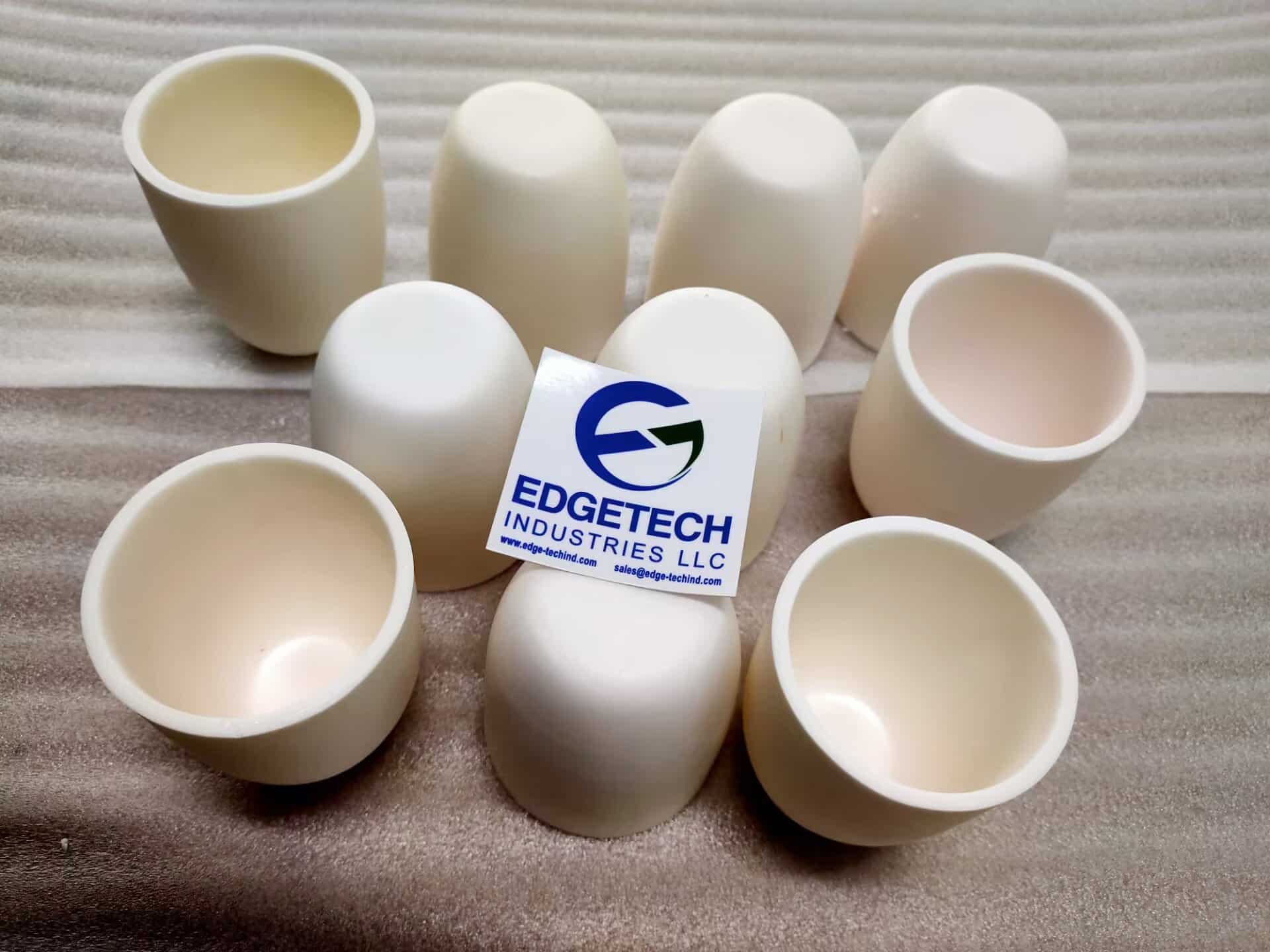
The global demand for high-performance ceramic materials has fueled rapid expansion in the alumina crucible market, driven by increasing applications in laboratory research, metallurgy, electronics, and advanced manufacturing. According to a 2023 report by Grand View Research, the global alumina ceramics market was valued at USD 12.8 billion and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.1% from 2023 to 2030. This surge is largely attributed to the material’s exceptional thermal stability, corrosion resistance, and electrical insulation properties—key factors that make alumina crucibles indispensable in high-temperature processing environments. Additionally, Mordor Intelligence forecasts similar momentum, citing rising investments in materials science and semiconductor fabrication as critical growth enablers. As industries prioritize precision and reliability, the need for high-purity, durable alumina crucibles has intensified, positioning leading manufacturers at the forefront of innovation and supply. In this evolving landscape, identifying the top producers is essential for sourcing reliable, high-quality components.
Top 10 Alumina Crucible Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Alumina High Form Crucibles
Domain Est. 2005
Website: lspceramics.com
Key Highlights: Alumina high form crucibles are specialized containers crafted by LSP Ceramics from high- purity aluminum oxide (Al2O3), renowned for their high-temperature ……
#2 High
Domain Est. 2017
Website: preciseceramic.com
Key Highlights: Buy high-purity alumina crucibles for laboratory and industrial applications from Advanced Ceramic Materials. Various sizes and forms available. Order now!…
#3 High Temperature Alumina Crucibles
Domain Est. 2023
Website: tkg-ceramics.com
Key Highlights: TKG Industrial Ceramics has been producing high-temperature alumina crucibles & refractory ramming materials for 15+ years. Call TKG today to learn more!…
#4 Alumina Crucibles
Domain Est. 1996
Website: zircoa.com
Key Highlights: Zircoa alumina crucibles deliver cost-effective performance up to 1700°C with hydraulically pressed precision and uniform surfaces for cleaner melts….
#5 Leading Supplier of Alumina Crucibles
Domain Est. 2000
Website: easterncrucible.com
Key Highlights: Our high temperature alumina crucibles are manufactured in sizes up to 4000# and can be constructed to your specific needs both in size and in material ……
#6 Crucibles
Domain Est. 2002
Website: mtixtl.com
Key Highlights: 48 products ; Quartz (SiO2) Cylindrical Crucible ; Quartz (SiO2) Boat Crucible ; Alumina (Al2O3) Cylindrical Crucible from 0.1 mL to 3000mL optional ; Alumina ( ……
#7 alumina ceramic pipe&fused quartz crucible
Domain Est. 2017
Website: xtlceramic.com
Key Highlights: With complete alumina ceramic pipe&fused quartz crucible production lines and experienced employees, can independently design, develop, manufacture, and test ……
#8 Alumina Material (Al2O3)
Domain Est. 2018
Website: almathcrucibles.com
Key Highlights: $57 deliveryAlumina. Browse our wide range of advanced ceramics and refractory crucibles available for sale within our online store. We hold over 1000 products in stock, ……
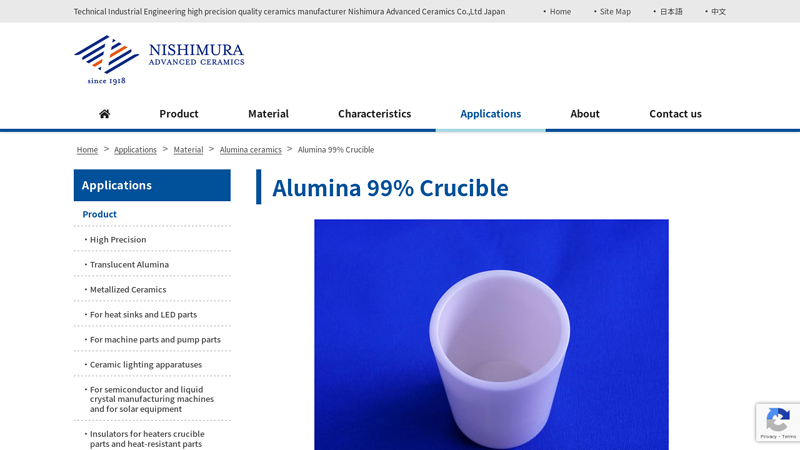
#9 Alumina 99% Crucible
Domain Est. 2018
Website: nishimuraac.com
Key Highlights: Our custom-made crucible contains 99.9% of alumina. We can have extra cutting work on it; therefore, we can make a hole, a tap hole, or a ditch….
#10 Alumina crucibles and pods
Domain Est. 2021
Website: umicore-ceramics.com
Key Highlights: The alumina ceramic crucibles offered within the product range are of various shapes and sizes. They are made of Kyocera DEGUSSIT AL23 pure alumina, DEGUSSIT ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Alumina Crucible

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Alumina Crucibles
The global alumina crucible market is poised for steady growth through 2026, driven by increasing demand across high-temperature industrial applications, advancements in material science, and expanding use in emerging technologies. Below is a detailed analysis of key market trends expected to shape the alumina crucible industry by 2026.
-
Rising Demand from Semiconductor and Electronics Manufacturing
Alumina crucibles are essential in the production of single-crystal silicon via the Czochralski (CZ) process, a core method in semiconductor manufacturing. With the global push toward advanced electronics, electric vehicles (EVs), and 5G infrastructure, demand for high-purity silicon is surging. This, in turn, is boosting the need for high-performance alumina crucibles capable of withstanding extreme temperatures and corrosive environments. By 2026, the semiconductor sector is anticipated to be the largest end-user segment for alumina crucibles, particularly in Asia-Pacific regions like China, South Korea, and Taiwan. -
Growth in Renewable Energy and Photovoltaic (PV) Industries
The solar energy sector, especially in the production of photovoltaic cells, relies on alumina crucibles for melting and processing silicon. As global investments in renewable energy continue to rise—driven by climate goals and government incentives—the PV industry is expected to expand significantly by 2026. This growth will directly increase the consumption of alumina crucibles, particularly those engineered for high thermal stability and purity. -
Technological Advancements and Product Innovation
Manufacturers are increasingly investing in the development of doped or reinforced alumina crucibles (e.g., with zirconia or yttria coatings) to enhance resistance to thermal shock and chemical corrosion. These innovations are critical for extending crucible lifespan and reducing contamination in sensitive processes. By 2026, crucibles with optimized microstructures and surface treatments are expected to gain market share, especially in high-end applications requiring ultra-pure materials. -
Regional Market Shifts and Manufacturing Localization
Asia-Pacific is projected to dominate the alumina crucible market by 2026, fueled by robust industrial growth, government support for high-tech manufacturing, and expanding semiconductor fabs. China and India are emerging as key production and consumption hubs. Meanwhile, in North America and Europe, reshoring of semiconductor production (e.g., via the U.S. CHIPS Act and EU Chips Act) is expected to stimulate regional demand, encouraging local sourcing and partnerships with crucible suppliers. -
Supply Chain Resilience and Raw Material Constraints
The availability and cost of high-purity alumina (HPA) remain critical factors. Geopolitical tensions and export restrictions on raw materials may impact supply chains. As a result, by 2026, leading manufacturers are anticipated to vertically integrate or form strategic alliances to secure raw material supplies. Recycling and reuse of spent crucibles may also become more common to address sustainability and cost concerns. -
Sustainability and Environmental Regulations
Environmental regulations are pushing industries to adopt cleaner and more energy-efficient processes. Alumina crucibles, being reusable and inert, align well with green manufacturing goals. However, their production involves energy-intensive sintering processes. By 2026, manufacturers are expected to adopt energy-efficient kilns and explore alternative binders or production methods to reduce carbon footprints, responding to ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) pressures. -
Competitive Landscape and Market Consolidation
The market is witnessing increased competition among key players such as Saint-Gobain, CoorsTek, and Rauschert, alongside rising regional manufacturers in Asia. By 2026, consolidation through mergers and acquisitions is likely, as companies seek to expand product portfolios, enhance R&D capabilities, and strengthen global distribution networks.
Conclusion
By 2026, the alumina crucible market will be shaped by technological innovation, sectoral demand from semiconductors and renewables, and strategic regional developments. Companies that invest in high-purity materials, sustainable practices, and supply chain resilience are expected to lead the market. As end-user industries continue to evolve, alumina crucibles will remain a critical enabler of high-temperature material processing across advanced manufacturing sectors.

H2: Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Alumina Crucibles – Quality and Intellectual Property (IP) Concerns
Sourcing alumina crucibles—especially for high-temperature applications in industries such as semiconductor manufacturing, metallurgy, and laboratory research—presents several critical challenges related to quality consistency and intellectual property (IP) protection. Below are common pitfalls under these two categories:
1. Quality-Related Pitfalls
a. Inconsistent Material Purity
Alumina crucibles must meet stringent purity requirements (e.g., 99.5% to 99.99% Al₂O₃) depending on the application. A common pitfall is sourcing from suppliers who provide inconsistent batch-to-batch purity. Impurities (e.g., Na₂O, SiO₂, Fe₂O₃) can lead to contamination, unwanted reactions, or crucible failure at high temperatures.
Impact: Compromised experimental results or process contamination in sensitive environments (e.g., crystal growth).
b. Poor Dimensional Accuracy and Tolerances
Low-cost manufacturers may not adhere to tight dimensional tolerances. This can lead to improper fit in furnaces or automated systems, causing thermal stress, uneven heating, or mechanical failure.
Impact: Reduced equipment lifespan, safety risks, or process inefficiencies.
c. Substandard Density and Microstructure
High-quality alumina crucibles require high sintering temperatures to achieve optimal density and grain structure. Some suppliers cut corners in sintering, resulting in porous or weak crucibles.
Impact: Reduced thermal shock resistance, shorter service life, and risk of cracking or spalling during rapid temperature changes.
d. Lack of Certifications and Traceability
Reputable suppliers provide material test reports (MTRs), ISO certifications, and full traceability. Many low-cost or unverified vendors lack proper documentation.
Impact: Inability to validate quality for regulated or critical applications; compliance risks.
e. Inadequate Thermal Shock Resistance
Not all alumina grades are equal. Some suppliers misrepresent the grade (e.g., passing off 95% alumina as 99%), leading to premature failure under thermal cycling.
Impact: Unexpected downtime and cost overruns due to frequent replacements.
2. Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
a. Reverse Engineering and Design Theft
Custom-designed crucibles (e.g., unique shapes, coatings, or composite structures) are vulnerable to reverse engineering, especially when sourced from regions with weak IP enforcement.
Impact: Loss of competitive advantage; unauthorized replication of proprietary designs by competitors.
b. Lack of IP Clauses in Contracts
Procurement agreements often omit clear IP ownership terms. If a supplier manufactures a custom design, they may claim partial rights or reproduce it for other clients.
Impact: Legal disputes, loss of exclusivity, and erosion of product differentiation.
c. Use of Counterfeit or Grey-Market Goods
Some suppliers may offer “branded” alumina crucibles at suspiciously low prices, which are actually counterfeit or diverted from authorized channels.
Impact: Poor performance, warranty voidance, and exposure to liability if failure causes damage.
d. Supplier Collaboration Risks
When working closely with a supplier to develop a new crucible specification, sensitive process data (e.g., operating temperatures, material interactions) may be disclosed without confidentiality safeguards.
Impact: Exposure of trade secrets; potential for supplier to serve competitors with similar solutions.
Mitigation Strategies
- Qualify Suppliers Rigorously: Audit manufacturing processes, request test reports, and verify ISO 9001 or equivalent certifications.
- Enforce IP Protections: Include clear IP ownership, non-disclosure agreements (NDAs), and anti-cloning clauses in contracts.
- Conduct Incoming Quality Inspections: Use techniques like XRF (X-ray fluorescence) or SEM/EDS to verify composition and microstructure.
- Source from Reputable Regions/Manufacturers: Prefer suppliers from countries with strong IP laws and quality control standards (e.g., USA, Germany, Japan).
- Use Proprietary Markings or Tracers: Embed unique identifiers in custom crucibles to track authenticity and deter counterfeiting.
Conclusion:
Sourcing alumina crucibles involves balancing cost with performance and security. Overlooking quality parameters or IP risks can lead to operational failures, safety hazards, and loss of competitive edge. A proactive, documented sourcing strategy is essential to mitigate these pitfalls.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Alumina Crucible
Overview
Alumina crucibles, made from high-purity aluminum oxide (Al₂O₃), are widely used in high-temperature laboratory and industrial applications such as melting metals, ash testing, and thermal analysis. Proper logistics and compliance procedures are essential to ensure safe handling, transportation, and regulatory adherence. This guide outlines key considerations for the international and domestic shipment of alumina crucibles.
Classification and Regulatory Status
Alumina crucibles are generally classified as inert ceramic laboratory ware. They are non-hazardous, non-toxic, non-flammable, and non-reactive under normal conditions. As such, they are not regulated as dangerous goods under major international transport regulations, including:
- IMDG Code (International Maritime Dangerous Goods) – Not regulated
- IATA DGR (International Air Transport Association Dangerous Goods Regulations) – Not regulated
- ADR (European Agreement concerning the International Carriage of Dangerous Goods by Road) – Not regulated
Note: Always confirm the composition of the crucible. If the crucible contains additives (e.g., zirconia, binders, or coatings), reassessment may be required.
Packaging Requirements
Proper packaging is critical to prevent breakage during transit. Recommended packaging steps include:
- Inner Packaging:
- Individually wrap each crucible in bubble wrap or foam.
-
Use compartmentalized trays or partitioned boxes to avoid contact between crucibles.
-
Outer Packaging:
- Use strong, double-walled corrugated cardboard boxes.
-
Fill void spaces with cushioning material (e.g., foam peanuts, air pillows, or paper).
-
Labeling:
- Mark the package as “Fragile” and “Handle with Care”.
- Include orientation arrows if applicable.
-
Attach shipping label with consignee and shipper details.
-
Stacking and Palletizing (for bulk shipments):
- Secure boxes on a wooden or plastic pallet using stretch wrap.
- Ensure load stability and avoid overhang.
- Max stack height should not exceed manufacturer or carrier recommendations.
Transportation Modes
Air Freight
- Alumina crucibles are eligible for air transport without restriction.
- Use IATA-compliant packaging to minimize damage risk.
- Ensure proper declaration on air waybill: “Ceramic Laboratory Ware – Non-Hazardous.”
Sea Freight
- Stow in dry, ventilated containers to prevent moisture exposure.
- Use moisture barrier bags or desiccants if shipping to humid climates.
- Declare as “Ceramic Articles – Non-Dangerous Goods” on the bill of lading.
Ground Transport
- Secure cargo to prevent shifting during transit.
- Avoid exposure to extreme temperature fluctuations or moisture.
Customs and Import Compliance
- HS Code (Harmonized System Code):
- Recommended HS code: 6914.90 – “Ceramic goods of a kind used in laboratories, pharmaceuticals or similar industries.”
-
Confirm with local customs authority, as classification may vary by country.
-
Documentation:
- Commercial Invoice
- Packing List
- Certificate of Origin (if required)
-
Bill of Lading or Air Waybill
-
Import Restrictions:
- No known import bans or restrictions for standard alumina crucibles.
- Verify destination country requirements (e.g., CE marking not required for raw labware, but may apply if sold as part of a kit).
Storage and Handling
- Storage Conditions: Store in a dry, clean environment at room temperature.
- Handling: Use gloves to avoid contamination; avoid dropping or impact.
- Shelf Life: Indefinite, provided storage conditions are maintained.
Environmental, Health, and Safety (EHS) Considerations
- Dust Generation: When broken or ground, alumina can produce fine particulate. Avoid creating dust; use PPE (mask, gloves) if handling damaged crucibles.
- Disposal: Non-hazardous waste. Dispose of according to local solid waste regulations.
- MSDS/SDS: A Safety Data Sheet is typically not required for intact alumina crucibles. However, one may be provided upon request for regulatory compliance.
Summary of Key Actions
| Action | Requirement |
|——-|————-|
| Classification | Non-hazardous, non-regulated goods |
| Packaging | Cushioned, labeled as fragile |
| Transport | Allowed by air, sea, and land without restriction |
| Customs | Use HS 6914.90; provide standard shipping documents |
| Storage | Dry, clean, room temperature environment |
| Disposal | Non-hazardous waste |
For further assistance, consult your logistics provider and verify requirements with national customs and transport authorities prior to shipment.
Conclusion for Sourcing Alumina Crucibles
In conclusion, sourcing high-quality alumina crucibles requires a careful evaluation of material purity, dimensional accuracy, thermal stability, and supplier reliability. Alumina crucibles, known for their excellent resistance to high temperatures, chemical inertness, and mechanical strength, are essential in demanding applications such as high-temperature processing, analytical chemistry, and materials research. To ensure optimal performance and longevity, it is critical to select crucibles made from high-purity alumina (typically 99.5% or higher) and to partner with reputable suppliers who adhere to strict quality control standards and provide consistent product specifications.
Additionally, considerations such as application requirements, volume needs, lead times, and cost-effectiveness should guide the sourcing decision. Establishing long-term relationships with trusted manufacturers or distributors not only ensures supply chain stability but also facilitates technical support and customization when necessary. By prioritizing quality, reliability, and supplier expertise, organizations can effectively source alumina crucibles that meet their performance needs and contribute to process efficiency and reproducibility.