The global anti seize paste market is experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing demand from automotive, industrial manufacturing, and oil & gas sectors. According to Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at approximately USD 1.2 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.3% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2029. This expansion is fueled by rising industrialization, the need for enhanced equipment longevity, and growing awareness of preventive maintenance practices. As high-temperature and high-pressure applications become more prevalent, anti seize pastes—which prevent galling, corrosion, and seizing of metal components—have become essential in both routine maintenance and large-scale operations. With Asia-Pacific emerging as a key growth region due to expanding infrastructure and manufacturing activities, the competitive landscape has intensified among leading suppliers. Below is a data-driven overview of the top 9 anti seize paste manufacturers shaping this evolving market.
Top 9 Anti Seize Paste Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Anti
Domain Est. 2001
Website: antiseize.com
Key Highlights: Anti-Seize Technology (AST) is a manufacturer and worldwide supplier of over 135 anti-seize products including Adhesives,Pipe Thread Sealants,Anti-Seize ……
#2 Anti-Seize & Thread Lubricant Manufacturer
Domain Est. 1996
Website: jetlube.com
Key Highlights: Jet-Lube’s premium anti-seize compounds are formulated to protect and lubricate metal fasteners and parts from rust, corrosion, galling, and metal-to-metal ……
#3 Anti Seize
Domain Est. 1997
Website: ellsworth.com
Key Highlights: 6-day deliveryBostik Never-Seez Regular Grade Anti-Seize Lubricant Silver 16 oz Aerosol Can. Part #: BNRG12AC12. Manufacturer SKU: 30803827….
#4 Anti Seize Paste & Powders
Domain Est. 2001
Website: superior-industries.com
Key Highlights: Our anti-seize pastes actively protect metals and alloys from stress, strain, galling, and corrosion for optimum productivity with the lowest possible ……
#5 Lubricant Pastes
Domain Est. 1987
Website: dupont.com
Key Highlights: MOLYKOTE® 1000 Paste. Lead- and nickel-free anti-seize paste used to reduce wear and optimize friction of threaded fasteners, or other ……
#6 Permatex® Anti
Domain Est. 1995
Website: permatex.com
Key Highlights: Permatex’s Anti-Seize Lubricant is a highly refined blend of aluminum, copper, and graphite lubricants. Use during assembly to prevent galling, corrosion, and ……
#7 JAX Food
Domain Est. 1995
Website: jax.com
Key Highlights: Rating 5.0 (1) Ensure lasting seals with JAX Food-Grade Anti-Seize, designed for high-pressure environments and easy disassembly. Protect your equipment today!…
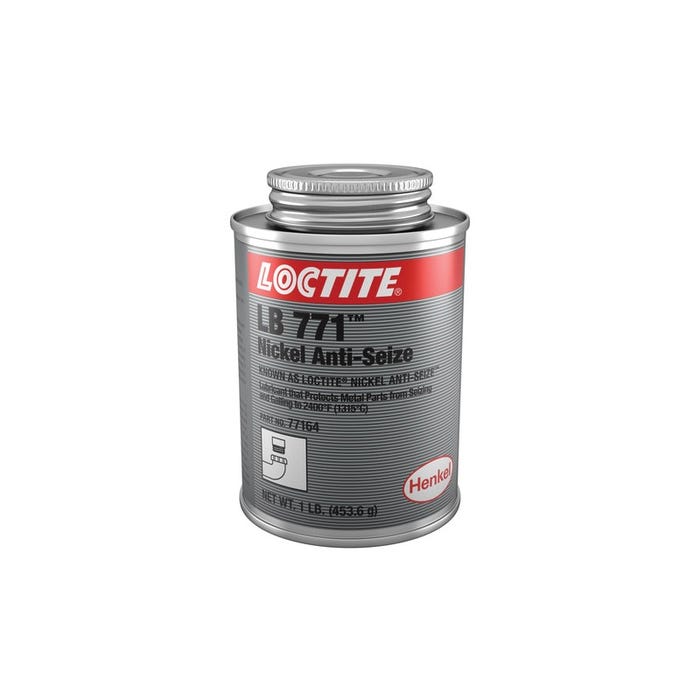
#8 Anti
Domain Est. 2000
Website: henkel-adhesives.com
Key Highlights: Our food grade anti-seize lubricants are designed to prevent friction, seizing, and galling in stainless steel and other metal parts within food processing ……
#9 Anti
Domain Est. 2013
Website: matrix-lubricants.com
Key Highlights: Ensure smooth operations with Paste Anti Seize, the ultimate Anti-Seize Paste designed for high temperatures and protecting against corrosion and seizing….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Anti Seize Paste

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Anti-Seize Paste
The global anti-seize paste market is poised for steady growth leading into 2026, driven by increasing industrialization, technological advancements in lubrication chemistry, and rising demand across key sectors such as automotive, aerospace, energy, and manufacturing. Several prominent trends are expected to shape the market landscape in the coming years:
1. Rising Demand from the Automotive and Transportation Sector
The automotive industry remains a dominant consumer of anti-seize pastes, particularly with the expansion of electric vehicle (EV) production. As EVs require specialized components that are exposed to high temperatures and corrosion, the need for high-performance anti-seize solutions is growing. Additionally, stricter emission standards are prompting manufacturers to use lightweight, high-strength materials that are more prone to galling—further increasing reliance on anti-seize compounds.
2. Growth in Renewable Energy Infrastructure
The global push toward renewable energy sources, especially wind and solar power, is creating new opportunities for anti-seize paste applications. Wind turbines, in particular, operate under extreme environmental conditions and require reliable lubrication and corrosion protection for bolted joints and high-torque assemblies. As wind farm installations increase, especially in offshore locations, demand for durable, temperature-resistant anti-seize products is expected to rise.
3. Advancements in Formulation Technology
By 2026, manufacturers are focusing on developing environmentally friendly, non-toxic, and copper-free anti-seize formulations to comply with increasingly stringent environmental regulations (e.g., REACH, RoHS). Innovations in nano-additives and ceramic-based compounds are enhancing performance under extreme pressure and high temperatures, offering longer service life and reduced maintenance costs.
4. Expansion in Emerging Markets
Rapid industrialization in Asia-Pacific (particularly India, Southeast Asia, and China), along with infrastructure development in Africa and Latin America, is driving demand for anti-seize pastes. Local production facilities and partnerships with global suppliers are expected to expand distribution networks and reduce costs, making high-performance pastes more accessible.
5. Supply Chain Resilience and Raw Material Volatility
The market may face challenges related to the availability and price volatility of key raw materials such as copper, nickel, graphite, and synthetic thickeners. Companies are responding by diversifying supply chains, investing in alternative materials, and improving inventory management strategies to ensure consistent product availability.
6. Increased Focus on Customization and Industry-Specific Solutions
End-users are demanding tailored anti-seize solutions for niche applications—such as high-vacuum environments in aerospace or food-grade formulations for the pharmaceutical industry. This trend is pushing suppliers to offer specialized product lines with certifications (e.g., NSF, API) and technical support services.
In summary, the anti-seize paste market in 2026 will be characterized by innovation, sustainability, and geographic expansion. Companies that invest in R&D, comply with environmental standards, and adapt to regional industrial needs will be best positioned to capture market share in this evolving landscape.
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Anti-Seize Paste (Quality & Intellectual Property)
Sourcing anti-seize paste may seem straightforward, but overlooking key quality and intellectual property (IP) considerations can lead to performance failures, safety risks, and legal exposure. Below are common pitfalls to avoid:
1. Prioritizing Cost Over Performance Specifications
Choosing the cheapest option without verifying compliance with technical standards (e.g., MIL-PRF-907, ASTM D6743, or OEM requirements) can result in inadequate protection against galling, seizing, or corrosion. Low-cost pastes may use inferior base oils, inconsistent metal particulates (e.g., nickel, copper, or graphite), or insufficient viscosity, compromising performance in high-temperature or high-stress environments.
2. Inadequate Verification of Raw Material Quality
Many suppliers source raw materials globally without stringent quality controls. Poorly refined metal powders or contaminated carriers can lead to inconsistent application, reduced shelf life, or chemical incompatibility with substrates. Always request Certificates of Conformance (CoC) and Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS/SDS), and conduct batch testing when critical.
3. Misrepresentation of Temperature and Load Ratings
Some suppliers exaggerate operating temperature ranges (e.g., claiming 1,800°F performance without third-party validation). Always cross-check claims with independent testing data or recognized industry benchmarks. Exceeding actual limits can cause paste breakdown, leading to seized components or system failure.
4. Ignoring Intellectual Property (IP) and Brand Infringement
Sourcing counterfeit or “look-alike” anti-seize products that mimic well-known brands (e.g., NeverSeez, Kopr-Shield) infringes on trademarks and patents. These knockoffs often lack R&D validation and may fail under specified conditions. Using IP-infringing products exposes your company to legal liability and supply chain risks.
5. Lack of Traceability and Documentation
Reputable suppliers provide full traceability—batch numbers, manufacturing dates, and test reports. Absence of documentation makes it difficult to investigate field failures or comply with quality audits (e.g., ISO 9001, AS9100). This is especially critical in regulated industries like aerospace, oil & gas, or automotive.
6. Overlooking Compatibility and Regulatory Compliance
Anti-seize pastes must be compatible with specific metals (e.g., avoiding graphite with aluminum or stainless steel in high-temp applications to prevent galvanic corrosion). Additionally, ensure compliance with environmental and safety regulations (e.g., REACH, RoHS), particularly when exporting.
7. Assuming All “Generic” Pastes Are Interchangeable
Different formulations serve different purposes—copper-based for general use, nickel for high-temp oxidation resistance, or ceramic for extreme environments. Substituting without engineering validation can lead to premature failure or contamination in sensitive systems (e.g., oxygen lines).
8. Failure to Audit Supplier Credentials
Not all suppliers are manufacturers. Trading companies or intermediaries may lack technical expertise or quality control. Conduct supplier audits or require evidence of in-house manufacturing, quality systems, and technical support capabilities.
By addressing these pitfalls proactively—focusing on verified performance, authentic IP compliance, and traceable quality—organizations can ensure reliable performance and mitigate operational and legal risks when sourcing anti-seize paste.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Anti-Seize Paste
Overview
Anti-seize paste is a lubricating compound used to prevent galling, seizing, and corrosion in threaded fasteners and other metal components. Due to its chemical composition and application, proper handling, storage, transportation, and regulatory compliance are essential to ensure safety and legal adherence.
Classification & Regulatory Compliance
Anti-seize paste is typically classified based on its ingredients, which may include metals (e.g., copper, nickel, aluminum), graphite, or synthetic lubricants suspended in a grease or oil base. Key regulatory considerations include:
- GHS Classification: Depending on formulation, anti-seize pastes may be classified as flammable, harmful if swallowed, or skin/eye irritants. Always consult the Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for exact hazard classification.
- REACH & RoHS Compliance: Ensure the product complies with EU REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals) and RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) directives, especially if containing restricted metals.
- TSCA Compliance (USA): Confirm the product meets U.S. Toxic Substances Control Act requirements for chemical substances.
Safety Data Sheet (SDS) Requirements
- Maintain an up-to-date SDS for each anti-seize product.
- SDS must be accessible to all personnel involved in handling, storage, and transportation.
- SDS includes information on composition, first aid measures, fire-fighting, accidental release, handling, and disposal.
Packaging & Labeling
- Use original manufacturer packaging that is sealed and leak-proof.
- Labels must include:
- Product identifier
- Hazard pictograms (e.g., GHS symbols)
- Signal words (e.g., “Warning” or “Danger”)
- Hazard and precautionary statements
- Supplier information
- Ensure labeling complies with local and international regulations (e.g., CLP in EU, HCS in USA).
Storage Guidelines
- Store in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area away from direct sunlight and heat sources.
- Keep containers tightly closed when not in use.
- Avoid storage near oxidizing agents, acids, or foodstuffs.
- Use compatible secondary containment to prevent environmental contamination in case of leakage.
- Implement a first-in, first-out (FIFO) inventory system to prevent product degradation.
Handling Procedures
- Use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including gloves, safety goggles, and protective clothing.
- Avoid skin and eye contact; wash hands thoroughly after handling.
- Do not eat, drink, or smoke in handling areas.
- Use in well-ventilated areas; consider local exhaust ventilation if used in enclosed spaces.
Transportation & Shipping
- Classify according to transport regulations (e.g., UN number, proper shipping name, hazard class).
- Most anti-seize pastes are non-regulated for transport if they are not flammable or do not exceed hazard thresholds. Confirm via SDS Section 14.
- For international shipping, comply with:
- IMDG Code (maritime)
- IATA DGR (air)
- ADR (road, Europe)
- Use UN-certified packaging if required.
- Include necessary shipping documents, including SDS and declaration of transport hazard.
Environmental & Disposal Considerations
- Do not dispose of in drains, sewers, or natural water bodies.
- Waste anti-seize paste and contaminated packaging should be treated as hazardous waste if classified as such.
- Follow local, national, and international waste disposal regulations (e.g., EPA in USA, WEEE or national waste codes in EU).
- Recycle metal-contaminated waste where possible through licensed facilities.
Training & Documentation
- Train all relevant personnel on safe handling, storage, emergency procedures, and regulatory compliance.
- Maintain records of SDS, training logs, inspection reports, and shipping documentation.
- Conduct periodic audits to ensure ongoing compliance with logistics and safety standards.
Emergency Response
- In case of spill: Contain with absorbent material (e.g., sand, vermiculite); avoid spreading. Collect waste and dispose of properly.
- Fire: Use dry chemical, CO₂, or foam extinguishers. Water may not be effective.
- First aid:
- Skin contact: Wash with soap and water.
- Eye contact: Rinse thoroughly with water for at least 15 minutes; seek medical advice.
- Ingestion: Do not induce vomiting; seek immediate medical attention.
Conclusion
Proper logistics and compliance management for anti-seize paste ensures operational safety, regulatory adherence, and environmental protection. Always refer to the product-specific SDS and consult regulatory authorities when in doubt.
Conclusion for Sourcing Anti-Seize Paste:
In conclusion, sourcing the right anti-seize paste is a critical decision that directly impacts the performance, safety, and longevity of mechanical assemblies in various industrial, automotive, and manufacturing applications. A thorough evaluation of key factors—such as base materials (e.g., copper, nickel, aluminum), lubricant carrier, temperature resistance, corrosion protection, and compatibility with specific metals and operating environments—is essential to ensure optimal performance.
It is equally important to source anti-seize paste from reputable suppliers who provide consistent quality, technical documentation, and compliance with industry standards (e.g., MIL-PRF-907, ISO, ASTM). Cost should not be the sole determinant; instead, a balance between value, reliability, and technical suitability must be achieved.
By implementing a strategic sourcing approach—considering formulation needs, supplier reliability, volume requirements, and long-term maintenance goals—organizations can prevent seizing, galling, and corrosion-related failures, reduce downtime, and improve operational efficiency. Ultimately, investing in the right anti-seize paste from a trusted source delivers both immediate and long-term benefits across maintenance and production systems.