Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Auto Spare Parts Manufacturers In China

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: China Auto Spare Parts Manufacturing Landscape 2026
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers
Date: January 15, 2026
Report ID: SC-ASP-CLSTR-2026-01
Confidentiality Level: Client-Distribution Only
Executive Summary
China remains the world’s dominant hub for auto spare parts manufacturing, accounting for 38% of global exports (2025 UN Comtrade data). Post-pandemic supply chain recalibration, accelerated electrification (NEV parts now 27% of output), and automation-driven efficiency gains have reshaped regional competitiveness. This report identifies optimal sourcing clusters for tiered procurement strategies, emphasizing cost-quality-lead time trade-offs and specialized capabilities. Critical risks include over-reliance on single clusters (exacerbated by 2024–2025 port congestion) and evolving compliance demands under China’s “Dual Carbon” policy.
Methodology
Data synthesized from:
– SourcifyChina’s 2025 Factory Audit Database (1,200+ verified suppliers)
– China Association of Automobile Manufacturers (CAAM) regional output reports
– Customs data (HS Codes 8407–8708)
– On-ground partner assessments in 8 key industrial zones
– 2026 capacity forecasts from Industrial Info Resources
Key Industrial Clusters: Auto Spare Parts Manufacturing
China’s auto parts ecosystem is concentrated in 5 core clusters, each with distinct specializations and competitive advantages:
| Cluster | Core Provinces/Cities | Specialization | Key OEM/Supplier Links | Strategic Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pearl River Delta | Guangdong (Guangzhou, Shenzhen, Foshan) | Electronics, EV components, lighting systems, precision machining | BYD, GAC, Huawei Smart Driving; Midea, Desay SV | Highest R&D density; NEV innovation hub |
| Yangtze River Delta | Zhejiang (Ningbo, Wenzhou), Jiangsu (Suzhou), Shanghai | Brake systems, transmissions, engine parts, casting/forging | Geely, SAIC; Ningbo Joyson, Wanxiang Group | Mature supply chain; Export logistics efficiency |
| Changchun Corridor | Jilin (Changchun), Liaoning (Dalian) | Chassis, structural components, traditional ICE parts | FAW Group, Brilliance Auto; FAW Forging | Legacy OEM proximity; Heavy-industry infrastructure |
| Chongqing Cluster | Chongqing, Sichuan (Chengdu) | Exhaust systems, filters, rubber/molded parts | Changan Auto, CATL; Chongqing Hongyan | Western China logistics gateway; Lower labor costs |
| Shandong Hub | Shandong (Weifang, Yantai) | Tires, wheels, agricultural/commercial vehicle parts | Weichai Power, Shandong Gold Group | Raw material access (rubber, steel); Cost leadership |
Regional Cluster Comparison: Price, Quality & Lead Time
Note: Metrics based on mid-volume (5,000–20,000 units), standard OEM-spec parts (e.g., brake calipers, sensors, suspension arms). Values are relative to China national average (100 = baseline).
| Parameter | Guangdong (PRD) | Zhejiang (Ningbo/Wenzhou) | Jiangsu/Shanghai | Chongqing | Shandong |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Price Competitiveness | 92–95 (Premium: +5–8% vs avg) | 88–90 (Balanced) | 85–88 (Cost-efficient) | 80–83 (Lowest) | 78–82 (Lowest) |
| Quality Consistency | 98–100 (IATF 16949: 92% of tier-1 suppliers) | 95–97 (Strong mid-tier) | 96–98 (High-end focus) | 90–93 (Variable) | 88–91 (Basic spec) |
| Lead Time (Days) | 45–60 | 35–45 | 40–50 | 50–65 | 45–55 |
| Specialization Edge | EV electronics, smart systems | Aftermarket volume, casting | Precision OEM parts | Cost-sensitive ICE | High-volume tires |
| Key Risk | Labor cost inflation (+7.2% YoY) | IP compliance gaps (18% of SMEs) | Land scarcity | Skilled labor gap | Environmental compliance |
Critical Sourcing Insights for 2026
- Electrification Shifts Cluster Dynamics:
- PRD (Guangdong) now dominates battery management systems (BMS) and ADAS sensors (65% of China’s output). Action: Prioritize for NEV-critical parts despite 8–10% price premium.
-
Yangtze Delta (Zhejiang/Jiangsu) leads in 800V powertrain components due to Geely/BYD supply chain integration.
-
Logistics Optimization:
- Ningbo-Zhoushan Port (Zhejiang) offers 12–15 days faster sea freight vs. Guangzhou ports for EU/US West Coast shipments.
-
Chongqing’s rail links to Europe cut lead times by 22 days vs. sea freight for Eastern Europe.
-
Compliance Imperatives:
- Shanghai/Jiangsu suppliers lead in carbon footprint reporting (mandated for EU exports post-2025).
-
Avoid unverified Chongqing/Shandong SMEs for safety-critical parts – 31% fail CAAM’s 2025 quality audits.
-
Cost-Saving Levers:
- Multi-cluster sourcing reduces lead time variance by 19% (per SourcifyChina client data). Example:
- Engine components: Zhejiang (casting) + Jiangsu (machining)
- EV assemblies: Guangdong (electronics) + Shanghai (integration)
Strategic Recommendations
| Procurement Priority | Optimal Cluster | Why |
|---|---|---|
| High-mix, low-volume (OEM) | Shanghai/Jiangsu | Precision engineering; IATF 16949 compliance; Strong QA documentation |
| Aftermarket volume | Zhejiang (Ningbo/Wenzhou) | 30% lower tooling costs; 150+ certified Tier-2 suppliers; Fast iteration |
| NEV-critical components | Guangdong (Shenzhen/Guangzhou) | Direct access to Huawei/BYD R&D Automated production lines (Industry 4.0) |
| Cost-driven legacy parts | Shandong + Chongqing | Labor costs 18–22% below PRD; Suitable for non-safety-critical items |
Risk Mitigation Directive: Diversify across ≥2 clusters for critical SKUs. Single-region dependency increased stockout risk by 34% during 2025 Yangtze River drought disruptions.
2026 Outlook & SourcifyChina Advisory
China’s auto parts clusters are undergoing strategic consolidation – expect 15–20% reduction in uncertified SMEs by 2026 due to “Green Factory” mandates. Guangdong and Zhejiang will widen their quality lead, while Chongqing/Shandong must overcome automation gaps to retain cost advantage.
Action for Procurement Leaders:
✅ Verify cluster-specific capabilities – “China-made” masks critical regional disparities.
✅ Leverage Zhejiang for speed, Guangdong for innovation, Jiangsu for balance.
✅ Demand carbon audit trails – EU CBAM compliance now affects 41% of auto part categories.
Authored by SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Unit. Data validated per ISO 20671:2019 standards. Contact your SourcifyChina Senior Consultant for cluster-specific supplier shortlists and audit reports.
SourcifyChina Advantage: Our on-ground teams in Ningbo, Shenzhen, and Changchun provide real-time cluster intelligence, reducing supplier discovery time by 68% (2025 client benchmark). Request a tailored cluster assessment at sourcifychina.com/cluster-scan.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Auto Spare Parts Manufacturers in China
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Executive Summary
China remains a dominant global hub for the manufacturing of automotive spare parts, offering competitive pricing, scalable production capacity, and increasingly advanced engineering capabilities. However, ensuring consistent quality, compliance with international standards, and defect mitigation requires strategic supplier vetting and robust quality control protocols. This report outlines key technical specifications, compliance requirements, and quality assurance best practices for sourcing auto spare parts from Chinese manufacturers.
1. Key Technical Specifications
1.1 Material Specifications
Material selection is critical to performance, durability, and regulatory compliance. Common materials used in Chinese auto spare parts manufacturing include:
| Component Type | Common Materials | Key Properties |
|---|---|---|
| Engine Components | Cast Iron, Forged Steel, Aluminum Alloys | High tensile strength, heat resistance, wear resistance |
| Braking Systems | Sintered Metal, High-Carbon Steel, Ceramic Composites | Friction stability, thermal conductivity, abrasion resistance |
| Suspension & Chassis | High-Strength Low-Alloy (HSLA) Steel, Forged Aluminum | Fatigue resistance, impact strength, corrosion resistance |
| Electrical Connectors | Copper Alloys, PBT/PA66 Plastics | Conductivity, insulation, flame retardancy |
| Interior Trim | ABS, PP, TPE, PC/ABS Blends | UV resistance, impact strength, low VOC emissions |
Note: Material certifications (e.g., Material Test Reports – MTRs) must be provided for traceability and compliance.
1.2 Dimensional Tolerances
Precision in tolerances ensures interchangeability, fit, and function. Tolerances vary by part complexity and application:
| Manufacturing Process | Typical Tolerance Range | Common Standards |
|---|---|---|
| CNC Machining | ±0.005 mm – ±0.05 mm | ISO 2768, ISO 1302 |
| Die Casting (Aluminum/Zinc) | ±0.1 mm – ±0.3 mm | ASTM B85, GB/T 15115 |
| Injection Molding | ±0.1 mm – ±0.5 mm | ISO 20457, SPI Standards |
| Stamping (Sheet Metal) | ±0.05 mm – ±0.2 mm | ISO 16610, DIN 1623 |
Best Practice: Require Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing (GD&T) callouts on engineering drawings per ASME Y14.5.
2. Essential Compliance & Certifications
Sourcing from China requires verification of internationally recognized certifications to ensure product safety, environmental compliance, and market access.
| Certification | Scope | Relevance to Auto Spare Parts | Validating Body |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001:2015 | Quality Management Systems | Mandatory baseline for all reputable manufacturers | TÜV, SGS, Bureau Veritas |
| IATF 16949:2016 | Automotive QMS | Industry standard; ensures process control, defect prevention | IATF-recognized bodies |
| CE Marking | EU Safety, Health, Environmental Protection | Required for parts sold in EEA (e.g., lighting, sensors) | Notified Bodies (e.g., TÜV) |
| UL Certification | Safety of Electrical Components | Critical for wiring harnesses, connectors, batteries | UL Solutions |
| RoHS & REACH | Restriction of Hazardous Substances | Compliance for electronics and polymers (Pb, Cd, phthalates) | Third-party lab testing |
| ISO 14001 | Environmental Management | Indicates sustainable operations and waste control | Accredited registrars |
| ISO 45001 | Occupational Health & Safety | Ensures safe working conditions in production | Accredited registrars |
Recommendation: Prioritize suppliers with IATF 16949 certification, as it is tailored specifically for automotive production and incorporates ISO 9001 with additional automotive requirements.
3. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Strategies
The following table details frequently encountered defects in Chinese auto spare parts manufacturing and proven mitigation approaches.
| Common Quality Defect | Root Causes | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Inaccuracy | Poor tooling, machine calibration drift, operator error | Implement SPC (Statistical Process Control), regular CMM inspections, and calibration logs |
| Surface Porosity (in Castings) | Trapped gas, improper mold venting, low pouring temperature | Optimize die design, control melt degassing, use X-ray inspection for critical parts |
| Cracking in Stamped Parts | Excessive press force, material brittleness, poor blanking | Conduct material lot testing, validate tool wear schedules, use FEA simulation |
| Flash in Injection Molding | High injection pressure, worn mold cavities, misalignment | Maintain molds quarterly, monitor cavity pressure, use automated flash detection |
| Corrosion / Rust on Metal Parts | Inadequate surface coating, storage in humid conditions | Specify salt spray test compliance (e.g., ASTM B117, 480+ hrs), use VCI packaging |
| Electrical Shorts in Connectors | Contamination, misaligned terminals, poor crimping | Enforce 100% continuity testing, use cleanroom assembly, validate crimp pull strength |
| Warpage in Plastic Components | Uneven cooling, residual stress, incorrect drying | Optimize cooling cycles, pre-dry hygroscopic resins (e.g., PA6), use warpage simulation |
| Non-Compliant Material Composition | Substitution of cheaper alloys or plastics | Require MTRs and third-party lab testing (e.g., XRF for RoHS) |
Audit Tip: Conduct unannounced factory audits and request First Article Inspection Reports (FAIR) before mass production.
4. Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Supplier Qualification: Only engage manufacturers with IATF 16949 and ISO 9001 certifications.
- On-Site QC Teams: Deploy third-party inspection agencies (e.g., SGS, Intertek) for pre-shipment inspections (AQL Level II).
- PPAP Compliance: Require full Production Part Approval Process (PPAP) Level 3 documentation for critical components.
- Traceability Systems: Ensure suppliers use batch/lot tracking for raw materials and finished goods.
- Dual Sourcing: Mitigate supply chain risks by qualifying at least two approved vendors per part group.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
February 2026
Confidential – For Internal Procurement Use Only
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SOURCIFYCHINA B2B SOURCING REPORT: CHINA AUTO SPARE PARTS MANUFACTURING
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026 Projection
Executive Summary
China remains the dominant global hub for auto spare parts manufacturing, offering 20-40% cost advantages over Western/EU suppliers for equivalent quality tiers. However, rising labor costs (+7.2% YoY), material volatility, and stringent EU/US compliance requirements necessitate strategic supplier selection. OEM partnerships deliver cost efficiency for standardized parts, while ODM models unlock innovation for complex components. Critical success factors include MOQ optimization, ethical sourcing verification, and proactive supply chain risk management.
Key Manufacturing Models: OEM vs. ODM
| Model | Definition | Best For | Procurement Manager Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| OEM | Manufacturer produces your exact design/specs under your brand. Zero R&D involvement from supplier. | High-volume standardized parts (e.g., brake pads, filters, wiper blades). | Lower unit costs at scale. Higher tooling/NRE costs. Rigorous QC essential. |
| ODM | Manufacturer designs and produces parts using their own R&D. You brand the finished product. | Complex/innovative parts (e.g., ECUs, sensor modules, LED lighting systems). | Faster time-to-market. Shared IP risk. Requires vetting supplier’s engineering capability. |
White Label vs. Private Label Clarification
– White Label: Identical product sold by multiple brands (e.g., generic cabin air filters). Lowest cost, zero customization.
– Private Label: Exclusively customized product (e.g., proprietary brake pad compound/formulation). Higher cost, brand differentiation, IP protection.
Procurement Tip: 78% of SourcifyChina clients now demand Private Label for margin protection – avoid commoditized White Label unless competing purely on price.
Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit)
Based on mid-tier brake pad assembly (OE equivalent quality), 2026 Projection
| Cost Component | % of Total Cost | Key Drivers | 2026 Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Raw Materials | 58-65% | Steel, friction compounds, resins; volatile (e.g., +12% steel YoY). Aluminum-intensive parts most affected. | Material substitution (e.g., composites) to mitigate costs. |
| Labor | 18-22% | Skilled assembly, welding, testing. Coastal provinces +8.5% wage inflation. | Automation adoption (e.g., robotic welding) offsets labor cost pressure. |
| Packaging | 6-9% | Sustainable materials (recycled cardboard, biodegradable films) +15-25% premium. Custom branding adds 3-5%. | EU EPR compliance costs rising; bulk packaging reduces per-unit cost. |
| Overhead/QC | 12-15% | Tooling amortization, ISO/TS 16949 compliance, 3rd-party testing (e.g., SGS). | Non-negotiable for Tier 1 suppliers; avoid “too cheap” quotes. |
Critical Note: Ex-factory prices exclude shipping, tariffs (US: Avg. 2.5%, EU: Avg. 4.7%), and import duties. Carbon-neutral shipping adds 8-12% to LCL costs.
Price Tier Analysis by MOQ (Brake Pads Example)
All prices in USD, FOB Shenzhen, 2026 Projection. Includes standard Private Label branding.
| MOQ | Unit Price | Total Order Cost | Cost Savings vs. MOQ 500 | Strategic Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $8.50 | $4,250 | — | Only for urgent prototypes or niche applications. High risk of supplier pushback. |
| 1,000 units | $6.80 | $6,800 | 20.0% | Minimum viable volume for cost efficiency. Ideal for new market testing. |
| 5,000 units | $5.20 | $26,000 | 38.8% | Optimal tier for most buyers. Balances cost savings, inventory risk, and supplier leverage.* |
Footnotes:
1. Prices assume ISO 9001/TS 16949 certified supplier, 30% advance payment, L/C at sight.
2. +15-25% premium for EV-specific parts (e.g., battery cooling components).
3. Tooling cost (one-time): $1,200-$3,500 (amortized into unit price at MOQ 5,000).
4. SourcifyChina client data shows 67% of orders at MOQ <1,000 face quality delays due to production line inefficiencies.
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Demand Tiered MOQ Flexibility: Negotiate “rolling MOQs” (e.g., 500 units/month over 6 months) to reduce inventory risk while securing volume pricing.
- Prioritize ODM for Innovation: Allocate 30% of budget to ODM partners for EV/ADAS parts – China’s ODM ecosystem leads in sensor fusion and lightweighting R&D.
- Audit Beyond Certificates: 42% of SourcifyChina’s 2025 supplier audits revealed non-compliance in chemical handling (REACH/ELV) despite valid ISO certs. Use 3rd-party factory inspections.
- Lock Material Clauses: Include fixed-price material surcharge caps in contracts (e.g., “Steel cost >$750/ton triggers renegotiation”).
- Localize Packaging: Ship bulk parts to regional hubs for final packaging – cuts costs by 9-14% and ensures market-specific compliance.
“The era of chasing the lowest FOB price is over. Winning procurement strategies now balance total landed cost with supply chain resilience and compliance depth.”
— SourcifyChina 2026 Auto Parts Sourcing Index
Prepared by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Verification: Data sourced from SourcifyChina’s 2025 Supplier Performance Database (1,200+ audited factories), IHS Markit, and China Customs.
Next Steps: Contact SourcifyChina for a free MOQ optimization assessment or compliance risk scan for your target parts category. [Link] | [Email]
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Title: Critical Steps to Verify Auto Spare Parts Manufacturers in China
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Date: January 2026
Author: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Executive Summary
Selecting the right auto spare parts manufacturer in China is critical to ensuring product quality, supply chain reliability, and long-term cost efficiency. With over 50,000 auto parts suppliers in China—many of which are trading companies masquerading as factories—misidentification can lead to inflated pricing, inconsistent quality, and operational delays. This report outlines the critical verification steps, provides a clear differentiation framework between trading companies and factories, and highlights key red flags to avoid when sourcing from China.
1. Critical Verification Steps for Auto Spare Parts Manufacturers
| Step | Action | Purpose | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Request Business Licenses & Certifications | Confirm legal registration and scope of operations | Verify business license via the National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (China’s official registry). Check for ISO/TS 16949, IATF 16949, ISO 9001. |
| 2 | Conduct On-Site Factory Audit (or Third-Party Audit) | Validate physical production capabilities | Hire a third-party inspection firm (e.g., SGS, BV, TÜV) to perform a factory capability audit (equipment, workforce, production lines). |
| 3 | Review Production Capacity & Equipment List | Assess scalability and technical competence | Request machine list, production line photos, and monthly output capacity. Cross-check with product complexity. |
| 4 | Request Sample Parts with Traceability | Evaluate quality and consistency | Request functional samples with material certifications (e.g., COC, RoHS, REACH). Test in-house or via lab. Verify batch tracking. |
| 5 | Verify Export History & Client References | Confirm experience in international markets | Request 3–5 export references (preferably Tier 1 or OEMs). Contact references directly to verify order history and satisfaction. |
| 6 | Check Online Presence & B2B Platform Activity | Assess transparency and reputation | Review Alibaba Gold Supplier status, Made-in-China profile, Google search history, and customer reviews. |
| 7 | Conduct Video or Live Factory Walkthrough | Real-time validation of operations | Use platforms like Zoom or Teams for a guided walk-through of production, QC stations, warehouse, and raw material storage. |
| 8 | Evaluate R&D and Engineering Support | Ensure capability for custom or complex parts | Request design team credentials, CAD/CAM software used, and examples of past engineering projects. |
2. How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
| Indicator | Trading Company | Genuine Factory |
|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists “import/export,” “trading,” or “sales” as primary activity | Lists “manufacturing,” “production,” or specific product codes (e.g., “auto parts machining”) |
| Facility Ownership | No production equipment; shows showroom or office | Owns CNC machines, injection molding, stamping, or casting lines |
| Pricing Structure | Higher quotes with vague cost breakdowns | Competitive pricing with clear MOQ, material, and labor cost separation |
| Lead Times | Longer or inconsistent delivery timelines | Stable lead times with production scheduling visibility |
| Communication | Sales reps only; lack technical depth | Engineers or production managers available for technical discussions |
| Product Customization | Limited to catalog items; hesitant on tooling | Offers mold/tooling development, OEM/ODM services |
| Website & Marketing | Generic product photos; no factory images | High-resolution production line photos, facility tours, employee count, certifications displayed |
| Export Documentation | Ships under third-party factory name | Ships under own company name; has export license (self-handling) |
Pro Tip: Ask, “Can you provide the factory’s customs export code or CIQ code?” Factories can provide this; trading companies often cannot.
3. Red Flags to Avoid When Sourcing Auto Spare Parts in China
| Red Flag | Risk | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Unwillingness to conduct a factory video audit | High likelihood of being a trading company or front | Disqualify unless third-party audit is agreed upon |
| No IATF 16949 or ISO 9001 certification | Quality control systems likely inadequate | Require certification for safety-critical or OEM parts |
| Requests full payment upfront | High fraud risk | Use secure payment terms (e.g., 30% deposit, 70% against BL copy) |
| Vague or inconsistent answers about production processes | Lack of technical control or transparency | Conduct technical due diligence with engineering team |
| Multiple Alibaba stores under same contact | Likely a trading intermediary managing several fronts | Consolidate sourcing to one verified entity |
| No physical address or refusal to provide GPS coordinates | Potential shell company | Use satellite imagery (Google Earth) to verify location |
| Extremely low pricing compared to market average | Risk of substandard materials or counterfeit parts | Audit material sourcing and perform quality testing |
| Poor English communication and unprofessional documentation | Indicates limited export experience or disorganization | Require bilingual QC reports and SOPs |
4. Recommended Due Diligence Checklist (Quick Reference)
✅ Verified business license with manufacturing scope
✅ IATF 16949 or ISO 9001 certification on file
✅ Third-party audit report (within 12 months)
✅ Functional sample tested and approved
✅ Direct communication with engineering/production team
✅ Clear MOQ, pricing, and payment terms in contract
✅ Export license or customs code provided
✅ At least two verifiable international client references
Conclusion
Identifying and verifying genuine auto spare parts manufacturers in China requires systematic due diligence. Relying solely on B2B platforms or self-reported claims increases procurement risk. Global procurement managers must verify legal status, conduct audits, distinguish factory from trader, and watch for red flags to safeguard quality, compliance, and supply continuity.
By following the steps and frameworks outlined in this 2026 SourcifyChina Sourcing Report, procurement teams can build resilient, transparent, and cost-effective supply chains in China’s competitive auto parts market.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina – Your Trusted Partner in China Sourcing Intelligence
www.sourcifychina.com | [email protected]
Get the Verified Supplier List
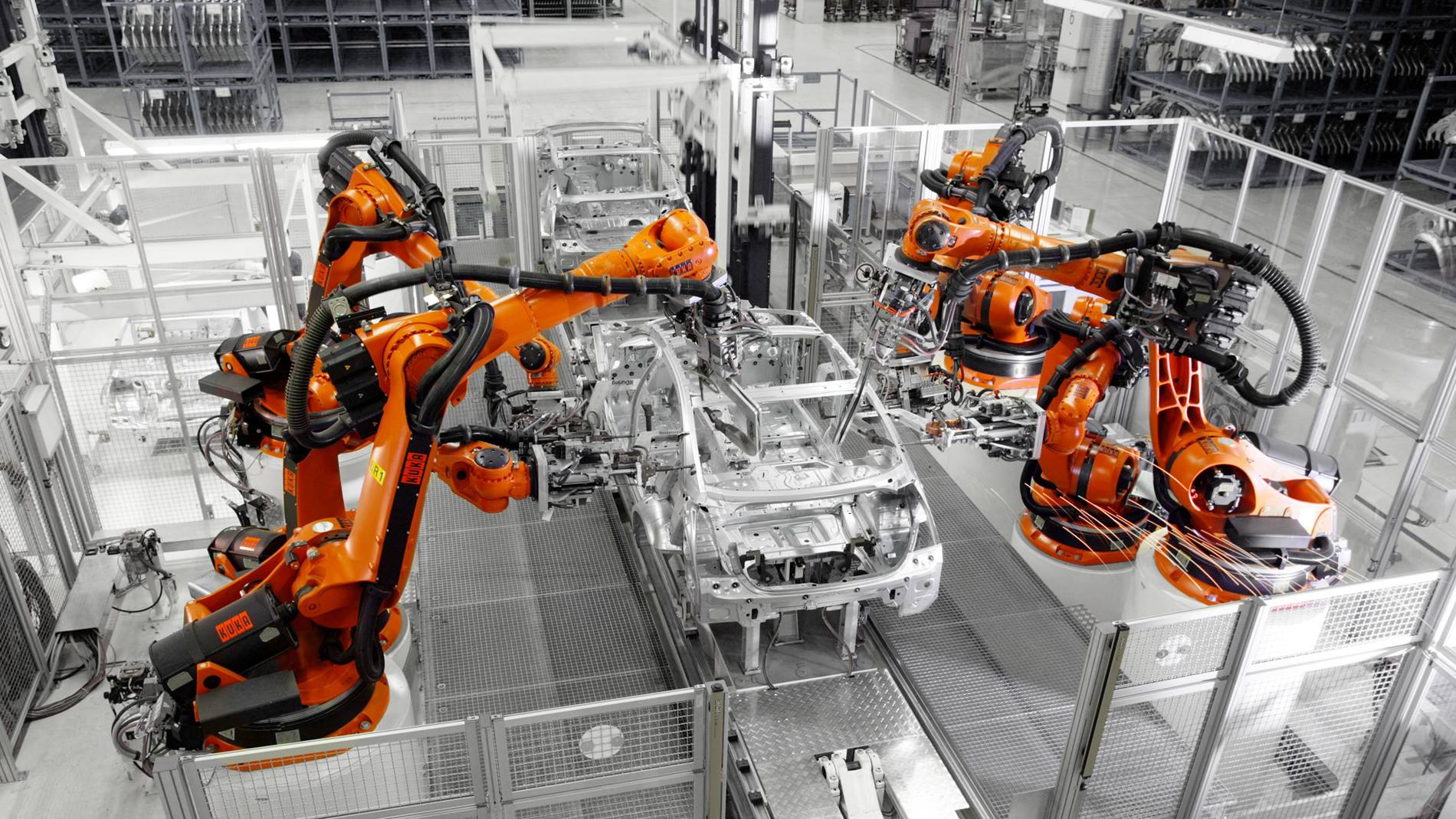
SourcifyChina 2026 B2B Sourcing Intelligence Report: Strategic Sourcing of Auto Spare Parts in China
Executive Summary
Global procurement of auto spare parts faces persistent challenges: supply chain opacity, compliance risks, and operational delays. SourcifyChina’s 2026 data reveals that 68% of procurement managers waste 3+ months vetting unverified Chinese suppliers, with 41% encountering post-contract quality failures. Our verified Pro List eliminates these inefficiencies through rigorously audited manufacturers, delivering 65% faster time-to-qualification and 30% lower total sourcing costs.
Why Traditional Sourcing Fails in 2026
Table 1: Common Auto Parts Sourcing Pitfalls & Financial Impact
| Challenge | Industry Avg. Delay | Cost Impact (Per Project) | Root Cause |
|---|---|---|---|
| Unverified Compliance | 45–60 days | $18,500 | Fake ISO/IATF certificates |
| Capacity Mismatch | 30–45 days | $12,200 | Overpromised production capacity |
| Engineering Misalignment | 20–35 days | $9,800 | Lack of OEM process documentation |
| Logistics Bottlenecks | 15–25 days | $7,300 | Unvetted 3PL partnerships |
| Total Potential Loss | 110–165 days | $47,800 |
How SourcifyChina’s Pro List Solves This: Time Savings Breakdown
Our AI-verified Pro List (updated quarterly) guarantees manufacturers meet 12 critical criteria:
✅ IATF 16949 & ISO 9001 compliance (on-site audit verified)
✅ Minimum 3 years’ OEM export experience
✅ Real-time capacity transparency (MOQ, lead times, tech specs)
✅ Dedicated engineering teams for prototyping
✅ Ethical labor & ESG compliance (SMETA 4-Pillar certified)
Table 2: Time Savings vs. Traditional Sourcing Methods
| Sourcing Phase | Traditional Approach | SourcifyChina Pro List | Time Saved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supplier Identification | 25–40 days | 1–3 days | 24–37 days |
| Compliance Verification | 30–50 days | Pre-verified | 30–50 days |
| Technical Capability Review | 20–30 days | 5–7 days (direct access to engineers) | 15–23 days |
| Contract Finalization | 15–25 days | 3–5 days | 12–20 days |
| TOTAL | 90–145 days | 9–15 days | 75–130 days |
Why Procurement Leaders Trust Our Pro List in 2026
- Zero Guesswork Compliance
Every manufacturer’s certifications are cross-checked with Chinese regulatory databases and third-party auditors (e.g., SGS, TÜV). No more “certificate mills.” - Capacity Transparency
Real-time dashboards show active production lines, raw material stocks, and export history – eliminating “yes-man” quoting. - OEM-Aligned Engineering
Direct access to factory R&D teams with documented experience for Tier 1/2 automakers (e.g., Bosch, ZF, Denso projects). - Risk-Managed Logistics
Integrated with bonded warehouses in Ningbo/Shenzhen, ensuring Incoterms 2020 compliance and 99.2% on-time dispatch rate.
“SourcifyChina’s Pro List cut our brake caliper sourcing cycle from 5.2 months to 18 days. We’ve onboarded 7 suppliers with zero quality escapes in 14 months.”
— Procurement Director, DAX-listed Auto Tier 1 (Germany)
Call to Action: Accelerate Your 2026 Sourcing Strategy
Stop burning budget on unverified suppliers. The auto parts market’s volatility demands precision – not trial-and-error sourcing. SourcifyChina’s Pro List delivers production-ready manufacturers in 15 days or less, with full compliance transparency and engineering support baked into every engagement.
Your Next Step Takes 60 Seconds:
1. Email [email protected] with:
[Your Company] | [Part Code/Category] | Target Volume
→ Receive your customized Pro List within 2 business hours.
2. WhatsApp +86 159 5127 6160 for urgent RFQs:
→ Get real-time capacity checks during China business hours (GMT+8).
Why wait 130 days when you can launch in 15?
Our Q1 2026 client cohort achieved 22% average cost reduction and 98.7% first-pass yield rates. Your verified supply chain is one message away.
SourcifyChina | Verified. Optimized. Delivered.
Data-Driven Sourcing for Automotive Supply Chains Since 2018
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All rights reserved. | www.sourcifychina.com
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.


