The global baghouse filters market is experiencing robust growth, driven by tightening environmental regulations and increasing demand for industrial air pollution control. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the baghouse filters market was valued at USD 1.78 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.2% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2029. This expansion is fueled by rising industrialization, especially in emerging economies, and the need for compliance with emission standards across sectors such as cement, power generation, metals, and chemicals. As industries prioritize cleaner production processes, the demand for high-efficiency particulate control solutions like baghouse filters continues to surge. With technological advancements enhancing filtration efficiency and durability, leading manufacturers are well-positioned to meet this growing demand. Below are the top 5 baghouse filter manufacturers shaping the industry through innovation, global reach, and comprehensive filtration solutions.
Top 5 Baghouse Filters Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Baghouse Filter Bags & Cartridges
Domain Est. 1998
Website: fabcoind.com
Key Highlights: FabCo Industrial Services provides baghouse filters and cartridge filters, plus parts and services for your dust collection systems….
#2 Baghouse.com – Dust Collectors
Domain Est. 1999
Website: baghouse.com
Key Highlights: Baghouse.com is a leading manufacturer of baghouse dust collection systems and equipment with 40+ years of experience serving all industries. Copyright © 2025 ……
#3 Baghouse Filters
Domain Est. 2006
Website: tysum.com
Key Highlights: Our modern factories manufacture baghouse filters that are tailored to trap a wide range of dust particle sizes, resulting in clean air in all areas with ……
#4 Dedusting solutions for air pollution control
Domain Est. 2007
Website: fivesgroup.com
Key Highlights: Fives’ dust control solutions consist of our proprietary baghouse filters, which remove particulates from air or gas released from industrial or combustion ……
#5 Baghouse America
Domain Est. 2011
Website: baghouseamerica.com
Key Highlights: Baghouse America is a leading dust collection and baghouse manufacturer with over 20 years of experience in the air filtration industry….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Baghouse Filters
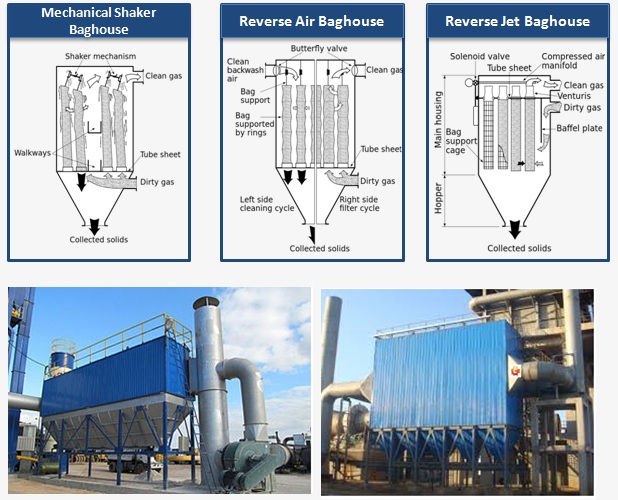
2026 Market Trends for Baghouse Filters
The baghouse filter market is poised for significant evolution by 2026, driven by tightening environmental regulations, technological advancements, and shifting industrial priorities. Here are the key trends shaping the industry:
Stringent Environmental Regulations Driving Demand
Governments worldwide are implementing stricter air quality standards, particularly targeting particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10) emissions from industrial processes. Regulations such as the U.S. EPA’s National Emission Standards for Hazardous Air Pollutants (NESHAP) and the European Union’s Industrial Emissions Directive (IED) are compelling industries—including cement, power generation, steel, and chemicals—to upgrade or install high-efficiency baghouse systems. This regulatory pressure is a primary growth driver, ensuring sustained demand through 2026.
Adoption of Advanced Filter Media and Nanotechnology
Innovation in filter media is a defining trend. Manufacturers are increasingly incorporating nanofiber and PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene)-coated fabrics that offer higher filtration efficiency, lower pressure drop, and extended bag life. These advanced materials improve performance in high-temperature, corrosive, or fine particulate environments, reducing maintenance costs and enhancing operational reliability—key selling points for end-users.
Integration of IoT and Predictive Maintenance
Smart monitoring systems are becoming standard in modern baghouse installations. By integrating sensors and IoT platforms, operators can track real-time parameters such as differential pressure, temperature, and emissions. This data enables predictive maintenance, minimizing unplanned downtime and optimizing cleaning cycles. By 2026, digitally connected baghouses are expected to dominate new installations, especially in large-scale industrial facilities.
Growth in Emerging Economies
Asia-Pacific, particularly India and Southeast Asia, is emerging as a high-growth region due to rapid industrialization and urban development. Expanding power plants, steel mills, and infrastructure projects in these regions are creating strong demand for cost-effective and efficient air pollution control. Local manufacturing and cost-competitive solutions are expected to accelerate market penetration.
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency Focus
With increasing emphasis on sustainability, industries are prioritizing energy-efficient baghouse systems. Innovations such as pulse-jet cleaning optimization, low-pressure drop designs, and heat-resistant bags for waste heat recovery are aligning baghouse technology with corporate ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) goals. Retrofitting older systems with energy-saving components is also a growing trend.
In summary, the 2026 baghouse filter market will be characterized by regulatory compliance, technological innovation, digital integration, and geographic expansion—positioning advanced filtration systems as essential components of sustainable industrial operations.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Baghouse Filters: Quality and Intellectual Property (IP) Concerns
Sourcing baghouse filters—critical components in industrial dust collection systems—can be fraught with challenges, particularly regarding quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) protection. Buyers and procurement teams often face hidden risks that can lead to system inefficiencies, increased maintenance costs, and even legal exposure. Below are two major pitfalls to avoid when sourcing these filtration products.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
One of the most common issues when sourcing baghouse filters is inconsistent or substandard quality, especially when procuring from low-cost suppliers or unfamiliar manufacturers.
1. Inadequate Material Specifications
Many suppliers may claim compliance with industry standards (e.g., ISO, ASTM, or EN) without providing verifiable test reports or material certifications. Filters made from inferior fibers, incorrect fabric weights, or poor stitching can lead to premature failure, reduced filtration efficiency, and higher operational downtime.
2. Lack of Performance Testing
Reputable manufacturers conduct rigorous testing for permeability, tensile strength, temperature resistance, and chemical compatibility. However, some suppliers skip these tests or falsify data. Without third-party validation, buyers risk selecting filters unsuitable for their specific operating conditions.
3. Counterfeit or Recycled Materials
There are documented cases of suppliers using recycled or reconditioned filter media passed off as new. These materials degrade rapidly under industrial conditions and can compromise air quality and emissions compliance.
4. Inconsistent Manufacturing Processes
Even with correct materials, poor quality control during production—such as inconsistent pleating, weak seams, or improper heat sealing—can result in leaks and reduced bag life.
Best Practice: Always request detailed material data sheets, perform supplier audits, and consider third-party lab testing of sample filters before full-scale procurement.
Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
Another often-overlooked risk involves the infringement of intellectual property rights, particularly when sourcing from regions with weak IP enforcement.
1. Replica or “Compatible” Filters
Many suppliers market filters as “compatible” with OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) designs (e.g., Donaldson, Donaldson® Torit®, GE Energy, etc.). While compatibility is legitimate, some suppliers cross the line by replicating patented filter designs, seals, or mounting configurations without authorization.
2. Trademark and Patent Infringement
Using filters that mimic patented geometries or branded components can expose the end-user to legal liability, especially in regulated industries. Even if the buyer is unaware, courts may hold them accountable for using infringing components, particularly if they were purchased at suspiciously low prices.
3. Voided OEM Warranties
Most OEMs void system warranties if non-approved or infringing filters are used. This can lead to costly repairs and loss of performance guarantees, negating any initial cost savings.
4. Supply Chain Transparency Issues
Some suppliers obscure the origin of their filters or fail to disclose design sources. This lack of transparency increases the risk of accidental IP violations.
Best Practice: Work only with reputable suppliers who can provide IP clearance documentation or confirm that their products are designed independently and do not infringe on existing patents. Include IP indemnity clauses in procurement contracts.
By proactively addressing quality and IP concerns, organizations can ensure reliable baghouse performance, avoid legal complications, and achieve long-term cost savings. Due diligence during the sourcing process is essential to mitigate these common but preventable pitfalls.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Baghouse Filters
Overview of Baghouse Filters in Industrial Operations
Baghouse filters, also known as fabric filters, are critical components in industrial air pollution control systems. They capture particulate matter from exhaust gases in industries such as cement, steel, power generation, and chemicals. Effective logistics and compliance management ensures operational efficiency, regulatory adherence, and environmental protection.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Baghouse filters must comply with local, national, and international environmental regulations. Key standards include:
– EPA Standards (USA): Compliance with National Emission Standards for Hazardous Air Pollutants (NESHAP) and New Source Performance Standards (NSPS).
– EU Industrial Emissions Directive (IED): Requires Best Available Techniques (BAT) for emission control.
– ISO 16890 & ISO 29463: Standards for air filter performance and testing.
Facilities must conduct regular stack testing, maintain emission records, and obtain necessary permits.
Emission Monitoring and Reporting
Operators must implement continuous monitoring systems (CEMS) or periodic testing to track particulate emissions. Data must be documented and reported to regulatory bodies as required. Non-compliance can result in fines, operational shutdowns, or legal action. Calibration and maintenance of monitoring equipment are mandatory.
Filter Media Selection and Handling
Choosing the correct filter media (e.g., polyester, PTFE, fiberglass) depends on temperature, chemical exposure, and dust characteristics. Proper handling during transport and installation prevents contamination or damage. Suppliers should provide Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) and compliance documentation.
Transportation and Storage Logistics
- Packaging: Filters must be sealed in moisture-resistant packaging to prevent degradation.
- Handling: Use appropriate lifting equipment to avoid physical damage; avoid sharp impacts.
- Storage: Store in a dry, temperature-controlled environment away from direct sunlight and contaminants. Stack vertically if required, following manufacturer guidelines.
Installation and Commissioning Procedures
Installation must follow manufacturer specifications and engineering designs. Key steps include:
– Verifying baghouse structural integrity.
– Ensuring proper gasketing and sealing.
– Conducting leak tests pre-commissioning.
Documentation of installation, including photos and checklists, supports compliance audits.
Maintenance and Replacement Scheduling
Regular inspection and preventive maintenance extend filter life and ensure compliance. Maintenance logs should record:
– Pressure drop across filters.
– Bag cleaning cycles (pulse-jet, reverse air, etc.).
– Bag replacement dates and conditions.
Scheduled replacements should be based on performance data, not just time intervals.
Waste Disposal and Environmental Responsibility
Used filter bags may be classified as hazardous or non-hazardous waste depending on captured particulates. Disposal must follow:
– RCRA regulations (USA) or equivalent.
– Waste characterization and manifesting.
– Use of licensed waste handlers.
Recycling options for clean filter materials should be explored where feasible.
Training and Documentation
Personnel involved in operation, maintenance, and logistics must be trained on:
– Safety procedures (lockout/tagout, confined space entry).
– Compliance requirements.
– Emergency response (e.g., filter fire, system breach).
All training, maintenance, and compliance records must be retained for audit purposes.
Conclusion
Effective logistics and compliance management for baghouse filters ensures environmental protection, regulatory adherence, and operational reliability. A proactive approach—integrating proper handling, monitoring, documentation, and training—is essential for sustainable industrial operations.
Conclusion for Sourcing Baghouse Filters:
Sourcing the right baghouse filters is a critical step in ensuring the efficiency, reliability, and compliance of dust collection systems. The selection process must consider key factors such as filter media type, filtration efficiency, temperature resistance, chemical compatibility, and dust characteristics. Additionally, evaluating supplier reliability, product quality, cost-effectiveness, and after-sales support contributes to long-term operational success.
Investing in high-quality, properly specified filters not only enhances air quality and regulatory compliance but also reduces maintenance downtime and extends equipment lifespan. By conducting thorough assessments of application requirements and supplier offerings, organizations can achieve optimal performance and cost savings. Ultimately, strategic sourcing of baghouse filters supports sustainable operations and improved workplace safety, making it a vital component of effective industrial air pollution control.