The global air-cooled chiller market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand for energy-efficient HVAC solutions across commercial, industrial, and institutional sectors. According to Mordor Intelligence, the air-cooled chiller market was valued at USD 10.2 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.8% through 2029. This expansion is fueled by increasing urbanization, stricter energy regulations, and the adoption of smart building technologies—particularly in regions like Asia-Pacific, where construction activity remains strong. As sustainability and operational efficiency become key priorities, leading manufacturers are innovating with advanced refrigerants, IoT integration, and higher coefficient of performance (COP) ratings. In this evolving landscape, identifying the top nine air-cooled chiller manufacturers provides critical insight into companies shaping the future of cooling technology through engineering excellence and market responsiveness.
Top 9 Air-Cooled Chiller Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Cold Shot Chillers
Domain Est. 1999
Website: waterchillers.com
Key Highlights: 40+ Years Specializing in Chillers. Reliable Air-cooled & Water-cooled Solutions. Cold Shot Chillers® offers both air-cooled and water-cooled chiller variants ……
#2 Drake Chillers
Domain Est. 2001
Website: drakechillers.com
Key Highlights: Drake Chillers is the industry leader in the design and manufacturing of industrial process chillers! Our systems focus on keeping your equipment running!…
#3 GEA ammonia chiller portfolio
Domain Est. 1995
Website: gea.com
Key Highlights: GEA offers an extensive product portfolio of ammonia chillers for virtually any application for industrial refrigeration and air conditioning….
#4 Quantech: High
Domain Est. 2014
Website: quantech-hvac.com
Key Highlights: Quantech chillers: High-efficiency air-cooled and water-cooled units by Johnson Controls. Save money, reduce costs, and carbon footprint….
#5 Air-cooled Chillers
Domain Est. 1995
Website: johnsoncontrols.com
Key Highlights: We create smaller, more energy efficient chillers tailored to fit almost any comfort or process cooling application–from new construction to retrofit….
#6 Premium Chillers & Components for Commercial HVAC Projects
Domain Est. 1995
Website: carrier.com
Key Highlights: Carrier is a leader in chiller options. With non-ozone depleting refrigerant, simple installation, superior efficiency and powerful controls….
#7 Air-Cooled Chillers
Domain Est. 1995
Website: york.com
Key Highlights: We engineer compact, energy-efficient air cooled chiller systems that are easy to maintain and tailored to fit almost any application. Absorption Chillers….
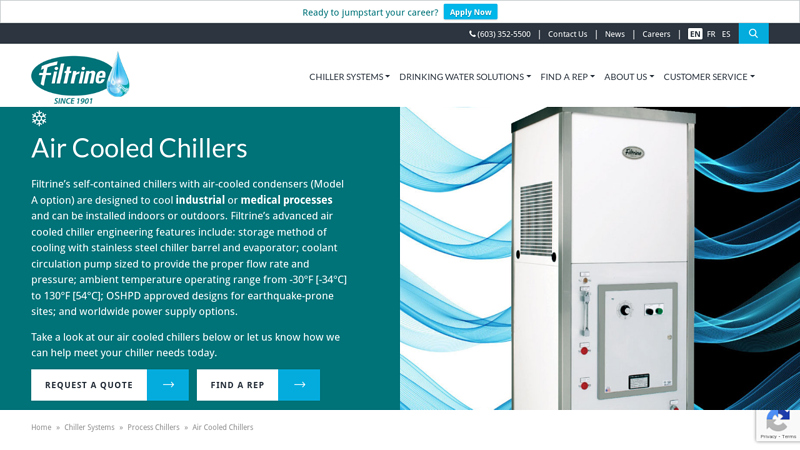
#8 Air Cooled Chillers
Domain Est. 1998
Website: filtrine.com
Key Highlights: Filtrine’s self-contained liquid chillers with air-cooled condensers (Model A option) are the most popular and can be installed indoors or outdoors….
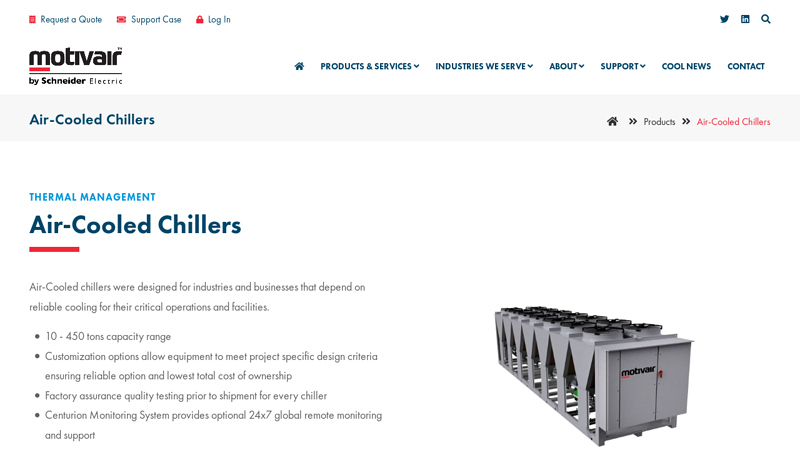
#9 Air
Domain Est. 1998
Website: motivaircorp.com
Key Highlights: Motivair’s Air-Cooled chillers were designed for industries and businesses that depend on reliable cooling for their critical operations and facilities….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Air-Cooled Chiller

H2. Market Trends for Air-Cooled Chillers in 2026
The global air-cooled chiller market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, shaped by technological innovation, regulatory changes, and shifting demand across key industries. Several interrelated trends are expected to influence growth, adoption patterns, and competitive dynamics in this sector.
-
Rising Demand in Emerging Economies
By 2026, air-cooled chillers are anticipated to see robust growth in emerging markets across Asia-Pacific (especially India, Southeast Asia), the Middle East, and parts of Africa. Rapid urbanization, expanding commercial infrastructure (shopping malls, data centers, hospitals), and industrialization are driving the need for efficient cooling solutions. The absence of reliable water sources in many of these regions makes air-cooled chillers—requiring no water for condenser cooling—particularly attractive. -
Energy Efficiency and Regulatory Compliance
Global energy efficiency standards are becoming more stringent, particularly under frameworks like the EU’s Ecodesign Directive and U.S. DOE regulations. By 2026, manufacturers will increasingly focus on high-efficiency models featuring variable speed compressors, advanced heat exchangers, and smart controls. Chillers with high Integrated Part Load Value (IPLV) ratings and low Global Warming Potential (GWP) refrigerants (e.g., R-1234ze, R-32) will dominate new installations, driven by both compliance and long-term operational savings. -
Integration of Smart Technologies and IoT
The adoption of Internet of Things (IoT) and Building Management Systems (BMS) will accelerate in the air-cooled chiller market. By 2026, smart chillers equipped with remote monitoring, predictive maintenance, and real-time performance analytics will become standard. These systems allow facility managers to optimize energy use, reduce downtime, and improve lifecycle management—key value propositions for commercial and industrial users. -
Growth in Data Center and Telecom Cooling
With the expansion of 5G networks and cloud computing infrastructure, data centers are expected to be one of the fastest-growing end-user segments for air-cooled chillers. Their ease of installation, lower maintenance needs, and scalability make them ideal for edge data centers and telecom facilities, especially in water-scarce regions. By 2026, modular and containerized air-cooled chillers will gain traction for such applications. -
Sustainability and Green Building Initiatives
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) goals and green building certifications (e.g., LEED, BREEAM) will continue to influence procurement decisions. Air-cooled chillers with lower carbon footprints, recyclable components, and compatibility with renewable energy sources will be preferred in sustainable construction projects. This trend supports a shift toward hybrid cooling systems and integration with solar-powered operations. -
Competitive Landscape and Regional Dynamics
Major HVAC manufacturers (e.g., Carrier, Trane, Daikin, Johnson Controls) will intensify R&D investments to capture market share. At the same time, regional players in China and India are expected to increase competitiveness through cost-effective, localized solutions. Consolidation and strategic partnerships are likely as companies aim to expand geographic reach and technological capabilities. -
Impact of Supply Chain and Raw Material Costs
Volatility in raw material prices (e.g., copper, steel, refrigerants) and logistical challenges may persist into 2026, influencing pricing and production strategies. Manufacturers are expected to adopt more resilient supply chains, including nearshoring and increased use of digital inventory management tools.
In summary, the 2026 air-cooled chiller market will be defined by a convergence of sustainability mandates, digitalization, and growing demand in non-traditional markets. Companies that innovate in energy efficiency, embrace smart technologies, and adapt to regional needs will be best positioned for success.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Air-Cooled Chillers (Quality & IP)
Sourcing air-cooled chillers involves more than just comparing price and cooling capacity. Overlooking critical quality and intellectual property (IP) aspects can lead to poor performance, high operating costs, and long-term reliability issues. Here are key pitfalls to avoid:
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Prioritizing Low Initial Cost Over Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
Focusing solely on the purchase price often leads to selecting units with lower-quality components (e.g., inefficient compressors, thin-gauge coils, substandard motors). These may fail prematurely, consume more energy, and incur higher maintenance and downtime costs. Always evaluate lifecycle costs, including energy efficiency (COP/EER), maintenance frequency, and expected lifespan.
2. Inadequate Attention to Component Quality
Not all chillers are built equally, even from the same brand. Watch for:
– Compressors: Non-OEM or reconditioned units may lack reliability.
– Condenser Coils: Aluminum or low-finned copper coils corrode faster, especially in coastal or polluted environments.
– Controls & Sensors: Cheap or non-standard controls lead to poor regulation and control instability.
– Fan Motors: Non-inverter or low-efficiency motors increase energy use and noise.
3. Poor Build Quality and Assembly Standards
Chillers assembled in facilities with weak quality control may suffer from refrigerant leaks, electrical faults, or misaligned components. Look for certifications like ISO 9001 and request factory audit reports or third-party inspection records.
4. Insufficient Environmental and Load Testing
Some manufacturers skip rigorous testing under real-world conditions. Ensure the chiller has been tested for performance across varying ambient temperatures and partial load conditions. Lack of AHRI certification or third-party validation increases risk of underperformance.
IP-Related Pitfalls
1. Sourcing from OEMs with Questionable IP Ownership
Many “brands” are merely marketing fronts for generic manufacturers who copy designs without innovation. This leads to:
– Lack of technical support and spare parts longevity.
– Inability to customize or upgrade systems.
– Higher risk of design flaws due to reverse engineering.
2. Use of Proprietary or Non-Standard Components
Some suppliers use custom or locked-down components (e.g., proprietary control boards or refrigerant circuits). This creates vendor lock-in, increases maintenance costs, and hampers integration with building management systems (BMS).
3. Lack of Transparency in Design and Documentation
Suppliers may withhold critical design data, performance curves, or control protocols. Without full access to engineering data, troubleshooting, retrofitting, and lifecycle management become difficult and expensive.
4. Risk of Infringement and Legal Exposure
Purchasing chillers that infringe on patented technologies (e.g., compressor designs, heat exchange methods) may expose your organization to legal risks, especially in regulated markets. Always verify the manufacturer’s IP legitimacy and compliance.
Best Practices to Mitigate Risks
- Demand full technical documentation and performance test reports.
- Require third-party certifications (e.g., AHRI, CE, UL, ISO).
- Conduct factory inspections or audits before finalizing contracts.
- Verify IP ownership and innovation history of the manufacturer.
- Prefer open-protocol controls (e.g., BACnet, Modbus) for integration and flexibility.
- Include warranty, service, and spare parts availability clauses in procurement agreements.
By focusing on quality and IP integrity—not just price—you ensure reliable, efficient, and supportable cooling systems that deliver long-term value.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Air-Cooled Chiller
Product Overview
An air-cooled chiller is a refrigeration system that removes heat from a fluid via air as the cooling medium. Commonly used in commercial and industrial HVAC applications, these units require careful handling, transport, and regulatory compliance due to their size, weight, refrigerants, and electrical components.
Packaging & Handling Requirements
Air-cooled chillers must be securely packaged on robust wooden pallets or skids, with corner protectors and weather-resistant wrapping to prevent moisture ingress. Lifting points should be clearly marked, and only forklifts or cranes using approved rigging gear should be used. Never lift by refrigerant lines, electrical panels, or fan motors. Units should remain upright during all handling and transport to prevent oil migration and component damage.
Transportation Guidelines
- Mode of Transport: Suitable for road, sea, or air freight. Oversized units may require special permits for over-dimensional loads.
- Securing Load: Use straps, chains, or load locks to anchor the chiller to the transport vehicle. Prevent shifting during transit.
- Environmental Protection: Protect from rain, snow, and extreme temperatures. Avoid prolonged exposure to direct sunlight.
- Documentation: Include packing list, bill of lading, and handling instructions with the shipment.
Import/Export Compliance
- Customs Documentation: Provide commercial invoice, packing list, certificate of origin, and bill of lading/air waybill.
- HS Code: Typically classified under 8415.81 (Air conditioning machines incorporating a refrigerating unit). Confirm with local customs.
- Export Controls: Verify if the chiller or its components (e.g., compressors, controllers) are subject to dual-use or technology export restrictions (e.g., EAR, ITAR).
- Destination-Specific Regulations: Comply with local energy efficiency standards (e.g., DOE in the U.S., Ecodesign in EU).
Environmental & Safety Regulations
- Refrigerant Handling: Most air-cooled chillers use HFCs (e.g., R-134a, R-410A). Comply with regulations such as:
- U.S.: EPA Section 608 of the Clean Air Act (proper handling, leak detection, technician certification).
- EU: F-Gas Regulation (No. 517/2014) – restrictions on GWP, leak checks, reporting.
- Pre-Charged Units: If shipped with refrigerant, ensure valves are sealed and warning labels are applied. Refrigerant quantity must be declared.
- RoHS & REACH (EU): Confirm compliance with restrictions on hazardous substances in electrical components and materials.
Electrical & Installation Standards
- Voltage & Frequency: Confirm compatibility with local grid specifications (e.g., 480V/60Hz in North America, 400V/50Hz in EU).
- Certifications Required:
- North America: UL or CSA certification (e.g., UL 1995 for unit heaters).
- Europe: CE marking with compliance to Machinery Directive, LVD, and EMC Directive.
- Other Regions: CCC (China), PSE (Japan), etc.
- On-Site Compliance: Installation must follow local codes (e.g., NEC in U.S., IEC standards internationally) and manufacturer guidelines.
Required Certifications & Documentation
- Factory Test Reports (performance, pressure, electrical)
- Material Declarations (RoHS, REACH)
- Refrigerant Safety Data Sheet (SDS)
- Energy Efficiency Certification (e.g., AHRI performance certification)
- Electrical Safety Certificates (UL, CE, etc.)
- Installation & Operation Manual (including compliance statements)
On-Site Receiving & Inspection
- Inspect for shipping damage before signing delivery receipt.
- Verify nameplate data (model, serial, voltage, refrigerant type).
- Check for oil leaks, dented coils, or loose components.
- Store indoors, elevated off the ground, if not installing immediately.
Disposal & End-of-Life Compliance
- Refrigerant Recovery: Must be extracted by certified technicians using recovery equipment. Never vent to atmosphere.
- Recycling: Follow WEEE (EU) or EPA guidelines for disposal of metals, electrical parts, and insulation.
- Hazardous Components: Capacitors and control boards may contain regulated substances; dispose through certified e-waste handlers.
Key Contacts & Support
- Manufacturer’s Technical Support: For compliance documentation and installation queries.
- Certified Refrigerant Handlers: For charging, servicing, and decommissioning.
- Customs Broker: For import/export clearance and tariff classification.
Ensure all logistics and compliance activities are documented and retained for audit purposes. Regular training for personnel on handling and regulatory updates is recommended.
Conclusion for Sourcing an Air-Cooled Chiller
In conclusion, sourcing an air-cooled chiller presents a practical, cost-effective, and efficient cooling solution for a wide range of commercial and industrial applications. The elimination of cooling towers, reduced installation complexity, and lower maintenance requirements make air-cooled chillers particularly advantageous in locations with limited water availability or higher water conservation priorities.
When selecting a supplier, key considerations such as energy efficiency, reliability, service support, warranty terms, and long-term operational costs should guide the decision-making process. Evaluating reputable manufacturers and suppliers with proven track records ensures access to high-quality equipment that meets performance and sustainability standards.
Furthermore, aligning the chiller specifications with the facility’s cooling demands, environmental conditions, and future scalability needs is essential for optimal performance. With advancements in technology—such as variable speed compressors, smart controls, and eco-friendly refrigerants—modern air-cooled chillers offer improved efficiency and reduced environmental impact.
Overall, a well-informed sourcing strategy, grounded in technical requirements and lifecycle cost analysis, will ensure the selection of an air-cooled chiller that delivers reliable operation, energy savings, and long-term value.