The global automotive air bag module market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by rising vehicle production, stringent safety regulations, and growing consumer demand for advanced driver protection systems. According to a report by Grand View Research, the global air bag market was valued at USD 13.1 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.8% from 2023 to 2030. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence forecasts continued momentum, citing increasing adoption of multi-airbag systems in economy vehicles and the proliferation of electric vehicles as key growth catalysts. As safety becomes a central differentiator in automotive purchasing decisions, air bag module manufacturers are investing heavily in innovation, scalability, and compliance with global standards. In this evolving landscape, eight manufacturers have emerged as leaders, combining technological expertise, broad product portfolios, and strong OEM partnerships to capture significant market share.
Top 8 Air Bag Module Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
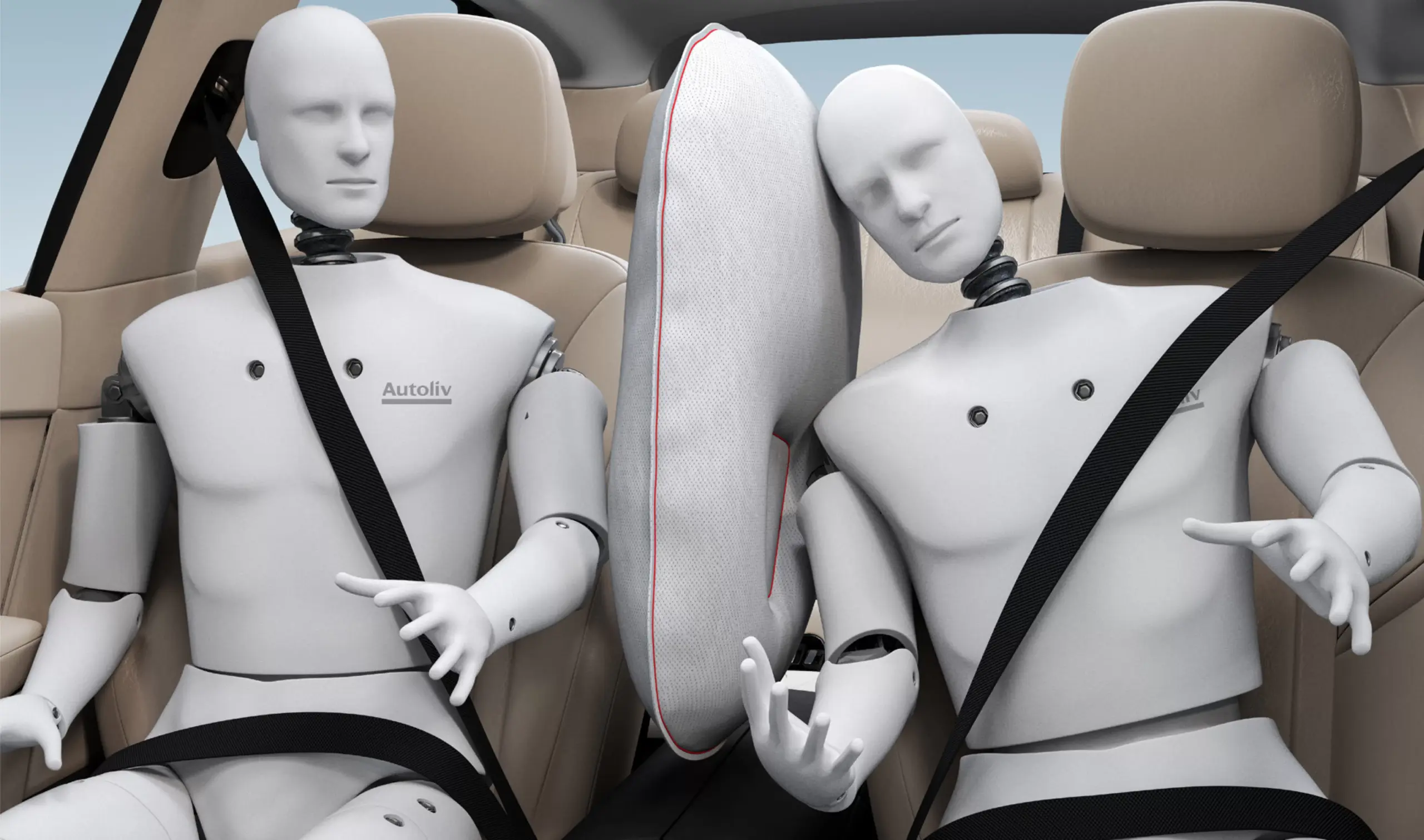
#1 Airbags for Cars from Autoliv
Domain Est. 1998
Website: autoliv.com
Key Highlights: Recognized as the foremost leader in airbag technology, Autolive airbags provide added safety protection and work best in combination with seatbelts….
#2 Airbag Computer Modules New, Used, Exchanged or Repaired …
Domain Est. 1996 | Founded: 1995
Website: airbagsystems.com
Key Highlights: Since 1995, Large Inventory of New and Used Airbag Computer Modules. Exchange and Repair Service also availiable….
#3 Airbag system
Domain Est. 1999
Website: infineon.com
Key Highlights: Enhance every airbag system design with the right semiconductor solutions from Infineon. Learn more now!…
#4 Airbag Control Modules
Domain Est. 1999
Website: airbagcenter.com
Key Highlights: Airbag Control Module: The airbag control module is also known as the airbag sensor, diagnostic unit, computer module, 591 and other names….
#5 Avalanche Airbags
Domain Est. 2004 | Founded: 1985
Website: abs-airbag.com
Key Highlights: Avalanche airbags and life-saving sports equipment from ABS, the original since 1985….
#6 Airbag control unit
Domain Est. 2011
Website: bosch-mobility.com
Key Highlights: The airbag control unit is flexible and scalable with respect to the number of firing loops and sensor interfaces for peripheral crash sensors….
#7 Airbag Systems
Domain Est. 2017
Website: joysonsafety.com
Key Highlights: Our production and quality systems are designed to provide airbag components and systems with the highest quality standards to handle challenging conditions….
#8 Airbag Master Tech
Domain Est. 2017
Website: airbagmt.com
Key Highlights: Experienced in automotive, airbags, electrical work also, works well with others, punctual & honest for a full-time position….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Air Bag Module
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Air Bag Modules
The global air bag module market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by advancements in automotive safety regulations, technological innovation, and evolving consumer demand for enhanced vehicle safety. Key trends shaping the market include:
1. Stringent Government Safety Regulations
Governments worldwide are tightening vehicle safety standards, mandating advanced air bag systems in both passenger and commercial vehicles. By 2026, regulations such as the Global NCAP (New Car Assessment Program) and Euro NCAP are expected to require more comprehensive air bag deployment systems, including side-curtain, knee, and rear-seat air bags. This regulatory push will drive higher penetration rates of multi-air bag modules, particularly in emerging markets like India, Southeast Asia, and Latin America.
2. Rise in ADAS and Autonomous Vehicles
The integration of Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) and the gradual rollout of autonomous vehicles are redefining air bag module functionality. By 2026, air bag systems are expected to become predictive and adaptive, using data from cameras, radar, and LiDAR to pre-tension seat belts and optimize air bag deployment timing and force. This intelligence will reduce injury risk and improve overall occupant protection, especially in complex collision scenarios.
3. Technological Advancements in Air Bag Design
Innovation in air bag module design is accelerating, with manufacturers focusing on lightweight materials, compact packaging, and multi-stage inflation systems. By 2026, expect increased adoption of center air bags (to prevent occupant-to-occupant impact), inflatable seat belts, and external air bags (for pedestrian protection). Additionally, the development of “smart” air bags with occupant sensing technology—detecting weight, position, and seating—will enhance safety customization.
4. Growth in Electric Vehicles (EVs)
The surge in electric vehicle production will influence air bag module demand. EVs often feature different structural layouts and higher-voltage systems, necessitating redesigned air bag modules with enhanced electromagnetic compatibility and crash sensors. By 2026, EV-specific air bag systems will become standard, particularly in battery protection zones and high-voltage disconnect scenarios during collisions.
5. Consolidation and Strategic Partnerships
The air bag module market is witnessing increased consolidation as Tier-1 suppliers like Autoliv, ZF TRW, Joyson Safety Systems, and Hyundai Mobis strengthen their R&D capabilities through mergers and partnerships. By 2026, collaboration between automotive OEMs and safety system providers will accelerate innovation, particularly in AI-driven crash prediction and integrated safety ecosystems.
6. Focus on Sustainability and Recycling
Environmental concerns are prompting manufacturers to develop recyclable air bag components and reduce hazardous materials (e.g., sodium azide alternatives). By 2026, sustainable manufacturing practices and end-of-life recycling programs for air bag modules will gain prominence, driven by EU circular economy directives and consumer awareness.
7. Regional Market Shifts
While North America and Europe remain key markets due to high safety standards, Asia-Pacific—especially China and India—will experience the fastest growth in air bag module demand. Rising vehicle production, urbanization, and government mandates for minimum air bag configurations will fuel this expansion.
In conclusion, the 2026 air bag module market will be defined by smarter, safer, and more integrated systems shaped by regulation, technology, and sustainability. As vehicles evolve, air bag modules will transition from passive safety components to active, data-driven elements of holistic vehicle safety platforms.
Common Pitfalls Sourcing Air Bag Modules (Quality, IP)
Sourcing Air Bag Modules—critical safety components in vehicles—presents significant risks if not managed carefully. Two of the most prevalent and serious pitfalls involve compromised quality and intellectual property (IP) infringement. Failing to address these can lead to safety hazards, legal liabilities, and reputational damage.
Quality Compromises in Sourced Air Bag Modules
One of the most dangerous pitfalls is receiving air bag modules that do not meet original equipment (OE) safety and performance standards. Common quality issues include:
- Use of Substandard Components: Suppliers may substitute lower-grade materials for inflators, sensors, or wiring harnesses, increasing the risk of deployment failure or unintended activation.
- Inconsistent Manufacturing Processes: Lack of adherence to ISO/TS 16949 or IATF 16949 standards can result in inconsistent product reliability and calibration.
- Improper Refurbishment or Recycling: Used or salvaged modules may be reprogrammed and resold as new, often without proper diagnostics or resetting, compromising functionality.
- Inadequate Testing and Certification: Non-compliant modules may lack proper crash simulation, thermal, or EMI testing, making them unsafe under real-world conditions.
These quality lapses can result in catastrophic failures during accidents, exposing buyers and end-users to severe legal and safety consequences.
Intellectual Property (IP) and Counterfeiting Risks
Air bag modules are protected by extensive patents and trademarks, making IP compliance crucial. Key IP-related pitfalls include:
- Counterfeit or Cloned Modules: Unauthorized manufacturers often reverse-engineer OEM designs, producing illegal copies that mimic genuine parts but lack safety validation.
- Unauthorized Reprogramming: Resetting crash data or re-flashing control units without OEM authorization may violate software copyrights and void warranties.
- Lack of Licensing Agreements: Suppliers may lack proper licensing to manufacture or distribute modules, exposing buyers to infringement claims.
- Traceability and Documentation Gaps: Absence of legitimate certification, part traceability, or OEM compliance documentation increases the risk of purchasing pirated or non-approved parts.
Sourcing modules without verifying IP legitimacy can lead to customs seizures, product recalls, and liability in the event of injury or litigation.
To mitigate these risks, buyers should conduct rigorous supplier audits, demand certification (e.g., FMVSS, E-Mark), and partner only with authorized distributors or OEM-approved manufacturers.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Air Bag Module
Air bag modules are critical automotive safety components that require strict handling, transportation, and regulatory compliance due to their pyrotechnic nature. This guide outlines key logistics and compliance considerations for the safe and legal movement of air bag modules across global supply chains.
Classification and Regulatory Framework
Air bag modules are classified as dangerous goods because they contain inflators with compressed gas and/or pyrotechnic materials. They are typically regulated under UN 0503, Class 1 Explosives (Division 1.4S), due to their limited hazard in transportation. Proper classification under the UN Model Regulations, IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations (for air), IMDG Code (for sea), and ADR (for road in Europe) is essential. Always verify the specific UN number, proper shipping name, and packing group assigned by the manufacturer.
Packaging and Marking Requirements
Air bag modules must be shipped in UN-certified packaging designed to withstand shocks, vibrations, and pressure changes. Packaging must meet performance standards (e.g., drop, stack, and vibration tests) and be marked with the UN specification mark. Each package must display the proper shipping name (“Explosives 1.4S”), UN number (UN0503), Class 1 label, and shipper/consignee information. Inner packaging should prevent movement and protect modules from damage.
Labeling and Documentation
All shipments must include appropriate hazard labels: Class 1 (Explosives) and Division 1.4S labels must be affixed to the outer packaging. Required documentation includes a Dangerous Goods Declaration (Shipper’s Declaration for Dangerous Goods), compliant with IATA or IMDG as applicable. Safety Data Sheets (SDS) must be available and reference the correct UN number and hazard class. Proper training certification for personnel preparing the shipment must be maintained.
Storage and Handling Procedures
During storage, air bag modules should be kept in a dry, temperature-controlled environment away from heat sources, sparks, and direct sunlight. They must be stored separately from incompatible materials (e.g., flammable substances, oxidizers). Handling should minimize mechanical shock and electrostatic discharge. Only trained personnel should handle these items, wearing appropriate PPE. Inventory should be rotated using the first-in, first-out (FIFO) principle to prevent aging.
Transportation Restrictions and Carrier Coordination
Air transport of UN0503 (1.4S) air bag modules is generally permitted on passenger and cargo aircraft under IATA DGR Special Provision A144, but airline-specific restrictions may apply. Always confirm with the carrier prior to shipment. Ground transportation must comply with national regulations (e.g., ADR in Europe, 49 CFR in the U.S.). Notify carriers in advance and ensure drivers are trained in handling dangerous goods. Avoid routes through high-risk zones or regions with strict explosive import controls.
Import/Export and Customs Compliance
Exporting or importing air bag modules may require licenses or permits, especially under dual-use or munitions control lists (e.g., ITAR, EAR in the U.S.). Verify export classification (e.g., ECCN) and ensure compliance with destination country regulations. Accurate Harmonized System (HS) codes must be used (e.g., 8708.29.50 in many jurisdictions). Customs declarations must align with dangerous goods documentation to prevent delays or penalties.
Risk Mitigation and Emergency Response
Implement risk assessments for all logistics operations involving air bag modules. Maintain emergency response plans including procedures for package damage, fire, or accidental deployment. Provide emergency contact information on packages. Train personnel in incident response, including evacuation and reporting. Consider using tamper-evident seals and tracking systems for high-value or high-risk shipments.
Training and Recordkeeping
All personnel involved in the handling, packaging, labeling, or shipping of air bag modules must receive recurrent dangerous goods training compliant with IATA, IMDG, or ADR requirements (typically every 24 months). Maintain training records, shipping declarations, and compliance documentation for a minimum of two years. Conduct internal audits to ensure adherence to regulatory standards and internal SOPs.
Disposal and End-of-Life Considerations
Defective or expired air bag modules must be disposed of according to local hazardous waste regulations and manufacturer guidelines. Coordinate with certified hazardous waste disposal providers. Never disassemble or attempt to deploy modules outside of authorized facilities. Document all disposal activities for compliance and audit purposes.
Conclusion for Sourcing Air Bag Module:
Sourcing an air bag module requires careful consideration of safety, quality, compliance, and compatibility. Given the critical role air bag modules play in vehicle safety systems, it is essential to procure components from reputable suppliers that adhere to stringent industry standards such as ISO/TS 16949, FMVSS, and ECE regulations. Whether sourcing new, remanufactured, or used modules, ensuring proper calibration, OEM specifications, and compatibility with the vehicle’s make, model, and year is crucial to maintain system integrity and passenger safety.
Additionally, sourcing from certified suppliers helps avoid counterfeit or substandard parts that could compromise air bag performance during a collision. Cost-efficiency should not come at the expense of reliability—investing in high-quality, properly programmed modules reduces long-term risks and liability. Leveraging strong supply chain partnerships, thorough vetting of vendors, and staying updated on evolving safety technologies further enhances the sourcing process.
In conclusion, a strategic, safety-first approach to sourcing air bag modules ensures optimal vehicle performance, regulatory compliance, and, most importantly, the protection of human life.