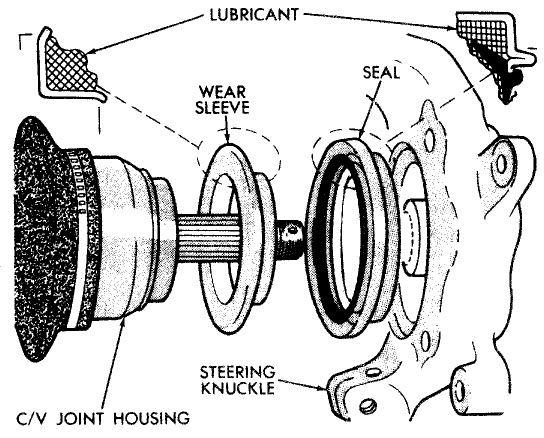
The global automotive seals market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing vehicle production, stringent emissions regulations, and rising demand for fuel-efficient and lightweight sealing solutions. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the automotive seals market was valued at USD 8.37 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 11.45 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of approximately 5.4% during the forecast period. This expansion is further supported by advancements in material technology—particularly the adoption of thermoplastic elastomers and fluorocarbon rubbers—as well as the growing emphasis on improving vehicle durability and performance under extreme conditions. With the automotive industry increasingly shifting toward electric vehicles (EVs), the need for high-performance sealing solutions that ensure battery safety, prevent fluid leakage, and withstand thermal fluctuations has become critical. As a result, leading manufacturers are investing heavily in R&D and strategic partnerships to maintain a competitive edge. In this dynamic landscape, the following nine companies have emerged as key players, demonstrating innovation, global reach, and strong market presence in the automotive seals sector.
Top 9 Automotive Seals Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Seals & Sealing Solutions For Automotive Industry
Domain Est. 1996
Website: trelleborg.com
Key Highlights: We are a leading supplier of advanced sealing solutions to automotive Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) and their component suppliers….
#2 Gallagher Fluid Seals
Domain Est. 1998
Website: gallagherseals.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $99Gallagher Fluid Seals, Inc. is a global distributor and manufacturer of fluid sealing products. GFS represents the strongest seal manufacturers in the world ….
#3 M Seals
Domain Est. 2004
Website: m-seals.com
Key Highlights: M Seals specialises in industrial seals, ensuring high quality in all our products. With over 50000 items readily available in our stock, we can deliver ……
#4 Colonial Seal Company
Domain Est. 2005
Website: colonialseal.com
Key Highlights: We are an ISO-certified sealing solutions company providing OEM seals, gaskets, and custom replacements for obsolete or hard-to-find parts….
#5 Seals and Gaskets
Domain Est. 1987
Website: dupont.com
Key Highlights: Specialized, high-performance seals, O-rings and gaskets made from DuPont elastomers provide durable solutions for high heat and aggressive chemical uses….
#6 Precision Premium Automotive Glass Parts
Domain Est. 1994
Website: prp.com
Key Highlights: Precision provided millions of extruded and molded EPDM rubber, PVC and HDPE based plastics for the automotive industry | Search, Parts, Product, ……
#7 Freudenberg Sealing Technologies
Domain Est. 1995
Website: fst.com
Key Highlights: Freudenberg Sealing Technologies is a proven supplier for demanding products and applications, and a development and service partner to customers….
#8 Seals
Domain Est. 1996
Website: skf.com
Key Highlights: Automotive seals We offer seals for engines, drivelines, suspensions, and wheel-end applications in traditional and hybrid/electric vehicles and two-wheelers….
#9 Hercules Sealing Products
Domain Est. 2006
Website: herculesus.com
Key Highlights: Hercules Sealing Products is a leading supplier of aftermarket hydraulic seals, seal kits, hydraulic cylinders, and cylinder repair parts….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Automotive Seals

H2: Key Market Trends Shaping the Automotive Seals Industry in 2026
By 2026, the automotive seals market is poised for significant transformation, driven by profound shifts in vehicle technology, sustainability demands, and evolving manufacturing practices. Here are the dominant trends expected to define the landscape:
1. Electrification Acceleration & Seal Material Revolution:
The rapid adoption of Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) and Plug-in Hybrids (PHEVs) is the single most influential trend. This shift necessitates a fundamental rethinking of seal materials and designs:
* High-Voltage & Thermal Management Focus: Seals must provide superior electrical insulation for high-voltage components (batteries, motors, charging systems) and withstand extreme thermal cycles in battery packs and power electronics. Materials like specialized fluoropolymers (FKM, FFKM), PTFE, and advanced thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs) will see increased demand over traditional nitrile rubber (NBR).
* Coolant System Complexity: The intricate liquid cooling systems for batteries and motors require highly reliable, chemically resistant seals capable of handling new coolant formulations (often more aggressive) under high pressure and temperature.
* Reduced Underhood Sealing Needs: While powertrain seals remain crucial, the simplification of the powertrain (no ICE, exhaust, complex fuel systems) reduces demand for certain traditional seals (e.g., valve stem seals, exhaust gaskets).
2. Sustainability & Circular Economy Integration:
Environmental regulations and consumer pressure are pushing sustainability to the forefront:
* Bio-based & Recycled Materials: Development and adoption of seals using bio-based polymers (e.g., bio-EPDM, bio-silicone) and incorporating recycled content (especially from post-industrial scrap) will accelerate. “Greener” production processes with lower VOC emissions will be essential.
* End-of-Life & Recyclability: Design for disassembly and recyclability of seals (often challenging due to material complexity and bonding) will gain importance, driven by regulations like the EU’s End-of-Life Vehicle (ELV) directive and corporate sustainability goals.
* Lightweighting: Continued pressure to reduce vehicle weight for efficiency (even in EVs for range) will favor lighter seal materials like advanced TPEs and specific silicones over heavier traditional rubbers.
3. Advanced Materials & Multi-Functionality:
Seals are evolving beyond simple barriers:
* Enhanced Performance Polymers: Demand will surge for seals offering superior resistance to oils, coolants, ozone, UV, and extreme temperatures (both high and low), particularly for EV components. Silicones (VMQ, FVMQ) for extreme temperatures and specialty fluorocarbons remain critical.
* Integrated Functionality: Development of “smart” seals with embedded sensors for monitoring pressure, temperature, or seal integrity (predictive maintenance) will move from niche to broader adoption, especially in commercial and premium vehicles.
* Multi-Material & Hybrid Designs: Combining different elastomers or integrating seals with plastic/metal components (overmolding) to achieve specific performance requirements (e.g., stiffness, sealing, damping) will become more common.
4. Supply Chain Resilience & Localization:
Geopolitical uncertainties and lessons from recent disruptions emphasize the need for robust supply chains:
* Nearshoring/Reshoring: Automakers and Tier 1 suppliers will increasingly prioritize regional sourcing of critical components like seals to mitigate risks, particularly for electric vehicle production hubs (North America, Europe, China). This benefits local seal manufacturers.
* Vertical Integration & Strategic Partnerships: Seal manufacturers may seek closer partnerships or vertical integration with material suppliers to secure access to specialized polymers and ensure quality control for EV-specific needs.
* Digitalization & Traceability: Enhanced use of digital tools (blockchain, IoT) for supply chain transparency, quality tracking, and ensuring material provenance (especially for sustainable materials) will grow.
5. Consolidation & Technology Leadership:
The market will likely see increased consolidation as companies compete on technology and scale:
* Focus on R&D: Leading players will heavily invest in R&D to develop next-generation EV-compatible, sustainable, and high-performance materials, creating barriers to entry for smaller players.
* M&A Activity: Larger seal manufacturers may acquire niche players with expertise in advanced materials or specific EV applications to strengthen their portfolios.
* Regional Growth Variations: Growth will be strongest in regions with aggressive EV adoption targets (China, Europe, North America), while markets with slower EV transitions may see more stable demand for traditional ICE seals, albeit gradually declining.
Conclusion:
The 2026 automotive seals market will be fundamentally different from today. Success will hinge on the ability of seal manufacturers to pivot decisively towards electrification-specific materials and designs, embrace sustainability throughout the product lifecycle, leverage advanced material science, ensure supply chain resilience, and drive innovation through technology leadership. The shift from simply sealing ICE components to enabling the performance, safety, and efficiency of complex electric powertrains will define the winners in this dynamic market.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Automotive Seals (Quality, IP)
Sourcing automotive seals involves significant risks related to both product quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Failing to address these areas can lead to supply chain disruptions, safety issues, recalls, legal disputes, and reputational damage.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inadequate Supplier Qualification
Selecting suppliers without rigorous audits or proven track records in automotive manufacturing can result in substandard seals. Many low-cost suppliers lack the necessary process controls, material traceability, or testing capabilities required for automotive applications, leading to premature failure under temperature, pressure, or chemical exposure.
Poor Material Specification and Traceability
Using incorrect elastomers (e.g., NBR instead of FKM for high-temperature environments) or failing to ensure full material traceability increases the risk of seal degradation and system failure. Suppliers may substitute cheaper or off-spec materials without approval, especially if oversight is weak.
Insufficient Testing and Validation
Relying solely on supplier-provided test reports without independent validation or real-world performance testing (e.g., compression set, fluid resistance, thermal cycling) can allow defective seals to enter production. Automotive environments demand rigorous validation per standards such as ISO 2230 or SAE J20.
Inconsistent Production Processes
Suppliers with unstable manufacturing processes may introduce variability in dimensions, hardness, and surface finish. This inconsistency leads to leaks, assembly issues, and non-compliance with tight OEM tolerances.
Intellectual Property-Related Pitfalls
Unprotected Design and Technical Documentation
Sharing detailed engineering drawings, material formulations, or performance specifications without proper non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) or legal safeguards exposes IP to misuse or reverse engineering by suppliers, especially in high-risk jurisdictions.
Lack of IP Ownership Clauses in Contracts
Failing to clearly define IP ownership in sourcing agreements may result in disputes over design rights. Suppliers could claim ownership of tooling, molds, or customized seal designs developed during production, limiting flexibility and increasing dependency.
Counterfeit or Reverse-Engineered Products
Unscrupulous suppliers may produce and sell copies of proprietary seal designs to third parties or even compete directly. Without robust monitoring and contractual penalties, this undermines market exclusivity and brand integrity.
Weak Supply Chain Oversight
Sub-tier suppliers or unauthorized subcontracting can lead to IP leakage. Without chain-of-custody controls and regular audits, sensitive designs and materials may be exposed to unauthorized parties, increasing the risk of IP theft.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires a strategic sourcing approach that combines technical diligence, legal protection, and continuous supplier management tailored to the high-stakes automotive environment.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Automotive Seals
Overview
This guide outlines the key logistics and compliance considerations for the manufacturing, transportation, storage, and distribution of automotive seals. Given their critical role in vehicle performance, safety, and emissions control, adherence to strict industry standards and regulatory requirements is essential throughout the supply chain.
Regulatory Compliance
ISO/TS 16949 and IATF 16949
All manufacturers of automotive seals must comply with IATF 16949, the international quality management standard for the automotive industry. This includes documented processes for design, production, and continuous improvement, with a focus on defect prevention and supply chain quality.
REACH and RoHS Compliance
Automotive seals must comply with EU regulations:
– REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals): Requires disclosure of Substances of Very High Concern (SVHC) in elastomers and other seal materials.
– RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances): Limits the use of lead, cadmium, mercury, and other hazardous materials, particularly relevant for seals used in electronic or sensor components.
FDA and NSF (if applicable)
For seals used in fuel systems, brake fluids, or potable water applications (e.g., in specialty vehicles), compliance with FDA 21 CFR or NSF/ANSI standards may be required to ensure material safety.
Material Traceability and Documentation
Full Material Disclosure (FMD)
Suppliers must provide complete FMDs, detailing all raw materials, additives, and processing aids used. This supports compliance with environmental regulations and enables customer audits.
Certificate of Conformance (CoC)
Each shipment must be accompanied by a CoC confirming that the seals meet specified technical drawings, material specs (e.g., ASTM D2000), and regulatory requirements.
Lot Traceability
Implement batch/lot tracking from raw material intake through final shipment. This enables rapid recalls and root cause analysis in case of non-conformances.
Packaging and Labeling
Protective Packaging
Seals must be packaged to prevent damage, deformation, or contamination during transit. Use anti-static, moisture-resistant, and cushioned packaging as appropriate for material type (e.g., NBR, FKM, EPDM).
Labeling Requirements
Labels must include:
– Part number and revision
– Lot/batch number
– Quantity
– Date of manufacture
– Compliance markings (e.g., RoHS, REACH)
– Handling symbols (e.g., “Do Not Stack,” “Keep Dry”)
– Customer-specific labeling (e.g., barcode, RFID)
Storage Conditions
Temperature and Humidity Control
Store seals in a clean, dry environment with temperatures between 15°C and 25°C (59°F–77°F) and relative humidity below 65%. Avoid exposure to direct sunlight, ozone, and UV radiation.
Shelf Life Management
Most elastomeric seals have a defined shelf life (typically 3–5 years). Implement FIFO (First In, First Out) inventory practices and monitor expiration dates. Conduct periodic requalification testing for aged stock.
Segregation
Store different materials (e.g., silicone vs. nitrile) separately to prevent cross-contamination. Clearly label storage areas.
Transportation
Mode Selection
Use enclosed, climate-controlled trucks or containers for long-distance or international shipments to protect against temperature extremes and moisture.
Handling Procedures
Train personnel to handle seals carefully to avoid kinking, stretching, or surface damage. Use appropriate lifting equipment for bulk shipments.
Customs and Export Compliance
For international logistics:
– Prepare accurate HS codes (e.g., 8484.10 for mechanical seals)
– Comply with export control regulations (e.g., EAR, ITAR if applicable)
– Provide commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin
Quality and Audit Preparedness
Incoming and Outgoing Inspections
Conduct dimensional checks, material hardness tests, and visual inspections per control plans. Retain records for at least 15 years, as required by IATF 16949.
Customer-Specific Requirements (CSRs)
Adhere to CSRs from OEMs such as Ford, GM, Volkswagen, or Toyota, which may include special testing, reporting, or packaging formats (e.g., AIAG standards).
On-Site Audits
Be prepared for customer or third-party audits. Maintain accessible records for quality, compliance, traceability, and corrective actions.
Sustainability and End-of-Life
Recycling and Waste Management
Partner with certified recyclers for production scrap and end-of-life seals. Document waste streams to support environmental reporting.
Carbon Footprint Reduction
Optimize logistics routes, consolidate shipments, and use returnable packaging where feasible to reduce environmental impact.
Conclusion
Effective logistics and compliance for automotive seals require a proactive, integrated approach across manufacturing, quality, and supply chain operations. Staying aligned with global standards and customer expectations ensures reliability, safety, and market access in the automotive sector.
Conclusion on Sourcing Automotive Seals
Sourcing automotive seals is a critical component in ensuring the reliability, safety, and performance of vehicles. As dynamic and static sealing solutions are integral to engines, transmissions, suspensions, and other systems, selecting the right seals requires a strategic approach that balances quality, cost, material compatibility, and supplier reliability.
Key considerations in the sourcing process include the selection of appropriate materials—such as NBR, silicone, FKM, or EPDM—based on environmental factors like temperature, pressure, and exposure to fluids. Additionally, adherence to industry standards (e.g., ISO, SAE) and OEM specifications is essential to ensure compatibility and longevity.
Working with suppliers who demonstrate proven manufacturing capabilities, quality control processes, and the ability to scale production is crucial. Building long-term partnerships with reliable vendors can enhance supply chain resilience, reduce lead times, and support innovation in seal design and performance.
In conclusion, effective sourcing of automotive seals demands a thorough understanding of technical requirements, market dynamics, and supplier ecosystems. By prioritizing quality, compliance, and collaboration, automotive manufacturers and suppliers can ensure optimal system performance and meet the evolving demands of the automotive industry.