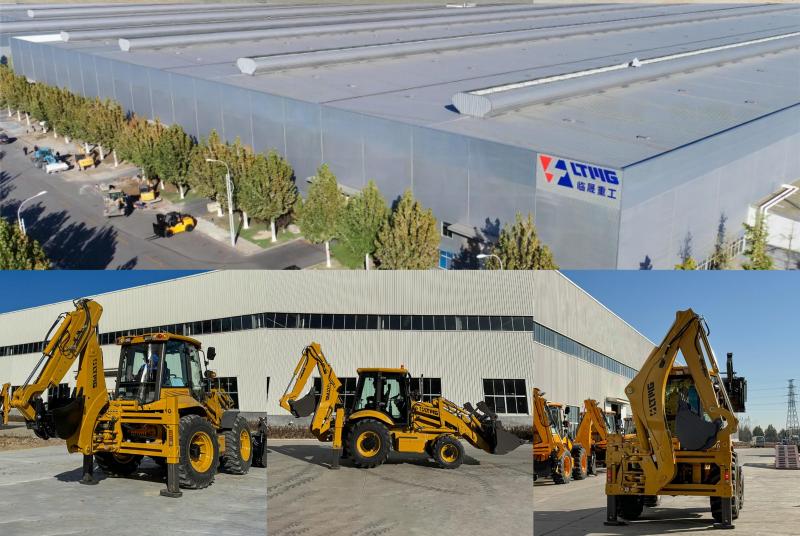
The global back loader market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand for efficient material handling equipment across construction, mining, agriculture, and logistics sectors. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the global loader market was valued at USD 9.57 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 4.8% through 2029, with back loaders representing a significant segment due to their versatility and cost-effectiveness. Similarly, Grand View Research highlights increasing infrastructure development and urbanization—particularly in Asia-Pacific and Latin America—as key growth accelerators. As operational efficiency becomes a top priority, manufacturers investing in fuel-efficient, technologically advanced, and compact back loader models are gaining competitive advantage. In this evolving landscape, the following ten companies have emerged as leading back loader manufacturers, combining innovation, global reach, and proven performance to meet the demands of modern industries.
Top 10 Back Loader Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Loadmaster
Domain Est. 2002
Website: loadmaster.org
Key Highlights: Loadmaster is a leading manufacturer of high quality refuse equipment. Located in Norway Michigan, our equipment is made in the USA with pride!…
#2 Wheel Loaders
Domain Est. 1990
Website: deere.com
Key Highlights: John Deere wheel loaders will elevate your reach, comfort, and control. With models ranging from 61.0-536.0 hp with 1-10 cubic yard bucket capacities….
#3 Backhoe Loaders / Backhoe Tractors
Domain Est. 1993
Website: cat.com
Key Highlights: 2-day deliveryCat backhoe loaders provide superior digging, trenching, back-filling and material handling capability and can be used for many applications….
#4 Backhoe loader
Domain Est. 1993
Website: manitou.com
Key Highlights: Discover all Manitou backhoe loaders and all their specs and features….
#5 CASE Backhoe Loaders
Domain Est. 1995 | Founded: 1957
Website: casece.com
Key Highlights: CASE backhoe loaders have been doing it right since 1957, pulling double duty on lots of tough jobsites including utility and emergency underground response….
#6 Gehl
Domain Est. 1995
Website: gehl.com
Key Highlights: We proudly design, build, test and manufacture machines that WORKS LIKE YOU. Dating back to 1859, GEHL has been deeply rooted in agriculture….
#7 Backhoe Loaders
Domain Est. 1997
Website: bobcat.com
Key Highlights: Explore the entire Bobcat backhoe loaders model lineup. View features, specs, compare models, attachment versatility to find the best machine for your ……
#8 Backhoe Loaders
Domain Est. 1997
Website: jcb.com
Key Highlights: 90-day returnsJCB knows a thing or two about designing the perfect backhoe loader. We were, after all, the first company who developed the concept back in 1953….
#9
Domain Est. 1997
Website: construction.newholland.com
Key Highlights: From loaders to mini excavators and forklifts, New Holland Construction equipment is built to help you get the job done….
#10 Wheel Loaders
Domain Est. 2022
Website: na.develon-ce.com
Key Highlights: DEVELON has been a leading wheel loader brand. Our redesigned lineup of innovative -7 Series models delivers the next generation of market-leading performance….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Back Loader

2026 Market Trends for Backhoe Loaders
The backhoe loader market is poised for notable shifts by 2026, driven by technological advancements, regulatory changes, and evolving construction and infrastructure demands. Here’s a comprehensive analysis of the key trends shaping the industry:
1. Sustainability and Emission Regulations Driving Electrification
By 2026, environmental regulations—particularly in North America, Europe, and parts of Asia—are expected to tighten further under initiatives like the EU Stage V and potential U.S. EPA Tier 5 standards. This will accelerate the shift toward low- and zero-emission machinery. Major manufacturers such as Volvo, John Deere, and JCB are investing heavily in electric backhoe loaders. Battery-electric models are projected to gain market share, especially in urban construction and indoor applications where noise and emissions are critical concerns. Hybrid models may serve as a transitional solution in regions with less developed charging infrastructure.
2. Smart Technology and Telematics Integration
Connectivity will be a defining feature of backhoe loaders in 2026. Advanced telematics systems will become standard, enabling real-time monitoring of machine health, fuel efficiency, location tracking, and operator behavior. This data will empower fleet managers to improve maintenance scheduling, reduce downtime, and enhance operational efficiency. Integration with construction management software and BIM (Building Information Modeling) platforms will allow for better project planning and equipment utilization on job sites.
3. Growth in Emerging Markets Fuels Demand
Emerging economies in Southeast Asia, Africa, and Latin America are expected to drive significant demand for backhoe loaders due to expanding infrastructure projects, urbanization, and government investments in rural development. The versatility of backhoe loaders—combining digging, lifting, and loading capabilities—makes them ideal for small to mid-sized contractors in these regions. Localized manufacturing and affordable models with simplified features will cater to price-sensitive markets.
4. Focus on Operator Comfort and Safety
By 2026, ergonomics and safety will be paramount in machine design. Enhanced operator cabins with improved visibility, climate control, noise reduction, and intuitive controls will become standard. Advanced safety features such as rear-view cameras, proximity sensors, and automated stability controls will be increasingly adopted to reduce worksite accidents and comply with stricter OSHA and equivalent global safety regulations.
5. Rise of Compact and Multi-Functional Models
Urban construction and renovation projects will drive demand for compact backhoe loaders that can operate in confined spaces. Manufacturers will respond with smaller, more maneuverable models that maintain performance. Additionally, modular attachments and quick-coupler systems will enable backhoe loaders to perform a wider range of tasks—from trenching and grading to paving and material handling—increasing their value proposition for multi-role operations.
6. Supply Chain Resilience and Localization
Ongoing geopolitical tensions and past disruptions (e.g., pandemic, semiconductor shortages) will push manufacturers to localize production and diversify supply chains. By 2026, companies are expected to increase regional manufacturing hubs to reduce dependency on global suppliers and ensure faster delivery times, particularly in high-growth markets.
Conclusion
The backhoe loader market in 2026 will be defined by innovation, sustainability, and adaptability. While traditional diesel-powered models will still dominate in many regions, the penetration of electric and smart machines will grow steadily. Contractors and fleet operators who embrace these trends—particularly electrification, connectivity, and versatility—will gain a competitive edge in an increasingly efficient and regulated construction landscape.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Back Loaders (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing back loaders—especially in industries involving software, technology, or proprietary components—can be fraught with risks related to both product quality and intellectual property (IP) rights. Overlooking these aspects can lead to legal disputes, financial losses, and reputational damage. Below are key pitfalls to watch for:
Poor Quality Assurance and Inconsistent Standards
Suppliers may deliver back loaders that fail to meet required performance or durability standards. This often stems from inadequate manufacturing oversight, use of substandard materials, or lack of proper testing protocols. Without rigorous quality control checks and clear specifications in procurement agreements, buyers risk receiving unreliable or unsafe equipment.
Lack of Transparency in Manufacturing Processes
Many suppliers, particularly in low-cost regions, do not fully disclose their production methods or component sourcing. This opacity can hide shortcuts that compromise quality or involve unauthorized third-party production—raising red flags for both performance and IP compliance.
Infringement of Intellectual Property Rights
One of the most critical risks is sourcing back loaders that incorporate patented technologies, proprietary designs, or copyrighted software without proper licensing. This exposes the buyer to legal liability, including infringement claims from original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) or IP holders, even if the buyer was unaware of the violation.
Use of Counterfeit or Reverse-Engineered Components
Some suppliers use cloned or reverse-engineered parts to cut costs. While these may appear functionally similar, they often lack reliability and can violate IP laws. Using such components may void warranties and lead to system failures or safety hazards.
Absence of IP Ownership Clauses in Contracts
Procurement agreements that fail to explicitly address IP ownership—particularly for custom-developed back loading systems or software—can result in disputes. Without clear terms, the supplier may retain rights to modifications or innovations, limiting the buyer’s ability to maintain, update, or resell the product.
Inadequate Due Diligence on Suppliers
Failing to vet suppliers’ credentials, certifications, and IP compliance history increases the risk of engaging with vendors involved in IP theft or poor manufacturing practices. Skipping audits or site visits can leave critical quality and legal risks undetected.
Insufficient Documentation and Traceability
Back loaders lacking proper documentation—such as bills of materials, software licenses, or compliance certificates—make it difficult to verify authenticity, ensure maintenance, or defend against IP claims. Traceability is essential for quality control and legal protection.
Overlooking Software Licensing and Embedded Code
Many modern back loaders include embedded software for control systems or data management. Sourcing units with unlicensed, pirated, or improperly licensed software can lead to cyber vulnerabilities and legal exposure, especially under international IP laws.
Failure to Secure Warranty and Indemnification
Without strong contractual warranties and indemnification clauses, buyers bear the full risk if a back loader turns out to be defective or infringes on third-party IP. Suppliers should be contractually obligated to cover liabilities arising from such issues.
Regulatory Non-Compliance
Back loaders used in regulated industries (e.g., construction, mining, logistics) must meet specific safety and environmental standards. Sourcing units that don’t comply—either due to poor quality or unauthorized modifications—can lead to fines, operational shutdowns, or liability in case of accidents.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Back Loader Operations
This guide outlines key logistics considerations and compliance requirements for the safe and legal operation of back loaders (also known as rear loaders), commonly used in waste collection and material handling.
Vehicle Specifications and Maintenance
Ensure all back loaders meet manufacturer specifications and local regulatory standards. Regular maintenance is critical to prevent mechanical failures and ensure operational safety. Key actions include:
– Conduct daily pre-trip inspections (brakes, lights, hydraulics, tires, backup alarms).
– Follow scheduled maintenance per manufacturer guidelines.
– Keep detailed service records accessible for audits.
Regulatory Compliance
Back loader operations must adhere to federal, state, and local regulations. Key areas include:
– Commercial Driver’s License (CDL): Operators must possess the appropriate class of CDL with required endorsements.
– Hours of Service (HOS): Comply with FMCSA regulations to prevent driver fatigue.
– Weight Limits: Adhere to axle and gross vehicle weight restrictions to avoid fines and road damage.
– Environmental Regulations: Follow EPA and local guidelines for fluid disposal and emissions.
Operational Safety Procedures
Safety is paramount in back loader operations. Implement the following procedures:
– Use backup alarms and cameras; ensure spotters are present when visibility is limited.
– Train operators on proper loading techniques to prevent equipment damage or injury.
– Prohibit riders on the vehicle during collection routes.
– Secure all compartments and compacting mechanisms before transit.
Waste Handling and Environmental Compliance
When used for waste collection, back loaders must comply with environmental standards:
– Prevent leakage or spillage during transport (use sealed containers and liners).
– Segregate recyclable, organic, and hazardous materials per local ordinances.
– Maintain manifests for special waste streams (e.g., medical or hazardous waste).
– Report spills immediately and follow cleanup protocols.
Route Planning and Logistics Efficiency
Optimize logistics to reduce fuel consumption, emissions, and labor costs:
– Use routing software to plan efficient collection schedules.
– Schedule collections during off-peak traffic hours where possible.
– Monitor fuel usage and idle time to improve fleet efficiency.
– Implement real-time GPS tracking for fleet management and customer service.
Documentation and Recordkeeping
Maintain accurate records to demonstrate compliance and support logistics management:
– Driver logs (electronic or paper-based per HOS rules).
– Vehicle inspection and maintenance reports.
– Waste manifests and disposal records.
– Training certifications for all operators.
Training and Operator Certification
All back loader operators must undergo comprehensive training, including:
– Safe vehicle operation and emergency procedures.
– Proper use of compaction and lifting mechanisms.
– Defensive driving techniques.
– Waste sorting and environmental compliance.
– Periodic refresher training to reinforce safety and regulatory updates.
By following this guide, organizations can ensure efficient, safe, and compliant back loader operations while minimizing environmental impact and regulatory risk.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Back Loader:
Sourcing a back loader requires a strategic approach that balances cost, performance, reliability, and long-term operational needs. After evaluating various suppliers, models, and specifications, it is evident that selecting the right back loader involves considering factors such as lifting capacity, fuel efficiency, durability, after-sales service, and total cost of ownership. Prioritizing reputable manufacturers with strong local support networks ensures timely maintenance and reduced downtime. Additionally, aligning the machine’s specifications with the intended application—whether for construction, landscaping, or waste management—enhances productivity and return on investment. Ultimately, a well-informed sourcing decision will lead to improved operational efficiency, reduced lifecycle costs, and sustained performance in demanding work environments.