The global aluminium market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand across automotive, construction, aerospace, and renewable energy sectors. According to Grand View Research, the global aluminium market was valued at USD 193.2 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by aluminium’s favorable strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and recyclability—qualities that make it indispensable in lightweighting initiatives and sustainable manufacturing. As industries increasingly adhere to stringent performance and regulatory standards, the need for precision-engineered aluminium material specifications has become paramount. Leading manufacturers are responding with advanced alloys and certified production processes that meet ASTM, ISO, and industry-specific requirements. In this evolving landscape, identifying the top suppliers of standardized aluminium materials is critical for procurement professionals and engineers seeking reliability, compliance, and innovation. The following list highlights the nine foremost manufacturers recognized for their technical expertise, global footprint, and consistent delivery of high-specification aluminium products.
Top 9 Aluminium Material Specification Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 AMG Aluminum
Domain Est. 2012
Website: amg-al.com
Key Highlights: AMG Aluminum is a customer-focused, technology-driven organization dedicated to innovation, quality, technical expertise, and rapid response to customer needs….
#2 Alcoa
Domain Est. 1986
Website: alcoa.com
Key Highlights: Explore how Alcoa offers commodity grade aluminum, as well as low-carbon aluminum, EcoLum, and aluminum with 50% minimum recycled content, EcoDura, ……
#3 MatWeb
Domain Est. 1997
Website: matweb.com
Key Highlights: MatWeb’s searchable database of material properties includes data sheets of thermoplastic and thermoset polymers such as ABS, nylon, polycarbonate, polyester, ……
#4 Industry Standards
Domain Est. 1998
Website: aluminum.org
Key Highlights: For 70 years, the Aluminum Association has worked with the industry to develop and maintain technical standards for aluminum production….
#5 Aluminum Suppliers
Domain Est. 1998
Website: americanelements.com
Key Highlights: Aluminum qualified commercial & research quantity preferred supplier. Buy at competitive price & lead time. In-stock for immediate delivery….
#6 Aluminium
Domain Est. 1999
Website: azom.com
Key Highlights: Pure aluminium is soft, ductile, corrosion resistant and has a high electrical conductivity. It is widely used for foil and conductor cables….
#7 Products
Domain Est. 2002
Website: kaiseraluminum.com
Key Highlights: At Kaiser, we don’t just make a wide spectrum of aluminum mill products. We make them better. Our products are highly sophisticated based on the metallurgy and ……
#8 We are Constellium
Domain Est. 2006
Website: constellium.com
Key Highlights: Constellium is a global leader in the development, manufacturing, and recycling of aluminum products and solutions. · Discover our products and solutions….
#9 Aluminum and Aluminum Alloys Subject Guide
Domain Est. 1998
Website: asminternational.org
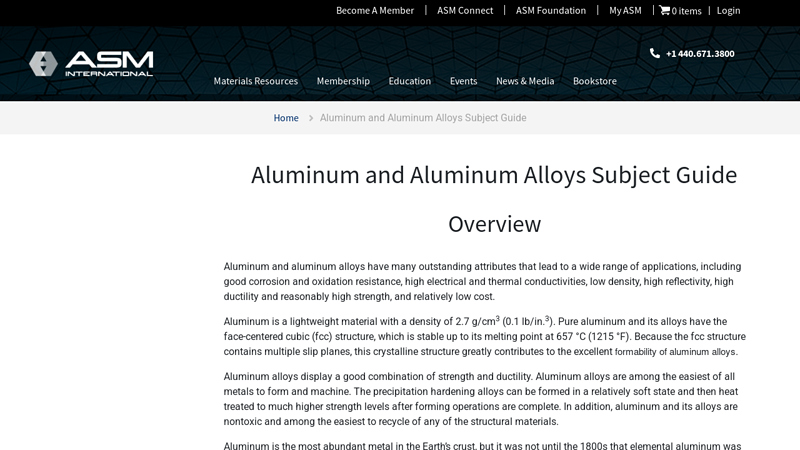
Key Highlights: Aluminum is a lightweight material with a density of 2.7 g/cm3 (0.1 lb/in.3). Pure aluminum and its alloys have the face-centered cubic (fcc) structure ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Aluminium Material Specification
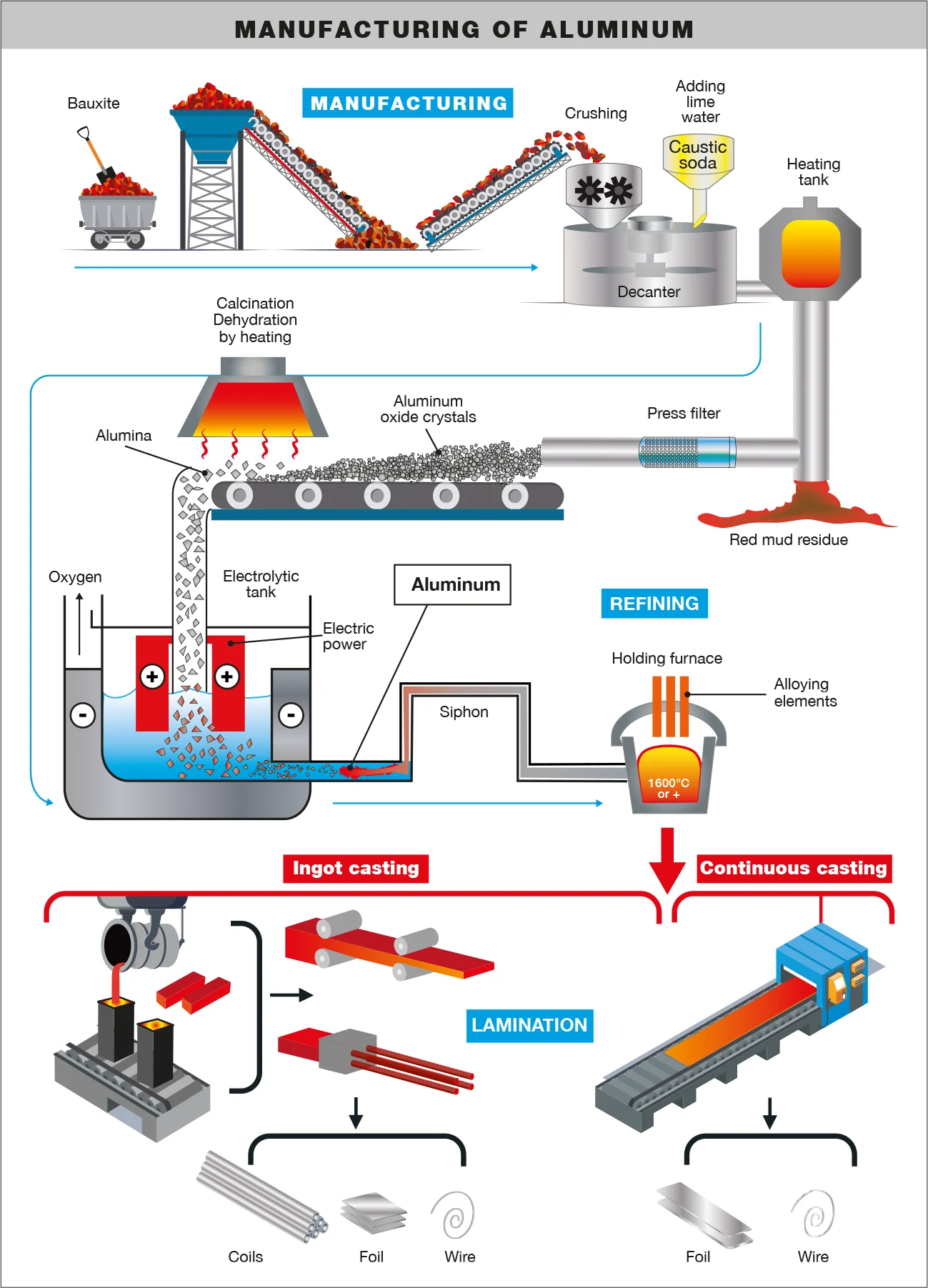
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Aluminium Material Specification
The global market for aluminium material specifications is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological advancements, sustainability mandates, and evolving industry demands. Key trends shaping the landscape include:
-
Increased Demand for High-Strength, Lightweight Alloys
The automotive and aerospace sectors are accelerating the adoption of advanced aluminium alloys—such as 7xxx (Al-Zn) and 6xxx (Al-Mg-Si) series—to meet fuel efficiency and emissions regulations. By 2026, material specifications will increasingly prioritize high strength-to-weight ratios, corrosion resistance, and improved formability, especially in electric vehicles (EVs) where weight reduction directly impacts battery range. -
Sustainability and Recycled Content Requirements
Regulatory pressures and corporate ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) goals are pushing manufacturers to adopt low-carbon aluminium. Specifications are expected to include mandatory thresholds for recycled content (e.g., minimum 50–70% post-consumer scrap) and verification of carbon footprint (e.g., <8 kg CO₂/kg Al). The EU’s Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) and similar policies will influence global standards. -
Standardization and Digital Material Passports
By 2026, digitalization of material traceability is expected to become mainstream. Industry consortia and certification bodies are likely to enforce standardized material specifications integrated with blockchain or digital product passports. This will ensure compliance with sustainability criteria and enable circular economy practices through precise recycling and reuse. -
Growth in Additive Manufacturing (AM) Specifications
The rise of aluminium-based 3D printing, particularly using AlSi10Mg and AlSi7Mg alloys, will drive demand for new material standards tailored to powder characteristics, flowability, purity, and mechanical performance post-printing. ASTM and ISO are expected to finalize more AM-specific aluminium specifications by 2026 to support aerospace, medical, and defense applications. -
Regional Divergence in Specifications
Regional regulatory frameworks will lead to divergent aluminium material standards. For example, Chinese GB standards may emphasize cost-efficiency and domestic supply chain resilience, while EU EN standards will focus on lifecycle emissions and recyclability. North American specifications (e.g., ASTM, SAE) will likely balance performance with environmental compliance. -
Innovation in Surface Treatments and Coatings
Enhanced material specifications will include stringent requirements for surface treatments—such as anodizing, chromate conversion, or ceramic coatings—to improve durability, aesthetics, and compatibility with adhesives in multi-material designs. These specifications will be critical in consumer electronics and transportation sectors.
In conclusion, the 2026 aluminium material specification landscape will be defined by performance optimization, environmental accountability, and digital integration. Stakeholders across the value chain—from producers to OEMs—must align with evolving standards to remain competitive and compliant in a rapidly decarbonizing global economy.
Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Aluminium Material Specifications (Quality, IP)
Sourcing aluminium with precise quality requirements and robust intellectual property (IP) protection involves several potential pitfalls. Overlooking these can lead to production delays, cost overruns, legal disputes, or compromised product performance. Below are key challenges to avoid:
Inadequate Definition of Material Specifications
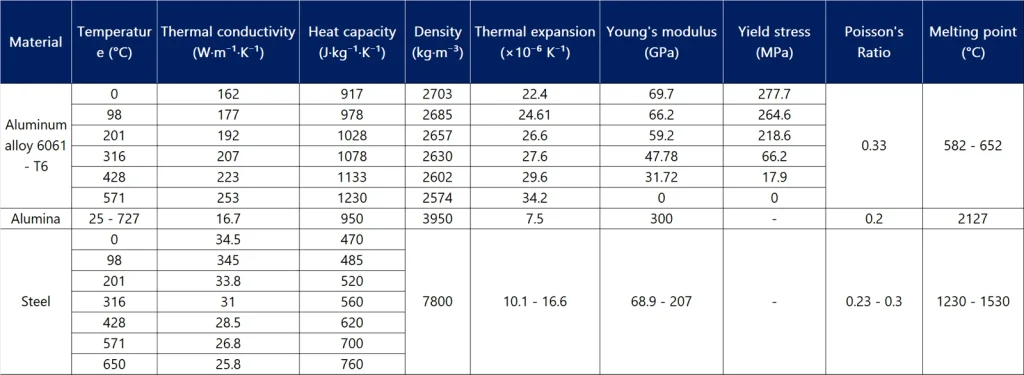
One of the most frequent issues is vague or incomplete material specifications. Buyers may cite generic standards (e.g., “6061-T6”) without defining critical attributes such as chemical composition tolerances, mechanical properties (tensile strength, yield strength, elongation), grain structure, surface finish, or anodizing requirements. This ambiguity can result in received material that technically meets a standard but fails in application due to uncontrolled variables.
Overlooking Regional or Industry-Specific Standards
Aluminium specifications vary across regions (e.g., ASTM in the U.S., EN in Europe, JIS in Japan) and industries (aerospace, automotive, construction). Assuming interchangeability without verifying equivalence can lead to non-compliant material. For example, aerospace-grade aluminium (e.g., AMS 4027) has stricter controls than commercial equivalents and requires full traceability and certification.
Insufficient Quality Assurance and Traceability
Failing to require proper documentation—such as mill test certificates (MTCs), heat lot traceability, and third-party inspection reports—can compromise quality control. Without full traceability, identifying the source of defects becomes difficult, especially in regulated industries. Suppliers in low-cost regions may provide falsified or incomplete documentation, increasing risk.
Misunderstanding Intellectual Property (IP) Rights
Aluminium alloys, especially proprietary ones (e.g., Alcoa’s 7050 or Novelis’ advanced automotive alloys), are often protected by patents or trade secrets. Sourcing such materials without proper licensing can lead to IP infringement. Buyers may assume that purchasing the material grants usage rights, but certain applications (e.g., resale, further processing, or integration into patented products) may require explicit permission.
Lack of Control Over Secondary Processing
Even if base aluminium meets specs, secondary processes like heat treatment, extrusion, or surface coating can alter properties. Relying on the supplier to manage these without defined process controls or approvals may result in inconsistent quality. For IP-sensitive components, uncontrolled processing could also risk reverse engineering or unauthorized replication.
Failure to Secure IP in Custom Alloy Development
When co-developing custom aluminium alloys with suppliers, companies often neglect to formalize IP ownership in contracts. Without clear agreements, the supplier may claim rights to the alloy composition or process, limiting the buyer’s freedom to manufacture elsewhere or protect their innovation.
Supply Chain Transparency and Sub-Tier Sourcing Risks
Complex supply chains may involve multiple tiers of suppliers. A primary vendor might source billets or ingots from sub-contractors with inferior quality controls or questionable IP compliance. Lack of visibility into the full chain increases exposure to counterfeit materials or unethical sourcing practices.
Currency and Contractual Risks in Long-Term Agreements
Aluminium prices are volatile. Fixed-price contracts without price adjustment clauses tied to LME (London Metal Exchange) rates can become financially unsustainable. Additionally, contracts may fail to address IP use duration, territorial rights, or audit rights, leading to disputes during renewal or scaling.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires detailed technical specifications, rigorous supplier vetting, clear contractual IP terms, and ongoing quality monitoring throughout the supply chain.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Aluminium Material Specification
This guide outlines key logistics and compliance considerations when specifying, handling, transporting, and documenting aluminium materials across the supply chain. Adherence ensures safety, regulatory conformity, and material integrity.
Material Specification Requirements
Aluminium materials must be specified according to recognized international or national standards (e.g., ASTM B209, EN 573, ISO 6361) that define chemical composition, mechanical properties, temper, dimensions, and surface finish. Specifications should include alloy designation (e.g., 6061-T6), product form (sheet, plate, extrusion, etc.), tolerances, and any required testing or certification (e.g., mill test certificates per EN 10204 3.1).
Regulatory Compliance
Compliance with environmental, health, safety, and trade regulations is mandatory. Key regulations include:
– REACH (EU): Ensure declaration of Substances of Very High Concern (SVHC) if applicable.
– RoHS (EU): Confirm absence of restricted hazardous substances in applicable end-use applications.
– TSCA (USA): Comply with Toxic Substances Control Act requirements.
– Local Emissions and Waste Regulations: Proper handling and disposal of swarf, grinding dust, and machining coolants containing aluminium fines.
Packaging and Handling
Aluminium materials must be packaged to prevent mechanical damage, contamination, and corrosion during storage and transit. Use:
– Edge protectors for sheet and plate.
– Desiccants in enclosed packaging to minimize moisture exposure.
– Non-abrasive, non-corrosive materials (e.g., plastic interleaving, VCI paper).
– Secure strapping and bracing on pallets or in containers.
Avoid direct contact with dissimilar metals (e.g., steel) to prevent galvanic corrosion.
Transportation and Storage
Transport aluminium in dry, well-ventilated conditions. Protect from rain, sea spray, and extreme temperatures. Store indoors on elevated, clean surfaces away from chemical fumes or high-humidity areas. Segregate by alloy and temper to avoid mix-ups. Label all batches clearly with material specifications, heat/lot number, and handling instructions.
Documentation and Traceability
Maintain full traceability through the supply chain. Required documentation includes:
– Material Test Reports (MTRs) or Certificates of Conformity.
– Batch/heat numbers linked to production records.
– Customs documentation for international shipments (e.g., commercial invoice, packing list, certificate of origin).
– SDS (Safety Data Sheet) for processed forms involving coatings or treatments.
Import/Export Controls
Verify export compliance per jurisdiction (e.g., U.S. EAR, EU Dual-Use Regulations). Some high-strength or specially processed aluminium alloys may be subject to licensing requirements due to strategic or defense applications. Accurate HS codes (e.g., 7606 for aluminium plates, sheets, strip) are essential for customs clearance.
Quality Assurance and Audits
Implement internal audits and supplier assessments to ensure ongoing compliance with material specifications and logistics practices. Validate that suppliers adhere to specified handling, packaging, and documentation standards. Perform periodic sampling and testing as needed to confirm material properties and surface integrity upon receipt.
Conclusion for Sourcing Aluminum Material Specification
In conclusion, the successful sourcing of aluminum material requires a comprehensive understanding of the required specifications, including alloy type, temper, mechanical properties, dimensional tolerances, surface finish, and compliance with relevant international standards (e.g., ASTM, EN, or ISO). Careful evaluation of supplier capabilities, quality assurance practices, and traceability is essential to ensure consistent material performance and reliability in the intended application. Additionally, considerations such as cost-effectiveness, lead times, sustainability, and supply chain resilience should be balanced against technical requirements. By establishing clear material specifications and partnering with reputable suppliers, organizations can achieve optimal performance, regulatory compliance, and long-term value in their aluminum procurement strategy.