The industrial air filtration market has experienced robust growth, driven by stringent environmental regulations and increasing demand for emission control across sectors such as power generation, cement, steel, and chemicals. According to Grand View Research, the global baghouse filter market was valued at USD 2.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.4% from 2024 to 2030. This growth is further fueled by rising awareness of air quality management and the adoption of cleaner production technologies worldwide. As industries prioritize compliance with environmental standards and operational efficiency, the role of reliable baghouse filter manufacturers becomes increasingly critical. In this context, six key players have emerged as leaders, combining technological innovation, global reach, and proven performance to meet the escalating demand for high-efficiency particulate control solutions.
Top 6 Bag House Filter Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 BHA Filters, Industrial Dust Collection And Baghouse Filters
Domain Est. 1995
Website: parker.com
Key Highlights: BHA filters, industrial dust collection filters quality-designed. Baghouse filters, dust cartridge filters, and aftermarket pleated filters – 24×7 support….
#2 Baghouse Filter Bags & Cartridges
Domain Est. 1998
Website: fabcoind.com
Key Highlights: FabCo Industrial Services provides baghouse filters and cartridge filters, plus parts and services for your dust collection systems….
#3 Baghouse.com – Dust Collectors
Domain Est. 1999
Website: baghouse.com
Key Highlights: Baghouse.com is a leading manufacturer of baghouse dust collection systems and equipment with 40+ years of experience serving all industries. Copyright © 2025 ……
#4 Dedusting solutions for air pollution control
Domain Est. 2007
Website: fivesgroup.com
Key Highlights: Fives’ dust control solutions consist of our proprietary baghouse filters, which remove particulates from air or gas released from industrial or combustion ……
#5 Baghouse America
Domain Est. 2011
Website: baghouseamerica.com
Key Highlights: Baghouse America is a leading dust collection and baghouse manufacturer with over 20 years of experience in the air filtration industry….
#6 12 inch x 10 foot Baghouse Tube Filter 1-micron Efficiency
Domain Est. 1998
Website: oneida-air.com
Key Highlights: In stock Rating 5.0 (1) Replacement filter bag for older OAS dust collector using external baghouse systems or custom filter plenum boxes. Constructed from 16 oz. polyester felt….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Bag House Filter

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Bag House Filters
The global bag house filter market is poised for significant evolution by 2026, driven by tightening environmental regulations, industrial expansion, and technological advancements. As industries prioritize air quality control and emission reduction, bag house filters—critical components in dust and particulate matter collection—will play an increasingly vital role. Below are the key market trends expected to shape the bag house filter industry in 2026:
-
Stringent Environmental Regulations Drive Demand
Governments worldwide are enforcing stricter air pollution control norms, particularly in industries such as cement, power generation, steel, and chemicals. Regulatory bodies like the U.S. EPA and the European Union are mandating lower particulate emission limits, compelling industries to upgrade or install high-efficiency filtration systems. This regulatory push is a primary growth driver for the bag house filter market through 2026. -
Growth in Industrial and Infrastructure Development
Emerging economies in Asia-Pacific (especially India and Southeast Asia) and Africa are witnessing rapid industrialization and infrastructure growth. Expansion in thermal power plants, steel mills, and construction activities will increase the demand for dust control systems, boosting the adoption of bag house filters in these regions. -
Adoption of Advanced Filter Media and Smart Monitoring
By 2026, the integration of smart sensors and IoT-enabled monitoring systems in bag house filters is expected to become mainstream. These technologies allow real-time tracking of filter performance, pressure drop, and dust loading, enabling predictive maintenance and minimizing downtime. Additionally, innovations in filter media—such as PTFE membrane, nanofiber, and high-temperature-resistant fabrics—will enhance filtration efficiency and lifespan, particularly in harsh environments. -
Shift Toward Pulse-Jet Bag Houses
Pulse-jet bag house filters are gaining dominance due to their continuous operation capability and high cleaning efficiency. Their ability to operate without shutting down the system makes them ideal for high-volume industrial applications. This technology is expected to capture a larger market share by 2026, especially in cement and metal processing industries. -
Rising Focus on Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
Industries are increasingly adopting energy-efficient filtration systems to reduce operational costs and carbon footprints. Bag house filters with lower pressure drops and optimized airflow designs are in demand. Moreover, recyclable and eco-friendly filter bags are being developed to support circular economy goals, aligning with corporate sustainability initiatives. -
Increased Aftermarket and Retrofitting Activities
As existing industrial plants seek to comply with new emission standards, retrofitting older filtration systems with modern bag house filters is becoming cost-effective. This trend is fueling growth in the aftermarket segment, including replacement bags, cartridges, and control system upgrades. -
Consolidation and Strategic Partnerships Among Key Players
Market consolidation is expected as major players like Donaldson Company, Parker Hannifin, and Nederman strengthen their portfolios through acquisitions and partnerships. These strategic moves aim to expand geographic reach, enhance R&D capabilities, and offer integrated air pollution control solutions.
In conclusion, the bag house filter market in 2026 will be shaped by regulatory compliance, technological innovation, and industrial growth. Companies that invest in smart, sustainable, and efficient filtration solutions will be best positioned to capitalize on emerging opportunities across key verticals.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Bag House Filters (Quality, IP)
Sourcing bag house filters involves critical decisions that directly impact the efficiency, safety, and longevity of dust collection systems. Overlooking key factors—particularly around quality and Ingress Protection (IP) ratings—can lead to premature failures, increased maintenance costs, and system downtime. Below are common pitfalls to avoid:
Poor Quality Materials and Construction
One of the most frequent mistakes is selecting filters based solely on cost rather than material quality. Low-grade filter media may degrade quickly when exposed to heat, moisture, or chemical contaminants. Inferior stitching, seam construction, or end-cap bonding can lead to early leaks or ruptures, compromising air quality and system performance. Always verify material specifications (e.g., PTFE coating, fiber type) and request test reports for efficiency, abrasion resistance, and temperature tolerance.
Mismatched Filter Specifications for Operating Conditions
Using filters not suited for the specific application environment is a major pitfall. For example, applying standard polyester bags in a high-temperature or corrosive environment leads to rapid degradation. Similarly, ignoring dust characteristics like particle size, moisture content, or stickiness can result in blinding (clogging) or poor cleaning efficiency. Ensure the filter media, micron rating, and surface treatment align with the process conditions.
Ignoring Ingress Protection (IP) Ratings for Filter Housings
While IP ratings typically apply to electrical enclosures and housings rather than the filter bags themselves, overlooking IP protection for control cabinets, solenoid valves, or pulse-jet cleaning systems can be detrimental. In dusty or humid environments, inadequate IP ratings (e.g., using IP54 instead of IP65 or higher) allow dust and moisture ingress, leading to electrical failures and compromised system control. Always confirm the IP rating of auxiliary components matches the site environment.
Lack of Certification and Compliance Verification
Failing to verify compliance with industry standards (e.g., ISO, EN, OSHA, ATEX for explosive atmospheres) is a serious oversight. Non-certified filters may not meet required filtration efficiency (e.g., MERV, HEPA) or flame resistance standards. This poses safety risks and may result in regulatory non-compliance or voided warranties.
Inadequate Supplier Qualification
Sourcing from unqualified or unreliable suppliers increases the risk of receiving counterfeit or substandard products. Avoid vendors who cannot provide technical data sheets, performance test results, or traceability documentation. Partner with suppliers who offer application support and after-sales service.
Overlooking Long-Term Cost of Ownership
Focusing only on initial purchase price can be misleading. Low-cost filters often require more frequent replacements and increase energy consumption due to higher pressure drops. Investing in higher-quality filters with longer service life typically reduces downtime and maintenance costs over time.
By addressing these common pitfalls—especially ensuring material quality and appropriate IP protection for system components—you can enhance the reliability and performance of your bag house filtration system.
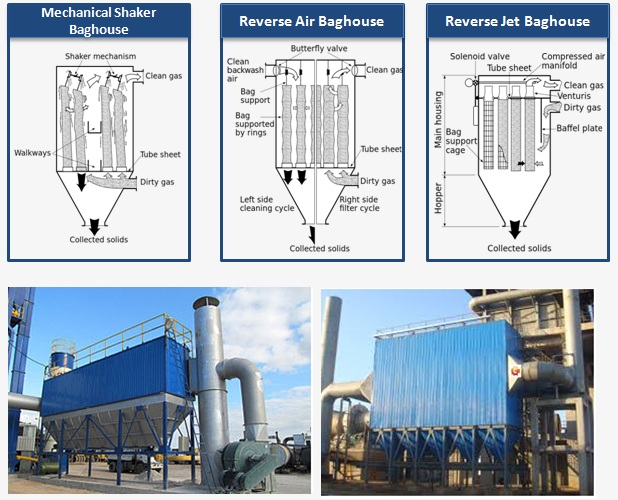
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Bag House Filter
Overview
A Bag House Filter, also known as a baghouse or fabric filter, is an air pollution control device used to remove dust and particulate matter from industrial exhaust gases. Proper logistics planning and regulatory compliance are essential for its safe transportation, installation, operation, and maintenance.
Transportation and Handling
Ensure the bag house filter is securely packaged and protected during transit. Use cranes or forklifts with appropriate lifting points to avoid structural damage. Confirm site access routes can accommodate the filter’s dimensions and weight. Protect filter bags from moisture, dust, and physical contact during transport.
Import/Export Regulations
Verify compliance with international trade regulations if shipping across borders. Required documentation may include commercial invoices, packing lists, certificates of origin, and conformity assessments. Check for restrictions on materials (e.g., certain filter media) under environmental or hazardous substance regulations such as REACH or RoHS.
Installation Requirements
Install the bag house filter on a stable, level foundation capable of supporting its operational weight. Ensure proper alignment with ductwork and exhaust systems. Follow manufacturer specifications for clearances, ventilation, and access for maintenance. Confirm electrical and control systems meet local codes (e.g., NEC in the U.S., IEC standards internationally).
Environmental Compliance
Bag house filters must meet emission standards set by environmental agencies such as the U.S. EPA, EU Industrial Emissions Directive (IED), or local environmental protection authorities. Conduct periodic stack testing to verify particulate matter (PM) removal efficiency. Maintain records of emissions data, maintenance, and filter changes to demonstrate compliance.
Operational Safety Standards
Adhere to OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) or equivalent workplace safety regulations. Implement lockout/tagout (LOTO) procedures during maintenance. Provide personnel with appropriate PPE (respirators, gloves, eye protection) when handling dust or replacing filter bags. Ensure dust collection systems prevent combustible dust accumulation in compliance with NFPA 652 or other applicable fire safety codes.
Maintenance and Waste Disposal
Schedule regular inspection and replacement of filter bags based on pressure drop and dust load. Used filter bags and collected dust may be classified as hazardous or non-hazardous waste depending on captured materials. Dispose of waste in accordance with local, state, or national regulations (e.g., RCRA in the U.S.). Maintain logs of maintenance, repairs, and waste disposal activities.
Documentation and Recordkeeping
Keep detailed records including equipment manuals, compliance certifications, inspection reports, emission test results, and training logs. These documents are essential for audits, regulatory inspections, and ensuring long-term operational compliance.
Training and Certification
Ensure personnel involved in operating and maintaining the bag house filter are trained on its safe use, emergency procedures, and relevant environmental and safety regulations. Maintain training records and update certifications as required by local authorities or industry standards.
Conclusion
Proper logistics planning and adherence to compliance requirements are critical to the effective and lawful operation of a bag house filter. By following regulatory guidelines and maintaining thorough documentation, facilities can ensure environmental protection, worker safety, and uninterrupted operations.
Conclusion for Sourcing Baghouse Filters:
Sourcing the right baghouse filters is a critical factor in ensuring the efficiency, longevity, and compliance of dust collection systems. The selection process must consider key parameters such as filter material (e.g., polyester, PTFE, fiberglass), filtration efficiency, temperature resistance, chemical compatibility, and dust characteristics. Additionally, evaluating suppliers based on quality certifications, consistency in manufacturing, technical support, and after-sales service is essential to maintain optimal system performance.
Investing in high-quality, application-specific filters not only enhances air quality and operational efficiency but also reduces long-term maintenance costs and downtime. By conducting thorough market research, comparing total cost of ownership, and considering sustainability aspects such as filter lifespan and disposability, organizations can make informed procurement decisions.
Ultimately, strategic sourcing of baghouse filters contributes to improved environmental compliance, worker safety, and overall process reliability—making it a vital component of effective industrial air pollution control.