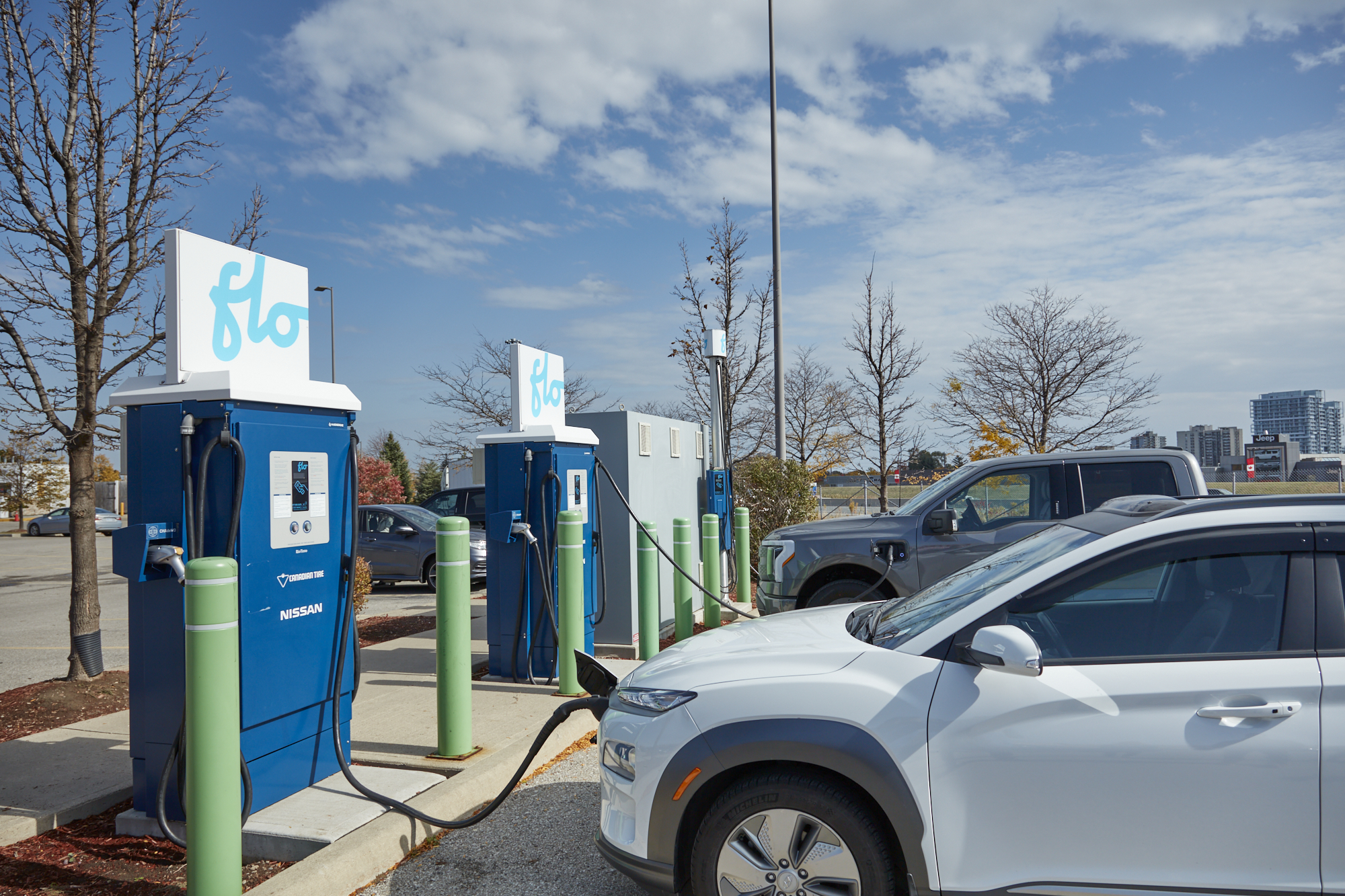
The global smart charger market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand for electric vehicles (EVs), increased adoption of portable electronics, and advancements in battery technologies. According to Grand View Research, the global smart charger market size was valued at USD 1.7 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 19.4% from 2023 to 2030. This expansion is fueled by growing consumer preference for energy-efficient charging solutions and the integration of IoT and AI in charging systems. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence projects a CAGR of over 18.5% during the forecast period of 2023–2028, highlighting the increasing deployment of automatic smart chargers in automotive, industrial, and consumer electronics sectors. As innovation accelerates, a select group of manufacturers are leading the charge in developing intelligent, fast, and adaptive charging solutions—setting new benchmarks for performance, safety, and connectivity. Here are the top 9 automatic smart charger manufacturers shaping the future of power management.
Top 9 Automatic Smart Charger Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Smart EV Charging Solutions
Website: ev.energy
Key Highlights: Soak up solar power EFFICIENTLY. We partner with solar manufacturers, distributors and installers to seamlessly integrate smart EV charging with solar power….
#2 EV Charging
Domain Est. 1990
Website: new.abb.com
Key Highlights: ABB offers a total ev charging solution from compact, high quality AC wallboxes, reliable DC fast charging stations with robust connectivity….
#3 MSI EV Charging
Domain Est. 1991
Website: evse.msi.com
Key Highlights: MSI Smart EV Chargers deliver up to 14.4 kW (60 A) of fast, safe, and reliable AC power through Type 1 (SAE J1772) or Type 2 (IEC 62196-2) connectors and up ……
#4 page
Domain Est. 2002
Website: ctek.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $50 30-day returnsPowered by APTO™ Adaptive Charging, CS ONE automatically identifies your battery and delivers a fully optimised charge. No buttons. No settings…
#5 WiTricity
Domain Est. 2004
Website: witricity.com
Key Highlights: WiTricity builds future-ready wireless EV charging systems that allow your customers to charge efficiently, safely, and conveniently….
#6 V2C
Domain Est. 2019
Website: v2charge.com
Key Highlights: We produce EV chargers suitable for any electric vehicle. 4 e-Chargers, 10 years innovating, 20.000 e-Chargers installed, 25 countries….
#7 Autel EV Charger
Domain Est. 2021
Website: autelenergy.com
Key Highlights: Autel EV Charger delivers smart, reliable charging for homes, fleets, and businesses, integrating solar and storage for a seamless energy solution….
#8 CURRENT
Domain Est. 2021
Website: current.eco
Key Highlights: Rating 4.0 (7) Launch and grow your EV charging business with CURRENT. Benefit from a hardware-agnostic, easy-to-use & OCPP-certified charge point management system….
#9 Autel Energy Electric Vehicle Chargers
Domain Est. 2022
Website: autelenergy.us
Key Highlights: The MaxiCharger AC Elite Home 40A EV Charger is up to 50 AMPS Level 2 Smart Charger compatible with all EV and Plug-in Hybrid vehicles….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Automatic Smart Charger

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Automatic Smart Chargers
The global market for automatic smart chargers is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by rapid technological advancements, rising demand for electric vehicles (EVs), and the expansion of smart infrastructure. These intelligent charging systems—capable of self-regulating voltage, optimizing charge cycles, detecting battery types, and integrating with IoT platforms—are increasingly becoming central to consumer electronics, automotive, and industrial applications. Below is an analysis of key market trends expected to shape the automatic smart charger landscape in 2026.
1. Surge in Electric Vehicle Adoption Fuels Growth
The accelerating global transition to electric mobility is the primary driver for automatic smart charger demand. By 2026, EV sales are projected to account for over 30% of new car sales worldwide, according to the International Energy Agency (IEA). This shift necessitates widespread deployment of smart charging solutions that support load balancing, grid integration, and user-friendly interfaces. Automatic smart chargers with features like dynamic power distribution and vehicle-to-grid (V2G) compatibility will be critical in managing energy demand and supporting grid stability.
2. Integration with IoT and AI Technologies
Smart chargers are evolving into intelligent nodes within the Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem. By 2026, most high-end automatic smart chargers will leverage AI algorithms to predict optimal charging times based on user behavior, electricity pricing, and grid load. Cloud connectivity enables remote monitoring, firmware updates, and energy usage analytics—features increasingly expected by both residential and commercial users. This integration enhances efficiency, reduces energy costs, and supports sustainability goals.
3. Growth in Consumer Electronics and Wearables
Beyond EVs, the proliferation of smart devices—including smartphones, laptops, wearables, and IoT gadgets—is boosting demand for intelligent charging solutions. Consumers are seeking fast, safe, and adaptive charging that prolongs battery life. Automatic smart chargers with multi-device compatibility, overcharge protection, and adaptive voltage regulation will dominate the consumer electronics market, especially in urbanized and tech-savvy regions.
4. Emphasis on Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
Regulatory frameworks and consumer preferences are pushing manufacturers toward energy-efficient and eco-friendly designs. By 2026, energy efficiency standards such as the EU’s Ecodesign Directive and ENERGY STAR certifications will likely mandate minimum efficiency levels for smart chargers. Chargers utilizing gallium nitride (GaN) and silicon carbide (SiC) semiconductors will gain market share due to their higher efficiency, smaller form factors, and reduced heat generation.
5. Expansion of Smart Home and Smart Grid Integration
Automatic smart chargers are increasingly being integrated into broader smart home ecosystems (e.g., Google Home, Apple HomeKit, Amazon Alexa). This allows users to manage charging via voice commands or mobile apps, synchronize with home solar systems, and optimize energy use. Similarly, utility companies are deploying smart chargers as part of demand-response programs to balance electricity loads during peak hours, especially in regions with high renewable energy penetration.
6. Regional Market Dynamics
North America and Europe are expected to lead in smart charger adoption due to strong EV incentives, robust charging infrastructure, and supportive government policies. Meanwhile, the Asia-Pacific region—particularly China, South Korea, and India—will witness the fastest growth, driven by booming EV production, urbanization, and government investments in green technology. China alone is projected to account for nearly 50% of the global automatic smart charger market by 2026.
7. Competitive Landscape and Innovation
The market will see intensified competition among established players (e.g., Tesla, ChargePoint, Belkin, Anker) and emerging startups. Innovation will focus on faster charging speeds (e.g., ultra-fast 350 kW chargers), bidirectional charging, and seamless payment integration (e.g., RFID, app-based billing). Strategic partnerships between charger manufacturers, automakers, and energy providers will become commonplace to deliver end-to-end charging solutions.
Conclusion
By 2026, the automatic smart charger market will be characterized by intelligence, connectivity, and sustainability. Driven by EV adoption, digital transformation, and energy transition goals, these chargers will evolve from simple power delivery devices into essential components of smart energy ecosystems. Companies that prioritize innovation, interoperability, and user-centric design will be best positioned to capture value in this rapidly expanding market.
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Automatic Smart Chargers (Quality and IP)
Sourcing Automatic Smart Chargers involves several potential risks, especially concerning product quality and intellectual property (IP). Being aware of these pitfalls can help buyers make informed decisions and avoid costly issues down the line.
Poor Product Quality
One of the most significant risks when sourcing smart chargers—especially from low-cost manufacturers—is receiving substandard products. Common quality issues include inconsistent charging performance, overheating, short circuit risks, and premature failure. These problems often stem from the use of low-grade components (e.g., counterfeit ICs, inferior capacitors), lack of proper quality control, and insufficient testing. Buyers may find that chargers do not meet advertised specifications or fail to comply with safety standards such as UL, CE, or RoHS.
Lack of Intellectual Property Protection
Many smart charger designs incorporate proprietary technology, including firmware algorithms for battery management and communication protocols. When sourcing from third-party manufacturers, especially in regions with weak IP enforcement, there’s a risk that your design or technology could be copied or sold to competitors. Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) may also use similar designs across multiple clients, leading to potential IP conflicts or loss of competitive advantage.
Inadequate Compliance and Certification
Automatic Smart Chargers must meet various international safety and electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) standards. However, some suppliers may provide false or forged certification documents. Chargers that are not properly tested or certified can pose safety hazards and result in legal liabilities, product recalls, or market access issues.
Hidden Design Flaws
Some sourced smart chargers may appear functional during initial testing but contain design flaws that emerge under real-world conditions—such as poor thermal management or incompatible charging profiles for certain battery types. These flaws may not be evident until after mass deployment, leading to warranty claims and reputational damage.
Supply Chain and After-Sales Support Risks
Reliability isn’t just about the product—it’s also about the supplier. Many low-cost manufacturers offer limited technical support, long lead times for replacements, or go out of business without notice. This lack of post-purchase support can severely impact your ability to service customers or scale production.
Conclusion
To mitigate these risks, conduct thorough due diligence: audit suppliers, request independent test reports, verify certifications, and consider using legal agreements to safeguard IP. Partnering with reputable manufacturers and investing in proper quality assurance can save significant time, money, and brand equity in the long run.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Automatic Smart Charger
This guide outlines key logistics considerations and compliance requirements for the distribution, import, and use of Automatic Smart Chargers. Adhering to these standards ensures product safety, legal market access, and efficient supply chain operations.
Product Classification & HS Code
Identify the appropriate Harmonized System (HS) code for customs purposes. For Automatic Smart Chargers, typical classifications include:
– HS Code 8504.40: Electric transformers, inductors, and charging equipment.
– HS Code 8543.70: Electrical apparatus for charging batteries.
Verify with local customs authorities, as classification may vary by region and output specifications.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Ensure compliance with regional safety and electromagnetic standards:
– North America (USA & Canada):
– FCC Part 15 (EMC)
– UL 62368-1 or UL 2089 (Safety)
– Energy Star or DoE Level VI (Energy Efficiency)
– European Union:
– CE Marking under Low Voltage Directive (LVD 2014/35/EU)
– EMC Directive (2014/30/EU)
– RoHS (2011/65/EU) and REACH compliance
– Ecodesign Directive (EU) 2019/1782 for energy efficiency
– United Kingdom:
– UKCA Marking (post-Brexit; UK LVD, EMC, RoHS)
– Australia & New Zealand:
– RCM Mark (AS/NZS 62368.1, AS/NZS CISPR 32)
– Other Regions: Consult local standards (e.g., KC for South Korea, PSE for Japan, BIS for India).
Packaging & Labeling
- Include required safety labels: voltage, current, model number, manufacturer, warnings.
- Use multilingual user manuals and safety instructions where applicable.
- Ensure packaging is durable and complies with ISTA 3A or similar standards for transport safety.
- Include compliance marks (CE, FCC, UKCA, etc.) visibly on product and packaging.
Import & Customs Documentation
Prepare the following for international shipments:
– Commercial Invoice
– Packing List
– Certificate of Origin
– Test Reports (from accredited labs)
– Declaration of Conformity (DoC)
– Safety and EMC certifications
– Battery UN38.3 test report (if integrated battery present)
Transport & Shipping Considerations
- Classify product correctly under IATA/IMDG for air/sea freight.
- If the charger includes a lithium-ion battery, comply with:
- UN 3481 (PI 966 Section IB) for batteries packed with equipment
- Proper hazard labeling and packaging
- Use electrostatic discharge (ESD)-safe packaging for sensitive electronics.
- Maintain temperature-controlled environments if specified.
Storage & Handling
- Store in dry, temperature-controlled warehouses (typically 5°C to 40°C).
- Avoid exposure to moisture, dust, and direct sunlight.
- Implement FIFO (First In, First Out) inventory management.
- Handle with ESD precautions during warehousing and fulfillment.
End-of-Life & Environmental Compliance
- Comply with WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) in the EU and similar e-waste laws globally.
- Provide take-back or recycling information to customers.
- Ensure materials are labeled for recyclability (e.g., plastic resins).
Quality Assurance & Audits
- Conduct periodic factory audits to verify production consistency.
- Maintain traceability via batch/serial numbers.
- Implement non-conformance reporting and corrective action processes.
Warranty & After-Sales Support
- Define clear warranty terms (e.g., 1–3 years).
- Establish reverse logistics for returns, repairs, or recalls.
- Train customer service teams on compliance and safety messaging.
Adherence to this guide ensures safe, legal, and efficient logistics operations for Automatic Smart Chargers across global markets. Always consult legal and regulatory experts for jurisdiction-specific requirements.
Conclusion:
After a comprehensive evaluation of available options, sourcing an automatic smart charger presents a strategic and forward-thinking decision. These chargers offer significant advantages, including enhanced safety features, optimized charging efficiency, extended battery lifespan, and compatibility with various battery types and chemistries. Their intelligent circuitry automatically detects battery status and adjusts charging parameters accordingly, minimizing risks of overcharging, overheating, or damage.
From a cost-benefit perspective, while the initial investment in automatic smart chargers may be higher than conventional models, the long-term savings in battery maintenance, reduced downtime, and improved reliability justify the expense. Additionally, sourcing from reputable suppliers ensures adherence to quality standards, warranty support, and compliance with safety regulations.
In conclusion, adopting automatic smart chargers aligns with goals of operational efficiency, sustainability, and technological advancement. It is recommended to finalize partnerships with suppliers offering proven performance, responsive customer service, and scalability to support future needs.