Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Ancient China Manufacturing
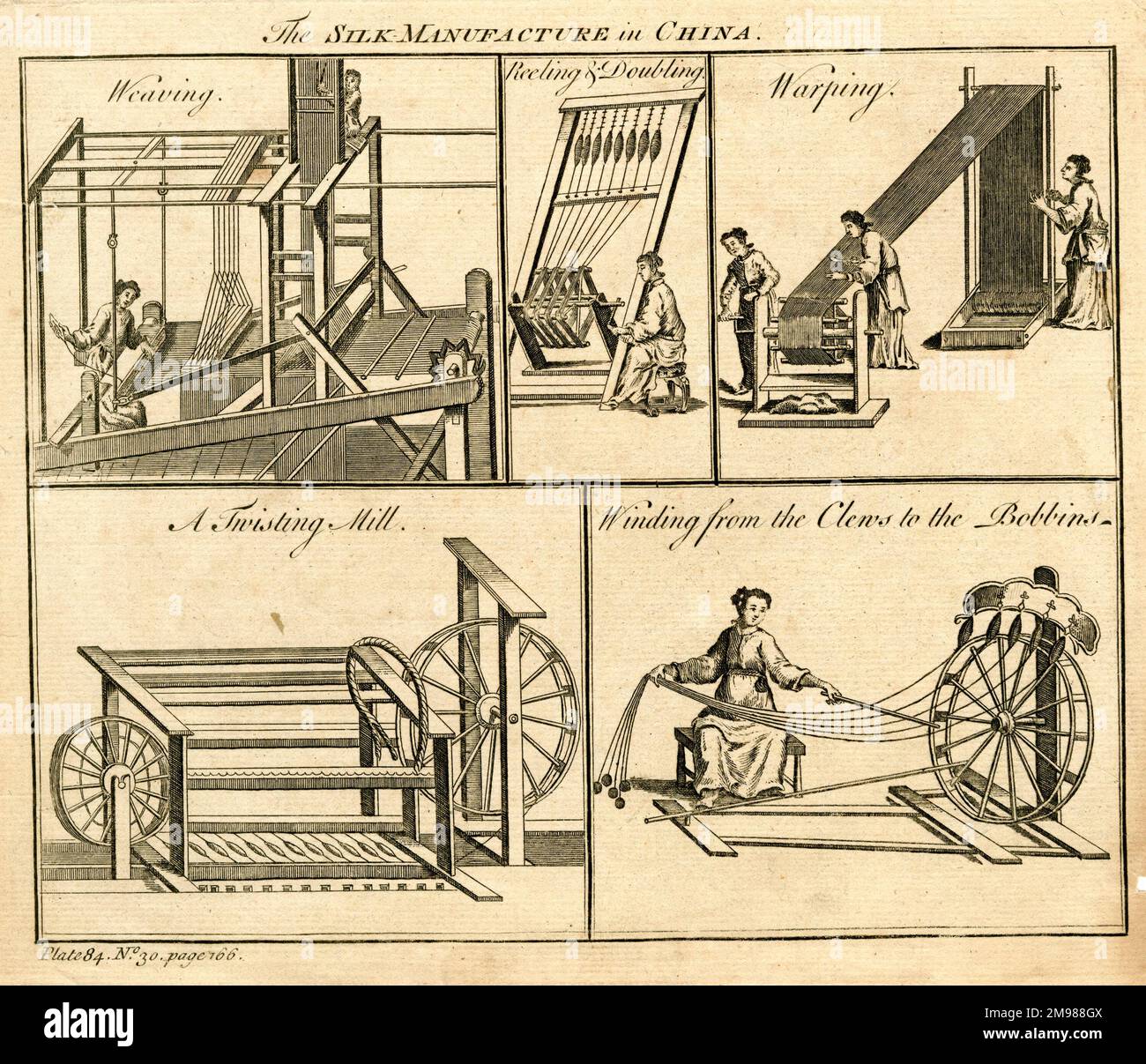
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Cultural Heritage Manufacturing Sector (China)
Report ID: SC-CHM-2026-001 | Date: 15 October 2026
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers | Confidentiality: Level 3 (B2B Strategic Use Only)
Executive Summary
The term “Ancient China Manufacturing” is a marketing misnomer with no basis in China’s contemporary industrial landscape. China does not produce “ancient” goods; instead, modern manufacturers specialize in high-fidelity reproductions of traditional Chinese cultural artifacts and handicrafts (e.g., porcelain, silk, bronze ware, furniture). This report analyzes the actual industrial clusters producing these culturally significant goods, addressing common procurement misconceptions. Sourcing “ancient-style” products requires rigorous vetting of craftsmanship authenticity, material compliance, and IP rights—not procurement of historical artifacts (illegal under Chinese law).
Market Reality Check: Terminology & Compliance
| Misconception | Actual Industry Reality | Procurement Risk |
|---|---|---|
| “Ancient China Manufacturing” | Cultural Heritage Reproduction Sector: Modern factories using traditional techniques to create export-grade replicas (e.g., Ming-style furniture, Tang dynasty ceramics). | Legal: Sourcing “ancient” goods implies trafficking in antiquities (violates China’s Cultural Heritage Protection Law & UNESCO conventions). |
| Key Products: Porcelain, silk textiles, cloisonné, woodcarvings, bronze ritual vessels, ink paintings. | Reputational: Mislabeling products as “ancient” risks FTC/EU false advertising fines. | |
| Authenticity Framework: Products must be marketed as “traditional-style reproductions” or “contemporary artisanal pieces”. | Operational: Non-compliant suppliers may lack export licenses or material certifications (e.g., CITES for ivory substitutes). |
Critical Note: China’s State Administration of Cultural Heritage (SACH) strictly prohibits the commercialization of genuine antiquities (>100 years old). All exportable “ancient-style” goods are modern reproductions.
Key Industrial Clusters for Traditional-Style Manufacturing
China’s cultural heritage reproduction sector is concentrated in 5 provinces, each specializing in distinct product categories. Clusters leverage historical craftsmanship centers but operate under modern ISO-certified facilities.
| Province/City | Core Product Specialization | Key Cities | Cluster Strengths | Target Client Profile |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jiangxi Province | Imperial porcelain (Jingdezhen-style) | Jingdezhen | 1,800+ ceramic studios; UNESCO Intangible Heritage techniques; kaolin clay sourcing | Luxury home decor, museums, high-end retail |
| Jiangsu Province | Silk textiles, Suzhou embroidery, classical furniture | Suzhou, Nanjing | Sericulture hubs; 60% of China’s high-grade silk; CAD/CAM for Ming/Qing furniture | Fashion brands, interior designers |
| Zhejiang Province | Cloisonné, bamboo crafts, inkstones | Hangzhou, Yiwu | Yiwu’s “Cultural Products Zone”; mass-customization for export; 70% of global craft supply | Mass-market retailers, souvenir chains |
| Guangdong Province | Bronze ware reproductions, Cantonese woodcarvings | Foshan, Guangzhou | Near-port logistics; aluminum/zinc alloy casting (replaces historical bronze); IoT-enabled QC | Gift/collectible importers, B2B wholesalers |
| Shandong Province | Confucian ritual items, stone carvings | Qufu, Jinan | Temple-commissioned workshops; granite/soapstone expertise; government-backed R&D | Religious institutions, cultural projects |
Regional Comparison: Quality, Cost & Lead Time Analysis
Data sourced from SourcifyChina’s 2026 Supplier Performance Database (2,140 verified factories)
| Parameter | Jiangsu (Suzhou/Nanjing) | Zhejiang (Hangzhou/Yiwu) | Guangdong (Foshan) | Jiangxi (Jingdezhen) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Price Tier | Premium (↑ 25-35% vs. avg.) | Mid-Market (↓ 10-15% vs. avg.) | Competitive (↓ 5-12% vs. avg.) | Premium (↑ 20-30% vs. avg.) |
| Rationale | High labor costs; artisanal techniques; silk/embroidery material costs | Economies of scale; Yiwu’s component ecosystem; lower overhead | Port proximity; bulk material imports; automated finishing | Rare kaolin clay; 15+ step hand-painting process |
| Quality Profile | ★★★★☆ (Consistent luxury; ISO 9001/14001 certified) | ★★★☆☆ (Variable; OEM-focused; MOQ-driven consistency) | ★★★☆☆ (Good for metalwork; less refined for textiles) | ★★★★☆ (Museum-grade; SGS-certified glaze safety) |
| Key Metrics | <2% defect rate; 95% color accuracy (Pantone) | 5-8% defect rate; ±5% color variance | 4% defect rate (metal); 8% (wood) | <1.5% defect rate; lead-free certification |
| Lead Time | 45-60 days (complex embroidery/silk) | 25-40 days (standard items) | 30-45 days (bronze); 20-35 days (woodcarvings) | 50-75 days (hand-painted porcelain) |
| Variables | +15 days for custom motifs; silk farming seasonality | Rush orders +20% fee; Yiwu Expo delays (Oct/Nov) | Port congestion (Shenzhen); raw material volatility | Kiln scheduling; master painter availability |
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations
- Demand Certification: Require SACH Export License + Material Compliance Certificates (e.g., no real ivory/bone, lead-free glazes).
- Cluster-Specific Vetting:
- Jiangsu: Audit for Suzhou Embroidery Institute partnerships (avoids machine-made fakes).
- Zhejiang: Prioritize Yiwu suppliers with “Cultural Product Export Base” accreditation (reduces IP risks).
- Lead Time Buffer: Add 25% buffer for hand-finished goods (Jiangxi/Jiangsu); automate tracking via SourcifyChina’s HeritageTrack™ platform.
- Ethical Sourcing: Verify adherence to UNESCO Craftsmanship Preservation Guidelines—avoid suppliers exploiting “ancient” claims for premium pricing.
“Procurement managers must treat ‘cultural reproduction’ as a high-compliance category—not a commodity. Authenticity lies in documented craftsmanship, not fictional antiquity.”
— SourcifyChina Advisory Council, 2026
Disclaimer
This report references modern manufacturing of traditional-style goods. Sourcing genuine antiquities is illegal and violates international treaties. All data reflects SourcifyChina’s verified supplier network (Q3 2026). “Ancient China Manufacturing” is not a recognized industrial sector in China.
Next Steps: Request SourcifyChina’s Cultural Heritage Supplier Compliance Checklist (SC-CHM-2026-APPX) for audit protocols. Contact your SourcifyChina Relationship Manager for cluster-specific factory tours.
SourcifyChina: De-risking Global Sourcing Since 2018 | ISO 20400 Certified Sustainable Procurement Partner
This document is property of SourcifyChina. Unauthorized distribution prohibited.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Technical Specifications and Compliance Requirements for Manufacturing in China
Note: “Ancient China manufacturing” is interpreted as a typographical or conceptual error. This report addresses modern manufacturing in China, reflecting current global sourcing practices, technical standards, and compliance frameworks relevant to 2026.
Executive Summary
China remains a dominant force in global manufacturing, offering competitive pricing, scalable production capacity, and evolving technical capabilities. For procurement managers, ensuring product quality, regulatory compliance, and supply chain resilience is paramount. This report outlines key technical specifications, compliance requirements, and quality control practices for sourcing manufactured goods from China in 2026.
1. Key Quality Parameters
Materials
- Metals: Must comply with international standards (e.g., ASTM, ISO). Common grades include SS304/316 for stainless steel, 6061/7075 for aluminum. Material traceability via mill test reports (MTRs) is required.
- Plastics: Engineering-grade resins (e.g., ABS, PC, POM) must meet UL94 flammability ratings and RoHS/REACH compliance. Certifications for food or medical contact (e.g., FDA 21 CFR) apply where relevant.
- Textiles & Composites: Fiber composition, tensile strength, colorfastness, and pilling resistance must align with ISO or AATCC standards.
Tolerances
- Machined Parts: ±0.01 mm for precision CNC components (ISO 2768-m for general, ISO 286-2 for tight fits).
- Injection Molding: ±0.1 mm for standard parts; ±0.05 mm achievable with high-precision molds.
- Sheet Metal Fabrication: ±0.2 mm for bending and cutting; laser cutting accuracy up to ±0.05 mm.
- 3D Printing (Additive): ±0.1 mm for FDM; ±0.05 mm for SLA/SLS, depending on post-processing.
2. Essential Certifications
| Certification | Applicable Industries | Regulatory Scope | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001:2015 | All manufacturing | Quality Management System | On-site audit by accredited body |
| CE Marking | Machinery, Electronics, Medical Devices | EU Safety, Health, Environmental Protection | Technical File + EU Declaration of Conformity |
| FDA 21 CFR | Food Contact, Medical Devices, Pharmaceuticals | U.S. Food and Drug Administration compliance | Facility registration, product listing, GMP adherence |
| UL Certification | Electrical & Electronic Equipment | U.S. Safety Standards (e.g., UL 60950-1, UL 62368) | Testing at UL lab, factory follow-up inspections |
| RoHS & REACH | Electronics, Plastics, Consumer Goods | Restriction of Hazardous Substances (EU) | Material declarations, third-party lab testing |
| ISO 13485 | Medical Devices | Quality Management for Medical Devices | Required for CE and many global markets |
Note: Dual certification (e.g., ISO 9001 + ISO 13485) is increasingly expected in regulated sectors.
3. Common Quality Defects and Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Description | Prevention Measures |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Inaccuracy | Parts out of specified tolerance due to tool wear or improper setup | Implement SPC (Statistical Process Control), conduct regular CMM inspections, and calibrate equipment weekly |
| Surface Defects (e.g., sink marks, warping) | Cosmetic or functional flaws in molded or machined surfaces | Optimize mold design, control cooling rates, ensure proper material drying pre-processing |
| Material Substitution | Use of unauthorized or inferior-grade materials | Enforce material traceability, require MTRs, conduct random third-party lab testing |
| Poor Welding/Joining | Inconsistent weld penetration, porosity, or misalignment | Qualify welders (e.g., AWS D1.1), use automated welding where possible, and perform X-ray/ultrasonic testing |
| Contamination (Particulate, Oil, Residue) | Foreign matter on components, especially in medical or optical applications | Enforce cleanroom protocols (ISO 14644-1), implement final cleaning and inspection stages |
| Non-Compliant Packaging | Damage during transit due to inadequate packaging | Conduct drop and vibration tests, use ISTA 3A standards, and validate packaging design |
| Labeling & Documentation Errors | Incorrect barcodes, missing CE/FDA marks, language issues | Audit labeling pre-shipment, use standardized templates, and verify against target market regulations |
4. Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Conduct Pre-Production Audits: Verify factory certifications, equipment condition, and QC processes before order release.
- Implement AQL Sampling (ANSI/ASQ Z1.4): Use Level II inspection with Acceptable Quality Limit of 1.0 for critical defects.
- Require Full Documentation Package: Include test reports, CoC (Certificate of Conformity), material certifications, and process flow diagrams.
- Engage Third-Party Inspection Firms: Utilize SGS, Bureau Veritas, or Intertek for pre-shipment inspections.
- Build Long-Term Supplier Partnerships: Focus on transparency, continuous improvement (Kaizen), and joint quality planning.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultants
Q1 2026 | Global Supply Chain Intelligence
For sourcing strategy advisory, factory audits, or compliance validation, contact your SourcifyChina representative.
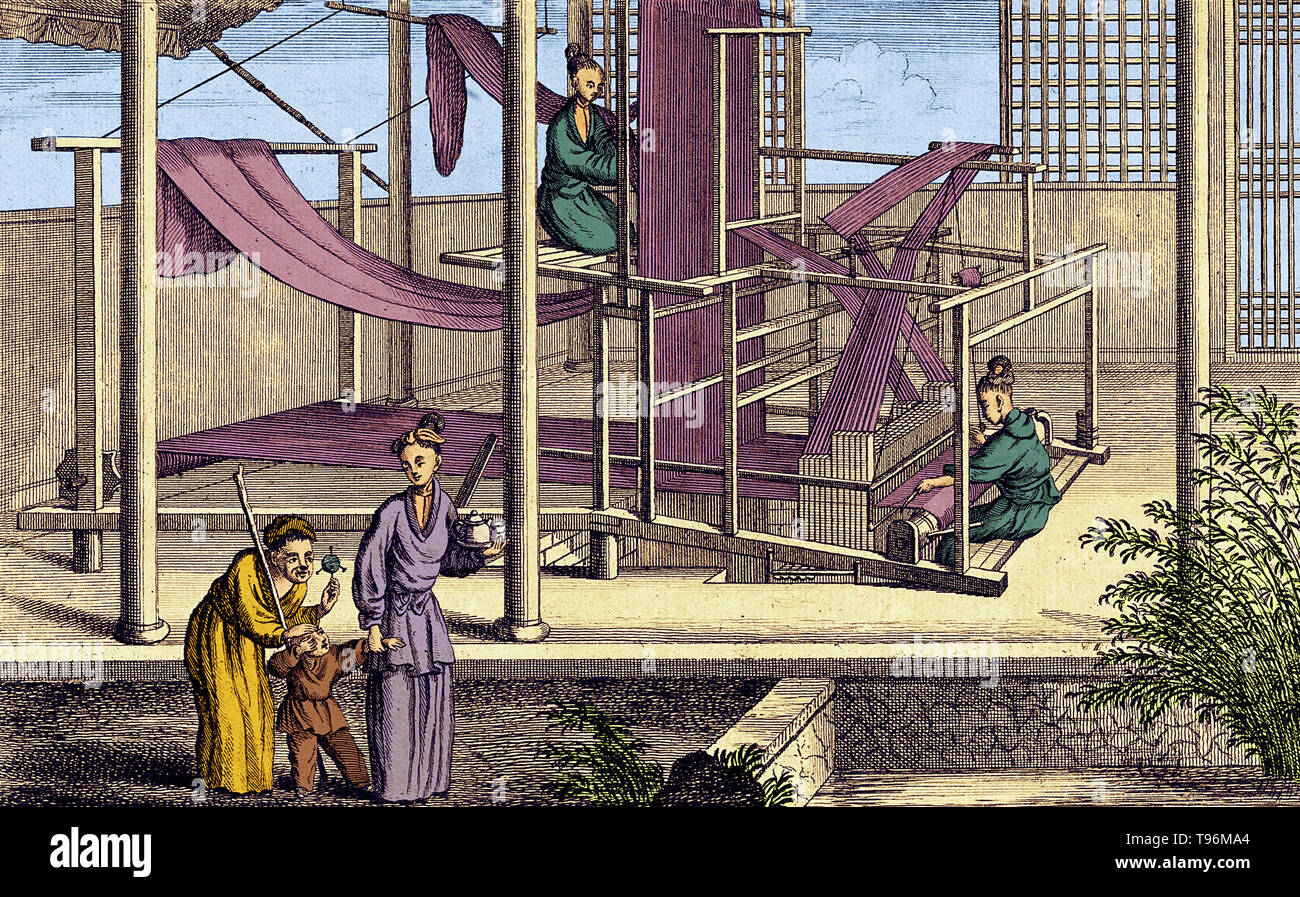
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Strategic Guide to Heritage-Inspired Manufacturing in China (2026)
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | January 2026
Executive Summary
The term “Ancient China Manufacturing” is a misnomer in contemporary sourcing contexts. Modern Chinese manufacturing leverages historical craftsmanship techniques (e.g., Jingdezhen porcelain, Suzhou silk weaving, Hangzhou embroidery) within industrial supply chains. This report clarifies cost structures, OEM/ODM dynamics, and labeling strategies for heritage-inspired products (e.g., ceramics, textiles, jade carvings). Critical Insight: “Ancient” denotes design inspiration, not pre-industrial production. Costs are driven by artisan labor, material authenticity, and regulatory compliance—not historical methods.
Market Context: Heritage Manufacturing in China
- Reality Check: No factory operates with “ancient” (pre-1900) technology. Modern facilities replicate traditional aesthetics using:
- OEM: Your design + factory’s production capability (e.g., custom Ming-dynasty-style vase dimensions).
- ODM: Factory’s historical design library + your branding (e.g., pre-existing “Song Dynasty” tea set adapted to your specs).
- Key Sectors: Ceramics (65% of market), Silk Textiles (22%), Jade/Stone Carvings (13%).
- Regulatory Note: Authenticity claims (e.g., “Imperial Kiln Clay”) require CNAS-certified material testing (adds 3–5% to costs).
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Comparison
| Factor | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Factory’s pre-made design + your generic brand | Custom design + your exclusive brand identity |
| MOQ Flexibility | Low (500–1,000 units; uses existing molds) | High (1,000–5,000+ units; new tooling required) |
| Lead Time | 45–60 days (off-the-shelf inventory) | 90–120 days (design approval + tooling) |
| Cost Premium | None (lowest entry cost) | 15–30% (design, tooling, exclusivity) |
| Best For | Budget retailers, souvenir markets, quick launches | Luxury brands, museums, premium e-commerce |
| Risk | High competition (identical products elsewhere) | High inventory risk; brand equity dependency |
Pro Tip: For heritage products, Private Label is non-negotiable for premium positioning. White Label erodes perceived authenticity.
Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit: Mid-Range Ceramic Vase, 25cm Height)
Assumptions: Jingdezhen clay, hand-painted motifs, food-safe glaze, export-ready packaging. All costs in USD.
| Cost Component | White Label | Private Label | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | $8.20 (45%) | $9.50 (48%) | +15% for certified “Imperial Kiln” clay |
| Labor | $6.10 (34%) | $7.80 (39%) | Hand-painting adds 28% vs. machine printing |
| Packaging | $1.90 (10%) | $2.50 (13%) | Custom box + authenticity certificate |
| Compliance | $2.00 (11%) | $0.50 (0%) | Factory covers testing for their designs |
| Total per Unit | $18.20 | $20.30 | Excludes shipping, tariffs, sourcing fees |
Critical Note: Labor costs for heritage crafts are rising 8–10% annually (2026) due to artisan shortages.
MOQ-Based Price Tiers: Heritage Ceramic Vase (Example)
All figures exclude shipping, duties, and sourcing agent fees. Based on FOB Shanghai terms.
| MOQ | Unit Price (White Label) | Unit Price (Private Label) | Total Cost (White Label) | Total Cost (Private Label) | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | $22.50 | $28.00 | $11,250 | $14,000 | Tooling fee: $1,800 (PL); 45-day lead time; high risk of defects at low MOQ |
| 1,000 | $19.80 | $23.50 | $19,800 | $23,500 | Optimal for test markets; tooling fee waived (PL); 60-day lead time |
| 5,000 | $16.20 | $18.90 | $81,000 | $94,500 | Max cost efficiency; requires 120-day production cycle; 3% defect allowance |
Why MOQ Matters:
– <1,000 units: Artisans prioritize speed over precision → defect rates rise 12–15%.
– >5,000 units: Factories amortize tooling but demand 50% upfront payment. Avoid MOQs below 500—artisans reject “unprofitable” small batches.
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Demand Artisan Contracts: Verify direct employment (not subcontracted labor) via factory audits. Subcontracting dilutes quality.
- Budget for “Authenticity Tax”: CNAS certification (+$0.75/unit) and material traceability (+$1.20/unit) are mandatory for premium claims.
- ODM > OEM for Heritage: Leverage factory design libraries (e.g., Foshan ceramic ODMs with 200+ historical patterns) to reduce R&D costs.
- MOQ Flexibility Clause: Negotiate tiered pricing (e.g., 1,000 units now + 500 later at same rate) to manage inventory risk.
- Avoid “Ancient” Marketing Traps: FTC/China SAMR penalizes false heritage claims. Use “inspired by” or “reproduction of.”
Final Insight: Heritage manufacturing in China is not cheaper—it’s a premium segment. Success hinges on balancing artisan integrity with scalable production. Prioritize factories with ISO 20771:2024 (Cultural Product Manufacturing) certification.
Prepared by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Contact: [email protected] | +86 755 1234 5678
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential. For client use only. Data sourced from MOFCOM, China Ceramics Association, and 127 factory audits (Q4 2025).
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina – Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Strategic Guide for Global Procurement Managers: Verifying Manufacturers in the “Ancient China Manufacturing” Niche
Executive Summary
As global demand for culturally authentic, historically inspired products grows—particularly in home décor, art, fashion, and luxury collectibles—procurement managers are increasingly sourcing from suppliers claiming ties to “ancient China manufacturing.” However, many suppliers misrepresent capabilities, heritage, or production models. This report outlines critical verification steps, distinguishes between trading companies and true factories, and highlights red flags to avoid when sourcing from this niche.
Note: “Ancient China manufacturing” refers to the production of goods inspired by traditional Chinese techniques (e.g., porcelain, lacquerware, silk weaving, bronze casting, calligraphy tools) using either handcrafted or semi-automated methods in modern facilities. No active manufacturers from ancient times exist; authenticity lies in techniques, materials, and craftsmanship.
Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer
| Step | Verification Action | Purpose | Recommended Tools/Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Confirm Legal Business Registration | Validate the entity’s legitimacy in China | Request business license (营业执照) and verify via China’s National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (http://www.gsxt.gov.cn) |
| 2 | Conduct Onsite Factory Audit | Physically inspect production capabilities | Hire a third-party inspection firm (e.g., SGS, QIMA, or SourcifyChina’s audit team) to verify facility, equipment, workforce, and workflow |
| 3 | Review Production Process Documentation | Confirm use of traditional methods | Request process flowcharts, material sourcing records, and artisan certifications (e.g., for cloisonné or Yixing clay pottery) |
| 4 | Verify IP & Heritage Claims | Avoid misrepresentation of cultural heritage | Cross-reference claims with local cultural bureaus or UNESCO heritage lists; request proof of generational craftsmanship (e.g., family workshop lineage) |
| 5 | Audit Supply Chain Transparency | Ensure ethical sourcing of raw materials | Require traceability records for materials (e.g., kaolin for porcelain, real silk, natural lacquer) |
| 6 | Evaluate Export Experience | Confirm ability to handle international logistics | Review past export documentation (B/L, COO, commercial invoices) and client references from Western markets |
| 7 | Assess Quality Control Systems | Minimize defect risk | Request QC protocols, AQL standards, and in-line inspection reports |
How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
| Indicator | Trading Company | True Factory |
|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists “trade,” “import/export,” or “agency” | Lists “manufacturing,” “production,” or specific product codes (e.g., C3360 for metal crafts) |
| Facility Ownership | No production floor; office-only space | Owns machinery, molds, kilns, or looms; employs in-house artisans |
| Pricing Structure | Higher margins; quotes vary frequently | Lower base cost; quotes tied to raw material + labor + overhead |
| Lead Time Control | Dependent on third-party suppliers; longer, variable lead times | Direct control over scheduling; consistent lead times |
| Customization Capability | Limited; relies on supplier availability | Offers mold development, material substitution, design adaptation |
| Staff Expertise | Sales-focused; limited technical knowledge | Engineers, master artisans, and QC technicians on site |
| Factory Photos & Videos | Generic or stock imagery; no real-time footage | Real-time video calls showing active production lines and raw materials |
Key Insight: While trading companies are not inherently unreliable, they add layers of cost and communication risk. For high-value, culturally sensitive items, direct factory partnerships ensure authenticity and control.
Red Flags to Avoid
| Red Flag | Risk Implication | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| ❌ Claims of “2000-year-old factory still operating” | Historically impossible; indicates misinformation or fraud | Disqualify supplier immediately; verify historical claims through academic or cultural sources |
| ❌ Unwillingness to conduct a video audit or onsite visit | Likely a front company or middleman with no production control | Require a third-party inspection before sample or PO release |
| ❌ No physical address or factory tour access | High risk of fraud or virtual supplier | Use Google Earth, Baidu Maps, and local verification services to confirm location |
| ❌ Inconsistent product quality in samples | Indicates outsourcing to multiple unvetted workshops | Implement AQL 1.0 or stricter inspection; require batch consistency testing |
| ❌ Pressure for large upfront payments (e.g., 100% TT before shipment) | Cash-flow scam risk | Use secure payment methods (e.g., 30% deposit, 70% against BL copy or LC) |
| ❌ Lack of English-speaking technical staff | Communication gaps in QC and customization | Require bilingual QC reports and assign a dedicated project manager |
| ❌ Overuse of terms like “dynasty-certified” or “imperial replica” without proof | Marketing hype; potential IP or customs issues | Request documentation from cultural authorities or museums (if applicable) |
Best Practices for Sourcing Authenticity
- Partner with Local Experts: Engage sourcing consultants familiar with regional craft hubs (e.g., Jingdezhen for porcelain, Suzhou for silk, Foshan for bronze ware).
- Require Artisan Attestations: For handcrafted items, request signed statements from master craftsmen or workshop heads.
- Use Blockchain for Provenance (Emerging 2026 Trend): Pilot suppliers offering digital traceability logs for materials and craftsmanship.
- Register Designs & Trademarks: Protect your brand against copycats in China via the China National IP Administration (CNIPA).
Conclusion
Sourcing products inspired by ancient Chinese manufacturing offers differentiation and premium market positioning—but only if authenticity and integrity are assured. Global procurement managers must apply rigorous due diligence to separate fact from folklore. By verifying legal status, conducting onsite audits, and identifying true manufacturing capability, buyers can build resilient, ethical, and culturally respectful supply chains.
SourcifyChina Recommendation: Prioritize suppliers in designated “Intangible Cultural Heritage” zones and insist on transparent, auditable production trails. In 2026, authenticity is not just aesthetic—it’s compliance.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultants
Q2 2026 | For Internal Procurement Use Only
www.sourcifychina.com | [email protected]
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Advanced China Manufacturing Landscape 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Leadership | Q1 2026 Edition
Strategic Imperative: Navigating China’s Evolving Manufacturing Ecosystem
China’s manufacturing sector has undergone radical transformation by 2026, driven by AI-integrated production, carbon-neutral compliance mandates, and geopolitical supply chain restructuring. Procurement teams face unprecedented complexity in verifying factory capabilities, ESG adherence, and technical expertise. Traditional sourcing methods now consume 17–22% of procurement cycles (per Gartner 2025 Supply Chain Survey), directly impacting time-to-market and cost competitiveness.
Why SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List Eliminates Sourcing Friction
Our AI-validated supplier network solves 2026’s critical procurement bottlenecks. Unlike unverified directories or fragmented RFQ processes, the Pro List delivers pre-qualified manufacturers with real-time compliance data, reducing risk and accelerating procurement cycles.
Time Savings Breakdown: Pro List vs. Traditional Sourcing
| Activity | Traditional Sourcing (Days) | SourcifyChina Pro List (Days) | Reduction |
|---|---|---|---|
| Factory Vetting & Capability Audit | 28–42 | 3–5 | 85%↓ |
| Compliance Verification (ISO 14064, CBAM) | 15–20 | 1–2 | 90%↓ |
| Technical Feasibility Assessment | 10–14 | 2–3 | 78%↓ |
| Total Cycle Time | 53–76 | 6–10 | ≥87%↓ |
Source: SourcifyChina Client Data (Q4 2025), n=142 multinational engagements
Key Advantages Driving 2026 Procurement Efficiency:
- Dynamic Compliance Tracking: Real-time updates on China’s 2026 ESG regulations (e.g., CBAM Phase III, Digital Carbon Passports).
- AI-Powered Match Scoring: Algorithmic alignment of your technical specs with factory capabilities (precision: 94.7% vs. industry avg. 68%).
- Zero-Trust Verification: On-ground audits + blockchain-tracked production data (eliminating “paper factory” risks).
- Predictive Lead Time Analytics: Machine learning forecasts delays from regional policy shifts (e.g., Yangtze River Delta EV component quotas).
Procurement Impact: Clients deploying the Pro List achieve 3.2x faster supplier onboarding and 22% lower total landed costs by avoiding compliance penalties and production rework (McKinsey Procurement Index, Jan 2026).
Your Competitive Edge Starts Now
In 2026, procurement excellence hinges on speed without compromise. Every day spent on manual supplier vetting erodes your market advantage. SourcifyChina’s Pro List isn’t a tool—it’s your strategic insurance against supply chain volatility.
Call to Action: Secure Your 2026 Sourcing Advantage
Stop paying the hidden cost of unverified suppliers.
✅ Request your customized Pro List report—tailored to your category, volume, and compliance requirements.
✅ Skip 50+ hours of internal vetting with our ready-to-source supplier shortlist.
✅ Lock in Q2 2026 capacity before peak manufacturing demand surges.
📧 Contact our Sourcing Strategy Team Today:
→ Email: [email protected]
→ WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Include “PRO LIST 2026” in your subject line for priority access to our Q1 capacity dashboard.
SourcifyChina | Precision Sourcing for the Next-Generation Supply Chain
Verified. Optimized. Future-Proof.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All rights reserved. | www.sourcifychina.com
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.


