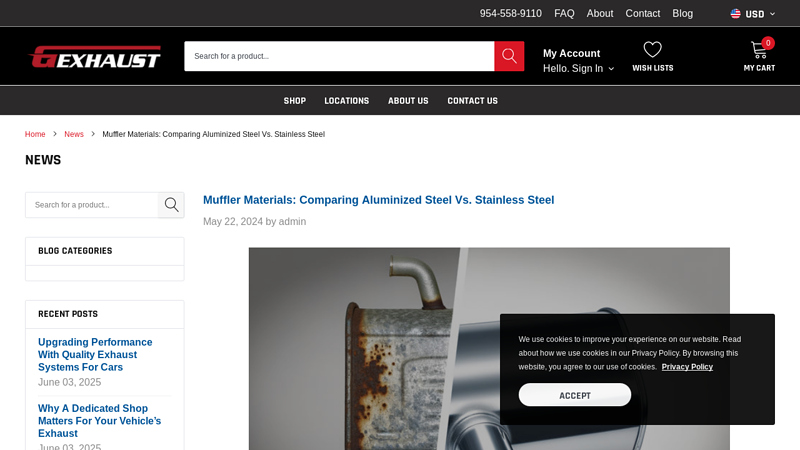
The global automotive exhaust systems market is undergoing significant transformation, driven by stricter emissions regulations, increasing vehicle production, and rising demand for high-performance materials. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the market is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 4.8% from 2023 to 2028, reaching an estimated value of USD 38.5 billion by 2028. A critical factor influencing this growth is the choice of materials used in exhaust systems, with aluminized steel and stainless steel emerging as the two dominant contenders. Aluminized steel, known for its cost-effectiveness and corrosion resistance due to its aluminum-silicon coating, remains a popular choice for mid-tier and mass-market vehicles. In contrast, stainless steel—particularly grades like 409 and 304—offers superior durability, heat resistance, and longevity, making it the preferred option for premium and performance applications. As automakers and aftermarket suppliers navigate this material dichotomy, the competitive landscape among manufacturers has intensified. This analysis identifies the top seven manufacturers excelling in the production of aluminized and stainless steel exhaust systems, evaluating their technological capabilities, market reach, and strategic positioning in a rapidly evolving industry.
Top 7 Aluminized Steel Vs Stainless Steel Exhaust Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 5 Differences Between Aluminized Steel and Stainless Steel
Domain Est. 1998
Website: blocksteel.com
Key Highlights: With an aluminum coating that helps reflect heat, Aluminized Steel can withstand high temperatures, making it a great option for exhaust systems ……
#2 Know the Difference
Domain Est. 2003
Website: mamotorworks.com
Key Highlights: Density. Stainless steel is denser than aluminized steel, which could be seen as an advantage. However, the tubing in exhaust systems made from aluminized ……
#3 Stainless Steel or Aluminized Exhaust
Domain Est. 2005
Website: cumminsforum.com
Key Highlights: Aluminized Steel is dull gray in color, similar to 409 Stainless Steel. Aluminized Steel will NOT turn gold/brown in color when it gets hot….
#4 Aluminized vs Stainless exhausts
Domain Est. 2006
Website: tacomaworld.com
Key Highlights: An “aluminized exhaust” is just steel exhaust but the steel has been coated with aluminum silicon ……
#5 Exhaust System Material Comparison
Domain Est. 2007
Website: afepower.com
Key Highlights: Aluminized steel is the most cost-efficient exhaust material and can last for several years if exposed to moderate climate and not damaged. Aluminized tubing ……
#6 Stainless Steel Exhaust vs Aluminized Steel Exhaust
Domain Est. 2013
Website: dbasilencing.ca
Key Highlights: DBA Silencing uses premium steel piping. We produce aluminized steel exhaust systems, however we can manufacture stainless steel exhaust systems…
#7 Muffler Materials
Domain Est. 2013
Website: gexhaust.com
Key Highlights: Stainless steel is stronger and more durable than aluminized steel, with higher rust resistance and tensile strength. Aluminized steel excels in ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Aluminized Steel Vs Stainless Steel Exhaust

H2: Market Trends in Aluminized Steel vs. Stainless Steel Exhaust Systems (2026 Outlook)
As the automotive industry evolves toward increased efficiency, sustainability, and performance, the choice between aluminized steel and stainless steel for exhaust systems remains a critical decision for manufacturers and consumers alike. By 2026, several key market trends are expected to shape the competitive landscape between these two materials.
1. Rising Demand for Longevity and Corrosion Resistance
Stainless steel continues to gain traction due to its superior corrosion resistance and durability. With consumers increasingly prioritizing vehicle longevity and reduced maintenance costs, stainless steel exhaust systems—particularly those made from 409 and 304 grades—are seeing higher adoption rates in both OEM and aftermarket sectors. In contrast, aluminized steel, while cost-effective, is more prone to degradation in harsh climates and salt-exposed regions, limiting its appeal in markets with severe weather conditions.
2. Cost Sensitivity vs. Premiumization
Aluminized steel maintains a strong foothold in budget-conscious markets and entry-level vehicles due to its significantly lower cost—typically 30–50% less than stainless steel. However, a growing trend toward premiumization in global automotive segments, especially in electric vehicles (EVs) and performance hybrids, is driving OEMs to opt for stainless steel for enhanced aesthetics and durability. By 2026, this shift is expected to widen the application gap, with stainless steel dominating mid-to-high-end segments.
3. Electric Vehicle (EV) Influence
Although EVs do not require traditional exhaust systems, hybrid models (PHEVs and HEVs) still rely on internal combustion engines and thus exhaust components. As hybrid production ramps up to meet transitional emissions targets, demand for durable exhaust materials remains relevant. Stainless steel is increasingly preferred in hybrid applications due to intermittent engine use, which can lead to increased internal condensation and corrosion—areas where stainless outperforms aluminized steel.
4. Regional Market Dynamics
In North America and Europe, stringent emissions and durability standards, coupled with consumer expectations for longer vehicle lifespans, favor stainless steel adoption. Meanwhile, emerging markets in Asia-Pacific and Latin America continue to show strong demand for aluminized steel due to price sensitivity and shorter vehicle ownership cycles. However, as infrastructure improves and vehicle quality expectations rise in these regions, stainless steel penetration is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 6% through 2026.
5. Technological and Manufacturing Advancements
Innovations in coating technologies are enhancing the performance of aluminized steel, narrowing the durability gap. New multilayer aluminized coatings with silicon and aluminum-silicon alloys are improving heat resistance and oxidation protection. At the same time, advancements in stainless steel manufacturing, including lean duplex grades and improved forming techniques, are reducing costs and expanding design flexibility.
6. Sustainability and Recycling
Both materials are highly recyclable, but stainless steel holds an edge in lifecycle sustainability due to its longer service life and reduced need for replacement. As automakers strengthen environmental commitments under ESG frameworks, material choices are being scrutinized for total lifecycle impact. Stainless steel’s durability supports circular economy goals, giving it a strategic advantage in sustainable vehicle design.
Conclusion
By 2026, the market for exhaust systems will reflect a bifurcation: stainless steel will dominate premium, long-life, and hybrid applications, driven by performance and sustainability demands, while aluminized steel will retain relevance in cost-sensitive and short-term-use segments. The overall trend points toward gradual market share erosion for aluminized steel, with stainless steel capturing an increasing portion of both OEM and aftermarket exhaust solutions.
Common Pitfalls Sourcing Aluminized Steel vs Stainless Steel Exhaust (Quality, IP)
When sourcing exhaust components, choosing between aluminized steel and stainless steel involves balancing cost, performance, and longevity. However, overlooking key quality and intellectual property (IP) considerations can lead to significant issues. Below are common pitfalls to avoid:
1. Prioritizing Initial Cost Over Total Lifecycle Value
Pitfall: Selecting aluminized steel solely due to its lower upfront cost without evaluating long-term durability.
Details:
Aluminized steel is typically 30–50% cheaper than stainless steel (especially 304 or 409 grades). However, in corrosive environments (coastal areas, high road-salt use), aluminized tubing may fail in 2–4 years, whereas stainless steel can last 8–15+ years. Sourcing based only on initial savings can result in higher TCO (Total Cost of Ownership) due to premature replacements, warranty claims, and customer dissatisfaction.
IP Consideration: Some proprietary aluminized coatings (e.g., ZAM, Galvalume variants) are patented. Unauthorized replication or misrepresentation of coating technology may lead to IP infringement.
2. Misunderstanding Material Specifications and Quality Consistency
Pitfall: Assuming all aluminized or stainless steel is the same, leading to inconsistent quality.
Details:
– Aluminized Steel: Quality varies significantly based on coating weight (e.g., Class 1 vs Class 2), base steel gauge, and coating adhesion. Poorly coated tubes may have bare spots or uneven layers, accelerating corrosion.
– Stainless Steel: Not all stainless is equal—304 offers superior corrosion resistance but is more expensive; 409 is common in OEM applications but more prone to rust if not properly passivated. Sourcing from suppliers without mill test reports (MTRs) risks receiving substandard or misrepresented material.
IP Consideration: Certain alloy formulations (e.g., proprietary stainless blends) may be protected under industrial design patents or trade secrets. Copying exact compositions without licensing may violate IP rights.
3. Overlooking Manufacturing Process and IP in Design
Pitfall: Failing to verify whether exhaust designs (mufflers, manifolds) are protected by design or utility patents.
Details:
Many high-performance or OEM exhaust systems incorporate patented designs (e.g., tuned header geometry, proprietary muffler baffle layouts). Sourcing replicas—even in different materials—can infringe on existing IP, especially if the design is substantially similar.
Example: A “universal fit” header made from aluminized steel but mimicking a patented stainless OEM design may still face legal challenges.
4. Inadequate Corrosion Testing and Environmental Mismatch
Pitfall: Sourcing aluminized steel for harsh environments without validating corrosion resistance.
Details:
Aluminized steel performs well in high-heat, dry environments but degrades rapidly in chloride-rich or humid conditions. Suppliers may claim “long life” without providing salt spray test results (e.g., ASTM B117). Stainless steel, particularly 304 or 321, outperforms in such conditions.
IP Angle: Some accelerated aging tests and corrosion-resistant coating methods are patented. Using a supplier that relies on proprietary testing methods without proper clearance could pose indirect IP risks.
5. Supply Chain Transparency and Material Traceability
Pitfall: Working with suppliers who cannot provide full material traceability or source from unauthorized mills.
Details:
Reputable stainless steel mills (e.g., Acerinox, Outokumpu) offer certified material with traceable heat numbers. Aluminized steel from unknown mills may use recycled or inconsistent base materials, affecting weldability and durability. Lack of traceability increases risk of receiving counterfeit or subpar materials.
IP Risk: Counterfeit materials may falsely claim compliance with patented metallurgical processes or certifications, exposing the buyer to liability.
6. Underestimating Welding and Fabrication Challenges
Pitfall: Assuming both materials can be fabricated identically.
Details:
– Aluminized Steel: Requires special welding techniques (e.g., back purging, specific wire types) to prevent zinc fume release and ensure joint integrity. Poor welding compromises durability.
– Stainless Steel: Needs inert gas shielding and clean tools to avoid contamination (e.g., iron pickup), which can lead to rust spots.
IP Consideration: Certain welding procedures or automated fabrication systems may be patented. Replicating a competitor’s production method—even with different materials—could infringe on process patents.
Conclusion
Sourcing aluminized vs. stainless steel exhausts demands more than material comparison—it requires due diligence in quality assurance, environmental suitability, and IP compliance. Always:
– Request mill certifications and test reports.
– Validate design freedom-to-operate (FTO) analyses.
– Audit suppliers for traceability and process control.
– Evaluate total lifecycle cost, not just unit price.
Neglecting these factors can lead to product failures, legal disputes, and reputational damage.
H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide: Aluminized Steel vs. Stainless Steel Exhaust Systems
Choosing between aluminized steel and stainless steel for exhaust systems involves more than just performance and cost—it significantly impacts logistics, regulatory compliance, and supply chain management. This guide outlines the key differences to help ensure efficient operations and adherence to standards.
H2: Material Sourcing & Supply Chain Considerations
Aluminized Steel:
– Availability: Widely available globally due to simpler manufacturing processes and lower material costs.
– Suppliers: Broad supplier base, including regional and international mills; often sourced from carbon steel producers with aluminizing capabilities.
– Lead Times: Typically shorter lead times due to high production volumes and standardization.
– Logistics: Heavier than stainless steel per unit volume; higher transportation costs per component due to weight.
– Storage: Requires dry, controlled environments to prevent moisture exposure and premature corrosion of the aluminized coating.
Stainless Steel:
– Availability: Subject to global supply fluctuations, especially for high-grade alloys (e.g., 304, 409, 321). May face longer lead times during peak demand.
– Suppliers: Concentrated among specialized alloy producers; sourcing may require long-term contracts.
– Lead Times: Longer due to complex production and higher global demand across industries (automotive, medical, construction).
– Logistics: Higher material density affects freight costs, but longer lifespan may reduce replacement shipments over time.
– Storage: More resistant to environmental degradation; can tolerate wider storage conditions but still benefits from dry, non-corrosive environments.
H2: Regulatory & Environmental Compliance
Aluminized Steel:
– Emissions & Coatings: Aluminizing process may involve zinc/aluminum dipping; facilities must comply with EPA (U.S.) or equivalent regional air and wastewater regulations (e.g., REACH in EU).
– End-of-Life Handling: Classified as mixed metal waste; recycling requires separation of coating from base steel. May not qualify for full recycling incentives.
– RoHS/REACH: Generally compliant if no restricted substances are used in coating; verify with supplier documentation.
– Transportation: Subject to standard hazardous material rules if coated with volatile compounds (rare); typically non-hazardous.
Stainless Steel:
– Material Sourcing Compliance: Must adhere to conflict minerals regulations (e.g., Dodd-Frank Act Section 1502) if containing tin, tantalum, tungsten, or gold (rare in exhaust, but due diligence required).
– Recyclability: Fully recyclable without degradation; supports sustainability reporting (e.g., ISO 14001, EPD programs).
– RoHS/REACH: Inherently compliant in most grades; minimal surface treatments reduce compliance risk.
– Export Controls: Certain high-nickel alloys may be subject to ITAR or dual-use regulations in specific jurisdictions (rare for automotive exhausts).
H2: Customs, Tariffs & Trade Regulations
Aluminized Steel:
– HTS Codes: Typically classified under 7210 (flat-rolled products, coated) or 7308 (tubes/pipes).
– Tariff Exposure: Often subject to anti-dumping duties (e.g., U.S. duties on Chinese or Indian steel products).
– Trade Agreements: May benefit from USMCA or other regional agreements if originating from qualifying countries.
Stainless Steel:
– HTS Codes: Usually classified under 7219/7220 (stainless flat-rolled) or 7304 (stainless tubes).
– Tariff Exposure: Higher scrutiny under Section 232 (U.S. steel tariffs); subject to quotas or duties in multiple markets.
– Rules of Origin: Critical for preferential treatment under trade pacts; requires detailed bill of materials and value-added tracking.
H2: Packaging, Handling & Transport Standards
Shared Requirements:
– Packaging: Both materials require protective wrapping (e.g., VCI paper, plastic) to prevent surface damage and corrosion during transit.
– Load Securing: Must comply with FMCSA (U.S.), ADR (Europe), or local road transport regulations for securement of metal cargo.
– Labeling: GS1-compliant barcodes, HTS codes, country of origin, and handling instructions (e.g., “Do Not Stack,” “Protect from Moisture”).
Material-Specific Notes:
– Aluminized Steel: More prone to scratching and coating damage; requires extra padding and handling care.
– Stainless Steel: Less susceptible to surface damage but vulnerable to iron contamination (e.g., carbon steel dust); requires segregation during transport and storage.
H2: Documentation & Traceability
Aluminized Steel:
– Certificates: Mill Test Certificates (MTCs) confirming steel grade and coating thickness (e.g., ASTM A792).
– Traceability: Batch-level tracking recommended to manage warranty and failure analysis.
Stainless Steel:
– Certificates: Full Material Test Reports (MTRs) per ASTM A240 or EN 10088, including chemical composition and mechanical properties.
– Traceability: Often requires full heat trace documentation for compliance with automotive OEM standards (e.g., IATF 16949).
H2: Summary & Strategic Recommendations
| Factor | Aluminized Steel | Stainless Steel |
|——-|——————|—————–|
| Supply Chain Risk | Low to moderate | Moderate to high (alloy dependency) |
| Compliance Burden | Moderate (coating regulations) | Low to moderate (recycling & sourcing) |
| Logistics Cost | Higher per unit (weight) | Higher per ton (material cost), but fewer replacements |
| Sustainability Profile | Lower recyclability, shorter life | High recyclability, longer service life |
| Best Fit | High-volume, cost-sensitive, short-to-medium duty cycles | Premium, long-life, environmentally regulated applications |
Recommendation: For high-volume OEM or aftermarket logistics, aluminized steel offers efficiency and lower upfront cost, but demands rigorous moisture control. For export-focused, eco-conscious, or heavy-duty applications, stainless steel’s durability and compliance advantages justify longer lead times and higher initial costs. Always validate supplier certifications and align material choice with regional regulatory landscapes.
Conclusion: Sourcing Aluminized Steel vs. Stainless Steel for Exhaust Systems
When sourcing materials for exhaust systems, the choice between aluminized steel and stainless steel involves a trade-off between cost, durability, and performance. Aluminized steel offers a cost-effective solution with good heat resistance and corrosion protection for short- to medium-term use, making it ideal for standard automotive applications and budget-conscious manufacturers. However, its lifespan is limited in harsh environments or high-moisture conditions due to its thinner protective coating.
In contrast, stainless steel—particularly grades like 409 or 304—provides superior corrosion resistance, longevity, and heat tolerance, making it the preferred choice for high-performance vehicles, marine applications, or regions with extreme weather conditions. While the initial cost is higher, the reduced need for replacement and maintenance often results in lower total cost of ownership over time.
Ultimately, the decision should align with the intended application, performance requirements, and budget constraints. For everyday consumer vehicles, aluminized steel remains a practical and economical option. For premium, heavy-duty, or long-life applications, investing in stainless steel delivers better durability and overall value. Careful sourcing from reputable suppliers is essential for both materials to ensure quality and consistency.