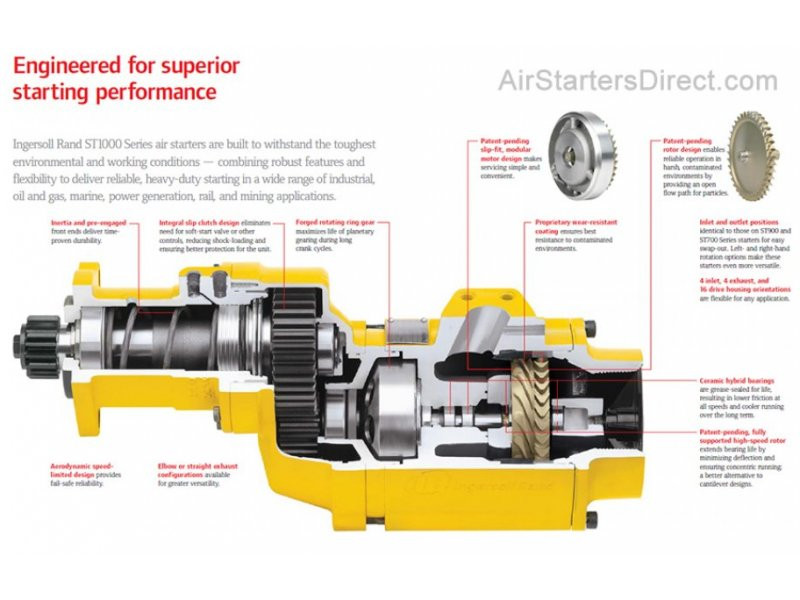
The global air starters market is experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing demand for reliable starting systems in heavy machinery and industrial engines. According to Mordor Intelligence, the starter motors market—which includes air starters—was valued at USD 10.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.2% from 2024 to 2029. This expansion is fueled by rising industrialization, the need for efficient engine ignition in harsh environments, and ongoing advancements in pneumatic technologies. Air starters, known for their durability and safety in explosive or high-temperature settings, are particularly critical in sectors such as oil & gas, marine, power generation, and construction. As demand for robust and maintenance-efficient starting solutions grows, leading manufacturers are focusing on innovation, material resilience, and global supply chain scalability. In this evolving landscape, nine key players have emerged as dominant forces, combining engineering excellence with broad market reach to meet the rigorous demands of modern industrial applications.
Top 9 Air Starters Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 TDI Air Starters
Domain Est. 2005
Website: tdi-airstarter.com
Key Highlights: TDI TurboTwin is the leading manufacturer of turbine air starters. T100, T50, T30, T20, Air Starters. Air Starter specialists. Air Starters for Caterpillar ……
#2 Air Starter Components
Domain Est. 2022
Website: mascoairstarter.com
Key Highlights: As a leading manufacturer of air starters, aftermarket components, and certified remanufactured starters, we are dedicated to providing exceptional quality and ……
#3 Air Turbine Starters
Domain Est. 1997
Website: unisonindustries.com
Key Highlights: For nearly seven decades, TDI has been recognized for designing turbine-powered air starters that deliver unmatched reliability and durability. Backed by ……
#4 Air Starters
Domain Est. 1998
Website: ascairstarter.com
Key Highlights: ASC is a leading global supplier of air starters that specializes in top quality starters, parts, and the best and most stable pricing in the industry….
#5 TDI Tech Development
Domain Est. 1999
Website: hatraco.com
Key Highlights: TDI Air Starters have become the world leader in quality and reliability. Not without reason, Hatraco is proud to be an official TDI air starter distributor….
#6 Air Starters
Domain Est. 2000
Website: rowlandcompany.com
Key Highlights: The Rowland Company is a proud supplier and distributor of genuine Tech Development Inc (TDI) and Ingersoll Rand (IR) air starters….
#7 Vane and Turbine Air Starters
Domain Est. 2001
Website: powertools.ingersollrand.com
Key Highlights: Ingersoll Rand air starters are flexible, efficient alternatives to electric sources. They create sheer power from the natural environment….
#8 Air Starter Sales And Service
Domain Est. 2004
Website: amairstarters.com
Key Highlights: A/M Air Starters has a complete line of new starters and replacement parts for the: 20BM, SM450, SS660offers the following models, 3AM, 3BM, 5AM, 5BM, 20BM, ……
#9 WEG
Domain Est. 2004
Website: weg.net
Key Highlights: WEG provides global solutions for electric motors, variable frequency drives, soft starters, controls, panels, transformers, and generators….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Air Starters

H2: Market Trends in Air Starters for 2026
The global air starters market is projected to experience steady growth by 2026, driven by increasing industrial automation, rising demand for reliable engine starting systems in harsh environments, and advancements in pneumatic technologies. Air starters—mechanical devices that use compressed air to initiate internal combustion engines—are widely used in oil and gas, marine, power generation, mining, and heavy construction sectors due to their safety, durability, and spark-free operation.
Key trends shaping the air starters market in 2026 include:
-
Growing Demand in Oil & Gas and Marine Industries:
The oil and gas sector continues to be a primary consumer of air starters, especially in offshore platforms and remote drilling sites where electrical systems pose explosion risks. Similarly, marine vessels—particularly commercial ships and offshore support vessels—favor air starters for their reliability in corrosive, high-humidity environments. The ongoing investments in LNG carriers and deepwater exploration are expected to further bolster demand. -
Focus on Safety and Explosion-Proof Equipment:
As industrial safety regulations become more stringent, especially in ATEX and IECEx-certified zones, the preference for air starters over electric starters is increasing. Their intrinsically safe design makes them ideal for use in hazardous locations, supporting market expansion in chemical plants, refineries, and mining operations. -
Technological Advancements and Product Innovation:
Manufacturers are investing in lightweight, corrosion-resistant materials (such as aluminum and composites) and improved gear mechanisms to enhance efficiency and reduce maintenance. Smart integration with digital monitoring systems—enabling predictive maintenance and remote diagnostics—is emerging as a differentiating factor among leading suppliers. -
Shift Toward Energy Efficiency and Sustainability:
While air starters rely on compressed air systems, there is a growing emphasis on integrating energy-efficient compressors and reclaiming exhaust air. Companies are optimizing air starter designs to reduce air consumption, aligning with broader industrial sustainability goals. -
Regional Growth Dynamics:
Asia-Pacific is expected to witness the highest growth rate by 2026, fueled by industrialization in India, China, and Southeast Asia, along with expanding infrastructure and power projects. North America and Europe will maintain steady demand, supported by modernization of aging power plants and maritime fleets. -
Supply Chain Resilience and Localization:
Post-pandemic disruptions have prompted manufacturers to localize production and diversify supply chains. This trend is leading to increased regional manufacturing of air starters, reducing lead times and improving after-sales service.
In conclusion, the 2026 air starters market will be characterized by technological innovation, regulatory compliance, and sector-specific demand growth. Companies that prioritize reliability, safety certification, and integration with Industry 4.0 systems are likely to gain a competitive edge in this evolving landscape.

H2: Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Air Starters – Quality and Intellectual Property (IP) Concerns
Sourcing air starters—pneumatic devices used to start internal combustion engines, especially in industrial, marine, and oil & gas applications—can present several challenges, particularly in the areas of quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) protection. Companies must navigate these pitfalls carefully to ensure reliability, compliance, and long-term operational safety.
1. Compromised Quality Due to Substandard Manufacturing
One of the most prevalent issues is receiving air starters that fail to meet performance or durability standards. This often stems from:
- Use of Inferior Materials: Low-cost suppliers may substitute high-grade alloys or seals with cheaper alternatives, leading to premature wear, corrosion, or failure under high pressure and temperature.
- Inconsistent Tolerances: Poor machining practices result in misaligned components, air leaks, or inefficient torque transmission, reducing starter reliability.
- Lack of Certification: Many suppliers, especially in unregulated markets, do not provide certifications such as ISO 8573 (compressed air quality), ATEX (explosive environments), or API standards, increasing risk in critical applications.
Impact: Equipment downtime, safety hazards, and increased total cost of ownership due to frequent replacements and maintenance.
2. Counterfeit or Reverse-Engineered Products
Air starters from certain regions are frequently reverse-engineered or counterfeit copies of established OEM designs (e.g., companies like Holset, Kelly Pneumatics, or Desoutter). These products:
- Infringe on IP Rights: Copy patented designs, trademarks, or technical specifications without authorization.
- Lack Design Integrity: Even if they resemble genuine parts, internal engineering flaws often compromise performance and safety.
- Expose Buyers to Legal Risk: Procuring counterfeit components—knowingly or unknowingly—can lead to liability, especially in regulated industries.
Impact: Legal exposure, voided warranties, and reputational damage, particularly if failures lead to accidents or non-compliance.
3. Inadequate Documentation and Traceability
Many low-cost suppliers fail to provide:
- Test Reports or Performance Data
- Material Certifications (e.g., mill test reports)
- Traceable serial numbers or batch records
This lack of documentation makes it difficult to verify compliance or conduct root cause analysis during failures, especially in safety-critical or audited environments.
4. Weak IP Protection in Supply Contracts
Procurement agreements often overlook IP clauses, leaving companies vulnerable to:
- Unauthorized replication of custom-designed or modified starters.
- Use of proprietary designs by suppliers for third-party sales.
- No recourse in case of IP breach due to vague or absent contractual terms.
5. Geopolitical and Supply Chain Risks
Sourcing from regions with lax IP enforcement increases the risk of:
- Design theft during production.
- Uncontrolled distribution of copied products into global markets.
- Difficulty enforcing contracts or quality claims across jurisdictions.
Recommendations to Mitigate Risks
- Source from Reputable, Authorized Distributors or OEMs with verifiable quality systems (e.g., ISO 9001).
- Conduct Factory Audits and request sample testing under real-world conditions.
- Include Strong IP Clauses in contracts, specifying ownership, confidentiality, and restrictions on replication.
- Require Full Documentation, including CE, ATEX, or API certifications where applicable.
- Use Legal Protections such as NDAs and design patents for custom-engineered starters.
By addressing these quality and IP-related pitfalls proactively, organizations can ensure reliable performance, regulatory compliance, and protection of their technical investments when sourcing air starters.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Air Starters
Air starters are essential tools used across industries such as oil & gas, marine, aviation, and power generation to initiate large diesel and gas engines. Due to their mechanical nature, pressurized components, and international usage, their logistics and compliance requirements must be carefully managed to ensure safety, regulatory adherence, and efficient delivery.
Regulatory Classification and Documentation
Air starters are typically classified under Harmonized System (HS) codes related to pneumatic tools or engine starting equipment. Common classifications include:
– HS Code 8414.80 – Other air or vacuum pumps, air or other gas compressors, and fans – Parts
– HS Code 8467.21 – Pneumatic hand tools
Documentation required for international shipment includes:
– Commercial Invoice
– Packing List
– Certificate of Origin
– Air Waybill or Bill of Lading
– Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS), if applicable (e.g., lubricants included)
Ensure correct classification to avoid customs delays or penalties. Consult local customs authorities or a trade compliance expert when in doubt.
Packaging and Handling Requirements
Proper packaging is crucial to prevent damage during transit:
– Use robust, moisture-resistant export crates or heavy-duty corrugated boxes.
– Secure air starters with foam inserts, corner boards, or wooden skids to prevent movement.
– Include desiccants in packaging to mitigate moisture exposure, especially in marine environments.
– Clearly label packages with:
– “Fragile”
– “This Side Up”
– Product name and model number
– Handling instructions (e.g., “Do Not Drop”)
Avoid stacking heavy items on top of air starter packages.
Transport Restrictions and Hazard Considerations
While air starters themselves are not classified as hazardous materials under IATA/IMDG regulations, certain conditions may trigger special handling:
– If shipped with compressed air tanks or nitrogen cartridges, these may be regulated as dangerous goods (e.g., UN1013, Compressed Gas).
– Lubricants or grease included with the starter may be subject to hazardous material regulations if flammable.
– Always verify contents and consult IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations (DGR) or IMDG Code when shipping by air or sea.
When in doubt, perform a hazard classification assessment before shipment.
Import/Export Compliance
Key considerations for global trade:
– Export Controls: Air starters may fall under dual-use export control regimes (e.g., EAR – Export Administration Regulations in the U.S.) if destined for restricted countries or end-users.
– Import Duties & Taxes: Duty rates vary by country. Some nations offer reduced tariffs under trade agreements (e.g., USMCA, CETA).
– Certifications: Certain markets require product certifications:
– CE Marking (European Union) – Indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental standards.
– UKCA Marking (United Kingdom) – Required for products sold in Great Britain.
– CRN (Canadian Registration Number) – May be needed if the air starter includes pressure vessels regulated under provincial codes.
Verify destination-specific requirements prior to shipment.
Storage and Inventory Management
For distributors and end-users:
– Store air starters in a dry, temperature-controlled environment to prevent corrosion.
– Keep units in original packaging until deployment.
– Implement FIFO (First In, First Out) inventory practices to reduce obsolescence.
– Periodically inspect stored units for seal integrity and corrosion, especially in coastal or high-humidity areas.
Maintenance and End-of-Life Compliance
- Follow manufacturer-recommended maintenance schedules to ensure operational safety and longevity.
- Dispose of obsolete or damaged air starters in compliance with local environmental regulations.
- Recycle metal components where possible; segregate and dispose of any hazardous materials (e.g., lubricants) according to EPA or equivalent standards.
Conclusion
Effective logistics and compliance management for air starters ensures operational safety, regulatory adherence, and uninterrupted supply chains. By focusing on accurate classification, proper packaging, regulatory compliance, and responsible handling throughout the product lifecycle, businesses can mitigate risks and enhance global distribution efficiency. Always consult with logistics providers and regulatory experts to stay current with evolving international requirements.
Conclusion for Sourcing Air Starters
Sourcing air starters requires a strategic approach that balances performance requirements, reliability, cost-efficiency, and supplier credibility. Air starters are critical components in various industrial and marine applications, particularly where electrical hazards, extreme temperatures, or explosive environments make traditional electric starters unsuitable. When selecting a supplier, it is essential to consider factors such as product quality, compliance with international standards (e.g., ATEX, ISO), technical support, delivery timelines, and after-sales service.
Opting for reputable manufacturers with a proven track record ensures durable and efficient operation, minimizing downtime and maintenance costs. Additionally, customization capabilities, global availability of spare parts, and responsive technical assistance further enhance operational continuity. By conducting thorough market research, evaluating multiple vendors, and performing cost-benefit analyses, organizations can make informed sourcing decisions that support long-term reliability and performance.
In conclusion, effective sourcing of air starters goes beyond price comparison—it involves a holistic assessment of technical compatibility, supplier reliability, and lifecycle value. Investing time in selecting the right partner and product ultimately leads to improved safety, operational efficiency, and return on investment across critical applications.