The global laser welding market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by rising demand for precision manufacturing in aerospace, automotive, and electronics industries. According to Mordor Intelligence, the laser welding market was valued at USD 3.86 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 7.5% from 2024 to 2029, fueled by advancements in high-power laser technologies and increased adoption of automation in production lines. Aluminum, with its high thermal conductivity and reflective properties, presents unique challenges in laser welding—making specialized equipment and expertise essential. As a result, leading manufacturers are innovating to deliver aluminum-optimized laser welding solutions with improved beam control, reduced porosity, and enhanced process stability. This evolving landscape has given rise to a select group of manufacturers at the forefront of performance, reliability, and technological integration. Based on market presence, technical capabilities, and industry reviews, here are the top 8 aluminum laser welder manufacturers shaping the future of advanced metal joining.
Top 8 Aluminum Laser Welder Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 LaserStar Technologies
Website: laserstar.net
Key Highlights: LaserStar Technologies designs and manufactures high-performance laser welding, marking, and cutting systems for industrial, jewelry, ……
#2 Laser Technology & Laser Machines from ALPHA LASER
Website: alphalaser.eu
Key Highlights: High-quality laser technology & laser sytems from ALPHA LASER: powerful laser machines for metalworking: mobile, flexible, & precise ✓ technical support ✓….
#3 Denaliweld
Website: denaliweld.com
Key Highlights: We Specialize in Laser Welding & Cleaning. DenaliWeld INC, is a proud employee-owned fiber laser welding machine manufacturer based in Chicago, USA. Bolstered ……
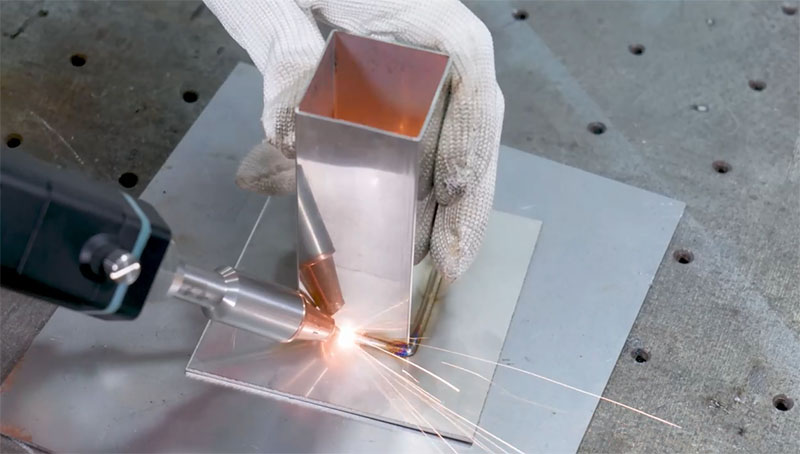
#4 Laser Welder
Website: laser-welder.net
Key Highlights: Laser welders are incredibly versatile and essential in any fabrication shop or factory welding parts from sheet metal….
#5 HobartWelders
Website: hobartwelders.com
Key Highlights: Hobart Welders is a leading welding manufacturer in the U.S. Browse a variety of welders, welding equipment, gear and projects to find the best match for ……
#6 Laser Welding
Website: ipgphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Laser welding creates exceptionally high-quality joints with excellent physical and electrical properties, even when joining challenging materials like aluminum ……
#7 Laser Welding Aluminum
Website: ebindustries.com
Key Highlights: Laser beam welding is one of our most popular services for welding aluminum. The process is ideal for fast, clean welds….
#8 Laser Welding Machine
Website: varisigns.com
Key Highlights: Our handheld fiber laser welder, with a power of 2000 watts, can weld aluminum letters up to 3mm thick. We can now supply a small weld head for 3D channel ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Aluminum Laser Welder

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Aluminum Laser Welder
The global market for aluminum laser welders is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological advancements, rising demand in high-performance industries, and evolving manufacturing standards. As industries increasingly adopt lightweight materials to enhance efficiency and reduce emissions, aluminum’s favorable strength-to-weight ratio has cemented its role in automotive, aerospace, and clean energy sectors—key drivers for laser welding solutions tailored to aluminum.
One of the dominant 2026 trends is the increased adoption of high-power fiber lasers with advanced beam control. These systems offer improved weld quality, greater penetration depth, and reduced porosity in aluminum joints—addressing long-standing challenges such as high thermal conductivity and reflectivity. Manufacturers are integrating real-time monitoring, artificial intelligence (AI), and adaptive optics to enhance process stability, especially for automated production lines.
The automotive industry remains a major growth engine. With electric vehicle (EV) production accelerating worldwide, aluminum-intensive battery enclosures, chassis components, and body structures require precise, high-speed welding. By 2026, OEMs and Tier-1 suppliers are expected to favor modular laser welding cells that support flexible manufacturing, enabling quick changeovers between aluminum alloys and hybrid material joints.
In aerospace and defense, stringent quality standards are pushing demand for laser welding systems with full traceability and compliance with AS9100 and NADCAP requirements. Vacuum laser welding and hybrid laser-arc techniques are gaining traction for critical aluminum airframe and propulsion components, offering superior joint integrity and fatigue resistance.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific—particularly China, Japan, and South Korea—is projected to lead market growth due to robust investments in EV infrastructure and advanced manufacturing. Meanwhile, North America and Europe are focusing on sustainability, with laser welding enabling recyclable aluminum structures and reducing waste compared to traditional joining methods.
Additionally, the rise of Industry 4.0 is fostering integration between laser welders and digital twin platforms, allowing predictive maintenance, remote diagnostics, and data-driven optimization. By 2026, suppliers offering comprehensive digital ecosystems—including cloud-based analytics and cybersecurity—will gain competitive advantage.
In summary, the 2026 aluminum laser welding market will be characterized by smarter, more adaptive systems focused on precision, productivity, and sustainability, aligning with broader industrial shifts toward automation, lightweighting, and digitalization.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing an Aluminum Laser Welder (Quality & IP)
Sourcing an aluminum laser welder, especially from new or unfamiliar suppliers, involves significant risks related to both equipment quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these pitfalls can lead to operational failures, safety hazards, and legal complications. Below are key challenges to avoid:
Poor Build Quality and Performance Inconsistency
Many budget laser welders, particularly those from less reputable manufacturers, suffer from substandard components and inconsistent manufacturing processes. This results in unreliable performance, frequent breakdowns, and an inability to maintain the precise beam control and stability required for welding aluminum—a highly reflective and thermally conductive material. Poorly calibrated optics, low-grade cooling systems, and inadequate power supplies compromise weld quality, leading to porosity, cracking, or weak joints.
Lack of Aluminum-Specific Engineering
Not all laser welders are suitable for aluminum. Aluminum requires specific wavelengths (e.g., green or blue lasers) or high-power fiber lasers with advanced beam delivery to overcome reflectivity and ensure proper penetration. Sourcing a general-purpose welder without verifying its compatibility with aluminum alloys can result in ineffective welding, excessive spatter, or equipment damage due to back-reflections. Always confirm the system is optimized for non-ferrous metals.
Inadequate After-Sales Support and Spare Parts Availability
Some suppliers, especially those operating online or through third-party marketplaces, offer little to no technical support, training, or access to replacement parts. When critical components fail—such as laser diodes, collimators, or protective windows—long lead times or unavailability can halt production. Verify the supplier’s service network, warranty terms, and responsiveness before purchasing.
Intellectual Property (IP) Risks and Counterfeit Technology
A major concern when sourcing from certain regions or unknown vendors is the potential use of cloned or reverse-engineered technology. Some manufacturers may replicate proprietary laser designs, control software, or optical systems without licensing, exposing buyers to IP infringement claims. Using such equipment could lead to legal liability, especially if deployed in industries with strict IP compliance (e.g., aerospace, medical devices).
Missing Safety and Regulatory Certifications
Laser systems must comply with international safety standards (e.g., FDA/CDRH in the U.S., CE in Europe, IEC 60825). Unverified suppliers may provide equipment without proper certification, increasing risk of workplace accidents and non-compliance penalties. Ensure the welder includes safety interlocks, proper labeling, and certification documentation.
Insufficient Documentation and Software Lock-In
Poorly documented systems—lacking user manuals, maintenance guides, or software APIs—can hinder integration and troubleshooting. Additionally, some vendors use proprietary software that limits customization or data access, potentially creating dependency and restricting process optimization. Confirm that control software is transparent, updatable, and compatible with your manufacturing ecosystem.
Hidden Costs and Misrepresented Specifications
Be cautious of exaggerated power ratings, duty cycles, or beam quality (e.g., M² values). Some suppliers inflate specs to appear competitive. Always request third-party test reports or conduct on-site verification. Hidden costs may include mandatory service contracts, expensive calibration tools, or region-specific power adapters.
Conclusion
To mitigate these pitfalls, conduct thorough due diligence: request references, perform factory audits, verify IP legitimacy, and insist on comprehensive testing with your aluminum materials. Partnering with established suppliers who provide full technical documentation, IP assurances, and robust support networks is crucial for long-term success in aluminum laser welding applications.
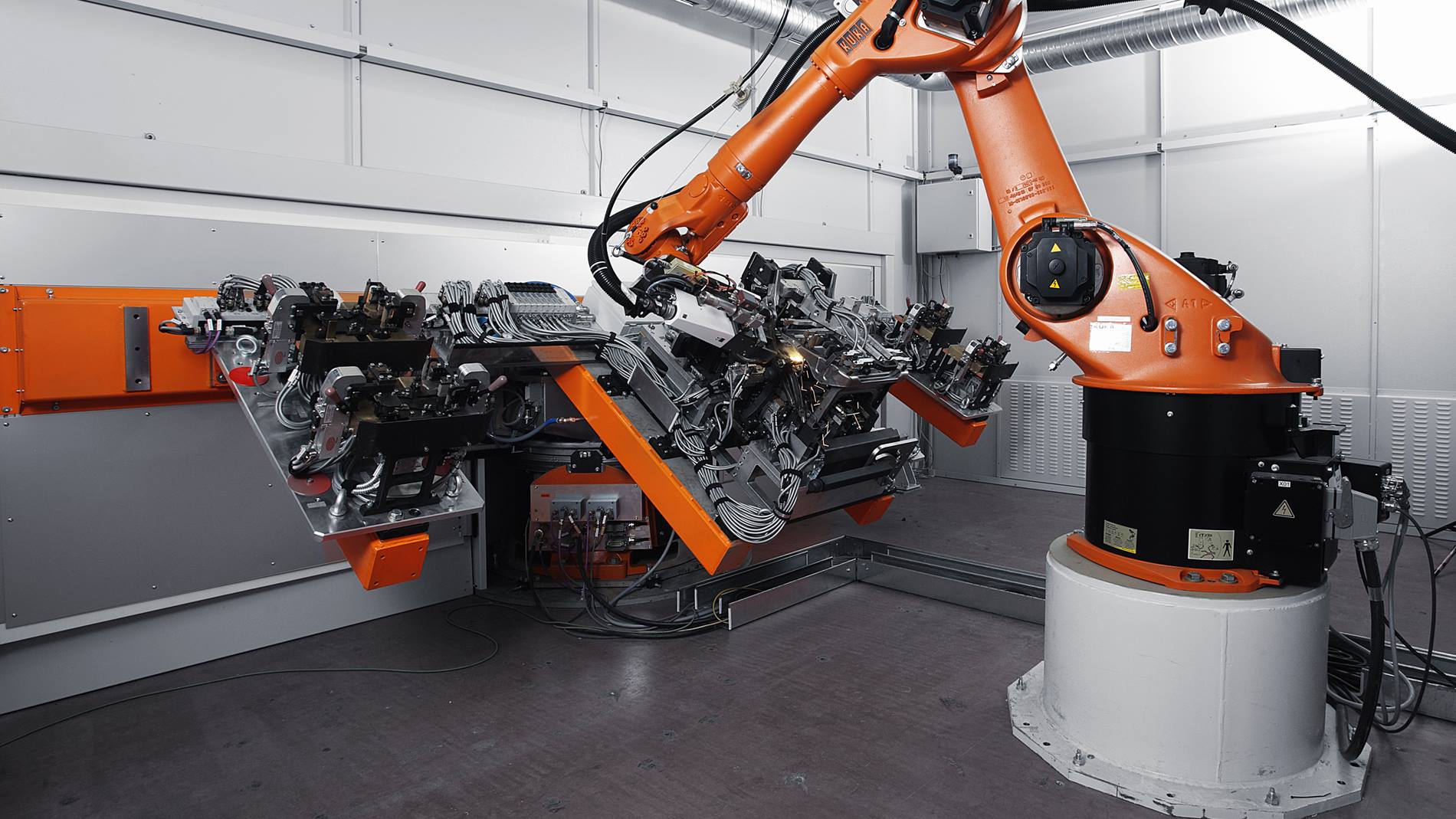
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Aluminum Laser Welder
Overview
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for the safe transport, handling, installation, and operation of an Aluminum Laser Welder. Adherence to these guidelines ensures regulatory compliance, operator safety, and equipment longevity.
Regulatory Compliance
Laser Safety Standards
The Aluminum Laser Welder must comply with international and regional laser safety regulations:
– IEC 60825-1: Safety of laser products – Equipment classification and requirements.
– ANSI Z136.1: Safe Use of Lasers (applicable in the United States).
Ensure the laser is properly classified (typically Class 4) and equipped with appropriate safety interlocks, emergency stops, and warning labels.
Electrical Compliance
- CE Marking (EU): Must meet Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC and Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Directive 2014/30/EU.
- UL/CSA Certification (North America): Required for electrical safety and fire hazard prevention.
- Voltage and frequency must match local supply specifications (e.g., 208–480V, 3-phase, 50/60 Hz).
Workplace Safety Regulations
- OSHA (US): Compliance with 29 CFR 1910 Subpart Q (Welding, Cutting, and Brazing) and general duty clause for hazard communication.
- EU Machinery Directive & ATEX (if applicable): If operating in explosive atmospheres, verify ATEX certification.
- Local Fire Codes: Flammable material storage and fire suppression systems must be in place.
Transportation & Handling
Packaging & Shipping
- Unit must be shipped in original, manufacturer-approved packaging with shock-absorbing materials.
- Clearly label with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Laser Radiation” warning symbols.
- Use carriers experienced in handling industrial machinery and laser equipment.
Import/Export Documentation
- HS Code: Typically 8456.90 (Machines for cutting by laser or other methods). Confirm with local customs authority.
- Required documents: Commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading, certificate of origin, and CE or UL certification.
- ITAR/EAR Compliance (US Exports): Verify if laser power/output falls under export control regulations (e.g., EAR99 or controlled under ECCN 2B201).
On-Site Handling
- Use forklifts or cranes with adequate lifting capacity; follow equipment lift points specified in the manual.
- Avoid tilting or impact during unloading.
- Store in a dry, temperature-controlled environment until installation.
Installation Requirements
Facility Preparation
- Floor Load Capacity: Verify structural support for machine weight (typically 1,000–3,000 kg).
- Ventilation & Fume Extraction: Required for aluminum welding fumes (containing aluminum oxide and ozone). Install local exhaust ventilation (LEV) meeting OSHA or EU EN 60335 standards.
- Power Supply: Dedicated circuit with stable voltage; include line filters if required. Grounding must meet local electrical codes.
- Cooling System: Ensure chiller unit is properly connected with correct coolant type and flow rate.
Laser Safety Enclosure
- Install in an interlocked safety enclosure compliant with ISO 13849-1.
- Include laser warning lights, access door interlocks, and beam shutters.
- Post appropriate safety signage (e.g., “Laser Radiation – Avoid Eye or Skin Exposure”).
Operational Compliance
Operator Training & Certification
- Operators must complete laser safety training (e.g., LSO – Laser Safety Officer certification per ANSI Z136).
- Training must cover emergency procedures, PPE use, and machine-specific operation.
- Maintain training records for audits.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
- Laser Protective Eyewear: Wavelength-specific (e.g., 1064 nm for fiber lasers) with adequate optical density (OD 5+).
- Respiratory Protection: NIOSH-approved respirators if LEV is insufficient.
- Flame-Resistant Clothing & Gloves: To protect against spatter and UV radiation.
Maintenance & Documentation
- Follow manufacturer-recommended maintenance schedule.
- Keep logs of service, calibration, and safety inspections.
- Perform annual laser safety audits and interlock testing.
Environmental & Disposal Compliance
Waste Management
- Collect and dispose of aluminum welding fumes and filter residues as industrial waste per local regulations (e.g., EPA or EU Waste Framework Directive).
- Do not dispose of in regular trash.
End-of-Life Disposal
- Recycle metal components through certified e-waste facilities.
- Laser diodes and optical components may contain hazardous materials; handle per RoHS and WEEE directives.
Emergency Procedures
Laser Incident Response
- Immediate shutdown via emergency stop.
- In case of eye or skin exposure, seek medical attention immediately; report incident to safety officer.
- Isolate area and investigate cause.
Fire Response
- Use Class D fire extinguishers for metal fires (aluminum).
- Never use water on aluminum fires.
Summary
Proper logistics and compliance for an Aluminum Laser Welder require coordinated attention to international standards, safe handling practices, regulatory documentation, and operator safety. Regular audits and training ensure ongoing compliance and workplace safety. Always consult the manufacturer’s manual and local authorities for site-specific requirements.
Conclusion for Sourcing an Aluminum Laser Welder
In conclusion, sourcing a laser welder specifically designed for aluminum requires careful consideration of several critical factors, including the type of laser technology (such as fiber or disk lasers), beam quality, power output, and the system’s ability to handle aluminum’s high thermal conductivity and reflectivity. Compatibility with automation, precision control, and cooling systems are also essential to ensure consistent, high-quality welds.
After evaluating various suppliers, technical specifications, and after-sales support, it is evident that investing in a high-performance, application-optimized aluminum laser welding system will significantly enhance production efficiency, weld integrity, and overall product quality. Additionally, partnering with a reputable manufacturer that offers training, service, and technical expertise ensures long-term reliability and return on investment.
Ultimately, the successful sourcing of an aluminum laser welder hinges on aligning machine capabilities with specific production requirements, material characteristics, and operational goals. With the right system in place, manufacturers can achieve superior weld strength, reduced distortion, and increased throughput—key advantages in competitive industries such as automotive, aerospace, and consumer electronics.