Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for Apple Sorting Machine
The difference between a profitable apple operation and a struggling one often comes down to post-harvest efficiency. With labor costs rising 15-20% annually across the USA and Europe, and retailers demanding increasingly stringent quality standards, manual sorting is no longer viable at scale.
The core challenge: How do you process thousands of tons of apples per season while meeting exact specifications for size, color, internal quality, and defect detection—without crushing margins or compromising fruit integrity?
Modern apple sorting machines address this directly. They combine optical grading, weight measurement, and internal quality assessment to classify fruit at speeds impossible through manual labor. But the market is complex:
| Decision Factor | Why It Matters |
|—————–|—————-|
| Throughput capacity | Must match harvest volumes and peak season demands |
| Grading technology | External vs. internal quality detection capabilities |
| Integration requirements | Compatibility with existing packing and palletizing systems |
| ROI timeline | Capital investment vs. labor savings and reduced waste |
This guide cuts through the noise. We’ll cover:
- Technology types: Roller-based systems, water flumes, and hybrid configurations
- Key specifications: What throughput, accuracy, and gentleness metrics actually mean
- Supplier evaluation: How to assess manufacturers with 50+ years of experience against newer entrants
- Total cost of ownership: Beyond purchase price to maintenance, training, and scalability
Whether you’re upgrading an existing line or building a new packing facility, this guide provides the framework for making an informed capital equipment decision.
Article Navigation
- Top 10 Apple Sorting Machine Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for apple sorting machine
- Understanding apple sorting machine Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of apple sorting machine
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘apple sorting machine’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for apple sorting machine
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for apple sorting machine
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘apple sorting machine’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for apple sorting machine Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing apple sorting machine With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for apple sorting machine
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the apple sorting machine Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of apple sorting machine
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for apple sorting machine
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
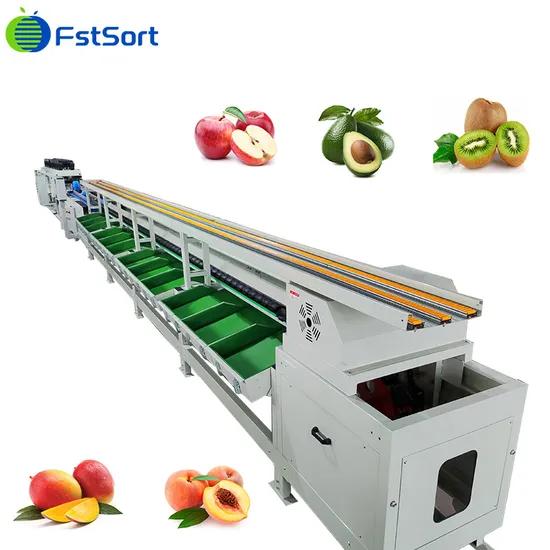
Top 10 Apple Sorting Machine Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Apple Sorting and Grading machines – TOMRA
Domain: tomra.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: TOMRA works with the world’s leading apple packhouses. We deliver unrivaled performance in terms of speed, handling, blemish detection and sorting accuracy….
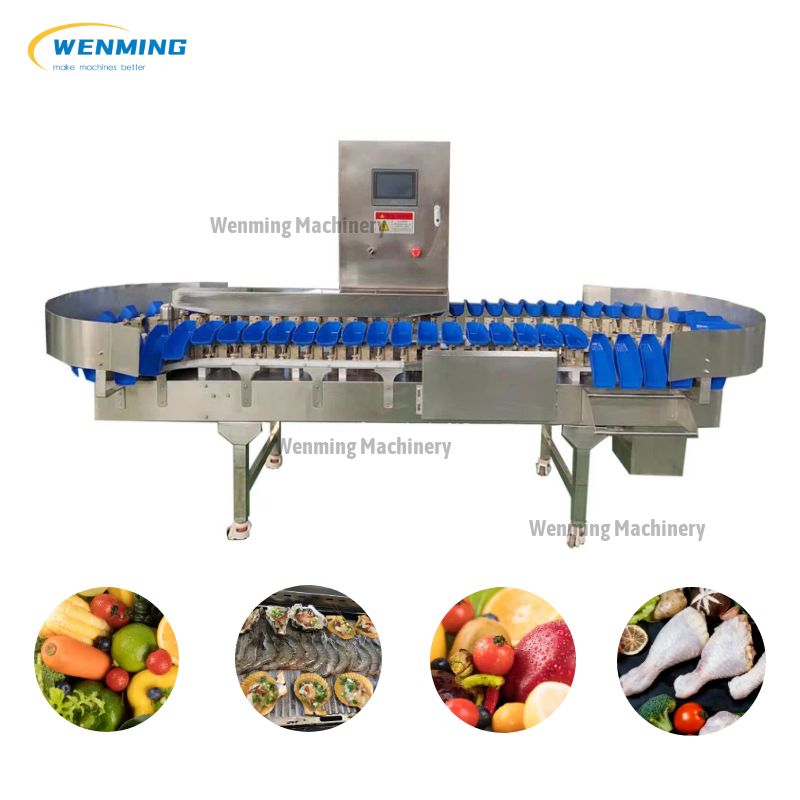

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
2. Apple Sorting, Grading and Packing Machines and Systems
Domain: unisorting.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: Unisorting produces Sorting and Grading Machines, processing equipment and Packing Systems for Apples with quality selection and traceability guaranteed….
3. Top Apple Sorting Machine Manufacturers in India | VMT Apple
Domain: vmtapple.com
Registered: 2023 (2 years)
Introduction: Apple Sorting Machine Manufacturers, VMT Apple provides high-quality grading solutions. Choose us for superior performance in apple grading!…
4. Manufacturer of flail mowers, circular mowers and sorting machines …
Domain: perfectvanwamel.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: PERFECT flail mowers, rotary mowers and grading machines for fruit and vegetables have been manufactured by PERFECT – van Wamel bv for over 70 years already….
5. GP Graders – Superior Sorting Technology – Fruit Grading Solutions
Domain: gpgraders.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: GP Graders have a well-earned reputation for being specialists in grading and sorting technology for cherries, blueberries, small tomatoes and stone fruits….

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
6. Manufacturer & Service provider
Domain: applecolorsorter.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: Apple color sorter is the leading manufacture,supplier, and service provider of Sorting Machine….
7. Key Technology: Food Processing Equipment & Sorting Machine …
Domain: key.net
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Key Technology is a sorting machine manufacturer committed to being the ultimate partner of choice in optical sorting and food handling solutions….
8. Fruit sorters – Green Sort
Domain: greensort.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: An innovative solution that can accurately and efficiently sort fruits, based on multiple parameters including size, color, and quality….
Understanding apple sorting machine Types and Variations
Understanding Apple Sorting Machine Types and Variations
Selecting the right apple sorting machine requires understanding the distinct technologies available and their operational applications. This section examines the primary machine types used in commercial apple processing facilities across North America and Europe.
Apple Sorting Machine Types: Comparative Overview
| Type | Key Features | Best Applications | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Optical/Vision Sorting Machines | High-speed cameras, AI-powered defect detection, color grading | Large-scale packhouses, export-grade sorting | High accuracy, consistent grading, handles high throughput | Higher capital investment, requires technical expertise |
| Weight-Based Sorting Machines | Precision load cells, individual fruit weighing, automated calibration | Size-grading operations, retail packaging lines | Accurate weight classification, lower maintenance | Limited quality assessment capabilities |
| Roller/Belt Sorting Machines (Pre-sizers) | Mechanical singulation, wet/dry handling, V-belt systems | Pre-sizing operations, initial sorting stages | Robust design, handles wet product, quiet operation | Less precise than optical systems |
| Internal Quality Sorting Machines | NIR spectroscopy, Brix measurement, internal defect detection | Premium markets, quality-focused operations | Detects hidden defects, measures sugar content | Premium pricing, slower processing speeds |
| Integrated Turnkey Systems | Combined infeed, grading, packing, palletizing | Full-line processing facilities | End-to-end solution, optimized workflow | Significant capital requirement, complex installation |
Detailed Type Analysis
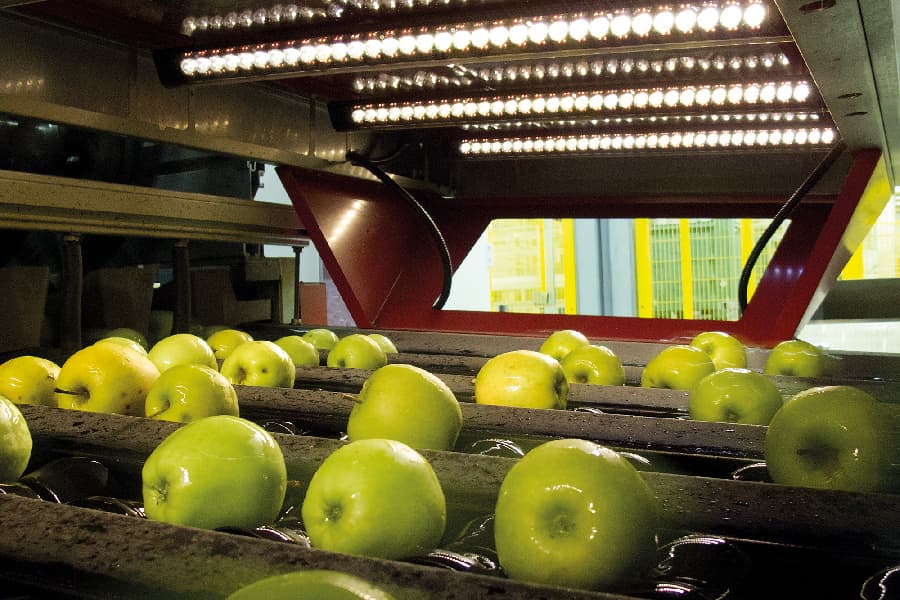
1. Optical/Vision Sorting Machines
Optical sorting machines represent the industry standard for high-volume commercial operations. These systems utilize multiple high-resolution cameras positioned around each fruit to capture 360-degree imagery, analyzing external characteristics including:
- Color uniformity and ripeness indicators
- Surface defects (bruising, scarring, disease marks)
- Shape irregularities
- Size classification
Modern optical systems incorporate AI and machine learning algorithms that improve accuracy over time. Facilities processing for major retail chains typically require this technology to meet stringent quality specifications.
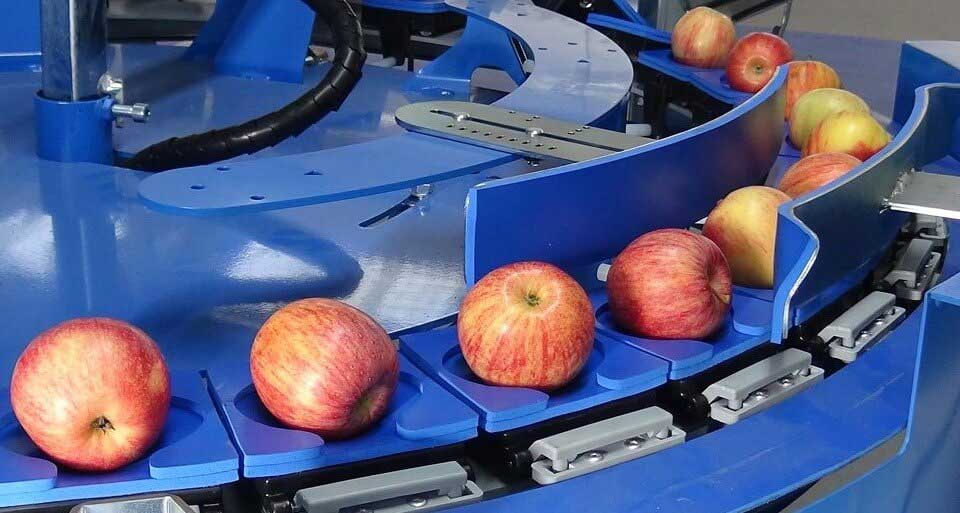

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Ideal for: Packhouses processing 10+ tons/hour requiring consistent external quality grading.
2. Weight-Based Sorting Machines
Weight sorting technology provides precise mass measurement for individual apples using calibrated load cells. These machines excel at:
- Sorting into weight categories for retail packaging
- Ensuring pack weight compliance
- Creating uniform product presentations
Weight-based systems often integrate with optical sorters, providing dual-parameter grading in a single pass. Accuracy typically reaches ±1 gram, meeting requirements for pre-packaged retail products.
Ideal for: Operations prioritizing pack-weight accuracy and retail-ready sizing.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
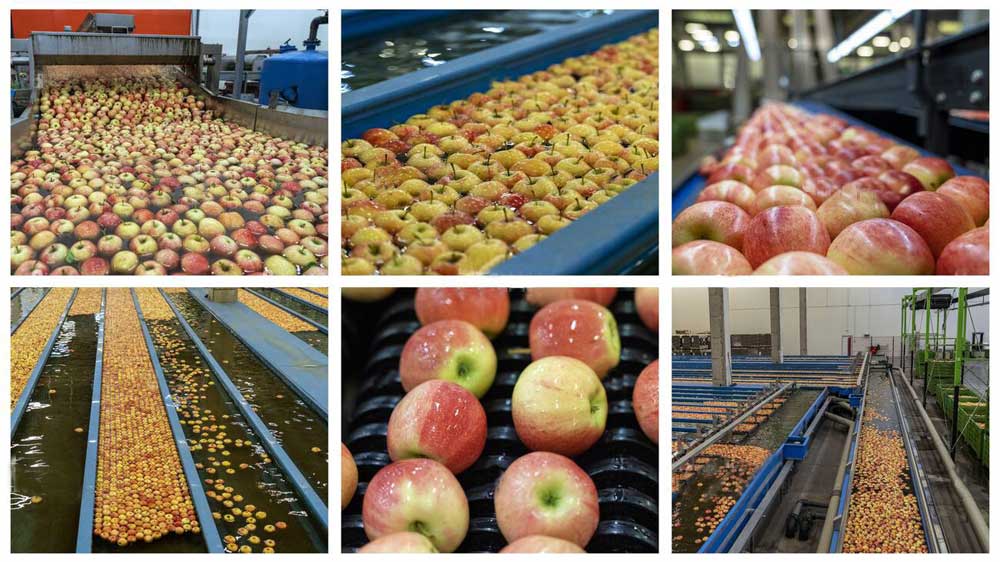
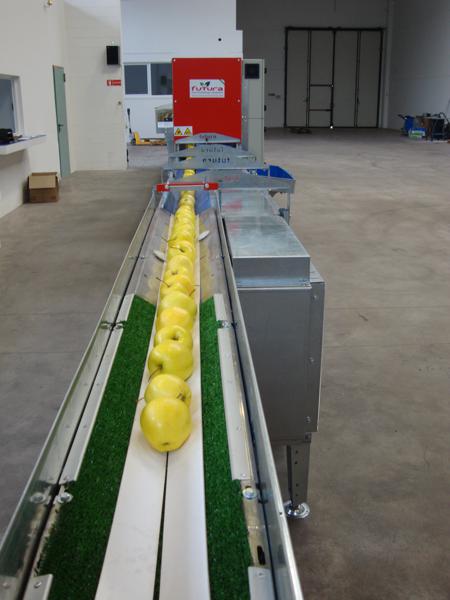
3. Roller/Belt Sorting Machines (Pre-sizers)
Pre-sizing machines like the Calistar system handle initial sorting stages, particularly effective when processing wet apples directly from washing systems. Key characteristics include:
- Gripper designs that function reliably with moisture present
- Gentle fruit handling to minimize bruising
- Quiet operation reducing workplace noise levels
- Robust construction for continuous operation
These machines ensure proper singulation before apples proceed to more sophisticated grading equipment.
Ideal for: Facilities requiring wet-product handling and initial size separation before final grading.
4. Internal Quality Sorting Machines
Internal quality assessment addresses the growing market demand for guaranteed eating quality. Using Near-Infrared (NIR) spectroscopy, these systems measure:

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
- Brix levels (sugar content)
- Internal browning and core rot
- Firmness indicators
- Dry matter content
This technology enables sorting for premium market segments where taste consistency commands price premiums. European retailers increasingly require internal quality documentation for supplier qualification.
Ideal for: Premium apple varieties, export markets, and operations serving quality-focused retail partners.
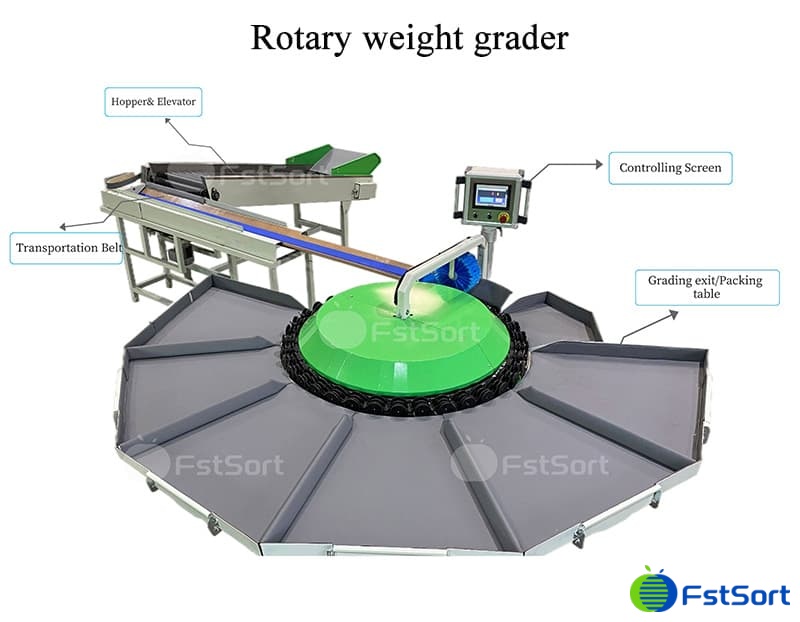
5. Integrated Turnkey Systems
Comprehensive sorting solutions combine multiple technologies into unified processing lines. These systems typically include:
- Infeed systems: Continuous submergers, bin dumpers, flume systems
- Grading stations: Combined optical and weight measurement
- Packing systems: Automated tray filling, bagging, carton packing
- Palletizing: Robotic stacking and stretch wrapping
- Software integration: Real-time data tracking, traceability, and reporting
Manufacturers like Aweta offer complete solutions with 55+ years of apple-specific expertise, providing single-source accountability for entire processing lines.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Ideal for: New facility construction, major capacity expansions, or complete line replacements.
Selection Considerations
When evaluating apple sorting machine types, assess:
- Throughput requirements — Match machine capacity to peak season volumes
- Market specifications — Align grading capabilities with buyer requirements
- Product handling — Ensure gentle handling appropriate for your varieties
- Integration needs — Consider compatibility with existing equipment
- Total cost of ownership — Factor maintenance, training, and operational costs
Key Industrial Applications of apple sorting machine
Key Industrial Applications of Apple Sorting Machine
Modern apple sorting machines serve diverse sectors within the produce supply chain, each with specific operational requirements and quality standards. Below is a comprehensive breakdown of primary industrial applications and their associated benefits.
Industry Applications Overview
| Industry Sector | Primary Application | Key Equipment Features Used |
|---|---|---|
| Commercial Apple Farms | Post-harvest processing, initial grading | Bin dumpers, continuous submergers, pre-sizing systems |
| Fruit Packing Houses | Quality grading, market-specific sorting | Rollerstar commit-to-pack lines, optical sensors, weight measurement |
| Fresh Produce Distributors | Inventory management, order fulfillment | Software integration, flexible design layouts, palletizing systems |
| Retail Supply Chain Operations | Specification compliance, traceability | External/internal grading technology, data management software |
| Export Processing Facilities | International standard compliance | Internal quality sensors, defect detection, precise calibration |
| Food Service Processors | Bulk sorting for commercial kitchens | High-throughput systems, size uniformity grading |
Detailed Benefits by Application
Commercial Apple Farms & Orchards
- Gentle fruit handling from bin or field box to sorting line minimizes bruising and product loss
- Continuous bin submergers and portico infeed systems maintain homogenous apple flow
- Reduced labor dependency during peak harvest periods
- Decreased maintenance costs through automated chain lubrication and tensioning
Fruit Packing Houses
- Commit-to-pack efficiency via Rollerstar systems with spreading V-belts for perfect singulation
- Accurate weight measurement ensures pack consistency and reduces giveaway
- Optimal camera presentation enables precise external quality assessment
- Flexible design layouts accommodate facility-specific configurations
Quality-Focused Processing Operations
- Internal quality detection identifies texture, taste indicators, and hidden defects not visible externally
- External grading technology assesses color, size, shape, and surface blemishes
- Pre-sizing capabilities (Calistar systems) handle wet products directly from water flumes
- Quiet operation improves working conditions in processing environments
Export & Compliance-Driven Facilities
- Multi-parameter sorting meets varying international market specifications
- Traceability software supports food safety documentation requirements
- Consistent grading accuracy reduces rejection rates at destination markets
Operational Efficiency Gains
| Benefit Category | Impact |
|---|---|
| Throughput | High-speed singulation and continuous processing |
| Product Quality | Extremely gentle handling preserves fruit integrity |
| Labor Optimization | Automated systems reduce manual sorting requirements |
| Flexibility | Tailor-made solutions adapt to specific use-cases |
| Maintenance | Self-lubricating, auto-tensioning mechanisms reduce downtime |
These industrial applications leverage over 55 years of proven sorting and packing technology, delivering measurable ROI through increased production capacity, reduced waste, and improved pack-out rates.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘apple sorting machine’ & Their Solutions
3 Common User Pain Points for Apple Sorting Machines & Their Solutions
Pain Point 1: Product Damage During Sorting Operations
Scenario: A mid-sized apple packing facility in Washington State processes 500+ bins daily. Despite investing in sorting equipment, they’re experiencing a 4-6% bruising rate, resulting in downgraded product and significant revenue loss.
Problem: Traditional sorting systems with aggressive handling mechanisms cause micro-bruising and surface damage that only becomes visible after storage. High-speed operations often prioritize throughput over gentle handling, leading to:
– Increased claims from retail buyers
– Higher volumes diverted to processing grades
– Reduced shelf life affecting customer satisfaction
Solution: Modern sorting systems now feature specifically engineered gentle handling technology. Look for equipment with:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Spreading V-belts | Smooth, controlled transfer onto carriers |
| Mid-positioned rotating axis | Even distribution to brushes without impact |
| Submerged infeed systems | Water-cushioned transitions from bin to line |
| Optimized singulation | Eliminates fruit-to-fruit contact damage |
Pain Point 2: Inconsistent Internal Quality Detection
Scenario: A European apple exporter faces recurring complaints from premium retail customers about internal browning and texture inconsistencies—defects invisible during visual inspection at packing.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Problem: External grading alone cannot identify:
– Internal browning or watercore
– Texture degradation affecting eating quality
– Early-stage decay not visible on the surface
This results in rejected shipments, damaged buyer relationships, and costly returns from export markets with strict quality standards.
Solution: Implement integrated internal and external grading technology. Advanced optical sorting systems now combine:
- External sensors: Color, size, shape, and surface defect detection
- Internal quality measurement: NIR (Near-Infrared) spectroscopy for Brix levels, firmness, and internal defect identification
- Commit-to-pack configurations: Grade once with comprehensive data capture
This dual-assessment approach ensures only apples meeting both visual and eating-quality standards reach premium market channels.
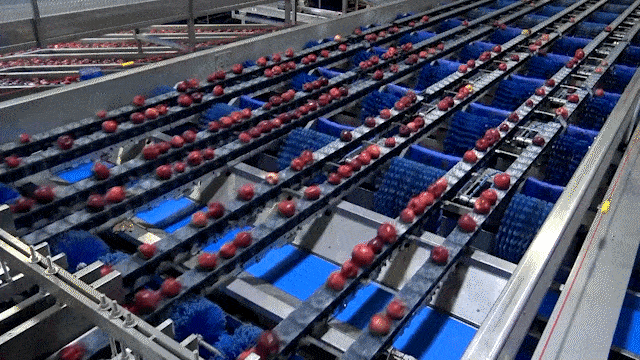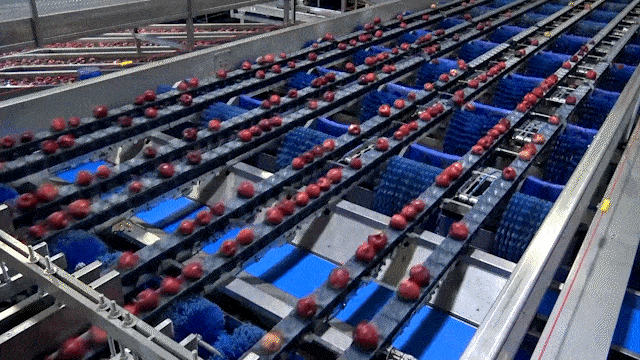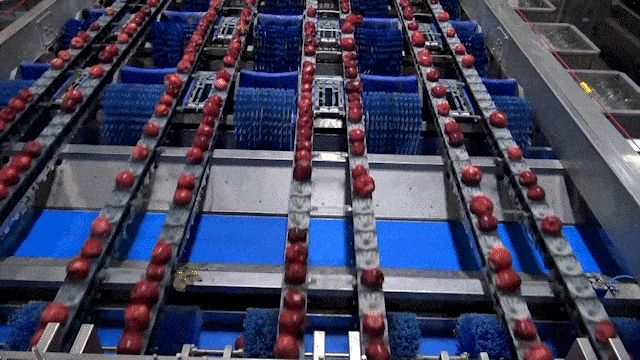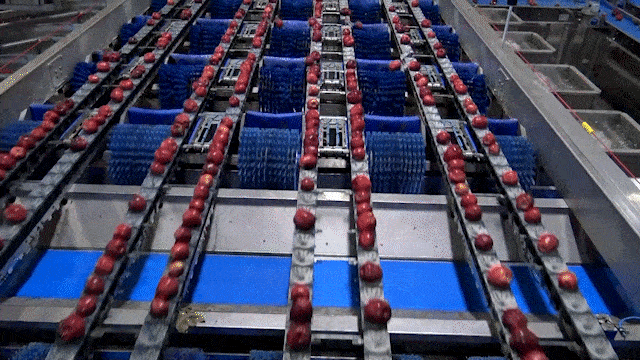
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Pain Point 3: High Maintenance Costs and Operational Downtime
Scenario: A large-scale apple processor in Poland runs their sorting line 16 hours daily during peak season. Frequent mechanical failures and manual maintenance interventions are causing 8-12 hours of unplanned downtime weekly.
Problem: Aging or poorly designed sorting equipment requires:
– Manual chain tensioning and lubrication
– Frequent component replacements mid-season
– Specialized technician callouts during critical harvest periods
Each hour of downtime during peak season directly impacts processing capacity and labor costs.
Solution: Prioritize sorting machines engineered for operational reliability:

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
| Maintenance Feature | Operational Impact |
|---|---|
| Automatic chain lubrication | Reduces manual intervention, extends component life |
| Automatic chain tensioning | Maintains consistent performance without adjustments |
| Robust wet/dry design | Handles variable conditions without system compromise |
| Modular construction | Enables rapid component swaps, minimizing line stoppages |
When evaluating equipment, request documented MTBF (Mean Time Between Failures) data and ensure local technical support availability within your region.
Key Takeaway: Selecting an apple sorting machine requires evaluating beyond throughput specifications. Prioritize gentle handling mechanisms, comprehensive quality detection capabilities, and maintenance-optimized designs to protect both your product and your operational efficiency.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for apple sorting machine
Strategic Material Selection Guide for Apple Sorting Machines
Selecting the appropriate materials for apple sorting machine components directly impacts operational longevity, maintenance costs, and fruit quality preservation. This guide examines critical material considerations for procurement decisions.
Frame and Structural Components
Stainless Steel (304/316 Grade)
The industry standard for primary structural elements. Grade 316 offers superior corrosion resistance essential for wet processing environments—particularly relevant for pre-sizing operations where fruit arrives directly from water flumes. Expect 15-25 year service life with proper maintenance.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Powder-Coated Carbon Steel
A cost-effective alternative for non-contact structural supports. Suitable for dry processing areas but requires more frequent inspection in humid environments.
Aluminum Alloys (6061-T6)
Increasingly specified for modular components and adjustable assemblies. Offers excellent weight-to-strength ratio, facilitating easier reconfiguration of sorting lines.
Fruit Contact Surfaces
Material selection here directly affects bruising rates and product quality—critical for premium apple varieties.
Food-Grade Polymers
– UHMW-PE (Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene): Preferred for guide rails and transition surfaces. Low friction coefficient minimizes surface damage.
– FDA-Compliant Silicone: Used in gripper mechanisms and cushioning elements. Provides gentle handling essential for commit-to-pack operations.
– Delrin/Acetal: Specified for precision components requiring dimensional stability.
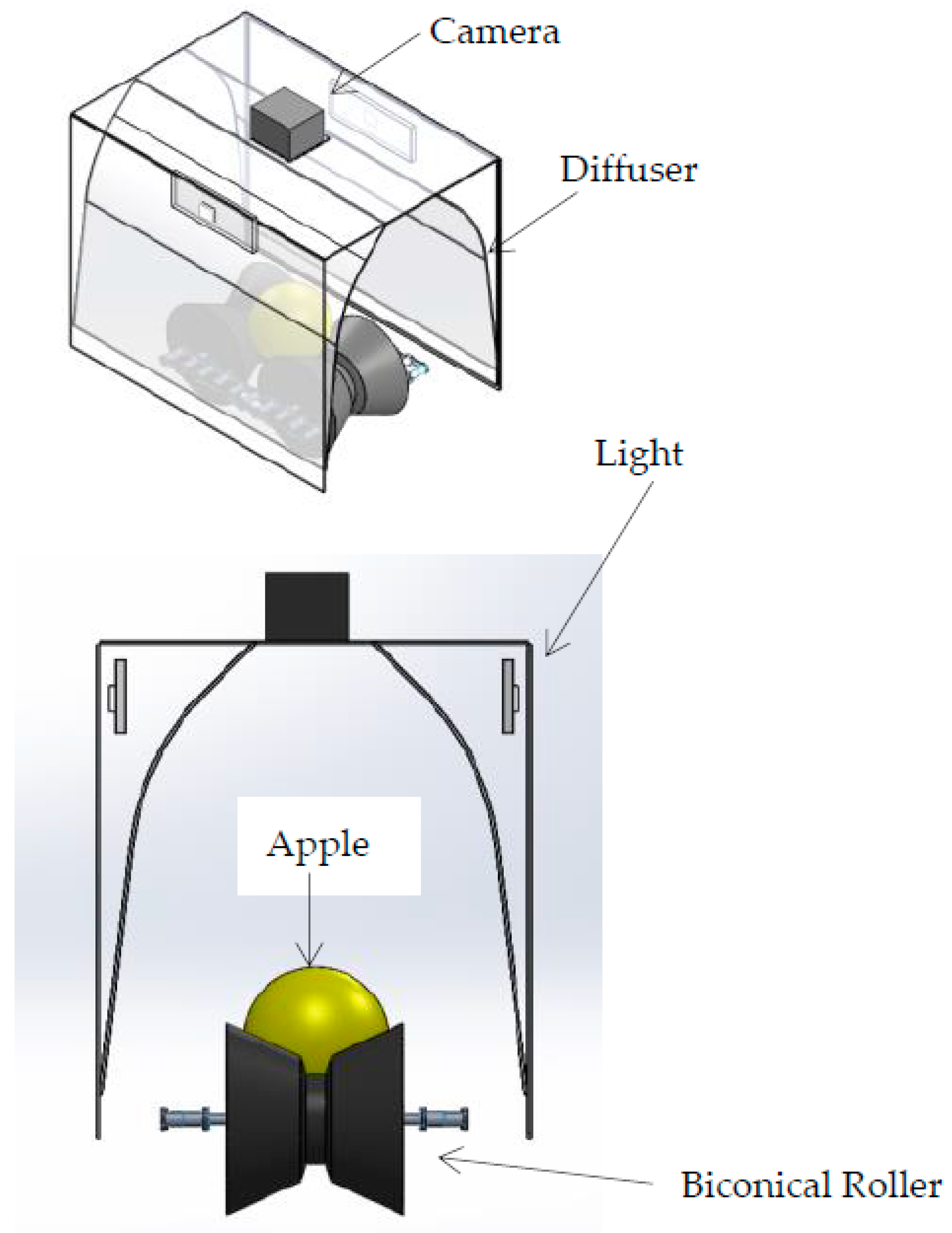
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Rubber Compounds
– EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer): Standard for conveyor belting and rollers. Excellent resistance to water and cleaning chemicals.
– Nitrile Rubber: Selected for oil-resistant applications in drive systems.
Conveyor and Transport Systems
V-Belt Materials
Spreading V-belts—as utilized in advanced roller-star systems—require materials balancing grip and gentle product transfer. Look for:
– Reinforced polyurethane construction
– Anti-static properties
– FDA food contact compliance
Roller Surfaces
Brush rollers for apple presentation typically feature:
– Nylon or polypropylene bristles (soft to medium density)
– Stainless steel or aluminum cores
– Quick-release mounting for sanitation access
Sensor and Grading Components
Optical System Housings
– Anodized aluminum preferred for camera enclosures
– Tempered glass or optical-grade polycarbonate for viewing windows
– IP65 or higher ingress protection ratings essential
Weighing Platforms
– Load cell housings: 316 stainless steel
– Platform surfaces: Brushed stainless or food-grade polymer
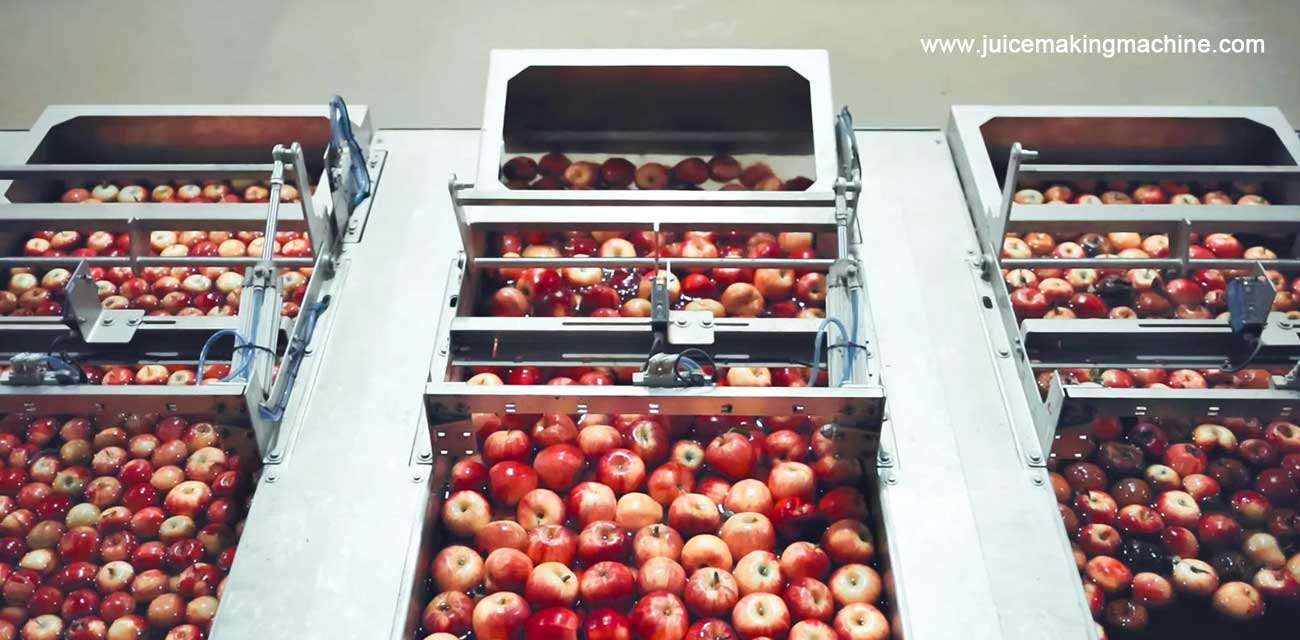
Water Management Components (Wet Processing Lines)
For operations utilizing water flumes and continuous submergers:
- Flume Construction: 304 stainless steel minimum; 316 recommended
- Pump Components: Bronze or stainless steel impellers
- Drainage Grates: Perforated stainless steel or reinforced polymer
- Seals and Gaskets: Silicone or EPDM rated for continuous water exposure
Chain and Drive Systems
Conveyor Chains
– Stainless steel side-flex chains for curved sections
– Acetal plastic chains acceptable for light-duty, dry applications
– Automatic lubrication compatibility increasingly standard
Sprockets and Gears
– Hardened stainless steel for primary drives
– Engineering plastics (PEEK, reinforced nylon) for secondary applications

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Material Comparison Table
| Component Category | Material Options | Corrosion Resistance | Durability Rating | Cost Level | Best Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Frame | 316 Stainless Steel | Excellent | High | $$$ | Wet processing, high-humidity |
| 304 Stainless Steel | Very Good | High | $$ | Standard processing environments | |
| Powder-Coated Carbon Steel | Moderate | Medium | $ | Dry areas, budget constraints | |
| Fruit Contact Surfaces | Food-Grade Silicone | Excellent | Medium | $$ | Grippers, cushioning elements |
| UHMW-PE | Good | High | $ | Guide rails, wear surfaces | |
| EPDM Rubber | Very Good | Medium-High | $ | Rollers, belting | |
| Conveyor Belts | Reinforced Polyurethane | Very Good | High | $$ | V-belt systems, precision transfer |
| PVC/Fabric Composite | Good | Medium | $ | General transport | |
| Optical Housings | Anodized Aluminum | Very Good | High | $$ | Camera enclosures |
| 316 Stainless Steel | Excellent | Very High | $$$ | Harsh/wet environments | |
| Chains | Stainless Steel | Excellent | Very High | $$$ | Primary drives, wet areas |
| Acetal Plastic | Good | Medium | $ | Light-duty, dry applications | |
| Water System Components | 316 Stainless Steel | Excellent | Very High | $$$ | Flumes, submergers |
| Reinforced Fiberglass | Very Good | High | $$ | Large tanks, non-structural |
Key Procurement Considerations
-
Processing Environment: Wet pre-sizing operations demand higher-grade stainless steel throughout; dry commit-to-pack lines offer more material flexibility.
-
Sanitation Requirements: Prioritize materials compatible with your cleaning protocols. Alkaline and chlorinated sanitizers require specific material grades.
-
Total Cost of Ownership: Higher-grade materials typically reduce replacement frequency and maintenance labor—calculate 5-10 year cost projections, not initial purchase price alone.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Verify FDA, EU 1935/2004, and relevant food contact certifications for all fruit-contact materials.
-
Spare Parts Availability: Standardized materials simplify inventory management and reduce downtime during repairs.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for apple sorting machine
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for Apple Sorting Machines
Understanding how apple sorting machines are manufactured provides critical insight into equipment reliability, longevity, and performance. This section examines the production stages and quality standards that distinguish industrial-grade sorting systems from inferior alternatives.
Manufacturing Process Overview
The production of commercial apple sorting machines follows a rigorous multi-stage process designed to ensure precision engineering and operational durability.
Stage 1: Material Preparation
| Component Category | Primary Materials | Preparation Process |
|---|---|---|
| Frame structures | Stainless steel (304/316), aluminum alloys | CNC cutting, laser profiling, surface treatment |
| Conveyor systems | Food-grade polymers, reinforced rubber | Extrusion, vulcanization, precision molding |
| Optical housings | Anodized aluminum, tempered glass | Precision machining, optical-grade finishing |
| Electronic enclosures | Powder-coated steel, IP-rated plastics | Sheet forming, injection molding |
Material selection prioritizes:
– Corrosion resistance for wet processing environments
– Food-contact compliance (FDA/EU regulations)
– Structural integrity under continuous operation

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Stage 2: Component Forming and Fabrication
Critical forming processes include:
Mechanical Components
– Precision CNC machining for roller assemblies and gripper mechanisms
– Laser cutting and robotic welding for frame construction
– Custom extrusion for conveyor tracks and guide rails
Specialized Systems
– Optical sensor housing fabrication with vibration-dampening mounts
– V-belt spreading mechanisms (patent-protected designs)
– Mid-positioned rotating axis carriers for optimal fruit presentation
Leading manufacturers like Aweta employ proprietary designs—such as their Rollerstar spreading V-belt system and Calistar gripper technology—that require specialized tooling and fabrication expertise developed over decades.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Stage 3: Assembly and Integration
Assembly follows a systematic build sequence:
- Base frame construction — Structural welding and alignment verification
- Drive system installation — Motors, gearboxes, automatic chain tensioning systems
- Conveyor integration — Singulation systems, transfer mechanisms, flume connections
- Sensor mounting — Camera systems, weight sensors, internal quality detection units
- Electrical integration — Control panels, wiring harnesses, safety interlocks
- Software loading — Grading algorithms, HMI configuration, calibration protocols
Critical Assembly Considerations:
– Automatic chain lubrication systems require precise alignment
– Optical sensors demand contamination-free installation environments
– Wet-processing configurations (bin submergers, flumes) require enhanced sealing protocols
Stage 4: Quality Control and Testing
Comprehensive QC protocols verify performance across multiple parameters:
Dimensional Verification
– CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine) inspection of critical tolerances
– Conveyor tracking alignment within ±0.5mm specifications
– Gripper spacing calibration for consistent singulation
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Functional Testing
| Test Category | Parameters Evaluated | Acceptance Criteria |
|————–|———————|———————|
| Throughput capacity | Units/hour at rated speed | ≥95% of specification |
| Sorting accuracy | Weight, color, size grading | ≥99% accuracy |
| Gentle handling | Bruise incidence rate | <0.1% product damage |
| Noise levels | Decibel measurement | Per manufacturer specification |
| Wet operation | Seal integrity, drainage | Zero leakage under pressure |
Burn-in Procedures
– Extended operation cycles (48-72 hours minimum)
– Load testing at maximum capacity
– Environmental stress screening for electronic components
Quality Standards and Certifications
Reputable manufacturers maintain certifications that validate production quality and equipment safety:
ISO Certifications
– ISO 9001:2015 — Quality management systems
– ISO 14001:2015 — Environmental management
– ISO 45001:2018 — Occupational health and safety

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Industry-Specific Compliance
– CE Marking — European conformity for machinery directive
– UL/CSA Certification — North American electrical safety
– FDA 21 CFR — Food contact surface requirements
– USDA/EU Organic Processing — Compatible materials for organic operations
Hygienic Design Standards
– EHEDG (European Hygienic Engineering & Design Group) principles
– 3-A Sanitary Standards compliance where applicable
– IP65/IP67 ratings for washdown environments
Evaluating Manufacturer Quality Credentials
When assessing suppliers, verify:
- Production facility certifications — Request current ISO certificates
- Component traceability — Documentation of material origins and specifications
- Testing documentation — Factory acceptance test (FAT) reports
- Warranty terms — Coverage scope reflecting manufacturing confidence
- Field service history — Track record with similar installations
Manufacturers with extensive experience—such as those with 55+ years in the industry—typically demonstrate refined production processes, proprietary technology development, and proven quality systems that newer entrants cannot match.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘apple sorting machine’
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for Apple Sorting Machines
Procuring an apple sorting machine represents a significant capital investment. This systematic checklist ensures you evaluate all critical factors before committing to a supplier.
Phase 1: Pre-Sourcing Preparation
Define Operational Requirements
- [ ] Calculate current and projected throughput needs (apples per hour)
- [ ] Document apple varieties processed and their specific handling requirements
- [ ] Assess available floor space and facility layout constraints
- [ ] Determine integration requirements with existing packing lines
- [ ] Establish budget range (equipment, installation, training, maintenance)
Identify Quality Parameters
| Grading Criteria | Priority Level | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| External defects (bruising, color) | High/Medium/Low | |
| Internal quality (brix, firmness) | High/Medium/Low | |
| Size/weight accuracy | High/Medium/Low | |
| Shape uniformity | High/Medium/Low |
Phase 2: Supplier Identification
Research Potential Suppliers
- [ ] Identify manufacturers with 10+ years industry experience
- [ ] Verify suppliers offer turnkey solutions (infeed, grading, packing, palletizing)
- [ ] Confirm availability of optical and sensor-based grading technology
- [ ] Check for patented innovations (e.g., spreading V-belts, gentle handling systems)
- [ ] Review case studies from comparable operations
Initial Supplier Screening Criteria
| Factor | Minimum Requirement |
|---|---|
| Industry experience | 10+ years |
| Service coverage | USA/Europe presence |
| Technology type | Optical + internal quality sensors |
| References | 3+ verifiable installations |
Phase 3: Technical Evaluation
Assess Core System Components
- [ ] Infeed Systems: Evaluate bin dumpers, continuous submergers, flume options
- [ ] Singulation: Confirm gentle transfer mechanisms to prevent bruising
- [ ] Grading Technology: Compare external vs. internal quality detection capabilities
- [ ] Packing Integration: Review palletizing system versatility
- [ ] Software: Evaluate user interface, data analytics, and reporting features
Performance Specifications to Request
- [ ] Sorting accuracy percentage
- [ ] Maximum throughput capacity
- [ ] Defect detection sensitivity thresholds
- [ ] Product damage rates during handling
- [ ] Energy consumption metrics
Phase 4: Supplier Engagement
Request for Proposal (RFP) Essentials
- [ ] Detailed equipment specifications
- [ ] Installation timeline and requirements
- [ ] Training program scope and duration
- [ ] Warranty terms (parts and labor)
- [ ] Maintenance contract options
- [ ] Spare parts availability and lead times
- [ ] Total cost of ownership projection (5-year)
Site Visit Checklist
- [ ] Observe equipment operating at comparable facility
- [ ] Speak with current customers independently
- [ ] Verify noise levels (critical for worker environment)
- [ ] Assess ease of maintenance access
- [ ] Confirm gentle fruit handling claims
Phase 5: Final Selection
Comparative Analysis Matrix
| Criteria | Weight | Supplier A | Supplier B | Supplier C |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Technical capability | 25% | |||
| Price competitiveness | 20% | |||
| Service/support infrastructure | 20% | |||
| References/reputation | 15% | |||
| Delivery timeline | 10% | |||
| Training quality | 10% |
Phase 6: Contract & Implementation
Pre-Contract Verification
- [ ] Confirm payment terms and milestone schedule
- [ ] Document performance guarantees with penalty clauses
- [ ] Establish acceptance testing criteria
- [ ] Define installation supervision responsibilities
- [ ] Secure operator training commitments in writing
Post-Installation Requirements
- [ ] Complete acceptance testing against agreed specifications
- [ ] Obtain all operational documentation and manuals
- [ ] Confirm spare parts inventory recommendations
- [ ] Schedule preventive maintenance calendar
- [ ] Establish direct contact with technical support team
Key Questions for Supplier Conversations
- What differentiates your internal quality detection from competitors?
- How does your system handle wet product processing?
- What is your average response time for service calls in our region?
- Can you provide ROI projections based on similar installations?
- What software updates are included post-purchase?
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for apple sorting machine Sourcing
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for Apple Sorting Machine Sourcing
Investing in apple sorting machinery represents a significant capital expenditure for packing houses and processing facilities. This analysis provides a detailed breakdown of costs, pricing structures, and strategic approaches to optimize your procurement budget.
Total Cost of Ownership Overview
When evaluating apple sorting machine investments, consider the complete cost picture beyond the initial purchase price:
| Cost Category | Percentage of Total Investment | Typical Range (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Equipment Purchase | 50-60% | $150,000 – $2,500,000+ |
| Installation & Integration | 8-12% | $25,000 – $300,000 |
| Shipping & Logistics | 5-10% | $15,000 – $150,000 |
| Training & Commissioning | 3-5% | $10,000 – $75,000 |
| First-Year Maintenance | 2-4% | $8,000 – $50,000 |
Materials Cost Breakdown
Core System Components
Infeed Systems
– Bin dumpers (single unit): $15,000 – $45,000
– Continuous bin submergers: $35,000 – $120,000
– Portico infeed systems: $50,000 – $180,000
– Apple flumes and water handling: $20,000 – $80,000
Grading and Sorting Technology
| Component | Entry-Level | Mid-Range | Premium |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic size/weight graders | $80,000 – $150,000 | $150,000 – $350,000 | $350,000 – $600,000 |
| External quality cameras | $40,000 – $80,000 | $80,000 – $150,000 | $150,000 – $250,000 |
| Internal quality sensors (NIR) | $100,000 – $200,000 | $200,000 – $400,000 | $400,000 – $700,000 |
| Defect detection systems | $50,000 – $120,000 | $120,000 – $250,000 | $250,000 – $450,000 |
Specialized Sorting Platforms
Rollerstar Systems (Commit-to-Pack Lines)
– Features: Spreading V-belts, automatic chain lubrication, accurate weight measurement
– Price range: $200,000 – $500,000 depending on lane configuration
Calistar Pre-sizers
– Features: Wet product handling, quiet operation, gentle fruit handling
– Price range: $150,000 – $400,000
Packing and Palletizing
– Semi-automatic packing stations: $30,000 – $80,000
– Automated tray/carton fillers: $75,000 – $200,000
– Robotic palletizing systems: $150,000 – $450,000
Software and Controls
– Basic sorting software: $15,000 – $40,000
– Advanced analytics packages: $40,000 – $100,000
– Integration with existing ERP: $10,000 – $50,000
Labor Costs
Installation Labor
| Market | Installation Cost per Day | Typical Project Duration |
|---|---|---|
| USA | $800 – $1,500/technician | 2-8 weeks |
| Western Europe | €700 – €1,300/technician | 2-8 weeks |
| Eastern Europe | €400 – €800/technician | 2-8 weeks |
Installation cost factors:
– System complexity and throughput capacity
– Integration with existing infrastructure
– Electrical and plumbing modifications required
– Local labor rates and union requirements
Operational Labor Considerations
Post-installation staffing requirements affect long-term ROI:
| System Type | Operators Required | Annual Labor Cost Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Manual sorting | 8-15 workers | $280,000 – $600,000 |
| Semi-automated | 4-8 workers | $140,000 – $320,000 |
| Fully automated | 2-4 workers | $70,000 – $160,000 |
Logistics Costs
Shipping and Freight
From European Manufacturers (Netherlands, Italy, France)
| Destination | Sea Freight | Air Freight (Critical Parts) |
|---|---|---|
| US East Coast | $18,000 – $45,000 | $8,000 – $25,000 |
| US West Coast | $22,000 – $55,000 | $10,000 – $30,000 |
| Intra-Europe | €5,000 – €15,000 | €3,000 – €12,000 |
From Asian Manufacturers (China, South Korea)
| Destination | Sea Freight | Lead Time |
|---|---|---|
| USA | $12,000 – $35,000 | 6-10 weeks |
| Europe | $14,000 – $40,000 | 8-12 weeks |
Additional Logistics Expenses
- Customs duties (USA): 0-4.5% depending on classification
- Customs duties (EU): 0-3.7% for machinery
- Insurance (transit): 0.5-1.5% of equipment value
- Crating and packaging: $3,000 – $15,000
- Local transport to facility: $2,000 – $8,000
- Rigging and crane services: $5,000 – $25,000
Pricing by System Capacity
| Throughput Capacity | System Configuration | Price Range (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| 2-5 tons/hour | Basic grading, manual packing | $120,000 – $300,000 |
| 5-10 tons/hour | Automated grading, semi-auto packing | $300,000 – $700,000 |
| 10-20 tons/hour | Full optical sorting, automated packing | $700,000 – $1,500,000 |
| 20+ tons/hour | Complete turnkey solution | $1,500,000 – $3,000,000+ |
Cost-Saving Strategies
Procurement Optimization
- Bundle purchases with packaging equipment
- Negotiate 8-15% discounts when purchasing complete lines from single suppliers like Aweta
-
Reduces integration complexity and warranty complications
-
Time your purchase strategically
- Order during off-season (January-March) for better pricing
- Fiscal year-end (Q4) often yields manufacturer incentives
-
Plan 6-12 months ahead to avoid rush premiums
-
Consider refurbished equipment
- Certified refurbished systems: 40-60% of new equipment cost
- Verify warranty terms and parts availability
-
Best for facilities testing automation before major investment
-
Lease vs. purchase analysis
- Operating leases: Preserve capital, predictable monthly costs
- Finance leases: Build equity, potential tax advantages
- Break-even typically occurs at 5-7 years for purchased equipment
Technical Specifications
- Right-size your system
- Avoid over-specifying throughput capacity
- Calculate actual peak season requirements plus 20% buffer
-
Modular systems allow future expansion at lower initial cost
-
Prioritize essential sensors
- Start with external quality cameras
- Add internal quality (NIR) sensors as ROI justifies
-
Phase implementation over 2-3 years
-
Standardize components
- Specify common parts across multiple machines
- Reduces spare parts inventory costs by 25-40%
- Simplifies technician training
Logistics Optimization
- Consolidate shipments
- Combine orders with neighboring facilities
- Use manufacturer’s preferred freight forwarders for volume rates
-
Schedule delivery during low-demand shipping periods
-
Regional sourcing considerations
- European buyers: Consider Dutch, Italian, or Spanish manufacturers to minimize duties
- US buyers: Evaluate USMCA benefits for Mexican assembly options
- Factor in ongoing service response times by geography
Operational Savings
-
Negotiate service agreements upfront
- Multi-year maintenance contracts: 15-25% savings vs. ad-hoc service
- Include software updates in initial purchase
- Secure spare parts pricing guarantees for 5+ years
-
Invest in operator training
- Comprehensive initial training reduces early-stage damage claims
- Cross-train multiple operators to minimize overtime costs
- Request training materials in local languages
Hidden Costs to Budget For
| Often-Overlooked Expense | Typical Cost |
|---|---|
| Facility modifications (electrical, plumbing) | $20,000 – $100,000 |
| Compressed air systems | $8,000 – $35,000 |
| Water treatment/recycling | $15,000 – $60,000 |
| Environmental permits | $2,000 – $15,000 |
| Production downtime during installation | $10,000 – $50,000 |
| Staff retraining and transition | $5,000 – $20,000 |
ROI Considerations
When justifying investment, document these measurable benefits:
- Labor reduction: 40-70% fewer sorting personnel required
- Throughput increase: 25-50% higher volumes with consistent quality
- Grade accuracy: 15-30% improvement in pack-out rates
- Waste reduction: 10-20% fewer rejected products
- Premium pricing: Access to export markets requiring certified grading
Typical payback period: 3-5 years for mid-range systems; 2-3 years for high-volume operations.
Recommended Procurement Process
- Define requirements (throughput, quality parameters, integration needs)
- Request detailed proposals from 3-5 qualified suppliers
- Conduct site visits to reference installations
- Negotiate total cost of ownership, not just equipment price
- Secure performance guarantees tied to payment milestones
- Plan installation timeline around harvest schedules
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing apple sorting machine With Other Solutions
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing Apple Sorting Machine With Other Solutions
When evaluating apple processing solutions, operations managers must weigh automated sorting technology against traditional alternatives. This analysis examines three primary approaches to help inform your capital investment decisions.
Comparison Overview
| Factor | Automated Apple Sorting Machine | Manual Labor Sorting | Semi-Automated Conveyor Systems |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Investment | $150,000 – $500,000+ | $5,000 – $20,000 (training/setup) | $50,000 – $150,000 |
| Operating Cost/Year | $15,000 – $40,000 | $200,000 – $500,000+ (labor) | $80,000 – $180,000 |
| Throughput | 10-20+ tons/hour | 0.5-2 tons/hour | 3-8 tons/hour |
| Sorting Accuracy | 95-99% (optical/internal sensors) | 70-85% (human variability) | 80-90% (basic sizing only) |
| Quality Detection | External + internal defects, brix, firmness | External defects only | External sizing/color only |
| Scalability | High (modular systems) | Limited by labor availability | Moderate |
| Consistency | Uniform 24/7 operation | Variable (fatigue, turnover) | Moderate consistency |
| ROI Timeline | 18-36 months | Immediate but ongoing costs | 24-48 months |
Alternative 1: Manual Labor Sorting
Best suited for: Small-scale operations under 500 tons annually, specialty/heirloom varieties requiring human judgment, or markets where labor costs remain low.
Advantages:
– Minimal capital outlay
– Flexibility for non-standard products
– No technical expertise required
Limitations:
– Labor shortages increasingly problematic in USA and Europe
– Rising minimum wages eroding cost advantage
– Cannot detect internal defects (browning, watercore)
– Inconsistent grading standards between workers
– Limited throughput during peak harvest windows
Critical consideration: With agricultural labor costs in the USA averaging $15-20/hour and European rates of €12-18/hour, manual sorting becomes economically unviable for operations exceeding 1,000 tons annually.
Alternative 2: Semi-Automated Conveyor Systems
Best suited for: Mid-sized operations seeking incremental automation, facilities with budget constraints, or those processing multiple fruit types with basic grading requirements.
Advantages:
– Lower capital investment than full automation
– Reduces labor requirements by 40-60%
– Basic size and color grading capability
– Simpler maintenance requirements
Limitations:
– Cannot perform internal quality assessment
– Limited integration with packing/palletizing systems
– Manual intervention still required for final quality checks
– Slower adaptation to changing market specifications
– Higher per-unit processing costs at scale
Why Automated Apple Sorting Machines Deliver Superior Value
Modern optical sorting systems—such as those incorporating Rollerstar and Calistar technologies—provide capabilities that alternatives cannot match:
Internal Quality Detection: Advanced sensors identify watercore, internal browning, and firmness variations invisible to human inspectors or basic conveyor systems. This capability is increasingly demanded by premium retailers in both USA and European markets.
Gentle Product Handling: Purpose-built systems like spreading V-belts and mid-positioned rotating carriers minimize bruising. Aweta’s technology, developed over 55+ years, achieves damage rates under 1%—critical for premium apple varieties commanding $0.20-0.50/lb price premiums.
Integration Capability: Full sorting lines connect seamlessly with bin handling, packing, and palletizing systems, eliminating manual transfer points and their associated labor costs and damage risks.
Data-Driven Operations: Sorting software provides real-time yield data, defect tracking, and traceability documentation required by major retail buyers and export markets.
Decision Framework
Choose automated apple sorting machines when:
– Annual volume exceeds 2,000 tons
– Premium/export markets demand internal quality verification
– Labor availability is constrained
– Consistency and traceability are contractual requirements
Choose semi-automated systems when:
– Budget limitations preclude full automation
– Processing multiple produce types with varying requirements
– Volume ranges between 500-2,000 tons annually
Choose manual sorting when:
– Operating under 500 tons annually
– Processing specialty varieties requiring subjective assessment
– Testing market viability before scaling
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for apple sorting machine
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for Apple Sorting Machines
Key Technical Specifications
When evaluating apple sorting machines for commercial operations, buyers should assess the following critical parameters:
| Technical Property | Description | Typical Range/Options |
|---|---|---|
| Throughput Capacity | Processing volume per hour | 2-20 tons/hour depending on configuration |
| Sorting Accuracy | Precision of grading measurements | 95-99%+ for premium systems |
| Grading Parameters | Measurable quality attributes | Size, weight, color, brix, internal defects |
| Carrier Speed | Lane velocity through sorting section | Variable, application-dependent |
| Number of Lanes | Parallel sorting channels | 4-12+ lanes typical |
| Weight Measurement Accuracy | Precision of individual fruit weighing | ±1-2 grams |
| Singulation Rate | Successful single-fruit presentation | 98%+ for quality systems |
Grading Technology Types
External Quality Assessment:
– Optical/camera-based color analysis
– Dimensional sizing (diameter, height)
– Surface defect detection
– Weight measurement per fruit
Internal Quality Assessment:
– NIR (Near-Infrared) spectroscopy for brix/sugar content
– Internal defect detection (browning, water core)
– Firmness/texture analysis
Infeed System Configurations
- Bin Dumpers — Single-bin or continuous operation
- Continuous Submergers — Water-based gentle handling for wet processing
- Flume Systems — Water transport channels
- Portico Systems — Dry infeed alternatives
Essential B2B Trade Terminology
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| MOQ | Minimum Order Quantity — smallest purchase volume a supplier will accept |
| OEM | Original Equipment Manufacturer — custom branding/specification options |
| Turnkey Solution | Complete, ready-to-operate system including installation and commissioning |
| Commit-to-Pack | Line configuration where all incoming fruit is packed (no pre-sizing rejection) |
| Pre-sizer | Initial sorting stage removing out-of-spec fruit before main grading |
| FOB/CIF | Shipping terms defining cost and risk transfer points |
| Lead Time | Duration from order confirmation to delivery |
| Spare Parts Availability | Critical for maintenance planning and uptime calculations |
System Integration Considerations
- Packing Line Compatibility — Downstream integration with tray packers, baggers, palletizers
- Software/Data Systems — Traceability, reporting, ERP integration capabilities
- Utility Requirements — Power consumption, water usage, compressed air needs
- Footprint Dimensions — Floor space and ceiling height requirements
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the apple sorting machine Sector
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the Apple Sorting Machine Sector
Market Evolution and Industry Trajectory
The apple sorting machine sector has undergone significant transformation over the past five decades. What began as simple mechanical sizing equipment has evolved into sophisticated systems integrating optical sensors, artificial intelligence, and automated packing solutions. Established manufacturers like Aweta, with over 55 years in the industry, have driven this evolution through continuous R&D investment and technology refinement.
Key Historical Milestones:
– Mechanical sorting (weight and size-based)
– Introduction of optical grading for external defects
– Development of internal quality assessment technology
– Integration of automated packing and palletizing systems
– Software-driven process optimization
Current Market Dynamics
Demand Drivers
| Factor | Impact on Sourcing Decisions |
|---|---|
| Labor costs and availability | Accelerating automation adoption in USA and Europe |
| Consumer quality expectations | Driving demand for internal quality detection |
| Retail consolidation | Requiring higher throughput and consistency |
| Export market requirements | Necessitating advanced grading capabilities |
| Food safety regulations | Mandating traceability and defect detection |
Technology Trends Shaping Procurement
External and Internal Grading Integration
Modern buyers increasingly require systems that assess both external appearance (color, size, surface defects) and internal quality (texture, taste indicators, internal defects). This dual-capability approach addresses the market reality that purchase decisions hinge on appearance, while repeat purchases depend on internal quality.
Gentle Handling Systems
Premium apple varieties command price premiums that justify investment in fruit-friendly technology. Features like spreading V-belts, mid-positioned rotating axes, and water-based singulation systems minimize bruising and maximize pack-out rates.
Modular, Scalable Solutions
Procurement trends favor systems offering:
– Flexible design layouts
– Commit-to-pack configurations
– Pre-sizing options for wet or dry processing
– Scalable throughput capacity
Sustainability Considerations
Environmental and operational sustainability now factor heavily into B2B sourcing decisions:
Operational Efficiency
– Automatic chain lubrication reduces maintenance intervals and consumable waste
– Automatic chain tensioning extends equipment lifespan
– Quiet operation (particularly in systems like the Calistar) improves workplace conditions
Resource Optimization
– Water recirculation in wet processing systems
– Energy-efficient motor designs
– Reduced product loss through gentle handling
Longevity and Serviceability
– Robust construction minimizing replacement cycles
– Local service networks reducing travel-related carbon footprint
– Modular components enabling targeted repairs versus full system replacement
Regional Sourcing Considerations
| Region | Primary Considerations |
|---|---|
| USA | Labor cost mitigation, throughput capacity, integration with existing packhouse infrastructure |
| Europe | Energy efficiency, noise regulations compliance, compact footprint for space-constrained facilities |
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations
- Assess total cost of ownership beyond initial capital expenditure—maintenance, throughput efficiency, and pack-out improvements significantly impact ROI
- Prioritize vendors with proven application expertise in your specific apple varieties and market requirements
- Evaluate software capabilities as a differentiator—measurement accuracy and user interface quality affect daily operational efficiency
- Request turnkey solution proposals covering infeed, grading, packing, and palletizing to ensure system integration
- Verify after-sales support infrastructure in your operating region before committing to equipment purchases
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of apple sorting machine
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of Apple Sorting Machines
1. What throughput capacity should I expect from a commercial apple sorting machine?
Commercial apple sorting machines typically handle between 5-15 tons per hour, depending on the model and configuration. High-capacity lines with continuous bin submergers can process significantly higher volumes. When evaluating capacity, consider:
- Peak season requirements
- Labor availability
- Downstream packing line speed
- Storage and logistics constraints
2. What grading parameters can modern apple sorting machines measure?
| External Parameters | Internal Parameters |
|---|---|
| Size/diameter | Brix (sugar content) |
| Weight | Internal defects |
| Color uniformity | Firmness/texture |
| Surface defects | Dry matter content |
| Shape | Internal browning |
| Stem/calyx identification | Water core detection |
Advanced optical sorting systems use multispectral cameras and NIR (near-infrared) technology to assess both external and internal quality simultaneously.
3. How do I choose between a pre-sizer and a commit-to-pack sorting line?
Pre-sizer (e.g., Calistar-type systems):
– Ideal for initial sorting from harvest
– Handles wet products directly from water flumes
– Removes obvious defects before storage
– Lower investment cost
Commit-to-pack lines (e.g., Rollerstar-type systems):
– Final grading before packaging
– Higher precision sorting
– Integrates with packing and palletizing systems
– Optimizes pack-out rates and premium grade yields
Many operations benefit from both systems in sequence.
4. What is the typical ROI timeline for an apple sorting machine investment?
ROI depends on operation scale, labor costs, and pack-out improvements. Most B2B buyers report:
- Payback period: 2-5 years
- Labor reduction: 30-60% in manual sorting roles
- Pack-out improvement: 5-15% increase in premium grade yields
- Waste reduction: Fewer false rejects with accurate grading
Request a site-specific ROI analysis from vendors based on your current throughput and labor costs.
5. What maintenance requirements should I budget for?
| Maintenance Item | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Calibration checks | Daily/Weekly |
| Belt and gripper inspection | Weekly |
| Chain lubrication | Automatic (on advanced systems) |
| Sensor cleaning | Daily |
| Full system service | Annually |
| Software updates | As released |
Modern systems feature automatic chain tensioning and lubrication, reducing manual maintenance. Budget 3-5% of equipment cost annually for maintenance and parts.
6. Can sorting machines integrate with my existing packing and ERP systems?
Yes. Leading manufacturers provide software platforms that integrate with:
- Existing packing and palletizing equipment
- Warehouse management systems (WMS)
- ERP platforms for traceability and inventory
- Customer-specific labeling requirements
Confirm API availability and integration support during vendor evaluation. Request references from operations with similar system configurations.
7. How do I ensure gentle handling to minimize bruising and product damage?
Key features that protect fruit quality:
- Water-based infeed systems: Cushioned transfer from bins
- Spreading V-belts: Smooth singulation onto carriers
- Rotating carrier axes: Even transfer to brushes and sensors
- Optimized drop heights: Controlled transitions between stages
Ask vendors for bruise damage data and request on-site demonstrations with your apple varieties.
8. What should I include in my RFQ when sourcing an apple sorting machine?
Include the following in your Request for Quotation:
- Throughput requirements: Tons/hour, peak and average
- Apple varieties: Size range, skin sensitivity
- Grading criteria: External, internal, or both
- Facility constraints: Floor space, ceiling height, utilities
- Integration needs: Existing equipment, software systems
- Service requirements: Installation, training, warranty, spare parts availability
- Budget range: Capital and operational
Request site visits, customer references, and detailed total cost of ownership (TCO) projections from shortlisted vendors.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for apple sorting machine
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion: Apple Sorting Machine Investment
Investing in advanced apple sorting technology delivers measurable ROI through reduced labor costs, minimized product waste, and premium pack-out rates. The strategic considerations outlined in this guide—from grading accuracy to integration capabilities—directly impact your operation’s competitive positioning.
Key Takeaways
| Priority | Business Impact |
|---|---|
| Grading precision | Higher pack-out percentages, premium pricing |
| Gentle handling | Reduced bruising, extended shelf life |
| Internal quality detection | Fewer customer rejections, brand protection |
| Scalable design | Future-proof investment, operational flexibility |
Market Outlook
The apple sorting equipment sector continues advancing toward:
– AI-enhanced defect detection with improved accuracy rates
– Internal quality measurement becoming standard, not optional
– Integrated data analytics for yield optimization and traceability
– Modular configurations supporting diverse packaging requirements
Final Recommendation
Partner with established manufacturers offering proven technology, comprehensive service networks, and demonstrated expertise in your specific market requirements. Prioritize suppliers with 50+ years of industry experience who provide turnkey solutions—from infeed systems through palletizing—ensuring seamless integration and single-point accountability.
The right sorting machine investment positions your operation for sustained profitability in increasingly quality-driven markets.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided is for informational purposes only. B2B buyers must conduct their own due diligence.