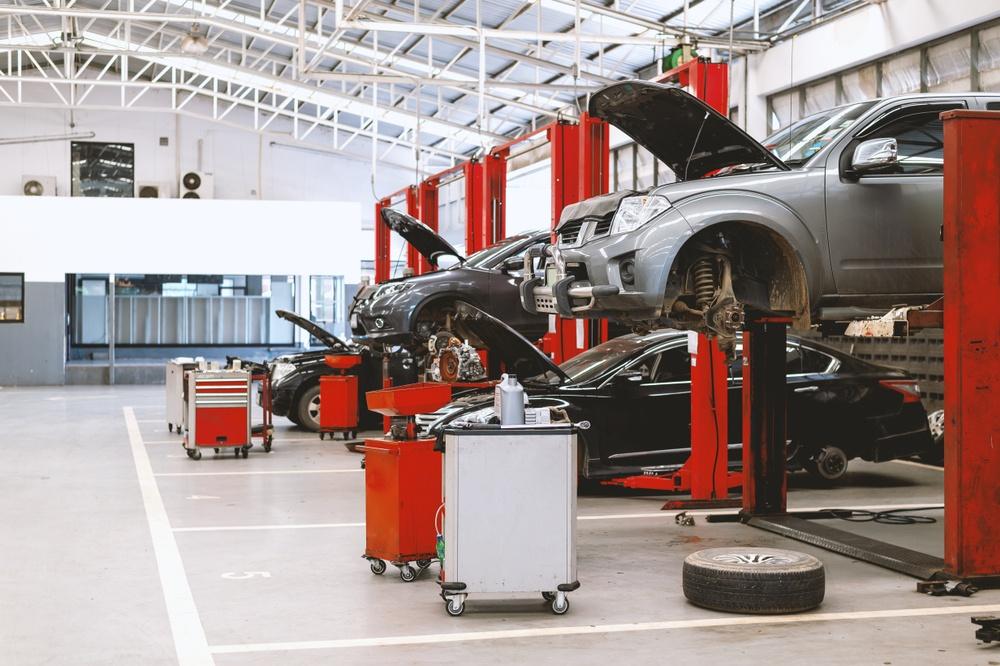
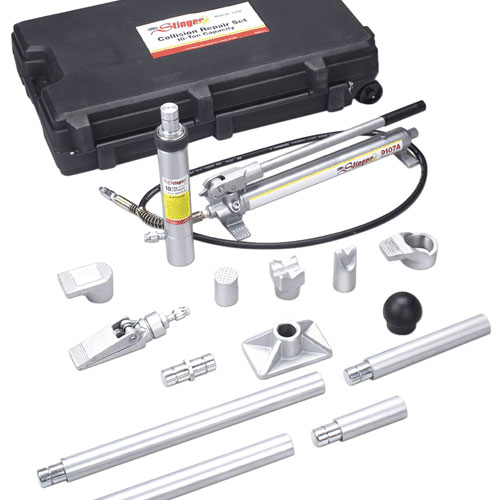
The global automotive repair equipment market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising vehicle ownership, increasing demand for advanced diagnostic tools, and the expanding aftermarket service sector. According to Grand View Research, the market was valued at USD 25.6 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8% from 2023 to 2030. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence estimates a CAGR of over 5.5% during the forecast period of 2023–2028, attributing this expansion to technological advancements in equipment automation and the growing need for efficient, precision-based repair solutions. As service centers and independent garages upgrade their capabilities to meet evolving vehicle complexities—particularly with the rise of electric and hybrid models—the role of innovative, reliable equipment manufacturers has never been more critical. In this landscape, a select group of global leaders are setting the standard for performance, durability, and smart integration, shaping the future of automotive maintenance and repair.
Top 10 Auto Repair Equipment Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 ATD Automotive Tools and Equipment
Domain Est. 1995
Website: atdtools.com
Key Highlights: Find top-quality automotive tools and equipment from ATD Tools, Inc. Trusted by professionals for over 46 years in the US and Canada….
#2 ACDelco: OEM & Aftermarket Auto Parts
Domain Est. 1996
Website: gmparts.com
Key Highlights: ACDelco offers the only aftermarket parts backed by GM. ACDelco’s Gold and Silver lines of premium aftermarket parts offer a precise fit for GM vehicles….
#3 Automotive Shop Equipment
Domain Est. 2016
Website: hofmann-equipment.com
Key Highlights: Discover the vast range of automotive shop equipment by Hofmann including Wheel Balancers, Aligners, Tire Changers, Automotive lifts, and OEM products….
#4 Snap
Domain Est. 1995
Website: snapon.com
Key Highlights: Providing a broad array of unique productivity solutions, Snap-on makes work easier for professionals performing critical tasks around the world….
#5 OTC Tools
Domain Est. 1995
Website: otctools.com
Key Highlights: Shop Equipment. Tough and sturdy for the shop professional. Power train lifts, transmission jacks, stands, cranes, presses, DPF equipment and more….
#6 Our Companies
Domain Est. 1995
Website: genpt.com
Key Highlights: The Automotive Parts Group distributes automotive replacement parts, accessories and solutions across the US, Canada, Mexico, Australasia, France, the UK, ……
#7 Automotive Equipment
Domain Est. 1996
Website: johnbean.com
Key Highlights: John Bean® is an industry leader in automotive equipment. Browse our line of modern Tire Changers, Auto Lifts, Wheel Balancers and more….
#8 Automotive Equipment
Domain Est. 2001
Website: asedeals.com
Key Highlights: We have car jacks, truck jacks, hydraulic and air jacks. Our biggest seller is hydraulic floor jacks, which is the staple of any auto shop or home garage….
#9 Atlas Automotive Equipment
Domain Est. 2009
Website: atlasautoequipment.com
Key Highlights: Atlas Automotive Equipment has grown to become one of the most well-known and well-respected names in the automotive Industry for Car Lifts and Automotive ……
#10 Rotary Solutions
Domain Est. 2009 | Founded: 1925
Website: rotarysolutions.com
Key Highlights: Trusted source for automotive shop equipment since 1925. Industry-leading vehicle lifts, collision repair tools, and A/C service equipment….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Auto Repair Equipment
2026 Market Trends for Auto Repair Equipment
The auto repair equipment market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological advancements, evolving vehicle designs, and shifting consumer behaviors. As electric vehicles (EVs), connected cars, and autonomous driving systems gain market share, repair shops and equipment manufacturers must adapt to meet new service demands. This analysis explores key trends expected to shape the auto repair equipment industry in 2026.
Growth in Electric Vehicle Service Equipment
By 2026, electric vehicles are projected to account for over 20% of global vehicle sales, according to the International Energy Agency. This shift is driving demand for specialized repair equipment such as EV battery testers, high-voltage safety tools, and regenerative braking system analyzers. Traditional repair tools are becoming obsolete for EV diagnostics, leading manufacturers to invest heavily in EV-compatible equipment. OEMs and third-party suppliers are launching modular diagnostic platforms that support both internal combustion engine (ICE) and electric powertrains, ensuring versatility for multi-brand service centers.
Integration of AI and Predictive Maintenance Tools
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are increasingly embedded in diagnostic and repair equipment. By 2026, AI-powered scanners and analysis tools are expected to dominate the market, offering predictive maintenance alerts and automated fault detection. These systems analyze real-time vehicle data to identify potential failures before they occur, reducing downtime and repair costs. Cloud-connected diagnostic platforms allow technicians to access updated repair procedures and performance benchmarks, improving accuracy and efficiency.
Rise of Augmented Reality (AR) in Technician Training and Repairs
Augmented reality is emerging as a key enabler in technician training and complex repair procedures. By 2026, AR-enabled smart glasses and repair tablets are expected to be standard in forward-thinking auto shops. These tools overlay 3D schematics and step-by-step instructions onto real-world components, improving repair accuracy and reducing training time. Equipment manufacturers are partnering with AR software developers to integrate these features directly into diagnostic tools, creating a seamless workflow from diagnosis to repair.
Consolidation and Expansion of Service Center Networks
The auto repair equipment market is witnessing increased consolidation as large distributors and OEMs acquire regional suppliers to expand their service offerings. By 2026, integrated service platforms that bundle equipment, software, training, and technical support are expected to dominate the market. This trend is particularly strong in North America and Europe, where independent repair shops seek turnkey solutions to remain competitive against dealership networks.
Emphasis on Sustainability and Equipment Lifecycle Management
Environmental regulations and consumer demand for sustainable practices are pushing equipment manufacturers to adopt greener production methods. In 2026, expect a rise in energy-efficient lifts, recyclable packaging, and remanufactured or refurbished equipment. Equipment lifecycle management platforms—offering tracking, maintenance, and resale options—are gaining traction, helping shops reduce costs and environmental impact.
Increasing Cybersecurity Requirements for Diagnostic Tools
As vehicles become more connected, the diagnostic equipment used in repairs must comply with stringent cybersecurity standards. By 2026, regulatory bodies in the EU and U.S. are expected to enforce cybersecurity certifications for all repair tools that interface with vehicle networks. This will drive demand for secure, encrypted diagnostic systems, particularly in franchised dealerships and certified independent shops.
Conclusion
The auto repair equipment market in 2026 will be defined by innovation, integration, and adaptation. Success will depend on manufacturers’ ability to deliver smart, EV-ready, and secure solutions while supporting the evolving needs of technicians and service providers. Companies that invest in AI, AR, sustainability, and cybersecurity today will be best positioned to lead the market in the coming years.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Auto Repair Equipment: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing auto repair equipment—especially from overseas suppliers—can offer significant cost savings, but it also comes with critical risks related to quality and intellectual property (IP). Failing to address these pitfalls can lead to safety hazards, legal liabilities, reputational damage, and costly product failures.
Quality Control Challenges
One of the most significant risks when sourcing auto repair equipment is inconsistent or substandard quality. Poorly manufactured tools and machinery can compromise vehicle safety, lead to customer dissatisfaction, and expose businesses to liability.
-
Inadequate Manufacturing Standards: Suppliers may cut corners by using inferior materials or outdated production processes to reduce costs. This can result in equipment that fails under normal operating conditions—such as lifts collapsing, diagnostic tools providing inaccurate readings, or brake lathes producing uneven results.
-
Lack of Certification and Testing: Reliable auto repair equipment must meet industry standards (e.g., CE, ISO, ANSI, or SAE). Some suppliers falsely claim compliance or provide counterfeit certifications. Without third-party verification, you risk importing non-compliant or unsafe products.
-
Inconsistent Batch-to-Batch Quality: Even if initial samples meet expectations, production batches may vary significantly due to poor process controls or workforce turnover. Without ongoing quality audits and inspections, these inconsistencies may go unnoticed until equipment is already in use.
-
Insufficient Technical Support and Documentation: Low-cost suppliers may not provide comprehensive user manuals, maintenance guides, or technical support, leading to improper use and premature equipment failure.
Intellectual Property Infringement Risks
Sourcing from markets with weak IP enforcement exposes buyers to legal and financial risks, particularly when suppliers replicate branded equipment without authorization.
-
Counterfeit or Knockoff Equipment: Many suppliers manufacture unlicensed replicas of well-known brands (e.g., knockoff Hunter alignment machines or Snap-on tools). Purchasing such equipment—knowingly or not—can expose your business to lawsuits for contributory infringement.
-
Design and Patent Violations: Even if equipment isn’t a direct copy, it may incorporate patented technologies (e.g., diagnostic algorithms, hydraulic systems, or calibration methods) without proper licensing. Your company could be held liable if the product is found to infringe on existing patents.
-
Trademark and Branding Issues: Suppliers may use logos, product names, or packaging that mimic established brands. Importing or selling such products—even if the supplier claims “generic” status—can trigger trademark enforcement actions from original equipment manufacturers (OEMs).
-
Limited Legal Recourse: In many sourcing regions, enforcing IP rights against suppliers is difficult or impractical. Once infringement is detected, recovering damages or halting production is often not feasible, leaving buyers to absorb the financial and legal consequences.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls:
– Conduct thorough due diligence on suppliers, including factory audits and third-party quality inspections.
– Verify certifications and demand test reports from accredited labs.
– Work with legal counsel to perform IP clearance searches and include IP indemnification clauses in supplier contracts.
– Consider sourcing through reputable distributors or OEM-authorized partners when possible.
By proactively addressing quality and IP concerns, businesses can protect their operations, customers, and brand integrity when sourcing auto repair equipment.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Auto Repair Equipment
Proper logistics and compliance management are essential for the safe, efficient, and legal distribution of auto repair equipment. This guide outlines key considerations for manufacturers, distributors, and retailers involved in the supply chain.
Regulatory Compliance
Product Safety Standards
Auto repair equipment must comply with safety standards established by regulatory bodies such as OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) and ANSI (American National Standards Institute). Equipment like lifts, jacks, and alignment machines must meet specific performance and structural requirements to ensure user safety.
Electrical and Mechanical Certification
Equipment with electrical components must be certified by recognized testing laboratories such as UL (Underwriters Laboratories) or ETL (Intertek). These certifications confirm compliance with national electrical codes and reduce fire or shock hazards.
Environmental Regulations
Shipping and storing certain equipment, especially those containing hydraulic fluids or batteries, must adhere to EPA (Environmental Protection Agency) guidelines. Proper handling, labeling, and disposal procedures are required to prevent environmental contamination.
Transportation & Shipping
Packaging Requirements
All auto repair equipment must be securely packaged to withstand transport stresses. Use durable materials, internal bracing, and moisture barriers. Clearly label packages with handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “This Side Up”).
Freight Classification
Classify equipment accurately using NMFC (National Motor Freight Classification) codes. Heavy or large items like vehicle lifts fall into high-density classifications, impacting freight costs. Proper classification avoids carrier disputes and billing adjustments.
Domestic & International Shipping
For international shipments, ensure compliance with destination country standards (e.g., CE marking in Europe, CCC in China). Prepare accurate commercial invoices, packing lists, and customs declarations. Be aware of import duties and restricted items.
Storage & Inventory Management
Warehouse Safety
Store heavy equipment on reinforced pallets and use proper racking systems. Maintain clear aisles and ensure forklift operators are certified. Follow OSHA guidelines for workplace safety to prevent accidents.
Climate Control
Protect sensitive electronic components from extreme temperatures and humidity. Store control units, sensors, and diagnostic tools in climate-controlled areas to maintain functionality and warranty validity.
Inventory Tracking
Use barcode or RFID systems to track equipment from receipt to dispatch. Accurate inventory records reduce overstocking, prevent stockouts, and support compliance audits.
Documentation & Recordkeeping
Certificates of Conformity
Maintain certificates proving compliance with relevant standards for each product line. These documents may be required during customs clearance or customer audits.
Shipping Logs & Bills of Lading
Keep digital and physical records of all shipping documents, including bills of lading, delivery confirmations, and proof of delivery. These records support dispute resolution and regulatory compliance.
Warranty & Recall Management
Establish a system to track product serial numbers and warranty registrations. In the event of a recall, quickly identify affected units and notify customers in accordance with FTC and CPSC guidelines.
Training & Employee Compliance
Handling Procedures
Train warehouse and logistics personnel on proper lifting techniques, equipment handling, and emergency procedures. Use visual aids and regular refresher courses to reinforce safety practices.
Regulatory Awareness
Ensure staff understand key regulations affecting auto repair equipment logistics, including hazardous material handling (if applicable) and export controls.
By adhering to this logistics and compliance framework, businesses can minimize risks, ensure product integrity, and maintain legal and operational efficiency throughout the supply chain.
In conclusion, sourcing auto repair equipment requires a strategic approach that balances quality, cost, reliability, and long-term value. It is essential to conduct thorough research, evaluate suppliers based on reputation, certifications, and after-sales support, and consider both immediate needs and future scalability. Whether purchasing locally or internationally, businesses should prioritize equipment that meets industry standards, enhances operational efficiency, and ensures technician safety. By leveraging competitive pricing, negotiating favorable terms, and staying informed about technological advancements, auto repair shops can make informed procurement decisions that contribute to improved service delivery and sustained business growth. Effective sourcing not only optimizes workshop performance but also strengthens competitiveness in an evolving automotive service market.