The global automotive fastener market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising vehicle production, increasing demand for lightweight materials, and the expansion of electric vehicle (EV) manufacturing. According to Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at USD 83.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 112.6 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of approximately 5.1% during the forecast period. This expansion is fueled by technological advancements in fastening solutions—such as high-tensile, corrosion-resistant, and composite-compatible fasteners—needed to meet increasingly stringent safety and fuel efficiency standards. Additionally, Grand View Research highlights the growing adoption of aluminum and magnesium alloys in vehicle bodies, which requires specialized fastening systems, further propelling innovation and demand. As automotive manufacturers seek reliable, high-performance partners in their supply chains, the role of leading fastener producers has become more critical than ever. The following list highlights the top 10 automotive fastener manufacturers shaping this evolving landscape through innovation, global reach, and advanced engineering capabilities.
Top 10 Automotive Fastener Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Auveco
Domain Est. 1996
Website: auveco.com
Key Highlights: For over 100 years, Auto-Vehicle Parts LLC (Auveco) has been manufacturing and distributing specialty automotive and industrial fasteners. Our company goal ……
#2 Fasteners, Industrial Supply
Domain Est. 1997
Website: automotivefasteners.com
Key Highlights: Largest inventory of threaded fasteners and industrial supply; offering VMI and service parts programs. Call 800-632-0340….
#3 The Auto Bolt Company
Domain Est. 2019
Website: autoboltusa.com
Key Highlights: The Auto Bolt Company has 70 years of experience manufacturing fasteners and bolts for a variety of industries including the Military, Automotive and OEM….
#4 PEM – PennEngineering
Domain Est. 1996
Website: pemnet.com
Key Highlights: PEM offers innovative fastening solutions for a variety of applications across industries like Automotive Electronics, Consumer Electronics, Datacom and more….
#5 Cold Heading Company
Domain Est. 1996 | Founded: 1912
Website: coldheading.com
Key Highlights: Discover industry-leading cold-formed fasteners for automotive applications from Cold Heading Company, a trusted source since 1912….
#6 ARP
Domain Est. 1997
Website: arp-bolts.com
Key Highlights: Fastener Tech • ARP Ultra-Torque • Find Your Kit Instructions • Fastener Installation Overview • Torque Value Lookup • Fastener Installation FAQs…
#7 ITW Automotive
Domain Est. 1999
Website: itwautomotive.com
Key Highlights: ITW Automotive partners with customers to solve challenges with fastening, assembly & component solutions that advance performance and sustainability….
#8 rightway fasteners inc
Domain Est. 2001
Website: rfiusa.com
Key Highlights: Righway Fasteners provides a wide variety of quality fasteners to the Automotive Industry. RFI specializes in Cold Forming, Thread Rolling, Heat Treatment, ……
#9 Auto Fasteners
Domain Est. 2008
Website: auto-fasteners.com
Key Highlights: Auto-Fasteners streamlines the supply of Fasteners, C-parts, Kits, and Assemblies for the world’s leading automotive brands….
#10 ITW fasteners
Domain Est. 2014
Website: itw-fasteners.com
Key Highlights: ITW Global Fasteners hold cars together. We develop, produce and market intelligent and innovative fastening solutions for the automotive industry….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Automotive Fastener

H2 2026 Market Trends Analysis: Automotive Fasteners
The global automotive fastener market in the second half of 2026 is poised for significant transformation, driven by deeper penetration of electrification, advanced materials, stringent regulations, and evolving manufacturing demands. While the full-year 2026 outlook sets the stage, H2 is expected to crystallize key trends and accelerate specific shifts.
1. Accelerated Shift Towards Lightweighting & Material Innovation:
* Dominance of High-Strength Steel & Aluminum: The relentless pressure for fuel efficiency (ICE) and extended EV range will solidify the use of advanced high-strength steels (AHSS) and aluminum alloys in vehicle structures. H2 2026 will see fastener manufacturers heavily invested in developing and qualifying fasteners specifically engineered for these materials – focusing on optimized thread designs, coatings, and installation parameters to prevent galling and ensure joint integrity.
* Growth in Multi-Material Joining: As vehicles integrate steel, aluminum, magnesium, and composites, fasteners enabling reliable joints between dissimilar materials become critical. H2 will see increased adoption of specialized fasteners like flow-drill screws, self-piercing rivets (SPRs), and tailored bolts with specific coatings (e.g., PVD, specialized polymers) to manage galvanic corrosion and differing expansion rates.
* Emergence of Premium Materials: Demand for titanium and specialized nickel alloys will grow, albeit from a small base, primarily in high-performance EVs and premium segments where weight savings are paramount, particularly in battery packs and suspension components.
2. Electrification-Driven Fastener Evolution:
* Battery Pack Focus: The EV battery pack remains a major growth driver. H2 2026 will emphasize fasteners with superior thermal management properties (e.g., thermally conductive adhesives combined with mechanical fasteners, specialized heat-dissipating coatings) and enhanced electrical insulation to prevent short circuits. Reliability under thermal cycling is paramount.
* Motor & Power Electronics: Fasteners for electric motors and power electronics require high precision, excellent heat resistance, and often specific electromagnetic properties. Demand for specialized, often smaller, high-tolerance fasteners (e.g., in stator assembly, inverter housing) will continue to rise.
* High-Voltage System Safety: Fasteners securing high-voltage cabling and connectors will demand rigorous certification for vibration resistance, electrical isolation, and tamper-proofing, becoming a distinct sub-segment with stringent quality controls.
3. Heightened Focus on Quality, Traceability & Automation:
* Zero-Defect Mandate: Safety-critical applications (brakes, steering, suspension, EV battery) will drive an absolute requirement for zero-defect fasteners. H2 2026 will see widespread adoption of automated in-line inspection (AI-powered vision systems, laser measurement, acoustic emission testing) integrated directly into production lines.
* End-to-End Traceability: Blockchain or advanced digital ledger technologies are expected to gain traction for critical fasteners, providing immutable records from raw material sourcing through manufacturing, logistics, and final assembly, enhancing recall management and quality assurance.
* Smart Fastening & Process Monitoring: Tooling systems with integrated sensors will be standard, providing real-time torque, angle, and yield data for every fastening operation. This data feeds into digital twins and quality control systems, enabling predictive maintenance and process optimization.
4. Supply Chain Resilience & Regionalization:
* Nearshoring/Reshoring Momentum: Geopolitical tensions and lessons from past disruptions will push OEMs and Tier 1s to further localize supply chains, particularly for critical components. H2 2026 may see announcements or expansions of fastener manufacturing capacity in North America and Europe, focusing on strategic materials and high-value fasteners.
* Strategic Sourcing & Dual Sourcing: Companies will prioritize diversifying suppliers and securing long-term agreements for key materials (e.g., specific steel grades, specialty alloys) to mitigate price volatility and supply risks. Focus on supplier financial and operational health will intensify.
* Focus on Sustainability in Sourcing: Pressure to reduce Scope 3 emissions will lead to increased scrutiny of fastener suppliers’ own sustainability practices (energy use, recycling rates, logistics).
5. Sustainability as a Core Driver:
* Circular Economy Integration: H2 2026 will see tangible progress beyond pledges. Expect increased use of recycled content in fastener production (especially steel) and the development of fastener designs that facilitate easier disassembly for end-of-life vehicle recycling (design for disassembly – DfD).
* Green Manufacturing: Fastener producers will invest in renewable energy for production, energy-efficient processes (e.g., advanced heat treatment), and closed-loop water systems to meet OEM sustainability targets and regulations.
* Lifecycle Assessment (LCA): LCA will become a standard requirement for major OEMs, influencing fastener material and process choices based on total environmental impact.
6. Consolidation and Specialization:
* Market Consolidation: The increasing complexity, capital requirements for automation/traceability, and need for global scale are likely to drive further consolidation among fastener suppliers, particularly among mid-tier players.
* Rise of Specialized Niche Players: Simultaneously, highly specialized suppliers focusing on specific technologies (e.g., multi-material joining, EV battery fasteners, smart fastening systems) or ultra-high-precision applications will gain prominence, offering deep technical expertise.
Conclusion for H2 2026:
The second half of 2026 will be a period of cemented transformation for the automotive fastener market. The trends initiated earlier in the year – particularly the deep integration of fastening solutions for electrification, the imperatives of lightweighting with dissimilar materials, and the non-negotiable demands for quality and traceability – will be fully operational and driving investment decisions. Suppliers who have successfully navigated the material science challenges, embraced digitalization and automation for quality, built resilient regional supply chains, and embedded sustainability into their core operations will be best positioned to capture growth. The market will increasingly bifurcate between large, integrated global players and agile, highly specialized innovators. Success will hinge on technical leadership, operational excellence, and deep collaboration with OEMs to solve the complex fastening challenges of next-generation vehicles.
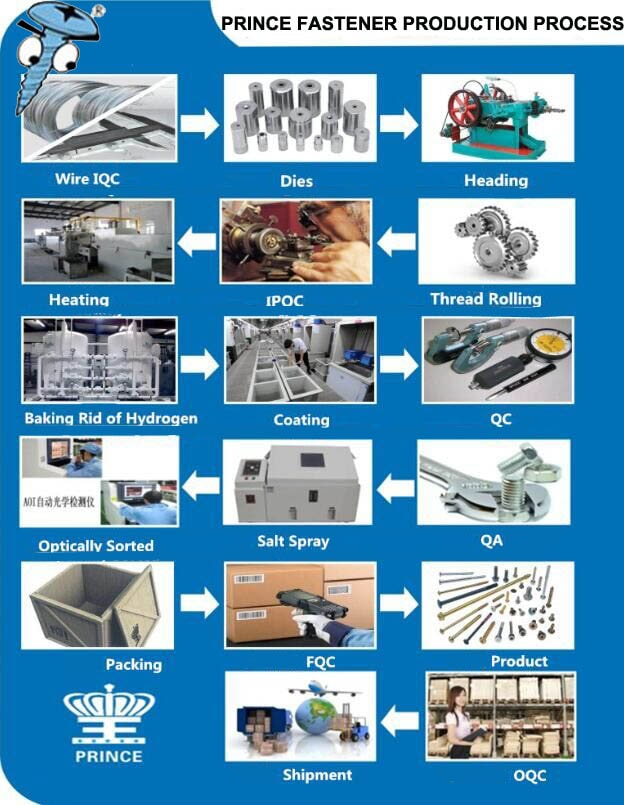
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Automotive Fasteners: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Poor Quality Control and Non-Compliance
One of the most frequent issues in sourcing automotive fasteners is inadequate quality control from suppliers. Fasteners must meet strict industry standards (e.g., ISO, DIN, ASTM, or OEM-specific specifications) to ensure safety and performance. Sourcing from suppliers with inconsistent manufacturing processes can result in dimensional inaccuracies, improper tensile strength, or poor surface treatments—leading to part failure, recalls, or safety hazards. Always verify supplier certifications (e.g., IATF 16949) and conduct regular audits and first-article inspections.
Counterfeit or Non-Genuine Components
The automotive supply chain is vulnerable to counterfeit fasteners, especially when sourcing from low-cost regions or unauthorized distributors. These parts may visually resemble genuine components but fail to meet required mechanical or material specifications. Using counterfeit fasteners can compromise vehicle integrity and expose the buyer to legal and safety liabilities. Establish traceability protocols and source only from authorized or vetted suppliers.
Intellectual Property (IP) Infringement
Many automotive fasteners, particularly those designed for specific OEM applications, are protected by patents, trademarks, or technical copyrights. Sourcing unlicensed copies—even if functionally adequate—can lead to IP infringement claims, legal action, or shipment seizures. This is especially risky when sourcing “copy” or “compatible” parts marketed as equivalents. Conduct due diligence on supplier IP compliance and avoid suppliers offering fasteners that replicate proprietary designs without authorization.
Lack of Traceability and Documentation
Automotive applications require full traceability of components for quality assurance and recall management. A common pitfall is sourcing fasteners without proper material certifications (e.g., mill test reports), batch/lot numbers, or production records. In the event of a failure, the inability to trace the origin can delay investigations and increase liability exposure. Ensure suppliers provide complete documentation with every shipment.
Inadequate Environmental and Regulatory Compliance
Fasteners may be subject to environmental regulations such as REACH, RoHS, or ELV directives, particularly regarding restricted substances like lead, cadmium, or certain chromates. Sourcing from suppliers unaware of or non-compliant with these regulations can result in shipment rejections or penalties. Confirm that fasteners meet all relevant chemical and environmental standards for the target market.
Overlooking Long-Term Supplier Reliability
Focusing solely on initial pricing can lead to partnerships with suppliers lacking the capacity, stability, or technical support for long-term performance. Fastener supply disruptions or quality drift over time can impact production schedules and product reliability. Evaluate suppliers not just on cost, but on financial health, technical capability, and track record in the automotive sector.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Automotive Fasteners
Overview
Automotive fasteners—such as bolts, nuts, screws, washers, and clips—are critical components in vehicle manufacturing and maintenance. Ensuring their reliable supply, safe transportation, and regulatory compliance is essential for automotive OEMs and Tier suppliers. This guide outlines key logistics and compliance considerations specific to automotive fasteners.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
International Standards
Automotive fasteners must comply with global and regional standards, including:
– ISO 898-1: Mechanical properties of carbon steel fasteners.
– ISO 3506: Corrosion-resistant stainless steel fasteners.
– DIN, ASTM, SAE, JIS: Regional standards used in Europe, North America, and Asia.
– IATF 16949: Quality management standard specific to automotive production.
Suppliers must provide certified test reports and material certifications (e.g., CoC, CoA) with each shipment.
REACH & RoHS Compliance
Fasteners may contain restricted substances (e.g., lead, cadmium, hexavalent chromium). Compliance with:
– REACH (EU): Requires disclosure of Substances of Very High Concern (SVHC).
– RoHS (EU): Restricts hazardous substances in electrical and electronic components.
Ensure all coatings, platings, and surface treatments meet these regulations.
Conflict Minerals & Responsible Sourcing
Under regulations such as the U.S. Dodd-Frank Act Section 1502, suppliers must disclose the use of conflict minerals (tin, tantalum, tungsten, gold—3TG) often used in plating or alloys. A robust supply chain due diligence process is required.
Packaging & Labeling Standards
Protective Packaging
Fasteners are prone to corrosion, contamination, and mechanical damage. Use:
– Anti-corrosion packaging (e.g., VCI paper, sealed bags).
– Moisture-resistant materials for sea freight.
– Industrial-grade cartons or reusable containers to prevent spillage.
Labeling Requirements
Each package must include:
– Part number, revision level, and quantity.
– Manufacturer name and location.
– Lot/batch number and date of production.
– Compliance markings (e.g., RoHS, REACH, IATF 16949).
– Handling symbols (e.g., “Fragile”, “Do Not Stack”).
Barcodes or RFID tags are recommended for traceability.
Transportation & Handling
Mode of Transport
- Air freight: For urgent or high-value shipments; requires proper classification and packaging.
- Ocean freight: Cost-effective for bulk shipments; requires moisture and salt protection.
- Road transport: Common for regional deliveries; ensure secure loading to prevent shifting.
Temperature & Environmental Controls
Avoid exposure to extreme temperatures, humidity, and contaminants. Use climate-controlled containers when necessary, especially for coated or pre-lubricated fasteners.
Load Securing & Stacking Limits
Fastener containers must be palletized and secured to prevent movement. Observe stacking limits to avoid crushing lower layers.
Inventory Management & Traceability
FIFO/FEFO Principles
Apply First-In-First-Out (FIFO) or First-Expired-First-Out (FEFO) for inventory rotation, especially for fasteners with protective coatings that may degrade over time.
Batch & Serial Traceability
Maintain full traceability from raw material to end customer. Use ERP or MES systems to track:
– Supplier batch numbers.
– Production dates.
– Inspection records.
– Shipping details.
This is critical for recalls or quality audits.
Customs & Trade Compliance
HS Code Classification
Correct classification is essential:
– Typical HS codes: 7318.15 (steel bolts), 7318.23 (steel nuts), or 7318.29 (other steel nuts).
– Accurate classification affects tariffs, duties, and trade agreements (e.g., USMCA, EU-Japan EPA).
Export Controls
Some high-strength or specialty fasteners may be subject to export control regulations (e.g., EAR in the U.S.). Verify if licenses are required for certain destinations.
Documentation
Include with every shipment:
– Commercial invoice.
– Packing list.
– Certificate of Origin.
– Material and compliance certificates.
– Dangerous Goods Declaration (if applicable, e.g., for lubricated fasteners with flammable coatings).
Quality & Inspection Protocols
Incoming Inspection
At receiving, verify:
– Quantity and part number accuracy.
– Packaging integrity.
– Compliance documentation.
– Dimensional and mechanical sampling per AQL standards (e.g., ISO 2859).
In-Process Audits
Regular audits of supplier logistics and quality systems ensure ongoing compliance with automotive requirements.
Sustainability & Reverse Logistics
Recycling & Waste Management
Work with suppliers who follow environmental standards (e.g., ISO 14001). Recycle packaging materials and manage metal waste responsibly.
Return & Recall Procedures
Establish clear procedures for:
– Defective or non-conforming fastener returns.
– Product recalls (including notification, retrieval, and root cause analysis).
– Documentation for regulatory reporting.
Conclusion
Managing the logistics and compliance of automotive fasteners requires attention to detail across the supply chain. Adherence to international standards, accurate documentation, robust traceability, and proactive risk management are essential for ensuring quality, safety, and regulatory conformity in the highly regulated automotive industry.
Conclusion for Sourcing Automotive Fasteners:
Sourcing automotive fasteners is a critical component in ensuring the safety, reliability, and performance of vehicles. As the automotive industry continues to evolve with advancements in electric vehicles, lightweight materials, and stringent regulatory standards, the demand for high-quality, precision-engineered fasteners has never greater. Successful sourcing requires a strategic approach that balances cost-efficiency with uncompromising quality, traceability, and compliance with international standards such as ISO/TS 16949, ISO 898, and others.
Key considerations include selecting reliable suppliers with proven expertise in automotive applications, ensuring material integrity and corrosion resistance, and implementing robust quality control and supply chain management processes. Additionally, local vs. global sourcing decisions must account for delivery lead times, total landed costs, and geopolitical risks.
Ultimately, effective sourcing of automotive fasteners supports not only operational efficiency but also contributes to vehicle safety and long-term customer satisfaction. By partnering with trusted suppliers and adopting a proactive, quality-driven sourcing strategy, automotive manufacturers and Tier 1 suppliers can maintain a competitive edge while meeting the ever-increasing demands of the modern automotive market.