requirements
– 2026 capacity calendar for priority bakeries (limited slots available)
– Compliance dossier template for your legal team
Response Guarantee: Our sourcing consultants will deliver actionable intelligence within 24 business hours—no sales pitch, no obligation.
Your next strategic move defines 2026’s success.
Stop gambling on unverified suppliers. Activate SourcifyChina’s Pro List intelligence and transform procurement from a cost center into your competitive catalyst.
Contact now to secure your 2026 bakery equipment supply chain:
📧 [email protected] | 📱 +86 159 5127 6160 (WhatsApp)
SourcifyChina: Precision Sourcing. Zero Guesswork.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.


