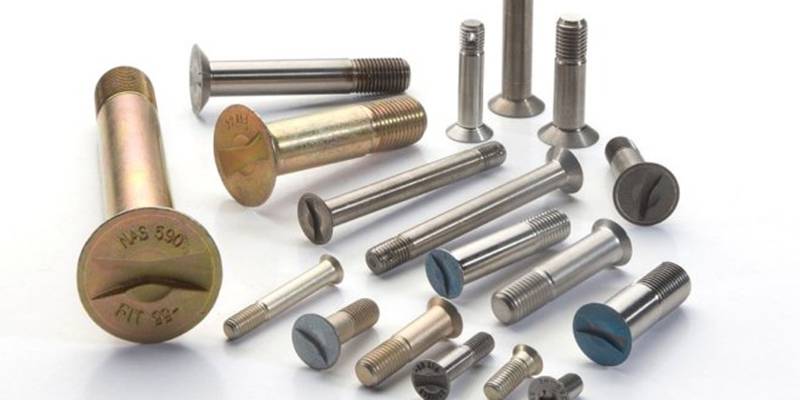
The global aerospace fasteners market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising aircraft production, increasing demand for fuel-efficient designs, and expanding commercial and military aviation sectors. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at USD 9.8 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.8% from 2023 to 2028. Similarly, Grand View Research estimates a CAGR of 6.5% during the forecast period of 2023–2030, citing advancements in lightweight materials and heightened maintenance, repair, and overhaul (MRO) activities as key drivers. With over 40,000 fasteners used in a single commercial aircraft, precision, reliability, and compliance with stringent aerospace standards remain critical. In this high-stakes environment, a select group of manufacturers lead the industry through innovation, quality, and global supply chain integration—here are the top 7 aerospace fasteners manufacturers shaping the future of flight.
Top 7 Aerospace Fasteners Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Monroe Aerospace
Domain Est. 2015
Website: monroeaerospace.com
Key Highlights: Monroe is a world leader in the manufacturing of industrial components with superior value, incredible customer service & fast shipping. We are certified to ……
#2 AS Aerospace
Domain Est. 2017
Website: asaerospace.com
Key Highlights: AS Aerospace manufactures a wide range of close tolerance, high temperature, and high strength aerospace precision NUTS including Barrel Nuts, bolts, studs, ……
#3 Consolidated Aerospace Manufacturing
Domain Est. 2019
Website: camaerospace.com
Key Highlights: Consolidated Aerospace Manufacturing (CAM) is a group of manufacturers of fittings, hardware, fasteners and engineered products solutions for the aerospace ……
#4 Cherry Aerospace
Domain Est. 1998
Website: cherryaerospace.com
Key Highlights: Cherry Aerospace is a global leader for aerospace blind fastening systems. CherryMAX products are the most widely-used blind fasteners in the industry….
#5 Aircraft Hardware
Domain Est. 2002
Website: aerospacefasteners.com
Key Highlights: We offer a wide variety of high-quality aircraft hardware and parts, that feature everything from bolts to rivets to every small piece in-between….
#6 Aerospace Manufacturing
Domain Est. 2002
Website: aero-space.us
Key Highlights: AMI manufactures a complete line of high strength, close tolerance & complex aerospace bolts and screws. We excel in the largest diameters….
#7 Fasteners
Domain Est. 2019
Website: avantusaerospace.com
Key Highlights: At Avantus Aerospace, we principally specialize in non-permanent precision fasteners such as a wide range of screws and bolts….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Aerospace Fasteners

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Aerospace Fasteners
The aerospace fasteners market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by advancements in aircraft manufacturing, increasing demand for fuel-efficient and lightweight aircraft, and the expansion of both commercial and defense aviation sectors globally. Here are the key trends shaping the aerospace fasteners market in 2026:
-
Growing Demand for Lightweight Materials
Aerospace manufacturers are increasingly adopting lightweight materials such as titanium, aluminum alloys, and composites to enhance fuel efficiency and reduce carbon emissions. This shift is driving the demand for high-performance fasteners made from advanced materials that offer high strength-to-weight ratios. Fasteners made from titanium and superalloys like Inconel are becoming critical in next-generation aircraft, particularly in airframes and engine components. -
Rise in Commercial Aircraft Production
Major aerospace OEMs such as Boeing and Airbus continue to ramp up production rates to meet strong global demand for narrow-body and wide-body aircraft. The backlog of aircraft orders, especially in emerging markets like Asia-Pacific and the Middle East, is directly boosting the need for reliable, high-volume aerospace fastening solutions. This trend supports steady growth in the fastener supply chain and encourages innovation in automated fastening systems. -
Increased Focus on Supply Chain Resilience
Lessons from recent global disruptions—including the pandemic and geopolitical tensions—are prompting aerospace companies to reevaluate their supply chains. By 2026, there is a noticeable shift toward regionalization and nearshoring of fastener manufacturing, particularly in North America and Europe. OEMs are partnering more closely with Tier-2 and Tier-3 suppliers to ensure continuity, quality control, and faster delivery times. -
Advancements in Smart and Integrated Fastening Systems
The integration of smart technologies into aerospace components is extending to fasteners. By 2026, there is increasing interest in smart fasteners equipped with sensors to monitor stress, temperature, and corrosion in real time. These innovations support predictive maintenance strategies, reduce downtime, and enhance aircraft safety—key priorities for both commercial and military operators. -
Sustainability and Regulatory Pressures
Environmental regulations and sustainability goals are influencing material selection and manufacturing processes across the aerospace industry. Fastener manufacturers are investing in eco-friendly production methods, including reduced-waste machining and recyclable materials. Additionally, compliance with stringent standards such as AS9100 and REACH is becoming a competitive differentiator. -
Growth in Defense and Space Applications
Rising defense budgets, especially in the U.S., China, and India, are fueling demand for military aircraft, drones, and space launch vehicles. These platforms require highly reliable and specialized fasteners capable of withstanding extreme conditions. The burgeoning space economy—including satellite constellations and reusable launch systems—is also creating new opportunities for high-precision fastener solutions. -
Adoption of Automation and Digitalization in Fastener Installation
Aerospace assembly lines are increasingly incorporating robotics and automated fastening systems to improve precision and throughput. By 2026, digital twin technology and AI-driven quality control systems are being used to monitor fastener installation processes, minimizing human error and ensuring compliance with rigorous aerospace standards.
Conclusion:
The aerospace fasteners market in 2026 is characterized by innovation, resilience, and strategic adaptation to evolving industry needs. With sustained growth in air travel, defense spending, and space exploration, the demand for advanced, reliable, and intelligent fastening solutions is set to rise. Companies that invest in material science, digital manufacturing, and sustainable practices will be best positioned to capitalize on these emerging opportunities.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Aerospace Fasteners: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing aerospace fasteners demands extreme diligence due to the critical nature of these components in aircraft safety and performance. Failure to address key risks can lead to catastrophic outcomes, regulatory penalties, and reputational damage. Two major areas of concern are quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) protection.
Quality Assurance Challenges
Aerospace fasteners must meet rigorous standards (e.g., NAS, MS, AN, AS) for materials, dimensions, strength, and environmental resistance. Common quality pitfalls include:
-
Use of Substandard Materials: Suppliers may substitute certified alloys (e.g., Inconel, titanium) with inferior or non-compliant materials to reduce costs, leading to premature failure under stress or extreme temperatures.
-
Inadequate Certification Documentation: Missing, falsified, or incomplete Material Test Reports (MTRs), Certificates of Conformance (CoC), or traceability records make it impossible to verify compliance with aerospace specifications.
-
Poor Manufacturing Processes: Inconsistent heat treatment, improper plating, or flawed threading can compromise mechanical properties. Non-accredited facilities often lack the process controls required for aerospace production.
-
Counterfeit Parts: The aerospace supply chain is vulnerable to counterfeit fasteners—re-marked, recycled, or fake components that do not meet required specifications. These pose severe safety risks and are difficult to detect without rigorous inspection.
-
Lack of Traceability: Failure to maintain full lot traceability from raw material to finished product impedes root cause analysis in the event of a failure and violates AS9100 and NADCAP requirements.
Intellectual Property and Compliance Risks
Aerospace fastener designs are often protected by patents, trademarks, or technical data rights, and sourcing from unauthorized or non-compliant sources introduces legal and operational dangers:
-
Unauthorized Manufacturing and Distribution: Sourcing fasteners from vendors who do not hold proper licensing or authorization from the original equipment manufacturer (OEM) can result in IP infringement, exposing the buyer to legal liability.
-
Use of Reverse-Engineered Designs: Some suppliers replicate proprietary fastener designs without permission, violating intellectual property rights and potentially producing parts that deviate from certified performance parameters.
-
Non-Compliance with ITAR/EAR Regulations: Fasteners used in defense or dual-use applications may be subject to International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR) or Export Administration Regulations (EAR). Sourcing from non-compliant suppliers can lead to export control violations.
-
Grey Market Procurement: Purchasing from unauthorized distributors or brokers increases the risk of receiving non-IP-protected, counterfeit, or non-conforming parts, undermining airworthiness and regulatory compliance.
To mitigate these risks, companies should source exclusively from OEMs or authorized distributors, conduct supplier audits, require full traceability and certification, and implement counterfeit detection protocols. Adherence to AS9120 and AS6496 standards further strengthens supply chain integrity.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Aerospace Fasteners
The aerospace industry demands the highest standards in safety, performance, and traceability. Aerospace fasteners—critical components used in aircraft assembly—require strict adherence to logistics and compliance protocols throughout their lifecycle. This guide outlines key considerations to ensure regulatory compliance, supply chain integrity, and operational efficiency.
Regulatory and Industry Standards
Aerospace fasteners must comply with a complex web of international and industry-specific regulations. Key standards include:
- AS/EN 9100: Quality management system standard specific to the aerospace industry, emphasizing defect prevention and continual improvement.
- AS9102: First Article Inspection (FAI) requirements verifying that production processes meet design specifications.
- AS9103: Criteria for managing key characteristics and special processes in production.
- NAS, AN, MS Standards: Specifications from National Aerospace Standards (NAS), Army-Navy (AN), and Military Standards (MS) that define fastener dimensions, materials, and performance.
- ITAR (International Traffic in Arms Regulations): U.S. regulations governing the export and import of defense-related articles, including many aerospace components. Compliance is mandatory for companies handling ITAR-controlled fasteners.
- EAR (Export Administration Regulations): Administered by the U.S. Department of Commerce, EAR applies to dual-use items, including certain aerospace fasteners.
Traceability and Documentation
Complete traceability is non-negotiable for aerospace fasteners. Each fastener must be traceable to:
- Raw material source (mill certification)
- Heat number and lot number
- Manufacturer and production date
- Certification documents (e.g., Certificate of Conformance, Material Test Reports)
Best practices include:
- Maintaining a documented traceability system (e.g., ERP or specialized aerospace software)
- Using serialized or batch-level tracking throughout the supply chain
- Ensuring all documentation travels with the product (digital or physical)
- Retaining records for the required retention period (often 10+ years)
Supply Chain Management
Aerospace fastener logistics require a secure, reliable, and compliant supply chain:
- Approved Suppliers Only: Source fasteners exclusively from suppliers approved by OEMs or through qualified manufacturer listings (QML).
- Counterfeit Prevention: Implement AS5553 or AS6496 counterfeit mitigation practices, including supplier vetting, inspection protocols, and secure storage.
- Chain of Custody: Maintain custody records at every transfer point to prevent tampering or substitution.
- Sub-tier Traceability: Require suppliers to provide full traceability down to raw material level.
Packaging and Labeling
Proper packaging ensures fasteners remain protected and identifiable:
- Use anti-corrosion packaging (e.g., VCI paper, sealed moisture barriers)
- Label with critical data: part number, revision, lot/heat number, quantity, manufacturer, and compliance markings (e.g., RoHS, REACH)
- Include handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “Keep Dry”)
- Comply with hazardous material regulations if applicable (e.g., cadmium-plated fasteners)
Storage and Inventory Control
Environmental and procedural controls are essential:
- Store in climate-controlled areas with low humidity to prevent corrosion
- Use FIFO (First In, First Out) or FEFO (First Expired, First Out) inventory rotation
- Segregate non-conforming or suspect material in quarantine areas
- Conduct regular cycle counts and audits to verify inventory accuracy
Transportation and Shipping
Compliance extends to logistics providers:
- Use freight forwarders experienced in aerospace shipments and ITAR/EAR compliance
- Classify shipments correctly under HS codes and export control classifications (ECCN)
- Prepare accurate shipping documentation: commercial invoice, packing list, export licenses (if required)
- Ensure temperature, shock, and humidity monitoring during transit when necessary
Customs and Export Compliance
Exporting aerospace fasteners requires diligence:
- Classify each fastener under the correct ITAR USML category or EAR ECCN
- Obtain necessary export licenses or validate license exceptions (e.g., License Exception STA)
- Screen all parties (end-user, consignee, freight forwarder) against government restricted party lists (e.g., OFAC, BIS Denied Persons List)
- Maintain detailed export records for at least five years
Quality Assurance and Audits
Continuous compliance requires proactive oversight:
- Conduct internal audits aligned with AS9100 and customer-specific requirements
- Perform supplier audits to verify compliance with quality and traceability standards
- Investigate and document non-conformances with root cause analysis and corrective actions (CAPA)
- Support customer and regulatory audits with complete, organized records
Conclusion
Managing aerospace fasteners demands rigorous attention to logistics and compliance at every stage—from sourcing to delivery. Adherence to industry standards, robust traceability, and proactive regulatory compliance not only meet legal requirements but also ensure the safety and reliability of aerospace systems. Companies that prioritize these practices strengthen their position as trusted partners in the global aerospace supply chain.
In conclusion, sourcing aerospace fasteners requires a meticulous and strategic approach due to the critical role these components play in ensuring the safety, reliability, and performance of aircraft systems. It is essential to partner with certified and reputable suppliers who adhere to stringent international standards such as AS9100, NAS, MS, and ISO. Key considerations in the sourcing process include material specification, traceability, quality assurance, compliance with regulatory requirements, and timely delivery.
Effective supply chain management, thorough vendor evaluation, and continuous monitoring are vital to mitigating risks associated with counterfeit parts, production delays, or non-conformance. As the aerospace industry evolves with advancements in technology and increasing demand for lightweight and high-performance materials, staying informed and agile in procurement strategies will be crucial.
Ultimately, a well-executed sourcing strategy for aerospace fasteners not only supports operational excellence but also upholds the highest standards of aviation safety and regulatory compliance.