The global automotive coil springs market is experiencing steady expansion, driven by rising vehicle production, increasing demand for improved ride comfort, and the growing adoption of lightweight suspension systems. According to Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at approximately USD 6.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 4.5% from 2024 to 2029. This growth is further fueled by advancements in materials, such as high-tensile steel and composite alloys, and the expanding electric vehicle (EV) sector, which demands optimized suspension solutions for enhanced handling and durability. With Asia-Pacific emerging as the largest consumer due to robust automotive manufacturing in China, India, and Japan, the competitive landscape among coil spring manufacturers is intensifying. In this dynamic environment, innovation, production scalability, and strategic partnerships are key differentiators. Below is a data-driven overview of the top 10 automotive coil springs manufacturers shaping the industry’s future.
Top 10 Automotive Coil Springs Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 EATON Detroit Spring
Domain Est. 1997
Website: eatondetroitspring.com
Key Highlights: EATON Detroit Spring – The leading manufacturer of leaf and coil springs for the street rod and restoration automotive industries….
#2 General Spring
Domain Est. 2005
Website: generalspringkc.com
Key Highlights: With over 9500+ five-star reviews, General Spring specializes in OEM replacement leaf springs and heavy-duty performance upgrades….
#3 Eibach
Domain Est. 1996
Website: eibach.com
Key Highlights: Experience the legacy of Eibach, crafting high-performance suspension systems and automotive components with engineering excellence and precision ……
#4 Coil Spring Specialties
Domain Est. 1998
Website: coilsprings.com
Key Highlights: Coil Spring Specialties stands as a beacon of excellence in the auto coil spring industry, serving the U.S. and Canada with unmatched expertise and dedication….
#5 Lesjöfors
Domain Est. 1998
Website: lesjoforsab.com
Key Highlights: Suspension Springs. Automotive aftermarket parts such as coil springs, gas springs, leaf springs, sport lowering springs, U-bolts. read more · Stock Springs….
#6 Dendoff Springs Ltd.
Domain Est. 1999 | Founded: 1906
Website: dendoff.com
Key Highlights: We have been manufacturing and designing all types of springs and wire forms for the automotive, rail and many more industries since 1906. Find Us On Facebook ……
#7 Deaver Spring Inc
Domain Est. 2003
Website: deaverspring.com
Key Highlights: Deaver Spring specializes in suspension work on cars, trucks, off-road and recreational vehicles. Deaver will repair springs on your family ……
#8 Kilen
Domain Est. 2005
Website: kilensprings.com
Key Highlights: We have over 150 years spring manufacturing experience, and today produce the world’s largest range of coils springs for the automotive aftermarket….
#9 Lesjöfors Automotive
Domain Est. 2007
Website: lesjofors-automotive.com
Key Highlights: Lesjöfors produce an extensive range of springs for the European Car and Light Commercial Vehicle market, offering high-quality products, professional service,…
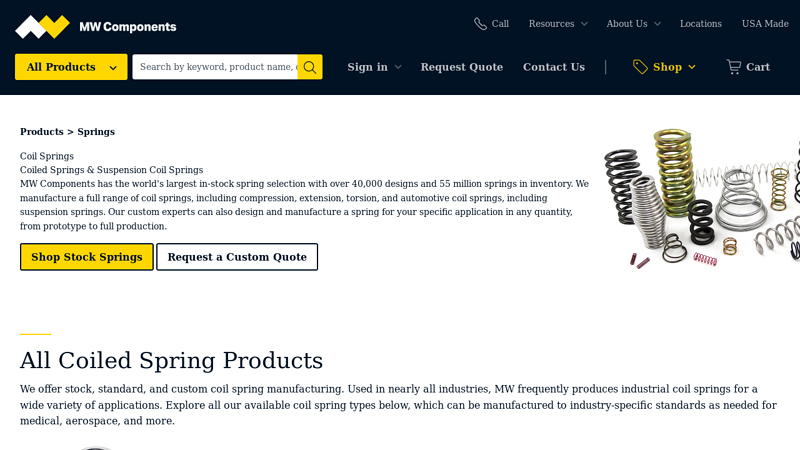
#10 Coiled Springs: Stock & Custom Options
Domain Est. 2017
Website: mwcomponents.com
Key Highlights: We manufacture a full range of coil springs, including compression, extension, torsion, and automotive coil springs, including suspension springs….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Automotive Coil Springs

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Automotive Coil Springs
The global automotive coil spring market is poised for notable transformation by 2026, driven by evolving vehicle technologies, shifting manufacturing priorities, and increasing demand for improved ride comfort and performance. Below are key market trends expected to shape the industry in the coming years:
-
Growth in Light Vehicle Production
Rising global production of passenger cars and light commercial vehicles, particularly in emerging economies such as India, Indonesia, and Brazil, is expected to bolster demand for coil springs. As coil springs remain a preferred suspension solution for their cost-effectiveness and reliability in non-luxury segments, this trend will sustain market growth through 2026. -
Shift Toward Lightweight Materials
The automotive industry’s focus on fuel efficiency and emission reduction is accelerating the adoption of lightweight materials. By 2026, manufacturers are increasingly exploring high-strength steel alloys and composite-based coil springs to reduce unsprung weight without compromising durability. This shift supports electrification goals and enhances vehicle dynamics. -
Expansion of Electric Vehicle (EV) Adoption
With EV sales projected to exceed 40% of global new car sales by 2026 in some regions, coil spring demand is adapting to the unique requirements of electric platforms. EVs often have higher curb weights due to battery packs, necessitating reinforced or redesigned coil springs. While air and adaptive suspensions are gaining traction in premium EVs, coil springs remain dominant in mid-tier models due to cost efficiency. -
Increased Focus on Ride Comfort and Handling
Consumer expectations for superior ride quality are pushing OEMs to optimize suspension systems. Coil springs, often paired with advanced dampers and electronic stability controls, are being redesigned for better responsiveness and noise, vibration, and harshness (NVH) performance. This trend is particularly evident in SUVs and crossovers, which dominate new vehicle sales. -
Regional Manufacturing Shifts and Localization
Geopolitical factors, supply chain resilience concerns, and trade policies are prompting automakers to localize production. By 2026, coil spring manufacturers are expanding regional facilities in Southeast Asia, Eastern Europe, and Mexico to serve nearby assembly plants. This reduces logistics costs and enhances supply chain agility. -
Aftermarket Growth and Replacement Demand
The growing vehicle parc worldwide, especially in aging fleets across North America and Europe, is fueling aftermarket demand for coil springs. Wear and corrosion from environmental exposure lead to frequent replacements, creating a steady revenue stream for suppliers. E-commerce platforms are further accelerating parts distribution. -
Consolidation Among Tier-1 Suppliers
The automotive supply base is seeing increased consolidation, with major Tier-1 suppliers acquiring specialized spring manufacturers to offer integrated suspension solutions. This trend enhances R&D capabilities and allows for greater innovation in coil spring design and integration with smart suspension systems. -
Sustainability and Recycling Initiatives
Environmental regulations are pushing manufacturers to adopt greener production processes. By 2026, leading coil spring producers are expected to implement closed-loop recycling systems for steel and reduce energy consumption in heat treatment processes. Sustainable sourcing of raw materials is becoming a competitive differentiator.
In conclusion, the automotive coil spring market in 2026 will be shaped by a balance of traditional demand drivers and emerging technological challenges. While innovation in materials and design continues, the coil spring’s role as a cost-effective and reliable suspension component ensures its relevance across diverse vehicle segments.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Automotive Coil Springs: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing automotive coil springs involves significant technical and legal considerations. Overlooking key quality and intellectual property (IP) aspects can lead to supply chain disruptions, safety issues, and costly legal disputes. Below are the most common pitfalls to avoid.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inadequate Material Specifications
Using substandard or non-compliant spring steel (e.g., failing to meet SAE J401 or DIN standards) compromises fatigue life and load capacity. Suppliers may cut costs with inferior alloys, leading to premature spring failure, reduced vehicle performance, or safety hazards.
Insufficient Dimensional and Load Testing
Failing to verify free length, wire diameter, pitch, and load deflection characteristics results in improper fitment and inconsistent ride quality. Without rigorous testing protocols (such as ISO 139 or OEM-specific load testing), springs may not meet vehicle requirements.
Poor Heat Treatment and Stress Relieving
Improper tempering or stress-relieving processes lead to residual stresses and reduced fatigue resistance. This increases the risk of cracking or deformation under cyclic loading, especially in performance or heavy-duty applications.
Inconsistent Surface Finish and Corrosion Protection
Inadequate shot peening or poor coating (e.g., zinc plating, epoxy) accelerates corrosion. Exposure to road salts and moisture can cause pitting and structural degradation, shortening service life and increasing warranty claims.
Lack of Traceability and Process Control
Suppliers without documented quality management systems (e.g., IATF 16949) often lack batch traceability and consistent process controls. This makes root-cause analysis difficult during field failures and impedes compliance with automotive industry standards.
Intellectual Property-Related Pitfalls
Sourcing from Unauthorized OEM Copycats
Procuring springs that replicate original equipment manufacturer (OEM) designs without licensing infringes on design patents, technical drawings, and registered IP. This exposes buyers to legal liability, product seizures, and reputational damage.
Ambiguous or Missing Licensing Agreements
Failing to verify that suppliers hold valid licenses for patented spring designs (e.g., progressive rate configurations or proprietary winding techniques) can result in indirect infringement claims against the buyer or end-user.
Use of Reverse-Engineered Designs
Suppliers offering “OEM-equivalent” springs may have reverse-engineered protected designs without authorization. Even if functional, these products often violate IP rights and may lack durability or safety validation.
Incomplete Design Rights Transfer
In custom spring development, failing to secure full ownership or usage rights in contracts can restrict production scalability or lead to disputes if the supplier claims IP over jointly developed features.
Lack of IP Due Diligence in Supplier Audits
Ignoring IP compliance during supplier qualification allows infringement risks to enter the supply chain. Buyers should require proof of design freedom-to-operate and audit documentation supporting legal use of spring geometries.
Mitigating these pitfalls requires thorough supplier vetting, strict quality agreements, IP risk assessments, and collaboration with legal and engineering teams to ensure compliance and performance reliability.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Automotive Coil Springs
Overview and Key Considerations
Automotive coil springs are critical suspension components that must meet strict performance, safety, and regulatory standards. Ensuring compliance and efficient logistics throughout the supply chain is essential for timely delivery, product integrity, and adherence to international regulations.
Material and Manufacturing Compliance
Coil springs are typically manufactured from high-tensile steel alloys such as silicon-chrome (e.g., 51CrV4) or patented steel wire. Compliance standards include:
– ISO 6892-1: Metallic materials — Tensile testing methods.
– SAE J1091: Performance requirements for automotive suspension springs.
– EN 10270-1: Steel wire for mechanical springs – Part 1: Patented cold drawn unalloyed steel wire.
Manufacturers must provide material test reports (MTRs) and production certifications to validate compliance.
Regulatory and Safety Standards
Automotive coil springs must comply with regional and international safety regulations:
– ECE R90: United Nations regulation for approval of vehicle components related to springs.
– FMVSS 126 (U.S.): Electronic Stability Control systems, indirectly affecting spring design and performance.
– IATF 16949: Quality management standard specific to the automotive industry.
Suppliers must maintain traceability records and demonstrate conformity through audits and documentation.
Packaging and Handling Requirements
Proper packaging prevents damage during storage and transportation:
– Use rust-inhibiting coatings or VCI (Vapor Corrosion Inhibitor) packaging to prevent corrosion.
– Secure springs in sturdy containers or pallets to avoid deformation.
– Clearly label packages with part numbers, batch/lot numbers, weight, and handling instructions (e.g., “Do Not Stack,” “Protect from Moisture”).
– Follow ESD (Electrostatic Discharge) protocols if applicable, though less common for springs.
Transportation and Logistics
Logistics considerations include:
– Mode of Transport: Road freight is most common; air freight for urgent shipments; sea freight for bulk international orders.
– Load Securing: Use strapping and dunnage to prevent shifting during transit.
– Temperature and Humidity Control: Avoid exposure to extreme conditions that may affect material properties or coatings.
– Customs Documentation: Include commercial invoices, packing lists, certificates of origin, and compliance certificates (e.g., IATF 16949, ISO 9001) for international shipments.
Import/Export Compliance
International shipments must adhere to:
– HS Code Classification: Typically 7320.20 (coil springs of iron or steel) under the Harmonized System.
– REACH and RoHS Compliance: Ensure no restricted substances are present, especially if coated or treated.
– Country-Specific Regulations: Verify local automotive component requirements (e.g., INMETRO in Brazil, KC Mark in South Korea).
– Export Controls: Confirm springs are not subject to dual-use or military export restrictions.
Quality Assurance and Traceability
Maintain full traceability throughout the supply chain:
– Implement batch/lot tracking systems from raw material to finished product.
– Conduct regular quality audits and first-article inspections (FAI).
– Retain documentation for a minimum of 15 years (per IATF 16949) to support recalls or warranty claims.
Returns and Reverse Logistics
Establish procedures for handling non-conforming or defective springs:
– Define return authorization (RMA) processes.
– Inspect returned parts for root cause analysis.
– Dispose of or rework non-compliant items according to environmental and safety standards (e.g., ISO 14001).
Sustainability and End-of-Life Management
Promote environmental compliance:
– Recycle scrap metal and packaging materials.
– Comply with ELV (End-of-Life Vehicles) Directive (EU) for recyclability.
– Minimize hazardous waste from coatings or cleaning processes.
Conclusion
Effective logistics and compliance management for automotive coil springs requires coordination across manufacturing, regulatory, transportation, and quality functions. Adherence to international standards, proper documentation, and robust traceability systems ensure reliable supply chain performance and regulatory conformity.
Conclusion for Sourcing Automotive Coil Springs
Sourcing automotive coil springs requires a strategic approach that balances quality, cost, reliability, and compliance with industry standards. As critical components of a vehicle’s suspension system, coil springs directly impact ride comfort, handling, safety, and overall vehicle performance. Therefore, selecting the right suppliers and materials is essential.
Key considerations in the sourcing process include material quality (typically high-grade steel such as SUP9 or chrome-silicon alloys), manufacturing precision, adherence to OEM specifications, and compliance with international standards such as ISO/TS 16949. Additionally, evaluating suppliers based on their production capabilities, quality control processes, scalability, and track record in the automotive industry is crucial to ensuring consistent supply and performance.
Developing long-term partnerships with reputable suppliers—whether domestic or global—can enhance supply chain resilience and reduce risks associated with downtime or component failure. Furthermore, incorporating dual-sourcing strategies and regular supplier audits helps mitigate disruptions and maintain high product standards.
In conclusion, effective sourcing of automotive coil springs involves a comprehensive evaluation of technical, operational, and strategic factors. By prioritizing quality, reliability, and collaboration with trusted manufacturers, automotive companies can ensure optimal performance of their suspension systems while maintaining cost efficiency and supply chain integrity.