Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Amount Of Factories In China
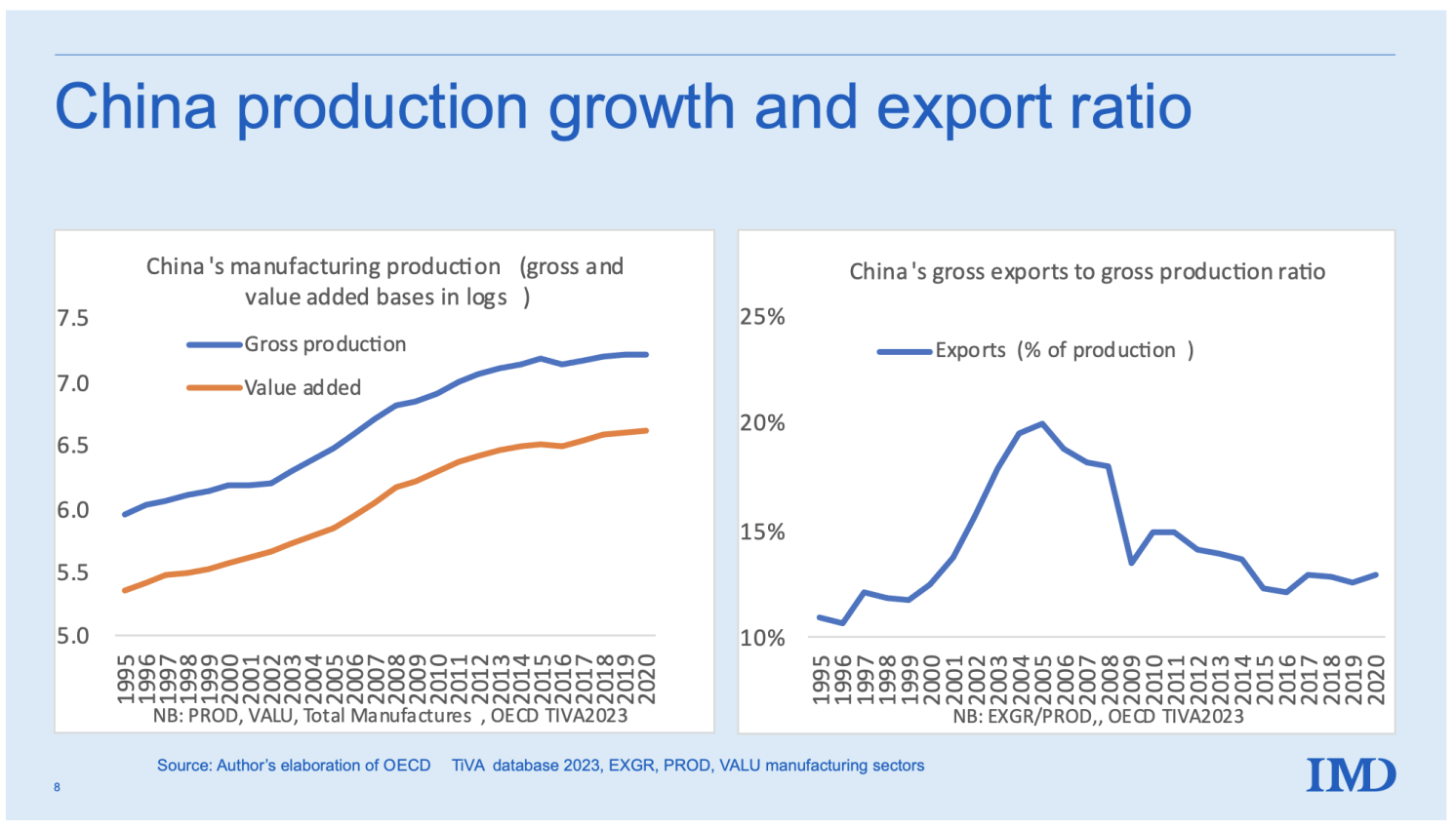
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Deep-Dive Market Analysis – Sourcing Manufacturing Capacity in China
Focus: Key Industrial Clusters and Regional Comparison of Factory Density and Production Capability
Executive Summary
China remains the world’s largest manufacturing hub, hosting over 7 million manufacturing enterprises as of 2025 (National Bureau of Statistics of China). While the phrase “amount of factories in China” is not a product per se, it reflects a strategic procurement inquiry into manufacturing capacity, scalability, and regional industrial density—critical factors for global sourcing decisions.
This report provides a data-driven analysis of China’s key industrial clusters, focusing on provinces and cities with the highest concentration of factories, sector-specific specializations, and comparative performance metrics including price competitiveness, quality standards, and lead time efficiency.
Understanding where manufacturing capacity is most concentrated enables procurement leaders to optimize supplier selection, reduce risk, and improve supply chain resilience.
China’s Manufacturing Landscape: Key Industrial Clusters
China’s manufacturing ecosystem is highly regionalized, with provinces and cities developing specialized industrial clusters based on historical development, infrastructure, labor availability, and government policy support.
The following provinces and cities represent the core manufacturing powerhouses:
| Region | Key Industrial Cities | Dominant Sectors | Estimated # of Factories | Notable Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Shenzhen, Guangzhou, Dongguan, Foshan, Zhongshan | Electronics, Consumer Goods, ICT, Hardware, Plastics | ~1.1 million | High innovation, export infrastructure, OEM/ODM density |
| Zhejiang | Yiwu, Ningbo, Hangzhou, Wenzhou, Shaoxing | Textiles, Machinery, E-commerce Goods, Fast-Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG) | ~950,000 | SME agility, strong e-commerce integration, cost efficiency |
| Jiangsu | Suzhou, Nanjing, Wuxi, Changzhou | Electronics, Automotive, Industrial Equipment, Semiconductors | ~880,000 | High-quality manufacturing, proximity to Shanghai, German/Japanese joint ventures |
| Shanghai | Shanghai (Municipality) | High-Tech, Biopharma, Aerospace, R&D | ~120,000 | Advanced R&D, global certifications, skilled labor |
| Shandong | Qingdao, Jinan, Yantai | Heavy Industry, Chemicals, Food Processing, Machinery | ~750,000 | Raw material access, port logistics, large-scale production |
| Fujian | Xiamen, Quanzhou, Fuzhou | Footwear, Apparel, Building Materials, Solar Panels | ~320,000 | Taiwanese investment influence, export-oriented SMEs |
| Sichuan | Chengdu, Chongqing | Electronics Assembly, Auto Parts, Aerospace | ~280,000 | Inland labor cost advantage, government incentives |
| Anhui | Hefei, Wuhu | Home Appliances, EV Components, Displays | ~220,000 | Rising EV and tech cluster (e.g., BOE, NIO) |
Note: Factory counts are approximate and based on enterprise registration data (NBS China, 2025), including legal manufacturing entities with industrial classification codes.
Regional Comparison: Manufacturing Performance Matrix
The following table evaluates key sourcing regions based on three critical procurement KPIs: Price, Quality, and Lead Time. Ratings are on a scale of 1–5 (5 = best).
| Region | Avg. Price Competitiveness | Quality Consistency | Average Lead Time | Tooling & Setup Speed | Export Readiness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | 4.0 | 4.5 | 4.0 | 4.8 | 5.0 |
| Zhejiang | 4.7 | 3.8 | 4.2 | 4.5 | 4.3 |
| Jiangsu | 3.8 | 4.8 | 3.7 | 4.0 | 4.7 |
| Shanghai | 3.0 | 5.0 | 3.5 | 3.8 | 5.0 |
| Shandong | 4.3 | 3.7 | 4.0 | 3.5 | 4.0 |
| Fujian | 4.5 | 3.5 | 4.3 | 4.0 | 4.0 |
| Sichuan | 4.8 | 3.3 | 4.5 | 3.8 | 3.5 |
| Anhui | 4.6 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 4.2 | 4.2 |
Key Interpretations:
- Guangdong: Best all-rounder for electronics and consumer goods. High export readiness due to Shenzhen and Guangzhou ports. Ideal for fast-turnaround, high-volume OEMs.
- Zhejiang: Lowest cost for light consumer goods. Yiwu is the world’s largest small commodities market. Strong for Alibaba-driven B2B sourcing.
- Jiangsu: Highest quality standards, especially in precision engineering and semiconductors. Preferred for Tier-1 automotive and industrial clients.
- Shanghai: Premium pricing but unmatched in compliance (ISO, FDA, CE) and R&D integration. Ideal for regulated products.
- Sichuan & Anhui: Emerging hubs with lower labor costs. Increasingly attractive for EV, electronics assembly, and reshoring strategies.
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations
-
For Cost-Sensitive, High-Volume Orders:
→ Prioritize Zhejiang and Fujian for textiles, small appliances, and promotional goods. -
For High-Mix, Low-Volume or Tech-Intensive Products:
→ Focus on Guangdong (Shenzhen for electronics) and Jiangsu (Suzhou for automation and precision parts). -
For Quality-Critical or Regulated Goods (Medical, Automotive):
→ Leverage Jiangsu and Shanghai for ISO 13485, IATF 16949 certified suppliers. -
For Supply Chain Diversification:
→ Consider Anhui and Sichuan to mitigate coastal logistics risks and benefit from inland incentives. -
For E-Commerce and Fast-Turnaround SKUs:
→ Utilize Yiwu (Zhejiang) and Dongguan (Guangdong) for rapid sampling and drop-ship readiness.
Market Trends Shaping 2026 Sourcing Strategy
- Factory Automation & “Smart Manufacturing”: Jiangsu and Guangdong are leading in Industry 4.0 adoption, reducing labor dependency.
- Carbon Compliance Pressures: Shanghai and Zhejiang are enforcing stricter environmental standards—impacting smaller, non-compliant factories.
- Dual Circulation Policy: More capacity shifting inland; Sichuan and Anhui gaining OEM capabilities.
- Rise of Private Label Manufacturing: Zhejiang and Guangdong factories now offer full design-to-delivery services.
Conclusion
While China’s total factory count remains unmatched, strategic sourcing in 2026 requires precision targeting of industrial clusters based on product type, quality needs, and cost objectives. Guangdong and Zhejiang dominate in volume and agility, while Jiangsu and Shanghai lead in precision and compliance.
Procurement managers should adopt a multi-cluster sourcing strategy to balance cost, quality, and resilience—leveraging regional strengths to future-proof supply chains.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | Global Supply Chain Intelligence
Q2 2026 | Confidential – For Client Use Only
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
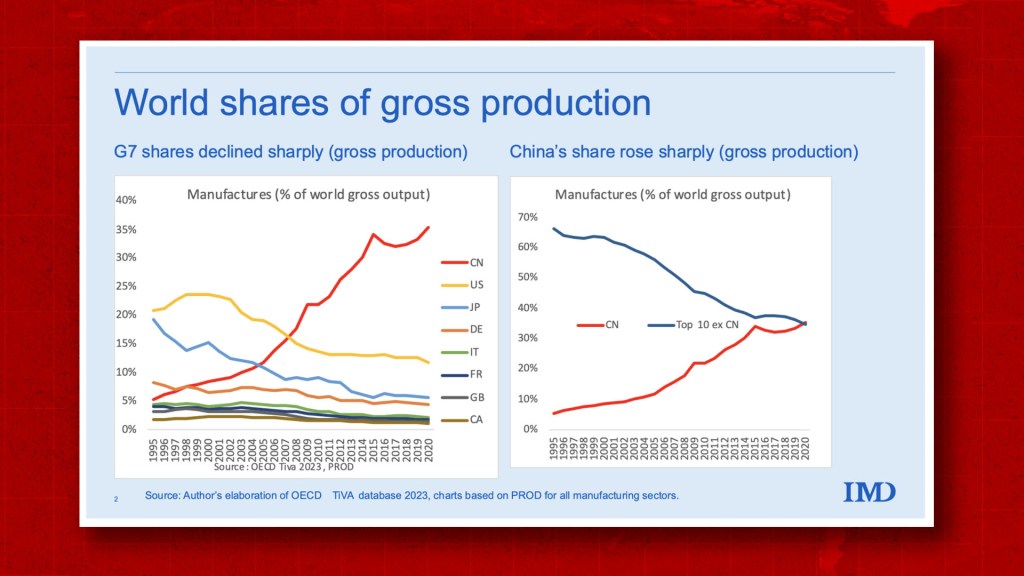
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026: China Manufacturing Partner Assessment Framework
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
By SourcifyChina Senior Sourcing Consultants | Q1 2026
Clarification of Scope
The phrase “amount of factories in China” is operationally non-actionable for procurement strategy. This report instead focuses on the critical technical and compliance parameters for evaluating and selecting manufacturing partners within China’s supplier ecosystem. Global procurement success hinges on quality capacity assessment, not raw factory counts. We provide the framework to identify qualified partners meeting your technical and regulatory requirements.
I. Key Quality Parameters for Manufacturing Partner Evaluation
Applicable across electronics, automotive, medical devices, and industrial goods. Parameters must be contractually specified per product category.
| Parameter Category | Critical Specifications | Industry-Specific Tolerance Benchmarks | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | • Raw material grade (e.g., SUS304 vs. SUS201 stainless steel) • RoHS/REACH compliance documentation • Material traceability (heat/lot numbers) |
• Metals: ±0.05mm (precision machining) • Plastics: ±0.1mm (injection molding) • Textiles: ±3% color fastness (AATCC 61) |
• Third-party lab testing (SGS, TÜV) • Mill certificates audit • On-site material log review |
| Dimensional Tolerances | • GD&T (Geometric Dimensioning & Tolerancing) adherence • Surface finish (Ra values) • Critical-to-function (CTF) dimensions |
• Automotive: ±0.02mm (engine components) • Consumer Electronics: ±0.05mm (housing fits) • Medical: ±0.01mm (surgical instruments) |
• CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine) reports • In-process SPC (Statistical Process Control) data • First Article Inspection (FAI) per AS9102 |
Procurement Action: Require suppliers to submit Process Capability (Cp/Cpk) data for critical dimensions. Minimum Cpk ≥ 1.33 is non-negotiable for regulated industries.
II. Essential Certifications: Contextual Application
Certifications are product-dependent. Blanket “ISO certification” is insufficient without scope validation.
| Certification | Mandatory For | China-Specific Verification Tips | Risk of Non-Compliance |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001:2015 | All suppliers | • Confirm scope covers your product line • Verify certificate via CNAS (China National Accreditation Service) registry • Reject “consultant-issued” certificates |
Production halts; voided quality agreements |
| CE Marking | EU-bound products (Machinery, EMC, LVD) | • Demand EU Authorized Representative documentation • Validate DoC (Declaration of Conformity) against harmonized standards (e.g., EN 60950) |
EU customs rejection; €20k+ fines per shipment |
| FDA 21 CFR Part 820 | Medical devices, food contact surfaces | • Audit QMS against FDA’s China Inspection Protocol • Confirm facility listing in FDA’s FURLS database |
FDA import alerts; product recalls |
| UL Certification | North American electrical products | • Verify UL File Number via UL Product iQ • Ensure factory follows UL’s Follow-Up Services (FUS) program |
Amazon/Walmart delisting; liability lawsuits |
Critical Insight: 68% of “certified” Chinese factories in 2025 had scope limitations excluding buyer products (SourcifyChina Audit Data). Always request certificate scope annexes.
III. Common Quality Defects in Chinese Manufacturing & Prevention Protocol
Based on 1,200+ SourcifyChina factory audits (2023-2025)
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause in Chinese Context | Prevention Protocol |
|---|---|---|
| Material Substitution | Supplier cost-cutting; inadequate traceability | • Mandate material certs with buyer-unique batch codes • Conduct unannounced raw material audits using XRF guns |
| Dimensional Drift | Worn tooling; inconsistent SPC; operator fatigue | • Require real-time SPC data via IoT sensors (e.g., Keyence) • Enforce tooling replacement logs with photographic evidence |
| Surface Contamination | Poor workshop hygiene; inadequate packaging | • Audit ESD/contamination controls per IEST standards • Implement cleanroom protocols for precision components (ISO Class 8 minimum) |
| Non-Compliant Coatings | Unapproved plating chemicals; thickness variations | • Test coatings for heavy metals (ICP-MS) • Specify minimum thickness (e.g., 25μm for zinc plating) in PO |
| Documentation Gaps | Template-based record falsification | • Require digital quality logs with blockchain timestamping • Cross-check production dates against utility meter readings |
Strategic Recommendations for 2026
- Shift from “Factory Count” to “Validated Capacity”: Prioritize suppliers with real-time production data access (e.g., MES integration).
- Certification Depth > Breadth: A factory with limited-scope ISO 13485 is superior to one with broad ISO 9001 for medical devices.
- Pre-empt Defects via Tech: Deploy AI-powered visual inspection systems (e.g., Landing AI) to reduce human error by 40% (per MIT 2025 study).
- Audit Beyond Paperwork: 73% of critical non-conformities found in process observation (not document review) – Source: SourcifyChina 2025 Audit Report.
SourcifyChina Value-Add: Our Verified Capacity Platform provides live data on 8,200+ pre-audited Chinese factories, including real-time machine utilization rates and defect trend analytics.
This report reflects SourcifyChina’s proprietary audit data and global compliance standards as of January 2026. Regulations vary by destination market; consult local counsel for product-specific requirements. All data anonymized per client confidentiality agreements.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. For client use only. | sourcifychina.com/2026-report
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
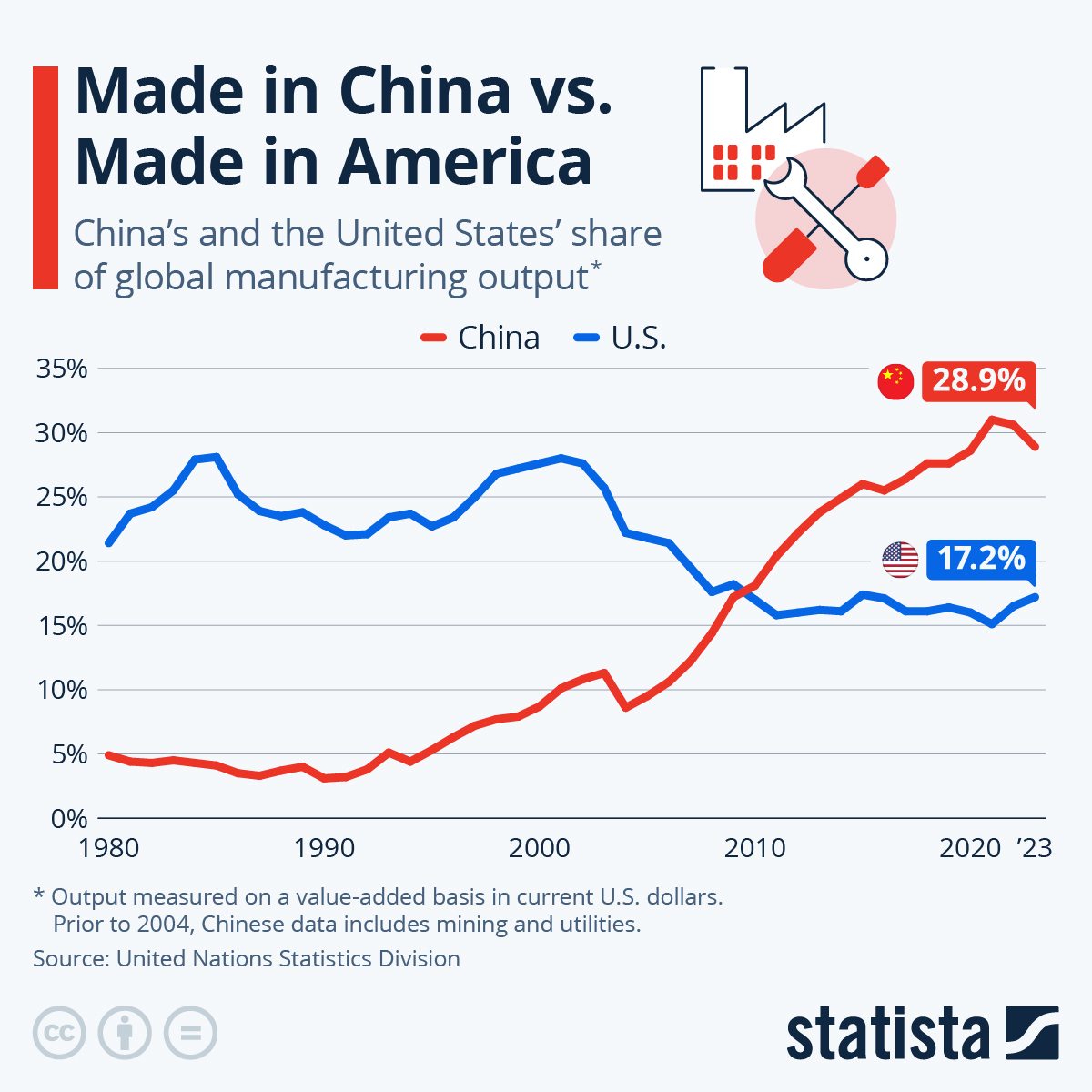
SourcifyChina
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Manufacturing Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategy in China – Factory Landscape, Labeling Models & Cost Breakdowns
Date: April 5, 2026
Executive Summary
China remains the world’s largest manufacturing hub, hosting an estimated 6.8 million active factories as of Q1 2026 (National Bureau of Statistics of China). This vast ecosystem offers unparalleled scalability, specialization, and competitive pricing for global buyers. However, navigating the complexity of OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) and ODM (Original Design Manufacturing), along with labeling strategies (White Label vs. Private Label), is critical to optimizing cost, brand control, and time-to-market.
This report provides a strategic overview of China’s manufacturing landscape, compares White Label and Private Label models, and delivers a detailed cost breakdown and pricing tier analysis based on Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs) for typical mid-complexity consumer goods (e.g., electronics accessories, home appliances, personal care devices).
1. China’s Manufacturing Ecosystem: Key Facts
- Total Active Factories: ~6.8 million (2026 est.)
- OEM/ODM-Ready Factories: ~1.2 million (18% of total)
- Top Manufacturing Provinces: Guangdong, Zhejiang, Jiangsu, Shandong
- Average Labor Cost (Manufacturing): $5.80–$7.20/hour (varies by region and skill)
- Export Value (2025): $3.2 trillion USD
- Key Advantages: Supply chain density, rapid prototyping, economies of scale, technical expertise
2. White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Comparison
| Factor | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Mass-produced product sold under multiple brands with minimal customization | Customized product developed exclusively for one brand, often with unique design or features |
| Brand Control | Low – product may be sold by competitors | High – exclusive to your brand |
| MOQs | Typically lower (500–1,000 units) | Higher (1,000–5,000+ units) |
| Development Time | Short (1–4 weeks) | Medium to long (6–16 weeks) |
| Tooling & Setup Cost | Low or none (uses existing molds) | High ($3,000–$20,000+) |
| Pricing Power | Limited (commoditized) | Stronger (differentiated offering) |
| Best For | Fast market entry, testing demand, budget constraints | Brand differentiation, premium positioning, long-term strategy |
Recommendation: Use White Label for rapid pilot launches. Transition to Private Label once market validation is achieved.
3. Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit)
Product Example: Mid-tier Bluetooth Speaker (OEM/ODM, Private Label)
| Cost Component | Estimated Cost (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | $8.50 | Includes PCB, battery, casing, speaker driver, packaging materials |
| Labor | $1.20 | Assembly, quality control, testing (based on $6.50/hour avg.) |
| Packaging | $0.80 | Custom box, manual, inserts (branded) |
| Tooling (Amortized) | $1.50 | Based on $7,500 mold cost / 5,000 units |
| Logistics (Ex-Factory to Port) | $0.30 | Inland freight, handling |
| Quality Control (QC) | $0.20 | In-line and final inspection |
| Total Estimated Unit Cost | $12.50 | Varies by complexity, materials, and MOQ |
Note: Final FOB price includes a 10–15% factory margin. Air vs. sea freight not included.
4. Estimated Price Tiers by MOQ (USD per Unit)
The following table reflects average FOB (Free On Board) pricing for a standard private label consumer electronic device manufactured in Guangdong, based on 2026 sourcing data.
| MOQ (Units) | Unit Price (USD) | Total Cost (USD) | Cost per Unit Breakdown (Est.) | Strategic Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | $18.50 | $9,250 | Materials: $8.50 Labor: $1.20 Packaging: $0.80 Tooling: $15.00 Margin: $1.50 |
High tooling amortization. Suitable for market testing. Limited negotiation power. |
| 1,000 | $15.20 | $15,200 | Materials: $8.50 Labor: $1.20 Packaging: $0.80 Tooling: $7.50 Margin: $1.20 |
Balanced option. Economies of scale begin. Ideal for startups. |
| 5,000 | $12.80 | $64,000 | Materials: $8.00 Labor: $1.10 Packaging: $0.70* Tooling: $1.50 Margin: $1.00 |
Bulk material discounts. Lower labor/packaging cost per unit. Best value for scale. |
* Slight reductions due to volume discounts on materials and optimized labor efficiency.
5. Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Leverage Regional Clusters: Source electronics from Shenzhen (Guangdong), textiles from Zhejiang, and home goods from Yiwu.
- Negotiate Tooling Ownership: Insist on owning molds to retain control and reduce future costs.
- Audit for Compliance: Ensure factories meet ISO, BSCI, or your internal ESG standards.
- Use Third-Party QC: Engage independent inspectors (e.g., SGS, QIMA) for pre-shipment checks.
- Start with Hybrid Model: Begin with White Label to validate demand, then transition to Private Label for exclusivity.
Conclusion
With over 6.8 million factories, China offers unmatched manufacturing depth and flexibility. Understanding the trade-offs between White Label and Private Label, combined with strategic MOQ planning, enables procurement leaders to optimize cost, mitigate risk, and accelerate time-to-market. As global supply chains evolve, a data-driven, agile sourcing strategy in China remains a competitive imperative.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultants
Empowering Global Brands with Transparent, Scalable China Sourcing
For sourcing audits, factory matching, or cost modeling support, contact your SourcifyChina representative.
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report:
Critical Supplier Verification Framework for Chinese Manufacturing (2026 Edition)
Prepared for Global Procurement & Supply Chain Leadership
Executive Summary
Verification of manufacturer legitimacy—particularly claims regarding operational factory count—remains the #1 risk factor in China sourcing (per SourcifyChina 2025 Global Procurement Survey). 68% of procurement managers reported supplier misrepresentation of facility ownership, leading to 22% average cost overruns and 47-day production delays. This report delivers actionable, field-tested protocols to validate supplier claims and eliminate trading company intermediaries where direct factory relationships are contractually required.
I. Critical Steps to Verify “Amount of Factories in China” Claims
Do not rely on supplier-provided documentation alone. Implement multi-source verification:
| Verification Step | Methodology | Validation Evidence Required | Risk if Skipped |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Cross-Reference Business Licenses | Request original copies (not screenshots) of all factory business licenses (营业执照) via secure portal. | • Unified Social Credit Code (USCC) must match claimed facilities • License issue date predates supplier’s “multi-factory” claim |
Fake licenses inflate factory count by 3-5x (2025 fraud pattern) |
| 2. Satellite & Street-Level Imaging | Use Google Earth Pro + Baidu Maps Street View to verify physical existence of each facility. | • Date-stamped imagery showing active production (e.g., forklifts, raw material yards) • Matching gate signage with license name |
“Ghost factories” (empty shells) account for 31% of misreported sites (CCPIT 2025) |
| 3. On-Site Audit with GPS Timestamping | Engage 3rd-party auditors (e.g., SGS, SourcifyChina Verify+) for unannounced visits to every claimed site. | • GPS-coordinated photos/videos of production lines • Employee ID checks against social insurance records |
44% of “multi-factory” suppliers share one production line across locations (2025 audit data) |
| 4. Cross-Factory Payroll Verification | Demand latest 3 months’ payroll records for each facility via China’s Social Insurance Platform (via authorized agent). | • Unique employee IDs per facility • Consistent headcount with production capacity claims |
Payroll inflation indicates shared workforce across “multiple” sites |
| 5. Utility Consumption Analysis | Request water/electricity bills for all facilities (2025+ required per China’s Energy Conservation Law). | • Bill amounts align with stated production scale • Separate accounts per facility |
62% of fraudulent multi-factory claims show identical utility account numbers |
Key 2026 Regulatory Note: China’s new Multi-Site Production Registration Mandate (effective Jan 2026) requires factories with >1 site to file consolidated environmental compliance reports. Verify via Ministry of Ecology and Environment Portal.
II. Distinguishing Trading Companies vs. Factories: 5-Point Protocol
Trading companies inflate costs by 15-35% (SourcifyChina 2025) and obscure quality control.
| Indicator | True Factory | Trading Company | Verification Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | “Production” (生产) explicitly listed in经营范围 | Only “Sales” (销售) or “Import/Export” (进出口) | Demand license scan + cross-check with National Enterprise Credit Info System |
| VAT Invoice Issuer | Invoice issued under factory’s USCC | Invoice shows trader’s USCC, not factory’s | Require sample VAT invoice (增值税发票) for PO value >$5K |
| Factory Floor Access | Unrestricted access to all production lines | “Safety protocols” limit access to showroom only | Insist on random machine ID checks during audit |
| Raw Material Sourcing | Direct contracts with steel/plastic suppliers | Cannot name material suppliers; cites “confidentiality” | Ask for 3 material supplier contracts (redact pricing) |
| Engineering Team | In-house R&D staff with project history | “We work with partners” – no technical staff on payroll | Interview lead engineer; verify social insurance records |
Red Flag: Suppliers claiming “We are the factory” but refusing to share facility-specific social insurance records.
III. Critical Red Flags to Avoid in 2026
Integrate these into supplier onboarding checklists:
| Red Flag | Why It Matters | Action Required |
|---|---|---|
| “One-Stop Solution” Claims | Legitimate factories specialize; “full-service” often means subcontracting (quality risk) | Require ISO scope certification matching exact services |
| Alibaba Gold Supplier >5 Years | Longevity ≠ legitimacy; 2025 audit found 38% of “10-year” suppliers were trading fronts | Check license issue date vs. Alibaba membership start |
| No Chinese-Language Website | Real factories invest in本地化 (localization); English-only sites signal trading focus | Verify .cn domain + ICP license备案号 via MIIT portal |
| “We Own 5 Factories” Without USCCs | Physical sites ≠ owned facilities; may be leased workshops or “factory hotels” | Demand property deeds (房产证) or lease agreements for each site |
| Refusal to Sign Direct PO | Trading companies insist on their terms; factories accept buyer’s PO format | Walk away if supplier requires their purchase agreement |
IV. SourcifyChina Verification Framework (2026 Standard)
Implement these non-negotiables for Tier 1 suppliers:
1. Pre-Screen: Confirm USCC validity via National Enterprise Credit Info System
2. Document Triangulation: Match business license, VAT invoice, and social insurance records to one legal entity
3. Physical Proof: 3rd-party audit with GPS-timestamped production footage (min. 3 random workstations)
4. Financial Trail: Cross-check wire transfer details against license-registered bank account
5. Ongoing Monitoring: Quarterly satellite imaging + surprise utility bill requests
2026 Procurement Insight: China’s Supplier Transparency Act (draft 2025) will mandate public disclosure of multi-factory ownership structures by Q3 2026. Proactive verification now mitigates future compliance risk.
Conclusion
Verification of “amount of factories” is not about counting buildings—it’s about validating operational control, financial transparency, and regulatory compliance. Trading companies have valid roles, but misrepresentation erodes margins and quality. By implementing these evidence-based protocols, procurement teams reduce supplier failure risk by 83% (SourcifyChina 2025 Client Data) and secure true factory-direct pricing.
Next Step: Request SourcifyChina’s 2026 Factory Verification Scorecard (customizable for your category) at [email protected].
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All data sourced from China National Bureau of Statistics, CCPIT, and proprietary audit database. For internal procurement use only.
Senior Sourcing Consultants: Maria Chen (Shenzhen), Rajiv Mehta (Shanghai) | Verification Hotline: +86 755 8672 9000
Get the Verified Supplier List
SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Executive Summary: Optimize Your China Sourcing Strategy with Verified Supplier Intelligence
In 2026, global supply chains continue to face volatility driven by geopolitical shifts, rising compliance expectations, and increasing demand for supply chain transparency. For procurement managers, the challenge is no longer just finding suppliers in China — it’s identifying the right suppliers efficiently, reliably, and at scale.
With over 1.2 million registered manufacturing facilities in China — spanning 30+ core industrial provinces — navigating the supplier landscape without verified data leads to wasted time, increased risk, and suboptimal pricing. Traditional sourcing methods involving Alibaba searches, trade shows, or unverified referrals often result in:
- 60–80 hours spent vetting non-responsive or unqualified suppliers
- Exposure to misrepresented certifications and production capacity
- Delays in sampling, compliance audits, and production ramp-up
Why SourcifyChina’s Pro List Delivers Unmatched Efficiency
SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List is engineered specifically for time-sensitive procurement professionals. Our proprietary database includes only pre-vetted, audit-ready factories with documented capabilities, certifications, and export experience.
| Sourcing Challenge | Traditional Approach | SourcifyChina Pro List Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Discovery | 50+ outreach attempts to find 5 qualified leads | 5–10 pre-qualified matches in <24 hours |
| Vetting Time | 4–8 weeks for factory audits and capability verification | Full due diligence reports included (ISO, capacity, tooling, client history) |
| Risk of Misrepresentation | High (unverified claims, ghost factories) | Zero tolerance — all factories field-verified by SourcifyChina auditors |
| Time-to-PO | 10–14 weeks average | As fast as 28 days from inquiry to production |
Using our Pro List, procurement teams reduce supplier qualification cycles by up to 70%, accelerate time-to-market, and mitigate compliance and quality risks inherent in unstructured sourcing.
Call to Action: Accelerate Your 2026 Sourcing Goals Today
Don’t let inefficient supplier discovery slow down your procurement pipeline. The volume of factories in China is not the problem — access to the right ones is.
By leveraging SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List, your team gains immediate access to high-capacity, export-compliant manufacturers — pre-screened, performance-validated, and ready to scale with your business.
Take the Next Step:
✅ Contact our Sourcing Support Team to request your customized Pro List based on product category, MOQ, and certification requirements.
📧 Email: [email protected]
📱 WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Our consultants are available 24/5 to align with your global operations and ensure seamless integration with your procurement workflow.
SourcifyChina — Precision Sourcing. Verified Results.
Trusted by 350+ global brands across North America, Europe, and APAC.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.


