The global alumina sheet market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising demand across aerospace, electronics, and industrial manufacturing sectors. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the global aluminum oxide (alumina) market was valued at approximately USD 16.5 billion and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 4.5% during the forecast period 2023–2028. This expansion is fueled by alumina’s exceptional thermal stability, electrical insulation properties, and mechanical strength, making it a preferred material for high-performance applications. Grand View Research further highlights increasing adoption in semiconductor substrates and LED lighting as key growth catalysts. As demand intensifies, a select group of manufacturers has emerged as leaders in producing high-purity alumina sheets with consistent quality and scalability. Here are the top 9 alumina sheet manufacturers shaping the industry’s future.
Top 9 Alumina Sheet Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Alumina (Al2O3)
Domain Est. 1993
Website: global.kyocera.com
Key Highlights: Alumina (Al2O3) is material of Fine Ceramics. KYOCERA is the global leading manufacturer of superior precision Fine Ceramics (Advanced Ceramics) products….
#2 Alumina Oxide (Al2O3)
Domain Est. 2002
Website: ortechceramics.com
Key Highlights: Alumina Oxide (Al2O3) Ceramics is the most widely used fine ceramics material. This material has superb material characteristics such as high electrical ……
#3 Alumina Sheet
Domain Est. 1993
Website: goodfellow.com
Key Highlights: In stock Free next-day deliveryAlumina Sheet is a high-purity aluminum oxide ceramic form characterized by exceptional hardness, electrical insulation capability, and resistance to…
#4 Aluminum Oxide
Domain Est. 1995
Website: ceramicsrefractories.saint-gobain.com
Key Highlights: Aluminum Oxide (Al2O3), often abbreviated as Alumina, is one of the most popular fine ceramic material families worldwide. Learn more about Al2O3 today….
#5 AluChem
Domain Est. 1997
Website: aluchem.com
Key Highlights: AluChem is a leader in the manufacture of specialty alumina and dedicated to producing the highest quality alumina products in our industry….
#6 Alumina
Domain Est. 1999
Website: coorstek.com
Key Highlights: CoorsTek offers an extensive line of aluminas (Al2O3). CoorsTek ceramics experts fine-tune the choice of alumina grade according to customer requirements….
#7 Chemshun Alumina Ceramic Mosaic Sheet
Domain Est. 2002
Website: chemshun.com
Key Highlights: The alumina mosaic sheet is an excellent wear resistance ceramic product.Hexagonal alumina tile sheet used as ceramic pulley lagging, rubber ceramic plate, ……
#8 Almatis
Domain Est. 2003
Website: almatis.com
Key Highlights: Global partner in the development, production and supply of high-quality alumina and alumina-based products….
#9 We are Constellium
Domain Est. 2006
Website: constellium.com
Key Highlights: Constellium is a global leader in the development, manufacturing, and recycling of aluminum products and solutions. · Discover our products and solutions….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Alumina Sheet

H2 2026 Market Trends for Alumina Sheet: Key Drivers and Outlook
The global alumina sheet market is poised for significant evolution in the second half of 2026 (H2 2026), shaped by confluence of industrial demand, technological advancements, and macroeconomic factors. Here’s an analysis of the key trends expected to dominate:
-
Accelerated Adoption in EVs and Lightweighting:
- Trend: Demand for alumina sheets will surge, particularly in electric vehicles (EVs) and next-gen aerospace. Alumina’s excellent strength-to-weight ratio, thermal stability, and corrosion resistance make it ideal for battery enclosures, heat shields, and structural components.
- Impact: Automakers and aerospace OEMs will prioritize lightweight materials to improve efficiency and range. Alumina sheets will increasingly replace heavier steel and compete with advanced composites in specific high-temperature applications. This sector will be the primary growth engine.
-
Advanced Manufacturing and Processing Innovations:
- Trend: Wider adoption of near-net-shape forming, precision machining (e.g., laser cutting, CNC), and improved sintering techniques (like spark plasma sintering) will enhance cost-effectiveness and design flexibility.
- Impact: Reduced material waste, shorter production cycles, and the ability to create complex geometries will lower the total cost of ownership for end-users, making alumina sheets more competitive against alternatives and opening new application avenues (e.g., intricate heat exchangers, micro-electromechanical systems – MEMS).
-
Supply Chain Resilience and Regionalization:
- Trend: Geopolitical tensions and past disruptions will drive a continued push for diversified and localized supply chains. Expect increased investment in alumina refining and sheet production capacity outside traditional hubs, particularly in North America and Europe.
- Impact: While this enhances security of supply for key industries (especially defense and critical infrastructure), it may lead to regional price variations and potential short-term bottlenecks as new facilities ramp up. Supply chain transparency and ESG compliance will become critical purchasing factors.
-
Sustainability and Circular Economy Focus Intensifies:
- Trend: Regulatory pressure (e.g., EU Green Deal, US climate initiatives) and corporate ESG goals will force the industry to address the high energy footprint of alumina production (Bayer process) and sheet sintering.
- Impact: Significant R&D investment will focus on:
- Low-Carbon Alumina: Scaling up inert anode technology, carbon capture and storage (CCS) for refineries, and increased use of renewable energy in production.
- Recycling: Developing efficient processes for recycling post-industrial and end-of-life alumina scrap. “Green alumina” with verifiable low carbon intensity will command premium pricing.
-
Competition and Material Substitution Dynamics:
- Trend: Alumina sheets will face intensified competition:
- From other Ceramics: Silicon Nitride (Si3N4) and Silicon Carbide (SiC) in ultra-high-temperature applications.
- From Advanced Metals: High-strength aluminum alloys and titanium in lightweighting, where lower cost or easier fabrication are paramount.
- From Composites: Carbon fiber reinforced polymers (CFRP) in structural aerospace parts.
- Impact: Alumina producers will need to emphasize their unique value proposition: exceptional cost-performance balance for high-wear, high-temperature, and electrically insulating applications, particularly where extreme thermal stability or chemical inertness is required.
- Trend: Alumina sheets will face intensified competition:
-
Digitalization and Smart Manufacturing:
- Trend: Integration of AI and IoT in production facilities for real-time process monitoring, predictive maintenance, and quality control will become standard.
- Impact: This will lead to improved consistency, reduced defects, optimized energy consumption, and faster time-to-market for new product grades tailored to specific customer needs.
H2 2026 Outlook Summary:
The alumina sheet market in H2 2026 is expected to be robust and growth-oriented, primarily fueled by the electrification of transport and advanced manufacturing needs. While price volatility related to energy costs and raw material supply (bauxite, caustic soda) remains a risk, the long-term demand fundamentals are strong. Success will depend on suppliers’ ability to innovate in low-carbon production, embrace advanced manufacturing, ensure supply chain resilience, and effectively position alumina’s unique advantages against competing materials in high-value applications. The market will increasingly bifurcate between standard grades and high-performance, sustainably produced specialty sheets.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Alumina Sheets: Quality and Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
Sourcing high-performance alumina (aluminum oxide, Al₂O₃) sheets requires careful attention to both material quality and intellectual property (IP) considerations. Overlooking these aspects can lead to product failure, supply chain disruptions, legal liabilities, and reputational damage. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
1. Inadequate Verification of Material Quality and Specifications
One of the most frequent issues is assuming that all alumina sheets meet the required technical standards without rigorous validation.
- Pitfall: Accepting supplier claims without independent verification of purity (e.g., 96%, 99.5%, 99.8%), grain size, density, mechanical strength (flexural, compressive), thermal conductivity, and electrical resistivity.
- Risk: Substandard materials may fail under operational stress (e.g., thermal cycling, electrical loads), leading to premature component failure in critical applications like electronics or aerospace.
- Best Practice: Require certified test reports (e.g., ASTM, ISO) and conduct third-party material testing. Define exact specifications in contracts, including tolerances and inspection criteria.
2. Inconsistent or Variable Manufacturing Processes
Alumina sheets produced via different methods (e.g., dry pressing, isostatic pressing, tape casting) can vary significantly in homogeneity and performance.
- Pitfall: Sourcing from suppliers who lack process control or traceability, resulting in batch-to-batch inconsistencies.
- Risk: Variability affects reliability in high-precision applications such as semiconductor substrates or medical devices.
- Best Practice: Audit supplier facilities for process controls (e.g., sintering profiles, powder handling) and demand material traceability (batch/lot numbers, production dates).
3. Misrepresentation of Intellectual Property Rights
Alumina formulations and manufacturing techniques may be protected by patents or trade secrets, especially for specialized grades (e.g., doped alumina, nanostructured variants).
- Pitfall: Unknowingly sourcing materials that infringe on third-party IP, particularly when suppliers offer “equivalent” or “generic” versions of proprietary products.
- Risk: Legal action from IP holders, product recalls, import/export bans, and financial penalties.
- Best Practice: Conduct IP due diligence. Require suppliers to warrant that their products do not infringe patents. Review relevant patent landscapes, especially for high-performance or specialty alumina.
4. Lack of Transparency in Supply Chain Origins
Raw material sourcing and intermediate processing can involve multiple tiers, increasing the risk of counterfeit or non-compliant materials.
- Pitfall: Relying on suppliers who cannot disclose the origin of alumina powder or processing steps.
- Risk: Exposure to counterfeit products, materials processed with uncontrolled methods, or conflict minerals (indirectly linked through additives or processing aids).
- Best Practice: Demand full supply chain transparency. Use suppliers who provide documentation on raw material sources and intermediate processing.
5. Overlooking Certification and Compliance Requirements
Certain industries (e.g., medical, aerospace, defense) require specific certifications (e.g., ISO 13485, AS9100, ITAR).
- Pitfall: Assuming standard industrial-grade alumina meets regulated industry standards.
- Risk: Non-compliance can result in rejected shipments, regulatory fines, or disqualification from contracts.
- Best Practice: Clearly define certification needs in procurement agreements and verify supplier certifications are current and applicable.
6. Insufficient Protection of Buyer’s Own IP
When custom formulations or geometries are involved, buyers risk IP exposure during sourcing.
- Pitfall: Sharing proprietary designs or specifications without non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) or protective clauses.
- Risk: Supplier reverse-engineering, unauthorized replication, or sharing designs with competitors.
- Best Practice: Implement robust NDAs and IP ownership clauses in contracts. Limit disclosure to only what is necessary for quoting or production.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP-related pitfalls, organizations can ensure reliable performance, legal compliance, and long-term supply chain security when sourcing alumina sheets.
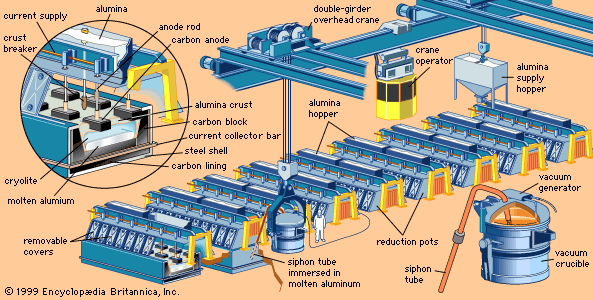
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Alumina Sheet
Product Overview and Classification
Alumina sheet, also known as aluminum oxide (Al₂O₃) ceramic sheet, is a high-performance industrial material valued for its excellent thermal stability, electrical insulation, hardness, and corrosion resistance. It is commonly used in electronics (e.g., substrates for power modules), aerospace, medical devices, and industrial machinery. Due to its ceramic nature and specific applications, alumina sheet is subject to various logistics and regulatory requirements.
Regulatory Compliance
Alumina sheet is generally non-hazardous and not classified under major hazardous material regulations such as OSHA HCS, GHS, or DOT Hazard Classes. However, compliance considerations include:
– REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals): Confirm that the alumina sheet formulation does not contain substances of very high concern (SVHCs) above threshold limits.
– RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances): Ensure compliance if the product is used in electrical/electronic equipment within the EU. Alumina itself is compliant, but coatings or binders may require evaluation.
– Export Controls: In some jurisdictions, advanced ceramic materials (including certain grades of alumina) may be subject to export control regulations (e.g., EAR in the U.S. under ECCN 1C013). Verify export license requirements based on end-use and destination.
– Customs Classification: Alumina sheets are typically classified under HS Code 8104.20 (Aluminum oxide, in powder or other forms) or 8547.20 (Insulating fittings for electrical machines), depending on form and application. Accurate classification is essential for import/export duties and documentation.
Packaging and Handling Requirements
To prevent damage during transit, alumina sheets must be carefully packaged:
– Protective Packaging: Use edge protectors, foam padding, or corrugated dividers between sheets to prevent chipping and cracking.
– Rigid Outer Containers: Pack in strong wooden crates or reinforced cardboard boxes to withstand stacking and handling.
– Moisture Protection: Include desiccants and moisture barrier wraps if stored or shipped in humid environments.
– Labeling: Clearly label packages as “Fragile” and “Handle with Care.” Include product identification, batch number, and handling instructions.
Transportation Guidelines
- Mode of Transport: Alumina sheets can be shipped via air, sea, or ground freight. Air freight is suitable for high-value or time-sensitive shipments, while sea freight is cost-effective for bulk orders.
- Stacking and Securing: In containers or trucks, secure loads with straps and dunnage to prevent shifting. Do not exceed weight limits per pallet or container.
- Temperature and Humidity: Avoid exposure to extreme temperatures and high humidity during transport, which may affect packaging integrity or material performance.
- Documentation: Provide commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading/air waybill, and any required certificates (e.g., Certificate of Conformance, RoHS/REACH compliance).
Storage Recommendations
- Environment: Store in a clean, dry, temperature-controlled area (15–30°C) with low humidity.
- Shelving: Keep sheets on flat, level surfaces; avoid leaning or stacking without proper support.
- Contamination Control: Prevent exposure to dust, oils, or chemicals that may compromise surface integrity, especially for precision applications.
Safety and Handling Precautions
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): When handling or machining alumina sheets, use gloves and safety glasses to protect against sharp edges or dust from cutting/grinding.
- Dust Control: If machining is performed on-site, use appropriate ventilation and respiratory protection, as alumina dust may be a respiratory irritant.
- Training: Ensure personnel are trained in safe handling procedures for brittle materials.
Documentation and Recordkeeping
Maintain comprehensive records for compliance and traceability, including:
– Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS/SDS) – though non-hazardous, a SDS should be available.
– Certificates of Analysis (CoA) or Conformance (CoC) for quality verification.
– Export documentation (e.g., ECCN classification, license if applicable).
– Customer-specific compliance declarations (e.g., conflict minerals, carbon footprint).
Disposal and Environmental Considerations
Alumina is chemically stable and non-toxic. Waste material can typically be disposed of in accordance with local non-hazardous waste regulations. Recycling or reuse is encouraged where feasible. Confirm with local authorities for specific disposal guidelines.
Summary
Proper logistics and compliance management for alumina sheet ensures safe handling, regulatory adherence, and customer satisfaction. Key focus areas include accurate classification, robust packaging, export compliance, and appropriate documentation. Always consult regulatory authorities or legal experts for jurisdiction-specific requirements.
Conclusion for Sourcing Alumina Sheet:
After a thorough evaluation of suppliers, material specifications, pricing, lead times, and quality certifications, it is concluded that sourcing alumina sheets from [Selected Supplier Name] offers the optimal balance of quality, reliability, and cost-effectiveness for our application. The supplier consistently provides high-purity alumina sheets (96–99.8% Al₂O₃) that meet required mechanical, thermal, and electrical specifications, ensuring suitability for demanding environments such as high-temperature insulation, wear resistance, and electronic substrates.
Additionally, the supplier demonstrates strong manufacturing capabilities, reliable delivery schedules, and compliance with international quality standards (e.g., ISO 9001), reducing supply chain risks. While alternative suppliers were considered, [Selected Supplier Name] stands out due to their technical support, customization options, and favorable long-term pricing agreements.
In conclusion, establishing a strategic partnership with [Selected Supplier Name] for the supply of alumina sheets is recommended to ensure consistent product performance, operational efficiency, and scalability for future production needs.