The global electric arc furnace (EAF) market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand for scrap-based steel production and increased focus on reducing carbon emissions in the metallurgical industry. According to Mordor Intelligence, the electric arc furnace market was valued at USD 2.87 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8% from 2024 to 2029. This expansion is further supported by Grand View Research, which highlights the growing adoption of EAFs in mini-mills due to their energy efficiency and lower capital investment compared to traditional basic oxygen furnaces. As the steel industry shifts toward sustainable and flexible production methods, leading manufacturers are innovating to deliver high-performance, digitally integrated arc furnace solutions. The following list ranks the top 10 arc furnace manufacturers based on market presence, technological advancement, installed capacity, and global project footprint.
Top 10 Arc Furnace Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Steel Dynamics
Domain Est. 1999
Website: lpg.steeldynamics.com
Key Highlights: Our mills have the capacity to produce 4.4 million tons of long product steel using state-of-the-art electric arc furnace (EAF) technology that produces fewer ……
#2 EAF technology: Electric arc furnace
Domain Est. 2003
Website: sms-group.com
Key Highlights: SMS group’s electric arc furnaces (EAF) and optimized processes offer you the most cost-effective solutions for liquid steel production….
#3 Electric Arc Furnace (EAF)
Domain Est. 1995
Website: ceramicsrefractories.saint-gobain.com
Key Highlights: Our Electric Arc Furnace Refractories can help you reuse scrap steel and can resist oxidation and corrosion. Find your EAF Refractory Solution now….
#4 Algoma Steel
Domain Est. 1996
Website: algoma.com
Key Highlights: Algoma Steel Announces First Arc and First Steel Production from its New Electric Arc Furnace Unit One. July 10, 2025 PDF Version SAULT STE….
#5 Part 1, The History of Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) Steelmaking
Domain Est. 1997
Website: nucor.com
Key Highlights: The history of the electric arc furnace (EAF) dates back to the late 19th century, representing a major shift from traditional steelmaking techniques….
#6 GrafTech International Ltd.
Domain Est. 2000
Website: graftech.com
Key Highlights: For generations, committed GrafTech employees have pushed the envelope of graphite electrodes and electric arc furnace productivity. Learn more….
#7 Electric Arc Furnaces (EAF)
Domain Est. 2000
Website: tenova.com
Key Highlights: An electric arc furnace (EAF) is a furnace that heats material by means of an electric arc, combined with the action of chemical power provided by the use ……
#8 EVRAZ North America
Domain Est. 2008
Website: evrazna.com
Key Highlights: The EVRAZ Regina facility is a zero liquid effluent electric-arc furnace steelmaking facility with 100% of water treated and recycled onsite and zero waste ……
#9 Arc furnace auxiliary equipment
Website: chugai.co.jp
Key Highlights: Arc furnace auxiliary equipment. Strong support for increased steelmaking capacity! Fully automatic operation with a high-performance oxygen burner provides ……
#10 JFE Steel to introduce advanced, high
Website: jfe-steel.co.jp
Key Highlights: JFE Steel Corporation announced today that it will construct and operate an advanced, high-efficiency, large-scale electric arc furnace at the Kurashiki ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Arc Furnace

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Electric Arc Furnaces (EAFs)
The global Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) market in 2026 is poised for significant expansion and transformation, driven by powerful forces centered on decarbonization, resource availability, technological advancement, and evolving steel demand. The H2 outlook for the year is particularly critical, building on full-year trends and potentially revealing acceleration or new challenges.
1. Dominant Driver: Decarbonization & Green Steel Push (H2 Intensification):
* Regulatory Pressure: H2 2026 will see the full impact of stricter environmental regulations (EU CBAM, potential US/Asian equivalents) and national net-zero targets. Steelmakers will face significant carbon costs for BF-BOF routes, making EAFs (especially those using renewable power) the de facto choice for new capacity and expansion.
* Green Premium & Investment: Demand for “green steel” (EAF + renewable energy + high scrap quality) from automotive, construction, and OEMs will solidify. This premium justifies higher investments in EAF upgrades and new facilities. H2 will be crucial for securing long-term off-take agreements and green financing.
* Hydrogen Integration (Emerging in H2): While not yet commercial at scale, H2 2026 will see increased piloting and feasibility studies for injecting hydrogen into EAFs to further reduce carbon emissions (replacing some fossil fuels). This positions EAFs as adaptable platforms for future deep decarbonization.
2. Scrap Availability & Quality: The Critical Constraint (H2 Focus on Solutions):
* Growing Shortfall: The primary challenge remains the gap between rapidly increasing EAF capacity and the availability of high-quality, low-residual scrap. H2 2026 will highlight this constraint, potentially limiting the operational capacity of new EAFs.
* Innovative Sourcing & Processing: Expect accelerated investment in H2 2026 in:
* Scrap Sorting & Preparation: Advanced sensor-based sorting (AI, XRF, LIBS) to produce higher-purity scrap streams.
* Alternative Ferrous Inputs: Increased use of Direct Reduced Iron (DRI) and Hot Briquetted Iron (HBI) as high-quality, low-residual diluents, particularly in regions with access to natural gas/renewables (Middle East, North America).
* Global Scrap Trade Dynamics: Geopolitical factors and export restrictions (e.g., potential from China/India) will heavily influence scrap flows and prices in H2.
3. Technological Advancements: Efficiency & Flexibility (H2 Deployment Acceleration):
* High-Efficiency EAFs (Quantum, Consteel, etc.): Wider adoption of advanced EAF designs focusing on shorter tap-to-tap times, higher productivity, lower energy consumption (kWh/ton), and reduced electrode consumption. H2 will see more retrofits and new installations.
* Digitalization & AI: Deep integration of AI for real-time process optimization (melting control, energy input, alloying), predictive maintenance, and quality prediction. H2 will showcase tangible ROI from these systems.
* Advanced Automation & Remote Operation: Increased use of robotics for charging, sampling, and tapping, improving safety and consistency. Remote monitoring and operation centers become more common.
* Hybrid Charging & Injection: Wider use of technologies like Consteel (continuous charging) and carbon/oxygen injection for faster melting and better energy efficiency.
4. Regional Dynamics: Shifting Landscapes (H2 Consolidation):
* Asia-Pacific (APAC): Remains the largest market, but growth shifts. China focuses on replacing older capacity and improving efficiency within its existing massive EAF base, driven by its own carbon goals. India sees significant new EAF capacity additions to meet rising domestic demand and reduce imports. Southeast Asia (Vietnam, Indonesia) continues strong growth for rebar and construction steel.
* North America: Sustained growth driven by scrap availability, relatively low energy costs (especially gas for DRI), and strong demand for semi-finished and finished products. H2 2026 may see announcements of new mini-mills or expansions.
* Europe: Driven almost entirely by decarbonization mandates. Focus is on upgrading existing EAFs and potentially replacing some BF-BOF capacity with EAFs using green DRI/HBI. H2 will be critical for final investment decisions (FIDs) on major green steel projects.
* Middle East: Leverages abundant natural gas to produce low-cost, low-CO2 DRI, making it a strategic supplier of high-quality feedstock for global EAFs and potentially expanding its own EAF capacity.
5. Raw Material & Energy Costs (H2 Volatility):
* Scrap Prices: Expected to remain relatively high and volatile in H2 2026, influenced by global demand, supply chain issues, and competition with DRI.
* Energy Costs: Electricity prices remain a critical factor. Regions with access to stable, low-cost renewable energy will have a significant competitive advantage. H2 may see increased Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs) for wind/solar to secure green power.
* DRI/HBI Prices: Linked to natural gas and iron ore pellet prices. Volatility in these markets directly impacts the cost-effectiveness of using DRI/HBI in EAFs.
H2 2026 Outlook Summary:
The second half of 2026 will likely confirm the EAF’s central role in the future of steelmaking. Growth will be robust, but tempered by scrap constraints. Success will depend on:
* Securing high-quality feedstock (scrap, DRI/HBI).
* Implementing cutting-edge technology for efficiency and quality.
* Integrating renewable energy to meet carbon targets and access green premiums.
* Navigating regional policy and cost landscapes.
H2 2026 will be a period of execution and scaling for the trends established earlier in the year, with increased focus on operational excellence, supply chain resilience, and demonstrating the economic viability of the green EAF pathway. Companies that secure feedstock and energy partnerships and deploy advanced technologies effectively will gain significant market share.
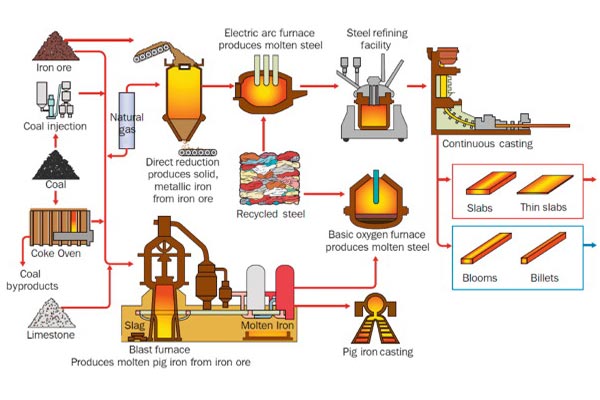
Common Pitfalls in Sourcing an Arc Furnace: Quality and Intellectual Property Concerns
Sourcing an electric arc furnace (EAF) is a significant capital investment, often critical to the viability and competitiveness of a steelmaking or metal recycling operation. While technical specifications and pricing are primary considerations, overlooking quality and intellectual property (IP) aspects can lead to long-term operational, financial, and legal repercussions. Below are key pitfalls to avoid in these two critical areas.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Inadequate Due Diligence on Supplier Track Record
A common mistake is selecting a supplier based solely on price or aggressive marketing without verifying their historical performance. Unproven or low-cost vendors may offer seemingly attractive deals but lack the engineering rigor or manufacturing consistency required for reliable furnace operation. This can result in frequent breakdowns, poor energy efficiency, and shorter equipment lifespan. Always request references, conduct site visits to existing installations, and review third-party audit reports before committing.
2. Compromised Material and Component Quality
Some suppliers cut costs by using substandard refractory linings, lower-grade electrodes, or inferior electrical components (e.g., transformers, busbars, or switchgear). These compromises directly impact furnace efficiency, safety, and maintenance cycles. Ensure the specification includes certified materials and reputable component brands. Verify that the supplier adheres to international standards such as ISO 9001 and ASTM for critical parts.
3. Poor Engineering Design and Lack of Customization
A “one-size-fits-all” approach to furnace design can lead to inefficiencies. Each operation has unique feedstock, production volume, and energy constraints. Sourcing a furnace without custom engineering for your specific needs may result in poor melting performance, excessive energy consumption, or inability to meet environmental regulations. Engage suppliers who offer tailored solutions backed by proven simulation and process modeling.
4. Incomplete or Inadequate After-Sales Support
Even high-quality furnaces require maintenance, spare parts, and technical support. Sourcing from a supplier with limited local service capabilities or unclear support terms can lead to extended downtime during failures. Ensure service agreements, spare parts availability, and training programs are clearly defined and contractually binding before purchase.
Intellectual Property-Related Pitfalls
1. Unlicensed or Infringing Technology
Some suppliers, particularly in emerging markets, may incorporate patented technologies (e.g., advanced electrode regulation systems, foaming slag control, or energy recovery systems) without proper licensing. Purchasing such equipment exposes the buyer to legal risks, including infringement claims from original IP holders. This can result in costly litigation, equipment seizure, or forced shutdowns. Conduct IP due diligence and require suppliers to provide warranties confirming freedom to operate.
2. Lack of Clear IP Ownership in Custom Designs
When investing in a custom-engineered furnace, ambiguous contracts may leave ownership of design improvements or process innovations unclear. If the supplier retains rights to modifications developed during the project, your competitive advantage could be compromised. Ensure contracts explicitly assign IP rights for custom designs and process optimizations to the buyer.
3. Insufficient Protection of Operational Data and Trade Secrets
Modern arc furnaces are increasingly integrated with digital control systems that collect sensitive operational data. If software or automation systems are provided by third parties, ensure data ownership, access rights, and cybersecurity measures are contractually defined. Failure to do so risks exposure of proprietary production metrics or process know-how.
4. Dependence on Proprietary Closed-Source Systems
Some suppliers use proprietary control systems that lock buyers into exclusive service and upgrade paths. This limits flexibility, increases long-term costs, and creates dependency. Where possible, opt for open-architecture systems or negotiate rights to access source code and interface protocols to maintain control over your operations.
Conclusion
Sourcing an arc furnace requires more than evaluating upfront cost and capacity. Overlooking quality assurance mechanisms and intellectual property risks can lead to operational failures, legal exposure, and loss of competitive edge. A thorough evaluation of supplier credibility, component quality, engineering expertise, and IP compliance is essential to ensure a reliable, legally sound, and future-proof investment.
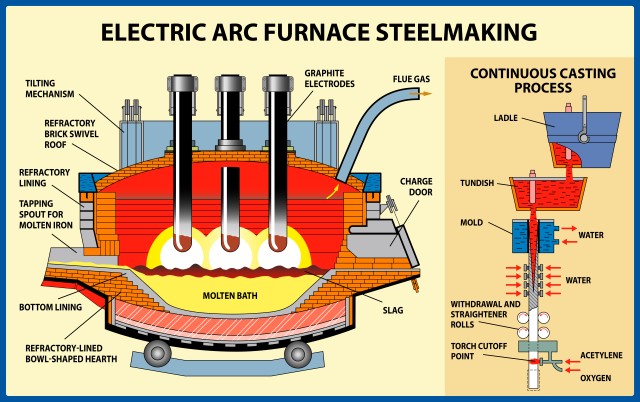
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Arc Furnace Operations
Introduction
Electric Arc Furnaces (EAFs) are critical in steel production, particularly in recycling scrap metal. Managing logistics and compliance for EAF operations involves coordination across material sourcing, transportation, environmental regulations, and safety standards. This guide outlines key considerations to ensure efficient, lawful, and sustainable arc furnace operations.
Material Sourcing & Scrap Procurement
- Establish reliable supply chains for ferrous scrap, direct reduced iron (DRI), and other metallic inputs.
- Verify scrap quality through standardized grading (e.g., ISRI specifications) to prevent contamination and ensure consistent melt chemistry.
- Maintain documentation for scrap origin and composition to support traceability and regulatory compliance.
- Partner with certified scrap suppliers adhering to environmental and ethical sourcing practices.
Transportation & Handling
- Optimize inbound logistics using rail, barge, or heavy-duty trucking based on proximity and volume.
- Implement covered storage and dust suppression systems for scrap yards to minimize particulate emissions.
- Ensure material handling equipment (cranes, shredders, conveyor systems) meets OSHA and ISO safety standards.
- Schedule deliveries to avoid bottlenecks and maintain continuous furnace operation.
Environmental Compliance
- Obtain and maintain permits under the Clean Air Act (e.g., Title V operating permit) for air emissions including particulates, NOx, and dioxins.
- Install and maintain effective off-gas treatment systems (e.g., baghouses, scrubbers) with continuous emissions monitoring (CEMS).
- Comply with EPA regulations for hazardous waste (e.g., baghouse dust classified as hazardous under RCRA).
- Manage wastewater from cooling systems per NPDES permit requirements; implement closed-loop systems where feasible.
- Conduct regular environmental audits and maintain records for regulatory inspections.
Occupational Health & Safety
- Follow OSHA guidelines for confined space entry, lockout/tagout (LOTO), and personal protective equipment (PPE).
- Implement hazard communication programs for handling molten metal, refractories, and electrical systems.
- Train personnel on emergency response procedures for arc flash, fire, and gas leaks (e.g., oxygen, natural gas).
- Conduct routine equipment inspections and maintenance on transformers, electrodes, and furnace covers.
Energy Efficiency & Carbon Reporting
- Monitor energy consumption (kWh/ton of steel) and optimize power usage through smart grid integration and demand response.
- Track and report greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions under EPA’s Mandatory Reporting Rule (40 CFR Part 98) or EU ETS, as applicable.
- Explore decarbonization options such as hydrogen-assisted melting or renewable energy sourcing.
- Pursue certifications like ISO 50001 (Energy Management) to demonstrate commitment to efficiency.
Regulatory Documentation & Recordkeeping
- Maintain logs for emissions, maintenance, operator training, and incident reports.
- Keep material safety data sheets (MSDS/SDS) for all chemicals and refractory materials.
- Archive calibration records for monitoring equipment (e.g., gas analyzers, flow meters).
- Prepare for compliance audits by federal, state, or third-party agencies (e.g., TSCA, REACH for imported materials).
International Trade & Customs Considerations
- Classify EAF equipment and consumables under correct HS codes for import/export (e.g., 8454 for furnaces).
- Comply with customs regulations and trade restrictions on scrap metal exports (e.g., BIS licensing if applicable).
- Ensure adherence to international standards (e.g., CE marking, IEC standards) for equipment safety and performance.
- Monitor changes in tariffs, sanctions, or environmental regulations affecting cross-border operations.
Conclusion
Effective logistics and compliance management in arc furnace operations enhances operational reliability, regulatory adherence, and environmental stewardship. Regular review of legal requirements, investment in modern control systems, and staff training are essential for sustainable steelmaking. Partnering with regulatory experts and industry associations can further support continuous improvement.
Conclusion for Sourcing an Arc Furnace:
Sourcing an electric arc furnace (EAF) is a strategic decision that requires careful evaluation of technical specifications, production requirements, supplier reliability, and long-term operational costs. Given the EAF’s critical role in modern steelmaking and metal recycling, selecting the right furnace directly impacts efficiency, product quality, and sustainability goals. Key considerations include furnace capacity, power requirements, automation capabilities, energy efficiency, and compliance with environmental regulations.
Partnering with reputable suppliers who offer robust after-sales support, technical expertise, and proven track records ensures smooth integration and long-term performance. Additionally, evaluating lifecycle costs—beyond the initial purchase price—such as maintenance, consumables, downtime, and energy consumption, contributes to a more informed and cost-effective decision.
In conclusion, a well-planned sourcing strategy for an arc furnace, aligned with current operational needs and future scalability, positions the organization for improved productivity, competitive advantage, and sustainable growth in the evolving metallurgical industry.