The global aluminum ingot mold market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising demand for aluminum across industries such as automotive, aerospace, and construction. According to Mordor Intelligence, the aluminum market is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 4.5% from 2024 to 2029, underpinned by increasing adoption of lightweight materials for fuel efficiency and emission reduction. This surge in aluminum production has elevated the need for high-quality ingot molds, crucial for shaping molten aluminum into standardized forms for further processing. With foundries expanding capacity and prioritizing efficiency, durability, and thermal conductivity in their tooling, manufacturers of aluminum ingot molds are witnessing heightened demand. As the industry evolves, innovation in mold design and materials—such as cast iron, steel, and graphite composites—has become a key differentiator among top suppliers. Based on production scale, engineering expertise, and global reach, the following nine companies have emerged as leading aluminum ingot mold manufacturers shaping the future of metal casting.
Top 9 Aluminum Ingot Mold Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
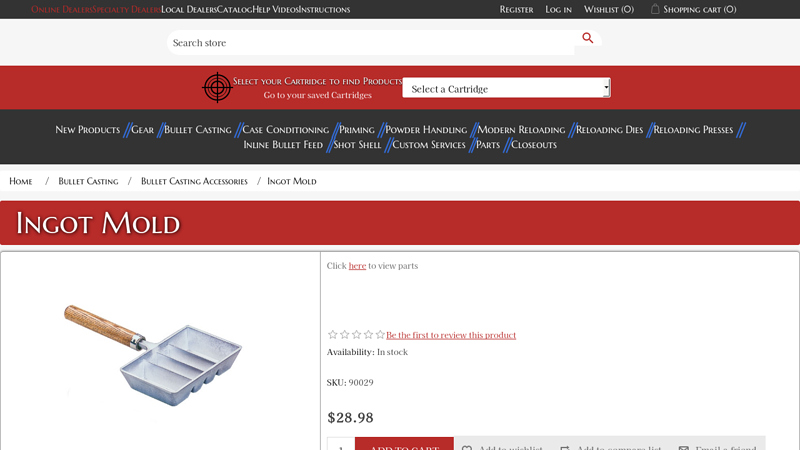
#1 Ingot Mold
Domain Est. 1997
Website: leeprecision.com
Key Highlights: Lee Ingot mold, made of rustproof aluminum mold casts 1/2 and 1 lb. ingots (2 of each). Perfect for re-melting and alloying. Click here to view parts….
#2 Aluminum Casting Equipment
Domain Est. 1995
Website: wagstaff.com
Key Highlights: Wagstaff is the global leader and trusted supplier of aluminum casting equipment, specializing in Direct Chill (DC) casting and providing billet and ingot ……
#3 INGOT MOLDS
Domain Est. 1997
Website: dykast.com
Key Highlights: Dy-Kast Supply offers a variety of Ingot Molds for Aluminum, Zinc, Lead, Brass, and Iron. Mold capacities vary depending on style….
#4 Open Mould Ingot Casting Systems
Domain Est. 1998
Website: hertwich.com
Key Highlights: Reliable air- or water-cooled open mould casting systems for aluminium ingots. Ensuring consistent quality, automation & seamless casthouse integration….
#5 Ingot Molds
Domain Est. 2002
Website: dynaformtech.com
Key Highlights: Ingot molds come in various shapes and sizes and are typically made of durable materials such as Cast Iron, Ductile Iron, Steel or Aluminum….
#6 Ingot molds
Domain Est. 2015
Website: acsleadtech.com
Key Highlights: We produce & Import Remelted Lead Ingots / Blocks. Ingot molds is useful in casting refined metal.( aluminum, copper, lead and zinc) into various shapes and ……
#7 Aluminum Ingot Mold, China Metal Ingot Molds supplier
Domain Est. 2019
Website: m.aluminumingotmold.com
Key Highlights: Good Quality Aluminum Ingot Mold, Metal Ingot Molds Supplier From China – LUOYANG SUPER FOLIAGE IMPORT&EXPORT TRADE CO,LTD….
#8 Aluminum Ingots/Billets, Slabs, & Cast Plates FAQS
Domain Est. 2019
Website: ellwoodaluminum.com
Key Highlights: Yes, ELLWOOD Aluminum produces aluminum ingots & billets, slabs, and cast plates for applications across the globe….
#9 Metal Ingot Molds, Lead Ingot Mold supplier & Wholesale
Domain Est. 2019
Website: aluminumingotmold.com
Key Highlights: Good Quality Metal Ingot Molds, Lead Ingot Mold, Deep Hole Drilling Machine From China – LUOYANG SUPER FOLIAGE IMPORT&EXPORT TRADE CO,LTD….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Aluminum Ingot Mold

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Aluminum Ingot Mold
The global aluminum ingot mold market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by evolving industrial demands, technological advancements, and shifts in aluminum production dynamics. Aluminum ingot molds—critical tools used in the casting and solidification of molten aluminum into standardized ingot forms—are experiencing increased demand due to the growing use of aluminum across aerospace, automotive, construction, and renewable energy sectors. The following analysis outlines key market trends expected to shape the aluminum ingot mold industry through 2026.
-
Rising Aluminum Production Capacity
Global aluminum output continues to expand, particularly in regions like Asia-Pacific (notably China, India, and Southeast Asia) and the Middle East, where investment in smelting infrastructure is robust. As primary aluminum production increases, so does the need for efficient and durable ingot molds. This uptick in production capacity is expected to directly fuel demand for high-performance aluminum ingot molds capable of withstanding repeated thermal cycling and ensuring consistent ingot quality. -
Shift Toward Energy-Efficient and Long-Lasting Mold Materials
Manufacturers are increasingly adopting advanced mold materials such as high-chrome cast iron, graphite composites, and specialized steel alloys to improve mold longevity and reduce downtime. The push for energy efficiency and lower operational costs is encouraging the adoption of molds with enhanced thermal conductivity and resistance to thermal fatigue. By 2026, molds engineered with proprietary coatings or surface treatments to resist corrosion and prolong service life are expected to gain market share. -
Automation and Smart Foundry Integration
The integration of automation and Industry 4.0 technologies in aluminum casting facilities is accelerating. Automated pouring systems, robotic handling, and real-time monitoring are transforming traditional foundries into smart manufacturing environments. In this context, aluminum ingot molds are being designed for compatibility with automated systems—featuring standardized dimensions, embedded sensors for temperature monitoring, and modular configurations. This trend is expected to grow through 2026, increasing demand for precision-engineered, IoT-enabled molds. -
Sustainability and Recycling Growth
With growing emphasis on circular economy principles, secondary aluminum production (from recycled scrap) is expanding rapidly. Recycling requires efficient remelting and casting processes, often involving ingot molds. As the share of recycled aluminum in total supply rises—projected to exceed 50% in some regions by 2030—the demand for molds suited to the variable composition and higher oxide content of recycled feedstock will increase. Molds resistant to slag adhesion and thermal shock will be particularly sought after. -
Regional Market Dynamics
Asia-Pacific will remain the dominant market for aluminum ingot molds due to its extensive smelting capacity and manufacturing base. However, North America and Europe are expected to see renewed investment in domestic aluminum production, driven by supply chain resilience strategies and green energy initiatives. This regional rebalancing will create opportunities for mold manufacturers offering energy-efficient and low-emission casting solutions. -
Customization and Niche Applications
Beyond standard slab and billet molds, there is growing demand for customized molds tailored to specific alloy compositions or end-use applications (e.g., aerospace-grade aluminum). By 2026, suppliers that offer modular, adjustable, or application-specific mold designs are likely to capture premium market segments.
Conclusion
By 2026, the aluminum ingot mold market will be shaped by a confluence of increased production, technological innovation, automation, and sustainability demands. Manufacturers that invest in durable materials, smart integration, and environmentally responsible solutions will be best positioned to capitalize on these trends. As the global aluminum industry evolves, aluminum ingot molds will remain a vital component—transitioning from simple casting tools to sophisticated elements of modern metal production systems.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Aluminum Ingot Molds (Quality & Intellectual Property)
Sourcing aluminum ingot molds, especially from offshore suppliers, presents significant risks related to both product quality and intellectual property protection. Overlooking these pitfalls can lead to production delays, increased costs, substandard products, and long-term competitive disadvantages.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inadequate Material Specifications
A frequent issue is receiving molds made from substandard or incorrectly specified materials. Suppliers may use lower-grade tool steels (e.g., non-pre-hardened or poorly heat-treated steels) that lack the necessary thermal conductivity, hardness, and resistance to thermal fatigue. This results in premature cracking, warping, or reduced mold life, increasing downtime and replacement costs.
Poor Dimensional Accuracy and Tolerances
Molds that do not meet precise dimensional requirements or surface finish standards can produce ingots with inconsistent weights, shapes, or surface defects. This compromises downstream processing and product quality. Without strict adherence to engineering drawings and quality control protocols, even minor deviations can lead to significant operational problems.
Insufficient Surface Treatment and Coating
Many aluminum ingot molds require specialized coatings (e.g., ceramic or chrome plating) to resist oxidation and aluminum adhesion. Failure to apply or verify these treatments properly leads to sticking, surface pitting, and difficult demolding, ultimately reducing productivity and ingot quality.
Lack of Proper Heat Treatment and Stress Relieving
Improper or skipped heat treatment processes—such as stress relieving after machining—can leave internal stresses in the mold. These stresses manifest as distortion or cracking during thermal cycling in production, drastically shortening mold lifespan.
Inadequate Quality Assurance and Documentation
Suppliers may lack robust quality management systems (e.g., ISO 9001), resulting in inconsistent production practices. Absence of material test reports (MTRs), heat treatment records, dimensional inspection reports, or non-destructive testing (NDT) results makes it difficult to verify quality or trace failures.
Intellectual Property (IP)-Related Pitfalls
Unauthorized Replication and Reverse Engineering
Providing detailed technical drawings or CAD files to suppliers without proper safeguards risks unauthorized copying. Unscrupulous manufacturers may reverse engineer the mold design and sell identical or modified versions to competitors, eroding market advantage and reducing return on R&D investment.
Weak or Unenforceable Legal Agreements
Many sourcing agreements lack comprehensive IP clauses or are governed by jurisdictions where IP enforcement is weak. Without clearly defined ownership, confidentiality obligations, and non-compete restrictions in legally binding contracts, protecting proprietary designs becomes nearly impossible.
Lack of Supplier Vetting and Transparency
Engaging suppliers without thorough due diligence increases the risk of IP exposure. Suppliers with a history of IP violations or those operating in regions with lax IP enforcement pose higher risks. Opaque subcontracting practices may also lead to designs being shared with unauthorized third parties.
Inadequate Control Over Prototypes and Samples
Sharing prototypes or initial production samples without non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) or tracking mechanisms allows suppliers to analyze and replicate critical design features. Failure to label materials as “Confidential” or “Proprietary” further weakens legal recourse.
Failure to Register and Protect IP in Target Markets
Even with strong agreements, unregistered designs or utility models in the supplier’s country offer little protection. Without local IP registrations (e.g., design patents), enforcement against copycats is impractical, leaving the original design vulnerable to exploitation.
To mitigate these risks, buyers should conduct rigorous supplier audits, enforce comprehensive legal agreements with clear IP terms, specify material and quality requirements in detail, and consider using trusted intermediaries or regional representatives to oversee production and compliance.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Aluminum Ingot Mold
This guide provides essential information for the safe, efficient, and compliant transportation, handling, and regulatory management of aluminum ingot molds—durable steel or iron molds used in the casting of aluminum ingots in primary and secondary smelting operations.
Classification and Identification
Aluminum ingot molds are classified as industrial tooling or capital equipment. They are typically fabricated from high-strength, heat-resistant materials such as cast steel or ductile iron to withstand repeated exposure to molten aluminum (approx. 700°C). Proper identification includes mold dimensions, weight, tare weight, material grade, and manufacturer markings. Ensure each mold is clearly labeled with a unique serial number or asset tag for traceability.
Packaging and Handling Requirements
Due to their heavy weight and robust construction, aluminum ingot molds generally do not require complex packaging. However, the following handling guidelines must be observed:
– Use appropriate lifting equipment (e.g., overhead cranes, forklifts with steel-tine extensions) rated for the mold’s weight (typically ranging from 100 kg to over 1,000 kg per unit).
– Protect lifting lugs or attachment points from damage; inspect for cracks or wear before each lift.
– Secure molds on pallets or in containers using steel strapping or chains during transport to prevent shifting.
– Avoid dropping or impact, which may compromise structural integrity and cause premature failure in high-temperature operations.
Transportation Logistics
Aluminum ingot molds are commonly shipped via flatbed trucks, open-top containers, or bulk cargo vessels, depending on volume and destination:
– Road Freight: Use low-boy trailers or flatbeds for oversized or heavy molds. Secure with load binders and comply with regional weight and dimension regulations (e.g., U.S. DOT, EU ADR).
– Ocean Freight: Stow molds in open-top or flat-rack containers. Ensure proper lashing to container corner castings per CTU (Cargo Transport Unit) Code guidelines.
– Rail Transport: Confirm axle load and stacking limits with rail operators; use cradles or dunnage to prevent movement.
– Provide accurate shipping documentation, including weight, dimensions, and handling instructions.
Import/Export Compliance
International movement of aluminum ingot molds may require adherence to various trade regulations:
– HS Code: Typically classified under 8481.80 (parts of machinery for working metal) or 7326.90 (other articles of steel), depending on design and function. Confirm with local customs authority.
– Export Controls: Generally not subject to ITAR or dual-use export controls unless integrated with advanced monitoring systems. Verify under EAR (U.S.) or equivalent national regulations.
– Documentation: Include commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading, and certificate of origin. For EU imports, ensure compliance with CE marking if applicable (e.g., integrated lifting components).
– Duties and Tariffs: Assess based on country of origin and destination; utilize free trade agreements where eligible.
Safety and Environmental Considerations
While aluminum ingot molds themselves are inert and non-hazardous, safety protocols must address:
– Workplace Safety: Follow OSHA (U.S.) or equivalent national standards for heavy lifting, crane operation, and hot work zones.
– Residue Management: Clean molds of residual aluminum, lubricants, or release agents prior to shipment to avoid contamination or classification as hazardous waste.
– Environmental Compliance: Adhere to local regulations regarding metal handling and waste disposal. No special environmental permits are typically required for the molds themselves.
Regulatory and Industry Standards
Ensure molds comply with relevant industry and safety standards:
– ASME B30.20 – Below-the-Hook Lifting Devices (for molds with integrated lifting features).
– ISO 4301 – Cranes — Classification (for compatibility with plant lifting systems).
– EN 13001 – Cranes — General design (for European market).
– Confirm mold design aligns with customer specifications and foundry operational protocols.
Maintenance and Inspection
To ensure longevity and compliance with operational safety:
– Conduct regular visual and non-destructive testing (NDT) for cracks, warping, or erosion.
– Recondition molds as needed through machining or welding using qualified procedures.
– Maintain a log of inspections, repairs, and service history for audit and traceability purposes.
Conclusion
Proper logistics and compliance management for aluminum ingot molds ensures operational safety, regulatory adherence, and supply chain efficiency. By following standardized handling, transportation, and documentation practices—and aligning with international trade and safety regulations—companies can minimize risk and optimize the lifecycle performance of this critical foundry equipment.
Conclusion for Sourcing Aluminum Ingot Molds:
Sourcing high-quality aluminum ingot molds is a critical step in ensuring efficient and reliable aluminum production. After evaluating various suppliers, materials, and manufacturing methods, it is clear that prioritizing durability, thermal conductivity, and dimensional accuracy in mold selection significantly enhances ingot quality and operational efficiency. Cast iron and ductile iron molds remain the most widely used due to their strength and heat resistance, while advancements in coatings and modular designs offer extended service life and easier maintenance.
Key factors in successful sourcing include supplier reliability, adherence to international quality standards (such as ISO certifications), cost-effectiveness, and technical support. Establishing long-term partnerships with reputable manufacturers helps ensure consistent supply, reduced downtime, and prompt resolution of any issues.
In conclusion, a strategic sourcing approach—balancing quality, cost, and service—will optimize production performance and support sustainable growth in aluminum casting operations. Regular evaluation of supplier performance and emerging technologies will further strengthen supply chain resilience and product quality.