The global aluminum PCB market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand in high-power LED lighting, automotive electronics, and power supplies. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the aluminum PCB market was valued at USD 1.76 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 2.61 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of approximately 6.8% during the forecast period. This expansion is fueled by the superior thermal conductivity and durability of aluminum substrates, making them ideal for applications requiring efficient heat dissipation. As industries increasingly shift toward energy-efficient and compact electronic systems, the need for reliable aluminum PCB manufacturers has never been greater. In this context, identifying the top players in the market becomes crucial for OEMs and design engineers seeking high-performance, thermally efficient circuit solutions. Based on production capacity, global reach, innovation, and industry reputation, the following are the top 10 aluminum PCB manufacturers shaping the future of electronic packaging.
Top 10 Aluminum Pcb Board Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Aluminum PCB – Amitron
Domain Est. 1995
Website: amitron.com
Key Highlights: Amitron is an experienced aluminum PCB manufacturer. Amitron has been producing Aluminum Printed Circuit Boards (also called Metal base PCBs) for over a decade….
#2 China PCB Prototype & Fabrication Manufacturer
Domain Est. 2012
#3 AdvancedPCB
Domain Est. 2018
Website: advancedpcb.com
Key Highlights: Prototype to Production PCBs from AdvancedPCB. Choose us as your trusted PCB board manufacturer and circuit board manufacturer….
#4 Multi Circuit Boards
Website: multi-circuit-boards.eu
Key Highlights: Multi Circuit Boards (Multi-CB) is a leading European supplier of high-tech low-cost PCB / multilayer boards with up to 48 layers, from 1WD production time….
#5 Sierra Circuits
Domain Est. 1997
Website: protoexpress.com
Key Highlights: Sierra Circuits can manufacture your PCB and have it expedited to you within 24 hours. Full turnkey boards, with assembly and components in as fast as 5 days….
#6 PCBCart
Domain Est. 2005
Website: pcbcart.com
Key Highlights: Expert of PCB manufacturing, we proudly offer PCB making & assembly services with certified quality standards for all your needs. Free online quote!…
#7 ALLPCB
Domain Est. 2011
Website: allpcb.com
Key Highlights: Explore the ALLPCB approach to PCB manufacturing and assembly: From prototype to production, we’ve got you covered….
#8 Millennium Circuits Limited
Domain Est. 2011
Website: mclpcb.com
Key Highlights: Millennium Circuits Limited is a leading PCB supplier specializing in custom circuit boards. Trust us for top-quality PCB services. Visit our site today….
#9 Aluminum PCBs
Domain Est. 2016
Website: nextpcb.com
Key Highlights: NextPCB offers a range of metal-core PCB manufacturing services, including aluminum, copper, iron and stainless steel PCB manufacture with support for pedestal ……
#10 PCB Manufacturing & Assembly Capabilities
Website: jlcpcb.com
Key Highlights: Printed Circuit Board manufacturing and assembly capabilities, PCB technologies or design rules for guide of PCB design and production….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Aluminum Pcb Board
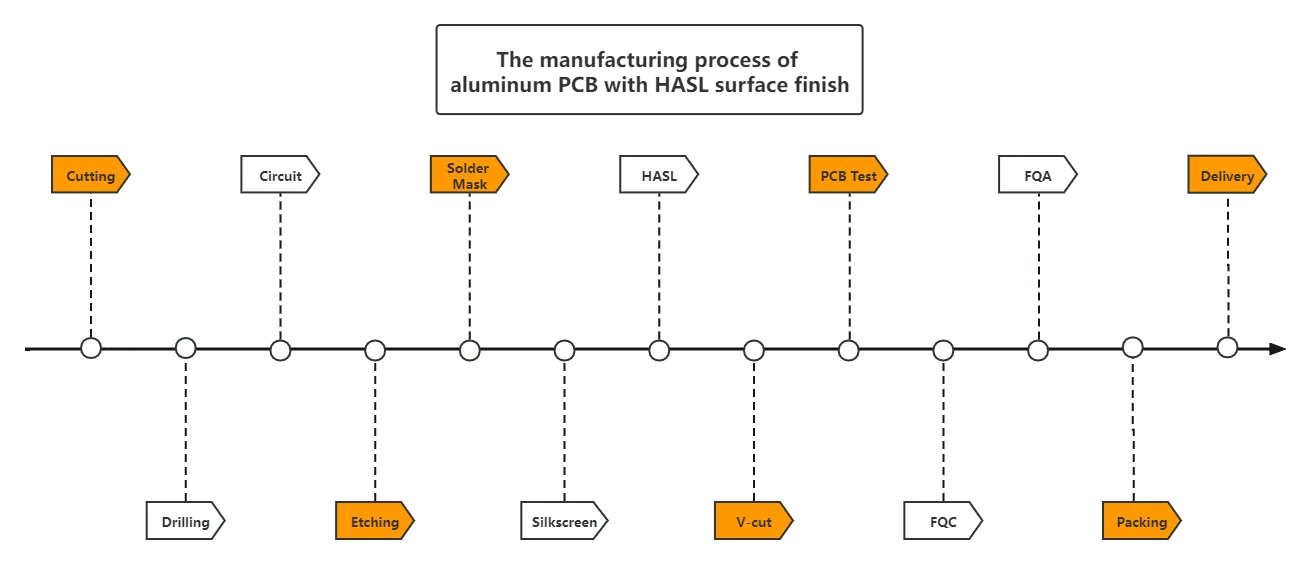
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Aluminum PCB Boards – Growth Drivers, Challenges, and Regional Outlook
The aluminum printed circuit board (PCB) market is poised for robust expansion by 2026, driven by escalating demand across high-growth industries prioritizing thermal management, energy efficiency, and reliability. This analysis examines the key trends shaping the market landscape.
H2: Key Growth Drivers for 2026
-
Explosive Growth in Electric Vehicles (EVs) and Automotive Electronics: The global shift towards electrification is the paramount driver. Aluminum PCBs are essential in EV powertrains (inverters, DC-DC converters, onboard chargers), advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), LED lighting, and infotainment systems. Their superior heat dissipation prevents component failure in the demanding under-the-hood environment. By 2026, stringent emissions regulations and falling battery costs will accelerate EV adoption, directly fueling aluminum PCB demand.
-
Dominance of LED Lighting Markets: High-power LED lighting for automotive (headlights, DRLs), general illumination, streetlights, and displays requires efficient heat sinking to maintain brightness, color consistency, and longevity. Aluminum PCBs provide the optimal thermal solution. The continued replacement of traditional lighting with energy-efficient LEDs, especially in smart cities and automotive applications, ensures sustained market growth.
-
Rise of Power Electronics and Renewable Energy: Applications like solar inverters, wind turbine converters, and industrial motor drives involve high currents and power densities generating significant heat. Aluminum PCBs offer the thermal stability and durability needed for these critical power conversion systems. The global push for renewable energy infrastructure will be a major growth vector.
-
Advancements in Thermal Management Technology: Ongoing R&D focuses on improving the thermal conductivity of dielectric layers in aluminum PCBs and developing thinner, more efficient insulating materials. This enhances heat transfer efficiency, allowing for more compact and powerful designs, meeting the demands of next-generation electronics.
-
Miniaturization and Integration: As electronic devices become smaller and more powerful, managing heat in confined spaces is critical. Aluminum PCBs enable higher component density by providing a direct thermal path to the heat sink (the metal base), facilitating miniaturization in consumer electronics, telecom infrastructure, and industrial controls.
H2: Key Challenges and Market Dynamics
-
Cost Sensitivity vs. Performance: While costs have decreased, aluminum PCBs remain more expensive than standard FR-4 PCBs. In highly cost-competitive segments, this premium can be a barrier, especially where thermal demands are lower. Manufacturers face pressure to optimize materials and processes to reduce costs without sacrificing performance.
-
Material and Supply Chain Constraints: The price volatility of aluminum and specialized dielectric materials can impact profitability. Geopolitical factors and supply chain disruptions (as seen recently) pose risks. Diversification of suppliers and strategic sourcing are crucial.
-
Design and Manufacturing Complexity: Designing for optimal thermal performance requires specialized expertise. Manufacturing processes (like precise drilling, plating, and lamination of the dielectric layer) are more complex than standard PCB fabrication, requiring specialized equipment and skilled labor, potentially limiting supply capacity.
-
Competition from Alternative Substrates: Ceramic substrates (like Al2O3, AlN) offer even higher thermal conductivity for the most extreme applications but at a significantly higher cost. Hybrid solutions and advancements in other metal-core PCBs (e.g., copper) also compete in specific niches.
H2: Regional Outlook and Competitive Landscape
- Asia-Pacific (APAC): Will remain the dominant market and manufacturing hub, driven by massive electronics manufacturing (especially China, Taiwan, South Korea), a strong automotive industry (including EVs), and government support for LED and renewable energy. China is the largest producer and consumer.
- North America and Europe: Significant growth is expected, primarily fueled by the rapid adoption of EVs, stringent energy efficiency regulations (boosting LED adoption), and investments in renewable energy and industrial automation. Demand for high-reliability and high-performance boards is strong.
- Competitive Landscape: Characterized by a mix of large, established PCB manufacturers (e.g., Bergquist, Rogers, Shinetsu, Kingboard, CMK, Nan Ya) and numerous specialized players. Competition is intense, focusing on technological innovation (higher thermal conductivity, thinner dielectrics), cost leadership, and vertical integration. Partnerships with end-equipment manufacturers are key.
H2: Conclusion: A Bright Future with Focused Innovation
The aluminum PCB market is on a strong upward trajectory towards 2026. The convergence of unstoppable megatrends – automotive electrification, LED lighting proliferation, and renewable energy expansion – creates a powerful tailwind. Success will depend on manufacturers’ ability to innovate in thermal performance and cost reduction, navigate supply chain complexities, and cater to the specific demands of high-growth application areas. While challenges exist, the fundamental need for effective thermal management in modern, high-power electronics ensures aluminum PCBs will remain a critical and growing technology platform.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Aluminum PCB Boards (Quality, IP)
When sourcing aluminum PCBs (also known as metal-core PCBs or MCPCBs), buyers often encounter significant challenges related to quality inconsistencies and intellectual property (IP) risks. Being aware of these pitfalls is essential for ensuring reliable performance and protecting proprietary designs.
Poor Thermal Performance Due to Substandard Dielectric Layers
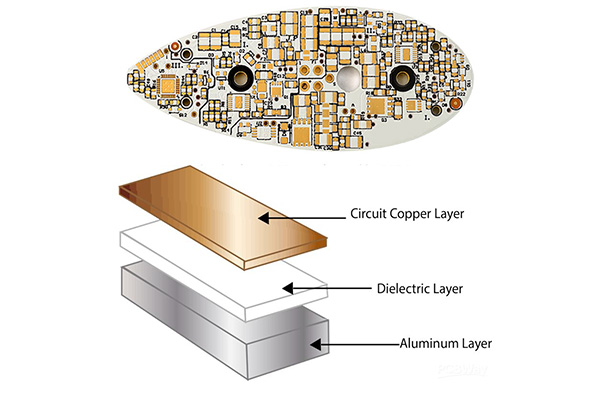
One of the primary reasons for using aluminum PCBs is their superior heat dissipation. However, low-quality suppliers may use inferior dielectric materials with low thermal conductivity or inconsistent thickness. This compromises heat transfer from the components to the aluminum base, leading to overheating, reduced component lifespan, and premature failure. Always verify the thermal conductivity (typically 1.0–3.0 W/mK for quality dielectrics) and request test reports.
Inconsistent Aluminum Base Quality and Thickness
Variations in the aluminum substrate—such as incorrect alloy type (e.g., 5052, 6061, or 1060), deviations in thickness, or surface oxidation—can impact both mechanical stability and thermal performance. Poorly finished or contaminated aluminum bases may also reduce adhesion, increasing the risk of delamination. Ensure specifications are clearly defined and validated through material certifications.
Solder Mask and Silkscreen Defects
Low-cost manufacturers may apply uneven solder masks or use subpar materials that crack or peel under thermal cycling. Misaligned or illegible silkscreen printing can complicate assembly and field service. These cosmetic issues often reflect deeper quality control problems in the production process.
Lack of IPC Compliance and Testing
Many budget suppliers do not adhere to IPC standards (e.g., IPC-6012 for rigid PCBs), leading to inconsistent plating, poor hole fill, and unreliable electrical connections. Without proper testing—such as thermal shock, peel strength, or insulation resistance tests—defects may go undetected until deployment. Require compliance documentation and third-party test results.
IP Theft and Design Leakage
Sharing Gerber files, schematics, or BOMs with untrusted suppliers poses a serious IP risk. Unethical manufacturers may duplicate designs, sell them to competitors, or produce counterfeit versions. This is especially prevalent in regions with weak IP enforcement. Always use NDAs, work with reputable partners, and consider watermarking or splitting design files when possible.
Inadequate Traceability and Documentation
Poor record-keeping from the supplier can make it difficult to trace material sources, production batches, or quality test results. This lack of traceability complicates root cause analysis during field failures and can hinder compliance with industry regulations (e.g., in automotive or medical sectors).
Hidden Costs from Rework and Failure
While low initial pricing may be attractive, poor quality often leads to high costs downstream—such as assembly line stoppages, rework, warranty claims, and reputational damage. Conduct a total cost of ownership analysis rather than focusing solely on unit price.
By carefully vetting suppliers, demanding quality certifications, and safeguarding IP through legal and technical measures, businesses can avoid these common pitfalls and ensure reliable, secure sourcing of aluminum PCBs.
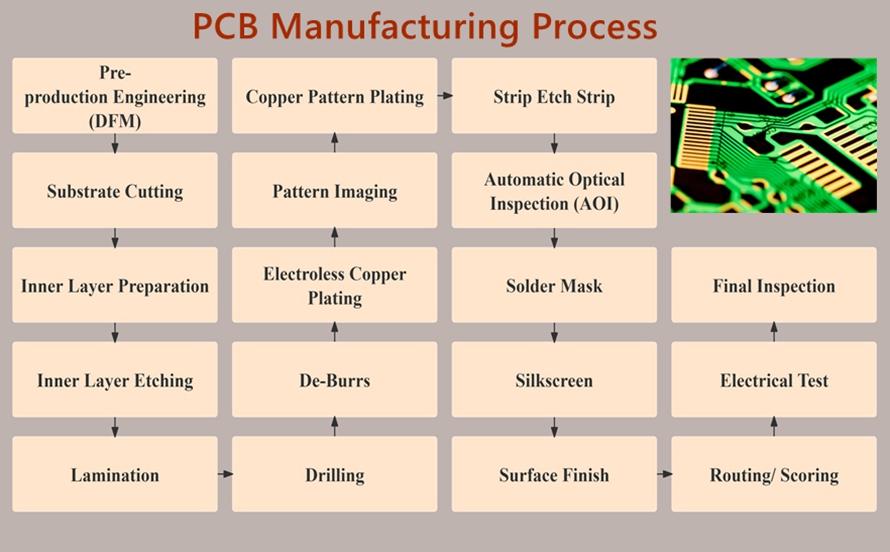
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Aluminum PCB Boards
Overview of Aluminum PCB Boards
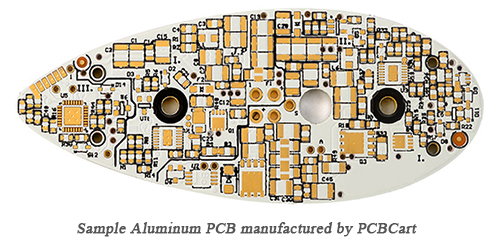
Aluminum Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are a type of metal-based PCB that use an aluminum alloy base layer to provide superior thermal management, mechanical strength, and durability. They are commonly used in high-power and high-temperature applications such as LED lighting, power supplies, automotive systems, and industrial equipment. Due to their unique composition and thermal properties, special considerations are required for their logistics, shipping, and regulatory compliance.
Packaging Requirements
Proper packaging is essential to prevent damage during transportation. Aluminum PCBs are sensitive to physical impact, moisture, and electrostatic discharge (ESD).
- ESD Protection: Use anti-static bags or conductive foam to shield PCBs from static electricity.
- Moisture Barrier: Employ moisture barrier bags (MBBs) with desiccant packs, especially for long-term storage or humid climates. Include humidity indicator cards.
- Rigid Packaging: Place boards in rigid corrugated cardboard or plastic containers to prevent bending or warping.
- Labeling: Clearly label packages with “Fragile,” “Electrostatic Sensitive,” and “This Side Up” indicators.
Storage Conditions
- Temperature: Store between 15°C and 30°C (59°F to 86°F). Avoid extreme temperatures that can affect solderability or adhesion.
- Humidity: Maintain relative humidity below 60%. Use dehumidifiers if necessary.
- Shelf Life: Observe manufacturer-recommended shelf life, typically 6 to 12 months when sealed. Once opened, use within 48–72 hours or bake before use if exposed to ambient air.
Transportation Guidelines
- Mode of Transport: Suitable for air, sea, and land freight. For air transport, ensure compliance with IATA regulations.
- Handling: Use proper handling procedures to avoid bending, scratching, or dropping. Forklifts and pallet jacks should use even support.
- Palletization: Securely stack and wrap pallets with stretch film. Use edge protectors to prevent damage.
- Documentation: Include packing lists, material declarations, and compliance certificates with each shipment.
Regulatory Compliance
Aluminum PCBs must meet various international standards and environmental regulations depending on the destination market.
RoHS Compliance (Restriction of Hazardous Substances)
- Ensure lead, mercury, cadmium, hexavalent chromium, PBB, and PBDE are within permissible limits.
- Provide RoHS compliance certificates for EU, UK, and other RoHS-regulated markets.
REACH Regulation
- Comply with REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) by disclosing Substances of Very High Concern (SVHC).
- Include a formal declaration if requested by EU customers.
IPC Standards
- Follow IPC-4101 (specifications for base materials) and IPC-6012 (qualification and performance of rigid PCBs).
- Maintain quality control records for audits.
Conflict Minerals (Dodd-Frank Act, Section 1502)
- Although aluminum is not a conflict mineral, suppliers should disclose any use of tantalum, tin, tungsten, or gold in components.
- Provide a Conflict Minerals Reporting Template (CMRT) if required.
Export Controls
- Check for export restrictions under ITAR or EAR (U.S. regulations) if shipping from the United States.
- Aluminum PCBs generally fall under EAR99 (low concern), but verify based on end-use (e.g., military or aerospace applications).
Customs and Import Documentation
- HS Code: Use appropriate Harmonized System code. Typical classification: 8534.00 (Printed Circuits).
- Commercial Invoice: Include detailed description, value, quantity, country of origin, and end-use.
- Certificate of Origin: May be required for preferential tariffs under trade agreements.
- Material Declarations: Provide IPC-1752 or IMDS (for automotive) if requested.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
- Waste Disposal: Follow WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) directives for end-of-life handling.
- Recycling: Aluminum substrates are recyclable; encourage proper e-waste recycling programs.
- Safety Data Sheets (SDS): While not always required, an SDS may be needed if adhesives or coatings contain hazardous substances.
Best Practices Summary
- Always use ESD and moisture protection.
- Monitor storage conditions and shelf life.
- Maintain compliance documentation for key markets.
- Verify export and import regulations based on destination.
- Train logistics staff on handling sensitive electronic components.
By adhering to these logistics and compliance guidelines, businesses can ensure the safe, legal, and efficient distribution of aluminum PCB boards globally.
In conclusion, sourcing aluminum PCB (Printed Circuit Board) boards requires careful consideration of several key factors to ensure quality, cost-efficiency, and reliability. Aluminum PCBs are particularly valued for their excellent thermal conductivity, mechanical durability, and suitability for high-power LED and power electronics applications. When sourcing these specialized boards, it is essential to evaluate suppliers based on material quality, manufacturing capabilities (such as metal core bonding and thermal layer precision), compliance with industry standards (e.g., UL, RoHS), and consistent quality control processes.
Additionally, lead times, scalability, and communication efficiency are vital, especially for large-volume or time-sensitive projects. Establishing relationships with reputable manufacturers—whether domestic or overseas—can significantly impact product performance and supply chain stability. Conducting sample testing, requesting certifications, and performing due diligence on potential suppliers will mitigate risks associated with performance failures or delays.
Ultimately, a well-strategized sourcing approach that balances cost, quality, and reliability will ensure the successful integration of aluminum PCBs into your applications, supporting long-term operational efficiency and product success.