The global laser welding machine market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for precision, automation, and high-speed manufacturing across industries such as automotive, electronics, and medical devices. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the global laser welding market was valued at USD 2.38 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 3.84 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of approximately 8.2% during the forecast period. This expansion is amplified by advancements in fiber laser technology and the rising adoption of automated systems to improve weld quality and operational efficiency. As manufacturers prioritize consistency and reduced labor costs, automatic laser welding machines have become integral to modern production lines. In line with this trend, a select group of companies are leading innovation in automation, integration, and smart manufacturing capabilities. Based on market presence, technological advancement, and customer adoption, here are the top 9 automatic laser welding machine manufacturers shaping the future of industrial joining processes.
Top 9 Automatic Laser Welding Machine Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Focus on laser
Website: hanslaser.net
Key Highlights: The machine is mainly used in the assembly and welding for the fixed structure parts of the back cover camera of IT products such as mobile phones and PADs….
#2 Laserax
Website: laserax.com
Key Highlights: Laserax offers solutions to automate laser welding for batteries, making sure the thousands of welds in battery packs, modules, and cells are done with speed ……
#3 Laser Technology & Laser Machines from ALPHA LASER
Website: alphalaser.eu
Key Highlights: As a pioneer in the field of mobile laser welding, ALPHA LASER GmbH offers a wide range of high-quality laser welding devices. This includes laser welding ……
#4 Denaliweld
Website: denaliweld.com
Key Highlights: DenaliWeld laser welding machine ensures precise laser welds in complex designs, enhancing safety and fuel efficiency. High-speed automation from laser fiber ……
#5 Laser Machines
Website: lclasers.com
Key Highlights: Distribution and manufacture of laser machinery. Sales of laser marking, laser cleaning, laser engraving and welding machines….
#6 Laser Welding
Website: ipgphotonics.com
Key Highlights: As a flexible and simple to integrate process, laser welding solutions can be easily automated at almost any scale of production….
#7 Orotig: Laser Machinery
Website: orotig.com
Key Highlights: Orotig, with +30 years of experience, specializes in engineering and manufacturing laser solutions for welding engraving and casting metals….
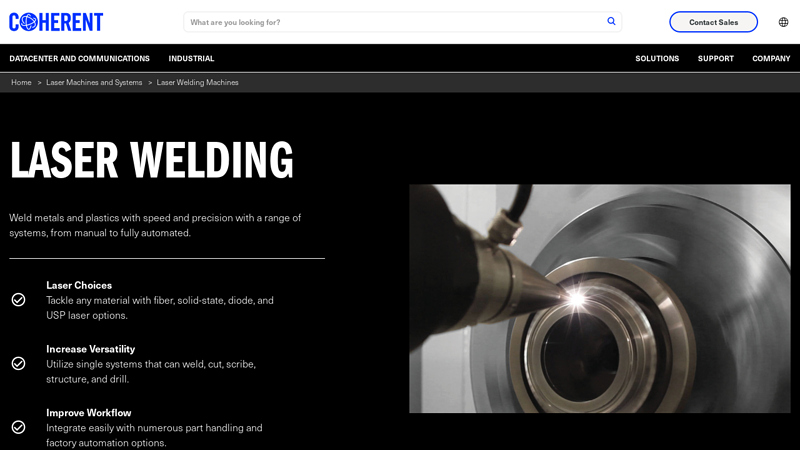
#8 Laser Welding Machines
Website: coherent.com
Key Highlights: Get manual to fully automated laser welding machines that weld plastics and metals with speed and precision while improving throughput….
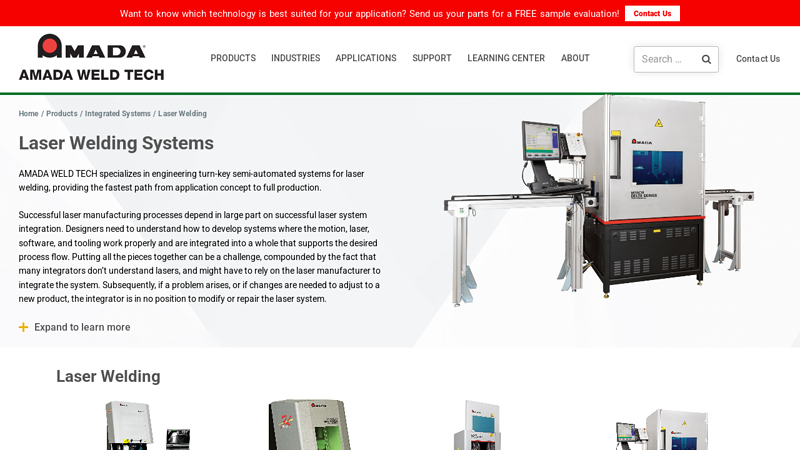
#9 Laser Welding Systems
Website: amadaweldtech.com
Key Highlights: AMADA WELD TECH is unique in that we not only manufacture the laser welders but also engineer and integrate laser systems, offering designers a one-stop shop ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Automatic Laser Welding Machine
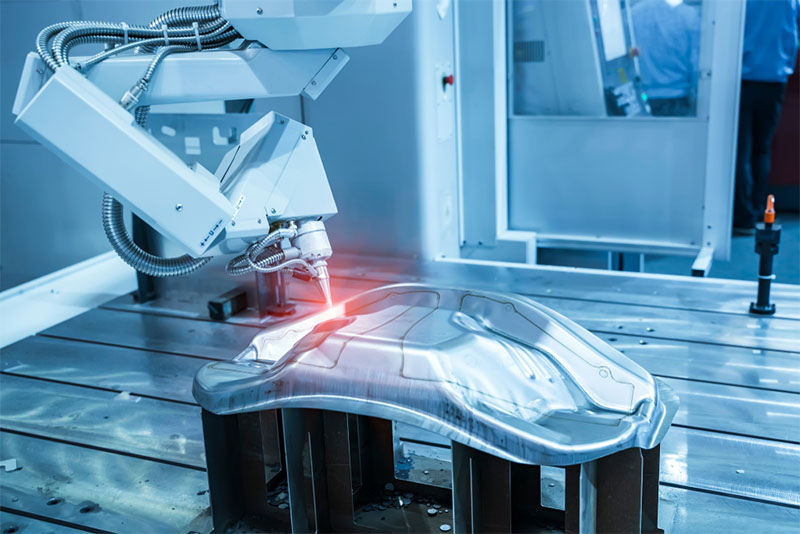

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Automatic Laser Welding Machines
The global market for automatic laser welding machines is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by advancements in automation, precision manufacturing demands, and the integration of Industry 4.0 technologies. Several key trends are expected to shape the landscape of this sector over the next few years.
1. Rising Adoption in Electric Vehicle (EV) Manufacturing
The booming electric vehicle industry is a major catalyst for the growth of automatic laser welding machines. These systems offer high-speed, precision welding essential for battery pack assembly, motor components, and lightweight vehicle structures. As automakers scale EV production to meet regulatory and consumer demands, investments in advanced laser welding automation are expected to surge through 2026.
2. Integration with AI and Smart Manufacturing Systems
By 2026, artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning will be increasingly embedded in laser welding systems. Predictive maintenance, real-time weld quality monitoring, and adaptive control systems will enhance operational efficiency and reduce downtime. Integration with digital twins and IoT platforms will enable seamless data exchange across production lines, supporting smart factory initiatives.
3. Growth in Miniaturization and Precision Applications
Industries such as medical devices, consumer electronics, and aerospace demand ultra-precise welding for smaller and more complex components. Automatic laser welding machines, especially those utilizing fiber and pulsed lasers, will see rising demand due to their ability to perform micro-welding with minimal heat distortion.
4. Regional Market Shifts and Expansion in Asia-Pacific
The Asia-Pacific region, particularly China, Japan, and South Korea, will remain a dominant market due to robust industrial automation, government support for advanced manufacturing, and strong electronics and automotive sectors. Local manufacturers are increasingly developing cost-competitive, high-performance systems, intensifying competition and driving innovation.
5. Emphasis on Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
As industries prioritize environmental sustainability, laser welding machines with lower energy consumption and reduced material waste will gain favor. Fiber lasers, known for their energy efficiency and long operational life, are expected to capture a larger market share compared to traditional CO2 lasers.
6. Increasing Demand for Robotic Integration
The convergence of robotic arms with laser welding systems will continue to grow, enabling fully automated, flexible production cells. Collaborative robots (cobots) equipped with laser welders will become more common in SMEs, offering scalable automation solutions without extensive infrastructure changes.
7. Technological Advancements in Laser Sources and Beam Delivery
Developments such as blue and green wavelength lasers for welding highly reflective materials (e.g., copper and aluminum) will expand application possibilities. Additionally, improved beam shaping and scanning technologies will enhance welding speed and quality, especially in high-volume production environments.
In conclusion, by 2026, the automatic laser welding machine market will be characterized by smarter, faster, and more adaptable systems, driven by cross-industry demand for precision, efficiency, and sustainability. Companies that invest in R&D, digital integration, and scalable automation solutions will be best positioned to capitalize on these evolving trends.
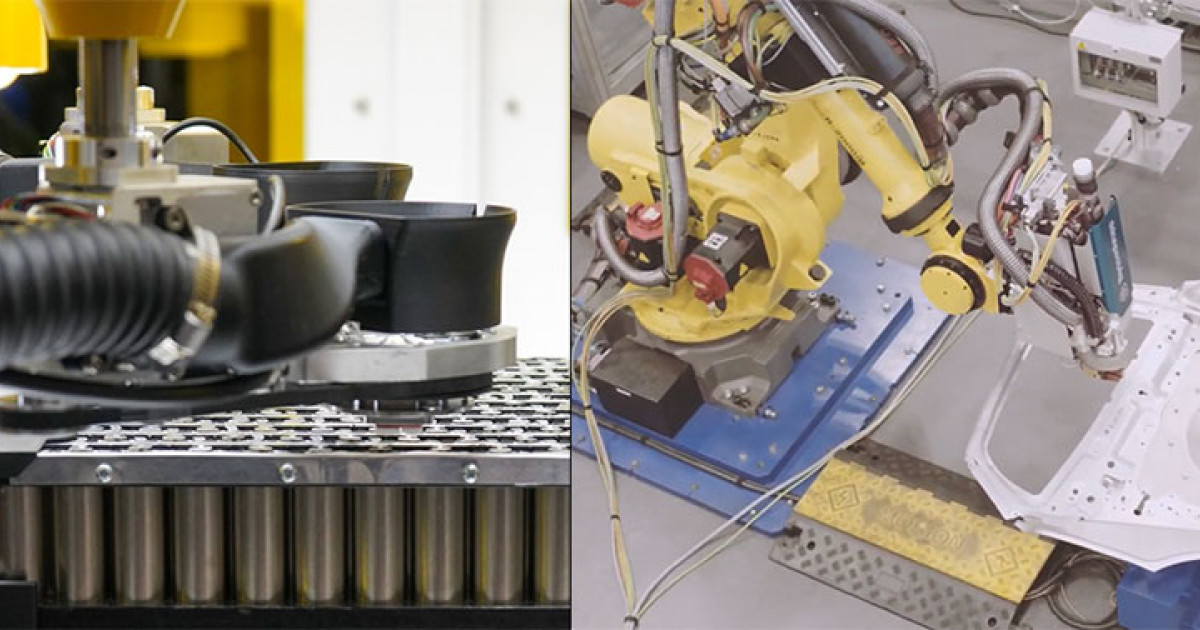

H2: Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Automatic Laser Welding Machines (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing an Automatic Laser Welding Machine involves significant investment and long-term operational impact, making it crucial to avoid common pitfalls related to both quality and intellectual property (IP). Failing to address these issues can result in production inefficiencies, legal risks, and financial losses.
1. Overlooking Machine Build Quality and Component Reliability
Many suppliers, particularly low-cost manufacturers, use substandard materials or outdated components to reduce prices. This can lead to frequent breakdowns, inconsistent weld quality, and high maintenance costs. Always verify the quality of core components such as the laser source, motion system, and control software through third-party certifications or site inspections.
2. Inadequate Validation of Laser Performance Specifications
Suppliers may exaggerate laser power, precision, or cycle time capabilities. Without independent testing or performance data, buyers risk acquiring a machine unsuitable for their application. Request real-world test runs with your specific materials and joint configurations before finalizing procurement.
3. Lack of After-Sales Support and Service Network
High-quality machines require prompt technical support, spare parts availability, and trained service engineers. Sourcing from overseas vendors with limited local presence can result in extended downtimes. Evaluate the supplier’s service infrastructure and response times in your region.
4. Ignoring Software and Control System Limitations
The software driving the welding process is as critical as the hardware. Proprietary systems with poor user interfaces, limited programmability, or lack of integration capabilities (e.g., with factory automation systems) can hinder productivity. Ensure compatibility with your existing production environment.
5. Intellectual Property (IP) Risks in Technology Transfer
When customizing or co-developing solutions, there’s a risk of IP leakage or unclear ownership of designs, control algorithms, or process parameters. Contracts must clearly define IP rights, confidentiality obligations, and restrictions on reuse of jointly developed technology.
6. Purchasing Counterfeit or Reverse-Engineered Machines
Some suppliers offer machines that mimic well-known brands but are built using copied designs or unauthorized components. These may infringe on patents or trademarks, exposing the buyer to legal liability. Conduct due diligence on the supplier’s manufacturing legitimacy and request proof of IP compliance.
7. Insufficient Protection Against Technology Replication
If you’re sourcing a highly customized solution, ensure contractual safeguards are in place to prevent the supplier from reselling similar machines to your competitors. Non-compete or exclusivity clauses may be necessary.
8. Underestimating Training and Integration Requirements
Even high-quality machines fail if operators lack proper training or if integration with existing workflows is poorly managed. Confirm that the supplier provides comprehensive training and integration support as part of the purchase agreement.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires thorough supplier vetting, clear contractual terms, and technical validation. Prioritizing quality assurance and IP protection from the outset safeguards both operational success and long-term innovation.
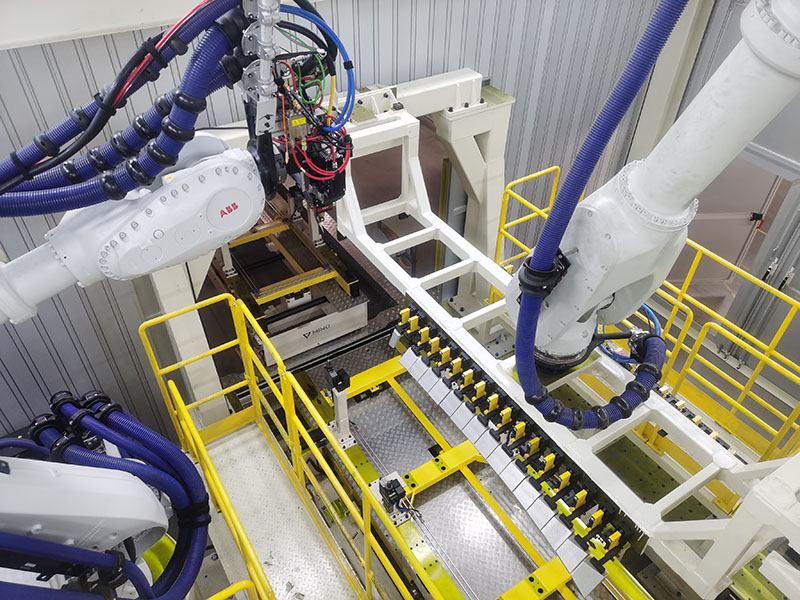

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Automatic Laser Welding Machine
This guide outlines essential logistics and compliance considerations when importing, transporting, installing, and operating an Automatic Laser Welding Machine across international or domestic markets. Adherence to these guidelines ensures safe delivery, regulatory approval, and legal operation.
Shipping and Transportation
Ensure the machine is securely crated and protected against shock, vibration, and moisture during transit. Use shock-absorbing materials and secure anchoring within the shipping container. Confirm compliance with international shipping standards (e.g., ISTA, ISO) and carrier-specific requirements. Provide clear handling labels indicating “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Do Not Stack.” Climate-controlled transport is recommended for sensitive laser and electronic components.
Import and Customs Compliance
Verify applicable Harmonized System (HS) codes for laser welding machines (typically under 8462.21 or 8515.21, depending on configuration) to determine import duties and taxes. Prepare complete documentation, including commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading, and certificate of origin. Ensure compliance with destination country import regulations, including potential requirements for import licenses or pre-shipment inspections. Address any country-specific restrictions on high-power laser equipment.
Regulatory and Safety Certification
Confirm the machine meets safety standards in the destination market. Key certifications include:
– CE Marking (European Union): Compliance with Machinery Directive (2006/42/EC), EMC Directive (2014/30/EU), and Laser Product Safety (IEC 60825-1).
– UL/CSA Certification (USA/Canada): Compliance with UL 1718 (Standard for Electric Arc Welding Machines) and applicable laser safety standards (ANSI Z136.1).
– RCM Mark (Australia/New Zealand): Compliance with AS/NZS standards for machinery and electrical safety.
– KC Mark (South Korea), PSE Mark (Japan), and other regional certifications as required.
Laser Safety and Classification
The automatic laser welding machine must be classified according to IEC 60825-1 (or ANSI Z136.1 in the U.S.). Most industrial laser welding systems fall under Class 4, indicating high-power lasers capable of causing skin and eye injury and posing fire hazards. Implement engineering controls such as interlocked enclosures, beam shrouds, and emergency stop systems. Provide appropriate laser warning labels and ensure operators are trained in laser safety protocols.
Installation and Site Requirements
Verify the installation site meets electrical, ventilation, and structural requirements. Ensure stable power supply with proper grounding and voltage matching. Provide adequate cooling (chiller or coolant system) and exhaust ventilation to remove fumes and particulates generated during welding. Install the machine on a level, vibration-free surface with sufficient clearance for maintenance and emergency access. Confirm compliance with local building and fire codes.
Operational Compliance and Training
Operators and maintenance personnel must receive documented training on machine operation, safety procedures, and emergency response. Establish a safety protocol including lockout/tagout (LOTO) procedures, personal protective equipment (PPE) requirements (e.g., laser safety goggles with appropriate optical density), and hazard signage. Maintain logs for maintenance, safety inspections, and incident reporting to demonstrate regulatory compliance.
Environmental and Waste Management
Implement measures to capture and filter welding fumes using local exhaust ventilation (LEV) and fume extraction systems compliant with OSHA (U.S.) or similar occupational health standards. Dispose of filters, consumables, and waste materials according to local environmental regulations. Ensure noise levels are within permissible workplace exposure limits; use enclosures or acoustic dampening if necessary.
Documentation and Recordkeeping
Retain all compliance documentation, including:
– Factory conformity certificates (CE, UL, etc.)
– Laser classification reports
– Risk assessments and safety manuals
– Installation and commissioning records
– Operator and maintenance training logs
– Calibration and inspection reports
Maintaining organized records supports audits, insurance claims, and ongoing compliance.
Ongoing Compliance and Audits
Schedule regular safety and compliance audits to ensure continued adherence to regulations. Stay informed about updates to laser safety, machinery, and environmental standards. Engage certified technicians for periodic maintenance and recalibration to ensure safe and compliant operation throughout the machine’s lifecycle.
Conclusion on Sourcing an Automatic Laser Welding Machine
Sourcing an automatic laser welding machine represents a strategic investment aimed at enhancing manufacturing efficiency, improving weld quality, and reducing long-term operational costs. After thorough evaluation of technical specifications, supplier reliability, cost implications, and integration capabilities, it is evident that selecting the right system requires aligning machine capabilities with specific production requirements.
Automatic laser welding technology offers superior precision, repeatability, and speed compared to traditional welding methods, making it ideal for high-volume, high-accuracy applications across industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics. Key considerations—such as laser type (fiber, CO₂, or disk), power output, automation compatibility, and safety features—must be carefully assessed to ensure optimal performance.
Additionally, partnering with reputable suppliers who offer strong after-sales support, training, and service is crucial for minimizing downtime and ensuring smooth integration into existing production lines. While the initial investment may be significant, the long-term benefits in terms of productivity gains, reduced material waste, and lower labor costs justify the expenditure.
In conclusion, sourcing an automatic laser welding machine should be approached systematically, balancing technical needs, budget constraints, and future scalability. With the right equipment and support, companies can achieve a competitive advantage through improved product quality and efficient manufacturing processes.